1. 引言
潮土是山东省面积最大的土类,也是黄淮海平原最主要的农业土壤 [1] 。潮土大部分区域属于中、低产土壤,其中磷作为农业生产中最重要的养分指标之一,对作物产量具有重要影响,而潮土具有全磷含量较高,有效磷含量较低的特点 [2] 。肥料在粮食生产中具有重要作用,但不合理施肥可导致肥料利用率低,作物产量不稳定,也不利于土壤培肥地力 [3] 。冬小麦-夏玉米轮作是该地区最普遍的种植制度。为保证粮食安全,研究合理施肥模式,掌握小麦玉米磷素吸收特征,提高磷肥回收率,对提高潮土区域作物产量具有重要意义。
有关磷肥回收率的研究报道很多,但磷肥回收率均较低 [4] [5] [6] 。由于土壤中特定的理化性状及磷酸盐的化学行为,作物对磷肥的利用率很低,当季利用率一般只有5%~10%,即使考虑作物的后效,一般也不会超过25%,我国小麦的磷肥利用率范围为6%~26%之间 [7] 。而且磷肥回收率受气候因素、土壤类型、作物品种和施肥模式等因素的影响,还存在当季利用和后续利用的问题,因此通过长期定位试验能够更加正确地评价磷肥回收率问题。谢如林研究发现施肥量是影响肥料利用率的最主要因素 [8] ;高静等通过研究表明磷肥回收率的变化速率与土壤中磷的形态密切相关 [9] ;韩瑛祚等通过不同施肥方式研究发现在常规施肥基础上减少磷肥用量、加入磷素活化剂可提高磷肥回收率 [10] 。
长期定位试验具有时间长期性和气候代表性等优点,因此通过山东潮土的长期定位试验,探索小麦玉米磷素吸收特征,掌握磷肥回收率规律,为潮土区施肥管理和土壤培肥提供科学依据。另外,通过研究提高磷肥回收率、减少施肥量对缓解资源不足的矛盾具有重要意义。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 试验地概况
长期定位试验监测点位于山东省济南市山东省农业科学院试验农场院内(北纬36˚40′;东经117˚00′),海拔高度为27.5 m,该区域地处亚热带属于暖温带半湿润季风型气候。年均降雨量为693.4 mm,年平均气温为14.8℃,气温大于10℃的积温4774℃,年蒸发量444.1 mm,无霜期216.4 d,年日照时数1870.9 h。
供试土壤为潮土,成土母质为近代河流沉积物,土壤中粘土矿物主要水云母,绿泥石为主。长期试验从1982年秋季开始,试验开始时的耕层土壤(0~20 cm)基本性质见表1。
2.2. 实验设计
供试小麦品种为:1983~2001年,济麦13;2002~2005年,济麦16;2006~2015年,济麦22。供试玉米品种为:1983年,鲁原单9号;1984年,鲁玉4号;1985年和1988年,鲁原单4号;1986年,鲁原单7号;1987年,鲁原单8号;1989~1992年,鲁原单15号;1993~2005年,掖单4号;2006~2015年,郑单958。
试验共设16个处理:前8个为无机施肥处理,后8个为增施有机肥处理,其化学施肥量与前8个处理相同。其处理分别为:1、不施肥耕作(CK);2、氮(N);3、氮磷(NP);4、氮钾(NK);5、磷钾(PK);6、氮磷钾(NPK);7、减量氮磷钾(N15PK);8、增量氮磷钾(N25PK);9、有机肥(CK+M);10、氮和有机肥(N+M);11、氮磷和有机肥(NP+M);12、氮钾和有机肥(NK+M);13、磷钾和有机肥(PK+M);14、氮磷钾和有机肥(NPK+M);15、减量氮磷钾和有机肥(N15PK+M)和16、增量氮磷钾和有机肥(N25PK+M)。每个试验小区面积为1 m2,无机施肥处理重复3次,增施有机肥处理未设重复(由于试验地空间原因)试验采取随机区组设计,各处理肥料施用量见表2,其中有机肥料为马粪,马粪养分含量平均为N 4.75 g/kg,P2O5 4.83 g/kg,K2O 9.90 g/kg。采用小麦-玉米一年两熟轮作制,小麦季氮肥按50%基肥和50%追肥施用,磷、钾肥均作基肥施用。玉米季氮、磷、钾肥全部基施。有机肥处理在此化学施肥的基础上于每年秋季小麦播种前施用25000 kg/ha马粪,其中,化肥处理中磷素外源投入量约为65.5 kg/ha,施入马粪投入的磷素约为33.5 kg/ha左右。处理作物地上部分带走,回田的秸秆N、P、K养分不计入总量。

Table 1. Basic physical and chemical properties of initial soil (0~20 cm)
表1. 初始土壤(0~20 cm)基本理化性质

Table 2. The amount of fertilizer application
表2. 肥料施用量
注:表中0-0-0代表N-P2O5-K2O的施肥量,以此类推。
2.3. 样品采集和处理
在作物成熟期,收获每个小区作物,籽粒和秸秆分离用于生物性状考察。籽粒、茎叶自然阳光下风干,然后在65℃烘干至恒重。籽粒和秸秆样品烘干称重后,用粉碎机进行粉碎用于籽粒和秸秆中氮、磷和钾等元素含量的分析测定。
2.4. 测定项目和方法
土壤样品分析按照统一的方法进行,测定方法见参考文献 [11] [12] 。植物样品的氮磷钾含量测定前处理:准确称取植物样品0.5 g左右放入100 ml 消煮管底部,加浓H2SO4 5.0 ml,摇匀,静置过夜。在消煮炉上先低温加热,待H2SO4发白烟后再逐渐升高温度,当溶液呈均匀的棕黑色时,稍冷后加10滴H2O2。再加热至微沸,消煮约7~10 min,稍冷后重复加H2O2,消煮,重复数次。每次添加的H2O2逐渐减少,消煮至溶液呈无色或清亮后,再加热30 min,除去剩余的 H2O2。冷却后,定容。澄清后吸取清液测定氮、磷、钾。同时进行空白试验,以校正系统误差。
土壤有机质使用重铬酸钾容量法。全氮用凯氏法,全磷用碱熔—钼锑抗比色法,全钾用NaOH熔融火焰光度法;碱解氮用扩散法,速效磷用Olsen法,速效钾用1 mol/L NH4OAC浸提—火焰光度法,采用烘干法测定土壤含水量。
2.5. 数据处理分析
磷肥回收率(%)=
{[某施磷处理作物总吸磷量(kg/ha)-对照处理作物总吸磷量(kg/ha)]/该施磷处理施磷量(kg p/ha)}x100% ;(1)
作物吸磷量(kg/ha)=籽粒产量(kg/ha)x籽粒含磷量(%)+秸秆产量(kg/ha)×秸秆含磷量(%) ;(2)
实验数据采用Sigmaplot 12.5进行统计分析,利用单因素分析进行显著性分析(p < 0.05),采用Excel 2010进行作图。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 磷肥回收率的演变趋势
长期不同施肥模式下,随年限增加磷肥回收率的变化趋势如下图所示(图1小麦作物,A为无机施肥处理、B和C为增施有机肥处理;图2玉米作物,A为无机施肥处理;B为增施有机肥处理)。
对于小麦作物,施用化肥的各处理(NP、PK、NPK、N15PK和N25PK),磷肥回收率呈波浪状变化,总体呈现先上升22年后逐渐下降的趋势。其中,PK处理磷肥回收率相对较低,平均为20%左右。而NP和氮磷钾化学平衡施肥处理磷肥回收率较稳定,保持在30%左右。
对于增施有机肥处理,不同施肥模式下磷肥回收率差异显著,NP+M和PK+M处理磷肥回收率相对较低,在20%以下;氮磷钾化肥配施有机肥处理磷肥回收率较稳定,维持在20%~30%之间;由于不施化学磷肥处理(CK+M、N+M和NK+M)的施磷量较低而作物产量相对较高导致磷肥回收率较高,其中以N+M处理磷肥回收率最大,达60%左右。

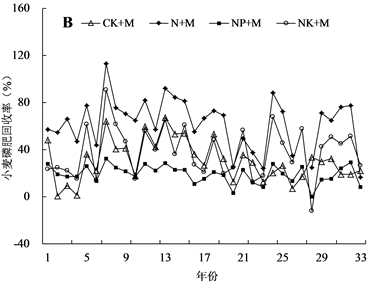

Figure 1. Changes of phosphate recovery efficiency in wheat season
图1. 小麦季磷肥回收率的变化

Figure 2. Changes of phosphate recovery efficiency in core season
图2. 玉米磷肥回收率的变化
对于玉米作物,无机施肥处理中,随着年限的增加,PK处理磷肥回收率呈现上升趋势,前13年磷肥回收率均在10%以下,而后稳定在15%左右,总体值均较小。前14年NP处理和NPK、N15PK、N25PK处理磷肥回收率变化趋势相似且大小相差不大,磷肥回收率平均维持在25%左右,14年后,NP处理中磷肥回收率小于氮磷钾平衡施肥处理。
对于增施有机肥处理,偏施化肥加有机肥处理(NP+M、PK+M)磷肥回收率在20%左右。氮磷钾化肥配施有机肥处理磷肥回收率较高且稳定在33%~37%之间,从小到大的顺序为N15PK+M < NPK+M < N25PK+M。
3.2. 磷肥回收率对土壤有效磷的响应关系
长期不同施肥模式下,不同作物磷肥回收率对有效磷的响应关系不同,如下图所示(图3小麦,图4玉米,A为无机施肥处理、B为增施有机肥处理)。
对于小麦作物,NP处理磷肥回收率随有效磷增加呈现一个先缓慢上升后达到平衡的趋势;PK处理呈下降趋势,且与其他化肥处理相比磷肥回收率最低;NPK、N15PK和N25PK处理磷肥回收率随土壤有效磷增加总体呈现上升的趋势。
对于增施有机肥处理,土壤有效磷含量明显增大,随着有效磷含量增大,CK+M、N+M、NP+M和NK+M处理磷肥回收率规律不明显;对于氮磷钾配施有机肥处理,磷肥回收率和土壤有效磷之间呈开口向下的抛物线形式,即先增加后下降的趋势;即平衡施肥下随着土壤有效磷含量增大磷肥回收率提高,当土壤有效磷含量高于120 mg/kg时,磷肥回收率降低。
对于玉米作物,在无机肥处理中,NP处理和PK处理中磷肥回收率和土壤有效磷的响应关系与小麦作物的完全相同。除N15PK处理外(可能存在一定的误差),氮磷钾处理均随有效磷的增加呈现上升的趋势。
对于增施有机肥处理,NP+M处理磷肥回收率和土壤有效磷之间关系不明显;PK+M和NPK+M处理两者之间呈现开口向上的抛物线形式,即磷肥回收率随土壤有效磷含量增加呈现先下降后上升的趋势。N15PK+M和N25PK+M处理磷肥回收率随着有效磷的增加呈上升的趋势。
3.3. 不同施肥模式下小麦玉米吸磷特征
长期不同施肥下,作物吸磷量统计计算如表3 (小麦)、表4 (玉米)。由表可知,除小麦的氮磷处理外,增施有机肥处理作物吸磷量显著高于不施有机肥处理(p ≤ 0.05)。相同处理不同年间作物吸磷量变化较大与气候和作物品种有关。

Figure 3. The correlation of phosphate recovery efficiency and soil available phosphorus in wheat season
图3. 小麦季磷肥回收率与土壤有效磷关系

Figure 4. The correlation of phosphate recovery efficiency and soil available phosphorus in core season
图4. 玉米季磷肥回收率与土壤有效磷关系

Table 3. Characteristics of phosphorus uptake of wheat in different fertilization
表3. 长期不同施肥小麦磷素吸收特征(kg P /ha)
图中同一行中不同小写字母表示两个处理差异显著(p ≤ 0.05),下同。

Table 4. Characteristics of phosphorus uptake of corn in different fertilization
表4. 长期不同施肥玉米磷素吸收特征(kg P /ha)
对于不施有机肥处理,对照和不平衡施肥作物吸P量低于化肥平衡施肥处理,具体表现为CK < N、NK < PK、NP < NPK、N15PK、N25PK。氮磷钾平衡施肥(NPK、N15PK、N25PK),小麦玉米吸收磷素33年内均稳定,吸磷量位于28.2~33.4 kg P/ha之间;偏施肥处理(NP、PK)小麦玉米磷素吸收量平均为26 kg P/ha左右,和平衡施肥处理相比,NP处理中的小麦吸磷量没有减少,玉米吸磷量减少20%左右;不施磷素(CK、N、NK)处理中,作物平均吸磷量位于10.7~15.4 kg P/ha之间;
对于增施有机肥处理,小麦吸磷量与玉米吸磷量持平,所有处理作物吸磷量平均位于22.9~43.4 kg P/ha之间,且33年内吸磷量均较稳定;平衡施肥增施有机肥处理作物吸磷量大于其他处理。所有处理均于2003~2007年出现上升趋势,氮磷钾处理上升幅度更大,上升趋势可能是这几年气候条件较好,作物产量较高。
4. 讨论
4.1. 磷肥回收率的演变分析
磷肥回收率是衡量施肥合理性的一个重要指标,提高磷肥效率可以提高有限资源的最大效益。
无机肥处理中,氮磷钾平衡施肥磷肥回收率明显高于偏施化肥处理,平衡施肥磷肥回收率于26.6%~31.8%,高于福州水稻磷肥回收率19%,低于南昌水稻磷肥回收率36% [13] 。PK处理中,不施氮肥明显影响作物对磷养分吸收。前14年NP处理和氮磷钾平衡施肥处理磷肥回收率变化趋势相似且大小相差不大,说明前期潮土土壤中本身含有的钾含量能满足作物的利用。化肥处理中玉米季磷肥回收率小于小麦季,而裴瑞娜 [14] 通过28年长期定位施肥处理发现,玉米季的磷肥回收率平均值均高于冬小麦。可见不同作物磷肥回收率的大小与土壤类型有关。
增施有机肥处理中磷肥回收率反而略降低可能与其施磷量增大有关,可见,磷肥回收率的大小不仅与肥料种类相关,和投入量的大小也有关。其中,氮磷钾化肥配施有机肥处理磷肥回收率较高且稳定,N15PK+M、NPK+M和N25PK+M处理中玉米磷肥回收率随施氮的增加而增加,可见种植玉米施入氮素越多,作物产量越高,磷肥利用率也越高。与小麦季时磷肥回收率相比,相同处理下玉米季磷肥回收率提高。可见,小麦季增施有机肥能提高玉米季磷肥回收率。
4.2. 磷肥回收率与土壤有效磷的响应关系
无机肥处理中,NPK、N15PK和N25PK处理磷肥回收率随土壤有效磷(0~80 mg/kg)增加总体呈现上升的趋势,可见,平衡施肥下土壤有效磷含量越高,磷肥回收率越高,即较高磷素供应下可提高作物产量。
土壤有效磷的增加可促进农田作物吸磷量的提高,有研究 [15] 表明,直角双曲线模型可以用来描述土壤有效磷与吸磷量之间的关系,即作物吸磷量存在一定的阈值,其大小与土壤类型和轮作制度有很大关系。对于氮磷钾配施有机肥处理,土壤有效磷含量明显增大,随着土壤有效磷含量(0~200 mg/kg)增大磷肥回收率提高,当土壤有效磷含量高于120 mg/kg时,磷肥回收率降低。且不同土壤类型中作物达到最大吸磷量时的土壤有效磷饱和点存在很大差异,武昌的有效磷饱和点仅为8 mg/kg,重庆水田的为15 mg/kg左右,郑州的为20 mg/kg左右,而祁阳红壤的土壤有效磷饱和点可达184 mg/kg [13] 。PK+M处理磷肥回收率随土壤有效磷含量增加呈上升趋势,与PK处理变化趋势相反;可见,有机肥提高氮源情况下,有效磷含量越高,作物吸收磷素越多。
4.3. 不同施肥模式下小麦玉米吸磷量分析
不同处理不同作物吸磷量差异显著,本研究中,无机肥处理中小麦吸磷量大于玉米吸磷量,增施有机肥处理中小麦和玉米吸磷量相当。本研究中小麦和玉米平衡施肥配施有机肥处理作物吸磷量比平衡施用化肥处理高出23.5%和16.9%,而南昌水稻吸磷量在增施有机肥处理中比化肥处理高出2% [9] 。出通过对照NP和NPK处理发现,钾素对小麦的吸磷量影响不大,可减少玉米季吸磷量。潮土中作物吸磷量明显高于祁阳红壤作物吸磷量,与土壤类型和施肥量有关 [16] 。综合来看,氮磷钾化肥处理或氮磷钾化肥配施有机肥能明显提高作物吸磷量。
5. 结论
施磷量、肥料种类和农田轮作制度从不同层次上影响作物的磷肥回收率和作物吸磷量。施肥量不同时,作物磷肥回收率符合报酬递减效应。山东潮土定位试验小麦玉米磷素吸收特征、磷肥回收率及与有效磷响应关系表明,磷肥回收率与施肥模式存在很大的关系,平衡施肥处理及平衡施肥增施有机肥可提高磷肥回收率。PK处理中由于缺失氮肥影响作物生长,土壤有效磷越高磷肥回收率越低。前14年,NP处理和平衡施肥处理磷肥回收率及作物吸磷量差距不大,可考虑潮土前期种植中减施或不施钾肥。不同施肥模式下,增施有机肥处理作物吸磷量明显大于无机肥处理;对于不同作物吸磷量的大小,无机肥处理中小麦吸磷量大于玉米吸磷量,增施有机肥处理中小麦和玉米吸磷量相当。
基金项目
国家重点研发计划子课题(2016YFD0300804-5),公益性行业(农业)科研专项(201303103和201203030),“海外泰山学者”建设工程专项经费,948项目(2014--S21)和小麦现代农业产业技术体系:平衡施肥(CARS-03),山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2016DB28)、山东省重点研发计划项目(2016CYJS05A01-3)。