1. 引言
近些年的全国高血压抽样调查显示,农村人群的患病率呈逐步上升趋势,其中辽宁农村的流行病学调查结果显示,2004~2006年35岁以上人群高血压患病率为37.8% [1] ,我国的大部分人口集中在农村,而高血压是具有高患病率、高致残率和高死亡率特点的心脑血管疾病的主要危险因素 [2] ,对高血压的控制可以有效地减少心脑血管疾病发生的可能性,因此对农村人群高血压的相关研究也就具有重要价值和意义。
高血压疾病研究的初期,研究者就已发现了其在性别上表现出的生理机制上的差异,随之有大量基于不同性别人群高血压发病机制的研究,研究表明:女性在更年期前后患病率与男性相比表现出现显著差异 [3] ,具体表现为:女性在更年期之前原发性高血压的患病率低于男性,但更年期后则与男性无显著差别,甚至高于男性 [4] [5] ;美国NHANES III调查 [6] 和一项采用24小时动态的方法检测结果都表明:绝经的女性相比同龄的男性患病率更高。国内的研究亦通过Logistic回归分析等的方法 [7] 表现出类似规律;在高血压的发病率上作用最明显的是年龄,随着年龄的增长,血压值呈现增长趋势。
国内对农村女性人群高血压影响因素的研究众多,考虑到女性特征绝经更不在少数,但大都止于高血压患病率的调查和对其影响程度的大小研究,很少涉及到该特征在血压各个等级上的表现,且作为另一重要女性特征的生育胎数也未具体到影响因素中去,而列联表分析方法对于医学疾病的分析具有一定的优势,但少于出现在统计类文献中,故本文针对这两个重要的女性特征分别在收缩压和舒张压不同等级上的表现做相关分析,以期发现更加细化和角度不同的结论。
2. 资料与来源
2.1. 数据来源
本文数据来源于辽宁省科技厅重大项目《辽宁省农村高血压流行趋势及低成本综合干预预防脑卒中研究》 [8] 。该项目包含基线调查、综合干预、两次随访过程的原始数据共计45,000多条,一二次变量共计500多个,历时7年左右的时间,首次摸清了农村地区高血压流行趋势,而且指出农村地区高血压处于高发态势;首次在我国农村地区进行以心脑血管疾病为观察终点的高血压低成本干预研究,为我国农村地区慢性疾病的预防和控制提供了低成本的解决方案;并且也是首次对农村高血压病人进行包括降脂治疗在内的综合防治,为我国农村地区心脑血管疾病的未来干预策略提供了理论依据,提出了新的方案。
2.2. 数据预处理
在原始数据中提取出在女性特征绝经与生育胎数上均为有效数值的样本,共计7251条。按年龄参考绝经与否将女性特征数据分成4个类型(下文将此分类下的数据简称为女性绝经数据),即:I型:年龄在40岁以下的未绝经女性;II型:年龄在40岁(含40)~54岁的未绝经女性;III型:年龄在40岁(含40)~54岁的绝经女性;IV型:年龄在55岁及以上的绝经女性。
对已有的文献初步分析发现,女性生育胎数同血压的改变可能有一定的联系,本文根据样本数据分布特征将女性生育胎数分为0、1、2、3和3以上5类。
3. 主要分析公式
疾病影响因素分析的主要统计学方法是基于列联表的相关分析 [9] 。疾病的影响因素X,与疾病表征变量Y的统计数据通常由r × c的二维列联表汇总,其中,nij表示因素的第i个状态下疾病的第j种特征的统计频数,mij为实测频数,n为样本总数,
,
。
关于X与Y的关联性度量,最基本的度量是MDS方法体系的χ2系数 [10] ,对其进行归一化得到关联系数θ [11] ,其计算公式为
(1)
其中,
,
θ度量具有严格的统计模型支撑,可以利用最小显著性概率p (θ ≠ 0的决策风险的度量)给出θ系数统计显著性的评价。
考虑到本文的讨论中女性特征值与血压水平值均是等级描述的,而变量取值状态的有序性对变量间关联性的度量有一定的影响,因此,本文引进Somers系数dYX、dXY [11] ,计算公式如下:
,
(2)
其中,C为X与Y值态的单调协调对总数,D为不协调对总数,TX、TY表示同行、同列两样本配对数。
一般情况下,dYX与dXY的度量是不一致的,因此引进二者的几何平均度量Kendall系数τb [11] ,计算公式如下:
(3)
另外,基于列联表的信息挖掘,常用的技术方法是建立在条件概率基础上的机会比分析。相关概念与计算公式如下:在同一个概率空间中,设相互关联的两个事件A和B,则
(4)
称为在事件B发生条件下事件A发生的条件概率。进而
(5)
称为在事件B发生条件下事件A的机会 [12] [13] ,而机会的比较由
(6)
给出,称为条件B1相对于B2事件A发生的机会比 [12] [13] 。
4. 结果与分析
4.1. 分布与关联性概述
女性绝经数据在4种类型下,血压正常与非正常(血压分为5个等级,将血压等级在正常和正常高值的合并为正常,其它的为非正常)比例分布情况如图1。
由于女性绝经数据包含着年龄特征,故从图1(a)收缩压(SBP)和图1(b)舒张压(DBP)级别处于正常与非正常的分布比例可以看出,随着年龄的增加,收缩压和舒张压处于正常级别的比例均在减少,而处于非正常级别的比例均在增加,且相比之下这种变化趋势在收缩压下更为明显,说明高血压患者比例随着年龄的增加有上升的趋势,且在收缩压下的表现更为敏感。
对绝经因素与血压进行相关系数的计算,从结果中发现:绝经特征与收缩压的关联系数θ = 0.18,大于舒张压下的0.11,收缩压下显著性概率p = 1.04 × 10−197,舒张压下p = 1.92 × 10−66,均是高度统计显著的,这有效说明绝经因素影响着血压值,且与收缩压的相关性更大,这符合文献 [14] 的结论。
女性生育子女个数数据在5个类别下,血压正常与非正常比例分布情况如图2。
从图2可以看出,生育胎数为0即无生育经历的女性在收缩压和舒张压的表现相同,并且明显有别于有生育经历的女性;对于有生育经历的女性来说,随着生育胎数的增加,收缩压和舒张压处于正常级别的比例均随之下降,但在舒张压下的趋势稍缓,这说明对于有生育经历的女性来说,随着生育胎数的增加,血压值升高的风险变大,高血压患者的比例在上升,且这种变化对收缩压更为敏感。
而这与一位学者对2014年美国心脏病学会年会(ACC)报道的达拉斯心脏数据的分析结果 [15] 是有所区别的,该学者得到“生育2、3胎的女性动脉粥硬化风险最低,生育0、1、4胎及以上的则有较高的临床动脉硬化风险”的分析结论,动脉硬化和高血压被称为“孪生姐妹”,那么与之相对的,生育胎数对高血压的影响也应类似,但图2中所表达的却不全是这样,虽然这种分析具有一定道理,因为无生育经历和生育胎数较多(3及以上)的女性,血压处于不正常级别的比例都更多些,但生育1胎的女性处于不正常级别的比例明显较其它胎数的均要低一些,而非具有“较高风险”。
对女性生育胎数特征与血压进行相关系数的计算,从结果中发现:与绝经特征相比,关联系数无论是在收缩压还是舒张压上都要小一些,分别为收缩压θ = 0.16和舒张压θ = 0.08,显著性概率分别为p = 5.08 × 10−140和p = 1.69 × 10−30,均是高度显著的,且出现了类似于绝经特征的结论,即:与收缩压的关
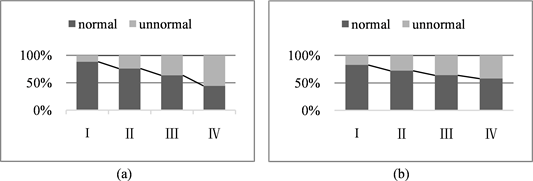
Figure 1. (a) Normal and abnormal proportion of SBP; (b) Normal and abnormal proportion of DBP
图1. (a) SBP正常与非正常比例;(b) DBP正常与非正常比例

Figure 2. (a) Normal and abnormal proportion of SBP; (b) Normal and abnormal proportion of DBP
图2. (a) SBP正常与非正常比例;(b) DBP正常与非正常比例
联系数大于舒张压。这说明生育胎数特征在某种程度上对血压的影响与绝经特征类似,但比绝经特征的作用弱一些。
4.2. 女性绝经II、III型特征与血压的关联性
重点分析40~54岁的女性即女性绝经II、III型与血压相关关系,首先,计算其相关系数,见表1。
从表1可以看出,较绝经4个类型数据一起,只包含II、III型的女性绝经数据与血压的关联系数变小了,而就Somers和Kendall这两个考虑到序关系的相关系数来说,它们的取值足以说明:年龄在40~54岁的女性,她们的绝经特征影响着血压的变化,且由于类别选取的原因,绝经在年龄较轻(40岁以下)和较大(54岁以上)女性身上的特异性影响已被减弱,故而严谨地验证了绝经特征在II、III型女性血压变化中的不可忽视的作用。
接下来,对II、III型女性进行机会比的分析,计算结果如表2。
由表2看出,对于II型特征即40~54岁的未绝经女性来说,除了由中度向重度级别,该类女性在舒张压由低到高相邻级别迁移的机会均大于收缩压,且在由正常向正常高值级别迁移的机会较之其它的更大些,舒张压下达到1.3187;而在由中度向重度级别迁移时,该类女性的影响却是收缩压略大于舒张压,但就数值而言0.6535、0.6142也较大;这说明40~54岁的未绝经的女性对由正常向正常高值和由中度向重度级别的敏感性较大。而与II型的数值相比,对III型的已绝经女性来说这种影响的变化是:无论收缩压还是舒张压,对于由正常高值向轻度和由轻度向中度级别迁移的机会变大,这说明绝经特征对于这两个相邻级别迁移的敏感性更强。
最后,对II、III型女性的机会比进行比较分析,计算结果如表3。
表1. 相关系数
表2. 机会比
注:SBP:收缩压;DBP:舒张压;表中第2行表示血压等级的迁移,如“1→2”表示血压级别由正常迁移为正常高值,依此类推,下面同此。
表3. 机会比
注:表中“III型/II型”表示III型与II型比较。
从表3的II、III型的比较中发现:绝经女性在收缩压级别由正常高值迁移为轻度的机会比是未绝经女性相应机会比的1.3320倍,舒张压下该机会比为1.0897 < 1.3320,绝经特征对收缩压的作用明显更大;而对于高血压患者来说,在由轻度级别迁移为中度级别时,绝经女性的机会比也大于未绝经女性,但是此处舒张压下的机会比1.2066却稍大于收缩压下的1.1604,这可能是由于存在其它影响更大的因素;且对于高血压患者来说,在由中度转变为重度时,绝经女性的机会低于未绝经女性,可能存在某些控制因素使得绝经特征在此处的影响变小。综上所述,绝经女性在由正常高值向轻度级别迁移的敏感性较未绝经女性更大,且具有一定的延续性。
4.3. 绝经II、III型与子女数对血压影响的双因素分析
由于样本的原因,以下重点分析绝经II、III型特征和生育1~3胎对血压的影响。样本数据的三维列联表如表4。
考虑绝经特征与生育胎数间的交互影响,依据表4三维列联表计算的机会比之比如表5。
为了使得观察更为直观,绘制了下面的II型的图3。
由图3(a)得到,在女性特征II型下,生育胎数的增加对收缩压各相邻等级的影响差异不大,值得注意的是在女性生育第3胎时出现的极小、极大值点,即生育3胎的女性收缩压由轻度等级迁移为中度等级的机会比是生育2胎的女性相应机会比的0.5787倍,而下一个相邻等级的变化,即由中度等级变为重度等级时,生育第3胎的机会比为1.8561。这是一个两极化的变化,也就是说,生育3胎的未绝经女性,

Table 4. Three-dimensional contingency table
表4. 三维列联表
注:表中第2行数字分别表示:1-正常、2-正常高值、3-轻度、4-中度、5-重度;第2列的数字表示女性生育的胎数;SBP/DBP表示分别在收缩压和舒张压下的频数,表中最后1列表示在收缩压和舒张压下频数一样。
表5. 机会比之比
注:表中第3列表示生育胎数的比较,如“1→2”表示生育2胎与生育1的比,称为生育第2胎,依此类推,下同。
 注:图中的横坐标均表示相邻血压等级的比,纵坐标表示机会比,图例表示生育胎数的比,下同。
注:图中的横坐标均表示相邻血压等级的比,纵坐标表示机会比,图例表示生育胎数的比,下同。
Figure 3. (a) SBP odds ratio changes; (b) DBP odds ratio changes
图3. (a) SBP机会比之比变化;(b) DBP机会比之比变化
收缩压由轻度等级变为中度等级的风险小于生育2胎的女性,而在由中度等级变为重度等级的风险却明显大于生育2胎的女性,由于前面3.1节得到“随着生育胎数的增加,收缩压处于不正常级别的比例在升高”,这样看来,这种比例的上升大部分是中度等级变为重度等级的比例增大造成的,这提出了一个警示:未绝经的女性在生育3胎后,收缩压极可能有危险的由中度等级向重度等级迁移的风险。
图3(b)舒张压的变化与收缩压的情况稍有些不同,值得注意的是在生育第3胎时也出现了与图3(a)类似的两极化变化,但与收缩压出现的位置不同,极大值在舒张压由轻度等级变为中度等级,也就是说,生育3胎的未绝经女性,有轻度等级迁移为中度等级的风险。
图4是III型的机会比之比变化。
由图4(a)可以看出,相邻收缩压等级的机会比在女性生育胎数的比较中差别不大,均较为平缓,虽有稍突出的极值点,但从数值上看影响还是不大的,而这个差异不明显的折线统计图说明的是:对于绝经的女性来说,她们的生育经历对于收缩压的影响变小,这很符合绝经与生育关系的认知,也就是说,生育胎数影响收缩压主要在女性未绝经时,而一旦绝经,这种影响就不应独立分析了。
在图4(b)中,舒张压机会比的情况其实和收缩压很类似,变化也较为平缓,但在由中度级别转变为重度级别时,生育第3胎的机会出现了较为突出的极大值点,说明生育3胎的绝经女性,舒张压由中度级别迁移为重度级别的机会比大,再次提醒的是舒张压处于中度级别的女性:生育3胎后,级别继续上升的风险很大。
将表5中II、III型的机会比做比较,得到表6的机会比之比。
图5是II型/III型的机会比之比变化。
从图5(a)可以看出,未绝经女性与绝经女性对于生育第2胎和第3胎在收缩压上机会比的影响的态势基本一致,而这种态势与图5(b)中舒张压下生育第2胎的机会比的态势也类似;而已绝经相对于未绝经特征,对于生育第3胎的女性来说,在舒张压由正常高值级别迁移为轻度级别的机会比的影响更加明显,且与生育第2胎的女性相比极为不协调,这说明绝经特征在舒张压上的影响是极为复杂的,它与收缩压较为一致的影响不同,无法简单地描述出来。

Figure 4. (a) SBP odds ratio changes; (b) DBP odds ratio changes
图4. (a) SBP机会比之比变化;(b) DBP机会比之比变化
表6. 机会比之比
注:表中“III型/II型”表示III型与II型的机会比之比。

Figure 5. (a) SBP type III/II; (b) DBP type III/II
图5. (a) SBP III型/II型;(b) DBPIII型/II型
5. 结果与分析
从女性绝经4个类型数据的得到结果上看,总体来讲:
1) 随着年龄的上升,高血压患者的比例有上升的趋势;
2) 绝经特征在收缩压上的影响大于舒张压;
3) 无生育经历的女性和有生育经历的女性,收缩压和舒张压的表现明显不同:
① 对于有生育经历的女性而言,随着生育胎数的增加,处于不正常级别的比例在增加;
② 无生育经历和生育较多(3及以上)胎数的女性,高血压的患病率风险较大,而生育1胎的女性风险与她们相比要小些;
4) 女性生育胎数在收缩压和舒张压的表现与绝经特征类似,对收缩压的影响更大些。
而从女性绝经II型、III型数据计算的机会比的结果上看,发现:
1) 在40~54岁的女性中,绝经特征仍与血压表现出较强的相关性,即绝经特征在女性血压的研究中必不可少;
2) 在不考虑生育胎数时:
① II型女性应注意收缩压、舒张压由正常上升为正常高值的高血压趋势;
② II型、III型相比下得到,绝经女性在由正常高值级别迁移为轻度级别的机会较未绝经女性更大,且具有一定的延续性;
3) 对于II型女性而言,生育3胎后,收缩压由中都迁移为重度级别的风险大,舒张压由轻度迁移为中度级别的风险大;
4) 对于III型女性而言,对于收缩压,生育胎数的影响主要在绝经前,绝经后对其的独立分析是不可靠的;而在舒张压上却是有一定影响的,主要是处于中度级别的女性在生育3胎后级别继续上升的风险增大;
5) 而II型、III型比较之下发现,无论是生育第2胎的女性还是生育第3胎的女性,绝经特征在收缩压各相邻级别机会比的态势较为一致,而对于舒张压的影响却是复杂不可简单描述。
从上面得到的结论可以看出,本文主要考虑的女性特征绝经和生育胎数,对于收缩压和舒张压的影响分开分析是有道理的,因为在两者的表现不尽相同;而女性生育胎数的确对血压表现出不同情况下的不同影响,是在之后的分析中值得考虑的因素;统计方法在医学上的应用远不止文中所提到的方法,但从结果上看,本文采用的方法是可以挖掘到一些较为有用的结论的;本文考虑的血压影响因素较少,并非是其它因素不重要,而是想通过一个侧面的切入点,得到更加细化的结论,但之后的分析可以尝试增加因素使研究更为全面。
基金项目
辽宁省自然科学基金项目(2015020570),国家自然科学基金(61304090)。