1. 引言
干旱通常是由于一地降水偏少而导致土壤水分与河流水量减少的自然现象,并随时间的持续而形成灾害。随着现代社会经济的快速发展,以及对水资源需求的增加,干旱愈演愈烈。因此,干旱一直是人类关注的重点问题之一。国内外学者从干旱监测、预测、影响机理与风险评估等方面进行了广泛探讨。自标准化降水指数提出以来 [1] ,许多学者基于降水序列资料,应用标准化降水指数,研究了干旱的时间变化趋势、空间分布特点,以及干旱发生频率等特征 [2] [3] [4] 。国内学者侧重分析干旱时空变化特征,如车少静等 [5] 应用标准化降水指数(SPI),研究了河北省旱涝变化特征;闫峰等 [6] 分析了近50年河北省干旱特征;龚艳冰等 [7] 分析了云南曲靖市的干旱特征。此外,国内学者在分析干旱变化的基础上,还探讨了区域干旱演变对作物产量的影响 [8] 。由于SPI多时间尺度、空间可比性等特点,已被世界气象组织推荐为国际气象干旱通用指标 [9] 。
巨鹿县地处河北省南部太行山东麓冲积平原,属黑龙港流域,暖温带半干旱大陆性季风气候,四季分明,日照充沛,降水集中且年际变化较大。巨鹿县是河北省粮食主产区,也是全国著名的金银花生产之地,受季风气候特征影响,气象灾害多发频繁,其中旱涝风雹等对农业稳产高产影响较大。本文以巨鹿县为例,根据近58年(1959~2016年)气象资料,根据标准化降水指数,探讨当地气候变化特征及干旱演变特征,为地方农业生产提供决策依据。
2. 资料与方法
本文所用气象资料来自河北省气象信息中心。包括1959~2016年(58年)巨鹿县气象局月平均气温与月降水量资料。
采用线性倾向估计方法 [10] ,分析年平均气温和年降水量的变化特征。
标准化降水指数(SPI)是基于自然降水的
分布,首先计算降水量的
分布概率,然后经过正态标准化处理,从而得到标准化降水指数。其计算方法见文献 [11] 。具体如下:
假设某时段降水量为随机变量
,则其
分布的概率密度函数为:
其中:
分别为尺度和形状参数,
和
可用最大似然估计方法求得:
其中:
式中,
为降水量资料样本,
为降水量多年平均值。
确定概率密度函数中参数后,对于某一年的降水量
,可求出随机变量
小于
事件的累积概率为:
由于
分布函数中不包含
的情况,而实际降水量可以为0,所以累积概率表示为:
式中,
,为降水量为0时的事件概率,
为降水量为0的样本数,
为总样本数。
利用下式对累积概率进行正态标准化处理:
对其进行近似求解可得:
其中,
,并当
时,
,
;当
时,
。
,
,
,
,
,
。
本文采用的SPI干旱分级标准如下(表1):

Table 1. Classification of drought on SPI
表1. SPI干旱等级
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 气温变化特征
近58年来,巨鹿年平均气温为13.3℃,年平均气温最大值出现在1998年,气温高达14.5℃,最小值则出现在1984年,仅为12.0℃。从图1中可以看出,20世纪60年代到70年代,气温出现了下降趋势,而自80年代以后开始出现升高趋势,与全球变暖一致,90年代后期达到了最高(1998)值;进入21世纪以来,出现了一定时段(2008以后)的下降趋势,2010和2011年年均气温出现了12.9℃的低值。近58年巨鹿气温经历了20世纪60年代下降、70~80年代缓慢升高、90年代明显增加和近期(2008年以来)下降的波动式变化过程,总体上以增加趋势为主,气温变化倾向率为0.19℃/10a,并通过了统计显著性检验(信度0.01)。气温变化倾向率低于全国0.25℃/10a [12] ,可能与资料年代长短有关。
巨鹿年均气温的年代际变化具有明显特点,20世纪60、70和80三个年代的平均气温均为12.9℃,90年代则为13.7℃,21世纪第一个10年为13.9℃,最近6年(2011~2016)为13.5℃。可见,当前巨鹿仍处于气温相对偏暖时期。
3.2. 降水变化特征
巨鹿近58年年平均降水量为509 mm。总体上年降水量呈现减少趋势,倾向率为−7.38 mm/10a,但未通过统计显著性检验(图2)。就不同年代来看,20世纪60年代是近58年降水最多时期,平均538 mm,70年代与80年代略有减少,分别为514 mm和507 mm,90年代虽然出现了极端干旱年份,包括 1997和1992年降水量分别为247.9 mm及281 mm,但也有多雨年份,如1993年降水量为714 mm,故平均降水较80年代略有增加,达到513 mm。进入21世纪以来,降水出现了减少趋势,21世纪第一个10年平均降水量仅为488 mm,最近6年(2011~2016)平均降水量为497 mm。因此,当前巨鹿处于降水量偏少时期。
3.3. 干旱基本特征及变化
不同时间尺度的标准化降水指数(SPI)具有不同的意义,通常1个月时间尺度SPI主要反映气象干旱变化,3个月时间尺度SPI可以反映农业干旱状况,6个月及以上时间尺度SPI可表示水文干旱变化。为此,本文分析3~12个月尺度的干旱演变情况。对于巨鹿本地而言,干旱发生的持续时间和干旱强度是表征干旱特征的主要参数,故以轻旱(−0.5)为标准,分析每次干旱的持续月数(3个月及以上),以每次干旱持续过程的SPI月平均值表示干旱强度,其中单月最大值为干旱峰值。

Figure 1. Annual variation of mean temperature for Julu during 1959~2016
图1. 巨鹿年平均气温变化(1959~2016)

Figure 2. Annual variation of precipitation for Julu during 1959~2016
图2. 巨鹿年降水量变化(1959~2016)
3.3.1. SPI3
在近58(1959~2016)年中,持续3个月及以上时间尺度的SPI3干旱共发生30次,频率达到了51.7%,表明巨鹿农业干旱出现频繁,见图3。其中,出现在3~10月期间的共23次,对农业生产影响较大。强度最大的农业干旱出现在1997年6~10月,单月最大干旱指数为−3.48,平均为−2.4,其中7~9月连续3个月均达到极旱程度;其次是出现在1972年4~10月,单月最大干旱指数为−2.79,平均强度为−1.81;其它为1978年4~6月,最大干旱指数−2.60,平均强度−1.73;1965年7~10月,最大干旱指数−2.02,平均强度−1.53;以及1992年6~9月,最大干旱指数−2.43,平均强度−1.48;1968年2~9月,最大干旱指数−2.34,平均强度−1.36。同时,平均干旱强度达到中旱及以上的干旱事件共出现24次,该结果与巨鹿县的重要农业干旱实际情况一致。
持续3个月及以上时间的干旱在2000年前出现较多,每10年出现5~7次,2000年以来共出现5次;而持续2个月时间的干旱在2000年以前和以后各出现9次,即长时间尺度干旱在进入21世纪后发生次数有所减少,但相对短时间尺度干旱出现次数增加。
3.3.2. SPI6
在近58年中,持续3个月及以上的SPI6干旱共出现23次,见图4,发生频率为39.7%。各次干旱平均强度为中旱等级(>1.0)出现21次。强度最大干旱出现在1997年,从6月开始持续到1998年的1月,单月最大SPI6为−3.15,平均值为−2.23,而且极旱时间持续5个月(8~12月);其次持续4个月以上强度较大的干旱发生在是1992、1972、1974等,其中1972年出现了长达6个月(6~11月)的极旱。2000年以来共出现5次,干旱有减轻的趋势。
3.3.3. SPI12
在近58年中,持续3个月及以上的SPI12干旱共出现15次(图5),发生频率为25.9%。强度最大的干旱出现在1997年,月最大干旱指数值为−3.23,平均干旱指数为−2.23,持续时间为12个月;其次为1972年,最大干旱指数为−2.55,平均干旱指数为−2.08,持续时间12个月;1992年的干旱处于第三,最大干旱指数为−3.34,平均干旱指数为−1.79,其持续时间达到了15个月。12个月时间尺度干旱的主要特点为:持续时间相对较长,一般干旱均在8个月及以上,最长持续15个月,仅4次持续时间少于8个月;该时间尺度干旱跨年度出现次数较多,共13次,而且多数干旱开始月份以夏季6~8月较多。
3.3.4. SPI24
持续4个月及以上的SPI24干旱在近58年共出现了15次(图6),其中13次均为跨年度,其开始发
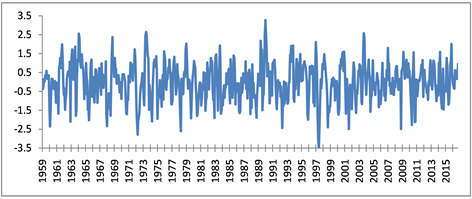
Figure 3. Time series of SPI3 for Julu during 1959~2016
图3. 1959~2016年巨鹿3个月时间尺度标准化降水指数变化(SPI3)
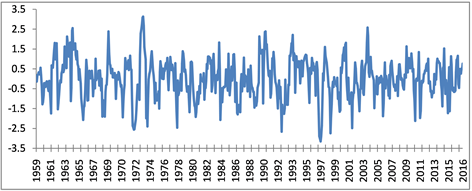
Figure 4. Time series of SPI6 for Julu during 1959~2016
图4. 1959~2016年巨鹿6个月时间尺度标准化降水指数变化(SPI6)

Figure 5. Time series of SPI12 for Julu during 1959~2016
图5. 1959~2016年巨鹿12个月时间尺度标准化降水指数变化(SPI12)
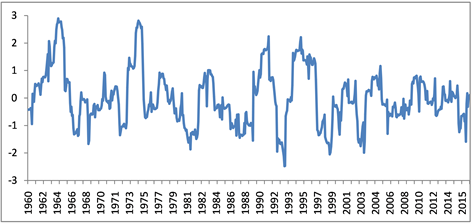
Figure 6. Time series of SPI24 for Julu during 1959~2016
图6. 1959~2016年巨鹿24个月时间尺度标准化降水指数变化(SPI24)
生时间有12次出现在7~8月,最长持续时间为1986年8月到1989年6月,共35个月。干旱强度最大为出现在1992年,单月最大干旱指数为−2.38,平均干旱指数为−1.67,持续时间长达15个月;其次为1997年,最大干旱指数−2.05,平均干旱指数−1.34,持续时间24个月,处于第三位的干旱是2002年8月到2003年9月,共持续14个月,单月最大干旱指数−1.99,平均干旱指数为−1.31。
综上所述,近58年巨鹿最严重的干旱时段集中出现在20世纪70年代和90年代,而且干旱强度较大,持续时间较长,对农业生产影响显著。
3.3.5. 干旱变化特征
以3个月时间尺度的干旱为例,巨鹿县20世纪干旱出现频繁,而且强度严重,其中2000年前3个月及以上持续性干旱共出现25次,平均强度为轻旱的仅发生4次,中旱14次,重旱7次,极旱1次;21世纪以来干旱强度和出现频率均有所减少,近16年共发生5次持续性干旱,轻旱和中旱分别为2次和3次。就年代际而言,20世纪60年代干旱发生5次,70年代发生7次,80年代发生6次,90年代发生7次,21世纪以来共发生5次。虽然干旱发生次数在减少,但总体上干旱没有显著的下降趋势。
虽然巨鹿年降水量自20世纪60年代以来出现了不显著的下降趋势,但在21世纪以来降水量变化相对平稳,极端干旱事件出现相对较少。
4. 结论与讨论
在近58年中,巨鹿气温出现了波动式变化趋势,其中60年代出现了气温下降趋势。总体上气温升高倾向率为0.19℃/10a,增温时段主要出现在20世纪90年代以后,而20世纪60年代到80年代当地气温变化相对平稳。年降水量则出现了不显著的下降趋势,降水减少倾向率为−7.4 mm/10a;年降水量近58年平均为509 mm,20世纪60年代平均为538 mm,但到21世纪第1个10年及最近6年则分别为488 mm和497 mm。
基于SPI的干旱分析表明:巨鹿持续3个月及以上的农业干旱(SPI3)发生频率超过50%,重大干旱出现时间以4~10月为主,平均强度达到中旱及以上的干旱发生频率为41%,故本地农业干旱发生频率高,强度大,影响严重,需要强化监测和减轻不利影响。
在全球气候变化(气温升高)背景下,巨鹿县干旱主要出现在20世纪70年代和90年代,进入21世纪以来,虽然平均降水量下降,干旱特别是重旱和极旱发生次数减少,但干旱下降趋势不明显。
气候变化既受大气候环境影响,同时也与本地地理环境有关。此外,站点观测资料长短及站址变化对其均有影响,时间长短不同的资料分析具有不同的结果。
致谢
本文部分工作受科技部公益性行业(气象)科研专项(重大专项)(中国干旱气象科学研究——我国北方干旱致灾过程及机理)项目资助。河北省气象科学研究所李春强研究员级高工给予指导,特此致谢。