Abstract:
In this paper, the arm force rod model is built to illustrate the microscopic mechanism of acoustic excitation and the vibrational modes of higher order are discussed ulteriorly. Five main factors, the height of the liquid level, liquid density, viscosity, temperature and the size of the wine glasses, are analyzed through experiments. The result shows the relationship between liquid levels or its density and frequency of wine glasses are negatively correlated and their value verifies the theoretical model well. Except that, the result also shows liquid viscosity and temperature are negatively correlated with the frequency, and the sensitivity of different size of wine glass to the liquid level and temperature is different.
1. 引言
由于发动机对飞机内部结构的声疲劳效应而对飞机构造进行破坏,所以在航空领域对声波激振的研究比较广泛 [1] [2] [3] 。激振声学检测作为一种新型的缺陷检测装置,以其效率高、范围广、劳动强度低等优点在检测结构缺陷领域得到国内外学者的广泛重视 [4] [5] 。因玻璃酒杯独特的可以明显表现共振现象、共振频率较低从而方便实现的构造,关于其声学与激振的研究对其他领域的推广显得尤为重要。
近些年,玻璃酒杯的声学已经被广泛研究,而基于此已经出现了两种乐器,Rossing T D讨论了这两种乐器的演奏方式,并讨论了不同激励方式与激励频谱之间的关系 [6] 。Matthieu Courtois在能量守恒模型的基础上,以搅拌液体和在酒杯中间加入一个圆柱形物体这两种模式下证明了液体的空间分布对产生的声音的频率起关键作用 [7] 。Jundt G采用平均时间下的全息干涉测量,得到液体的存在虽然能显著影响唱歌酒杯的声音频率但并没有改变酒杯的振动结构 [8] 。Joubert通过求解拉普拉斯方程,模拟出用手指在杯口摩擦产生声音时杯内水波的形状 [9] 。Uchida K指出玻璃琴的音色可以通过改变酒杯玻璃泡(即盛液体部分)的形状加以改进 [10] 。
虽然玻璃酒杯的声学已被广泛关注,但对玻璃酒杯的声波激振的原理及其影响因素的研究较少,而有关内部其液体性质对其共振频率影响的研究更是缺乏。2017年第30届国际青年物理学家锦标赛(the 30 th International Young Physicists Tournament)上出现过该类问题 [11] 。本篇文章将从以“臂力棒”模型解释产生共振的原因出发,结合French的能量模型,得到玻璃酒杯共振频率的表达式,并通过高度和液体密度的实验对其进行验证;并进一步讨论基础振动模式与高阶振动模式的关系;最后对杯中液体的黏度系数、温度和玻璃酒杯的尺寸对频率的影响进行实验并做探讨。
2. 共振的理论模型
2.1. 臂力棒模型
共振是指一个物理系统在特定频率下,比其他频率以更大的振幅做振动的情形;这些特定频率称之为共振频率。在共振频率下,很小的周期振动便可产生很大的振动,因为系统储存了动能,而声波激振则是产生共振的主要形式之一。
如图1,当声波传至玻璃酒杯壁时声音所具有的部分能量会表现为声压,这个压力会使具有弹性的玻璃酒杯壁产生形变,从而使玻璃酒杯内部产生应力,由于能量源源不断的传入,在靠近扩音器一侧不断产生应力,这时能量就会以应力波的形式在沿玻璃酒杯的侧壁进行传播。
下面讨论应力波传播的微观机制。在玻璃酒杯中,粒子与粒子之间是以弹性结合力的形式存在 [12] ,就像两粒子之间的存在一个弹簧钢丝一样,应力波的传播实际上就是粒子间结合力变化的传播的体现,而结合力的变化则可以概括为“臂力棒运动”。外界的声波激励使粒子发生相对振动位移,由于传播的应力波为纵波,物体振动的方向与传播方向一致,则两粒子a和b由于形变受到挤压,他们之间的结合力就会发生“形变”,向上弯曲如图2。
而结合力要恢复形变,就会有回到原有的平衡位置的趋势,此时结合力就会推动两粒子分离,而在这个过程的同时b与c又会相互挤压使结合力弯曲,此时就完成了一个应力波的传导过程,如图3。
由于固有频率的存在,当固有频率与声波频率不同,或者不是其整数倍时,粒子间的作用力表现为很强的阻力,应力波很难进行传播;当两者相等或固有频率为声波频率的整数倍时,此时表现为声波对应力波的不断激励加强,从微观看上述的传播过程将不断的重复,宏观上看系统的阻尼大大减低,玻璃酒杯的振动表现出较大的振幅,表现出玻璃共振的现象。
2.2. 共振频率的计算方法
由于实际的玻璃酒杯较为复杂,尤其是盛酒部分与杆的连接位置,首先对模型进行简化,将玻璃壳部分看成一个具有一定厚度的圆柱形玻璃壳 [13] ,简化示意图如图4所示。其中,
为水面圆半径、
表示水面的相对高度、
是玻璃壳的长度、
为玻璃壳的厚度。
当声波激励酒杯产生共振时,玻璃壳上任意一点的
可以表示为
(1)
其中,
表示共振的最大振幅,其数值由声音的响度和系统的阻尼有关;
描述玻璃酒杯的参数,其大小对厚度、半径、刚度、密度有关。
是形状因子,其表示的是共振时偏离原状态的程度,对于玻璃酒杯的共振可以看成两个椭圆的快速转化,如图5所示。
可以发现,当
时,玻璃酒杯上的点并没有偏离,这四处就是波节点,由于玻璃酒杯的圆形结构,就会有反向应力波的存在,正向波与反向波的矢量叠加形成会在玻璃壳上形成驻波,而上述四个点就是驻波的波节点。实验现象如图6,可以看到很明显的四极振动模式。其中标红点为声波传
Figure 1. Diagram of the acoustic excitation of the wine glasses
图1. 酒杯的声波激振示意图

Figure 6. Diagram of resonance phenomenon
图6. 共振现象示意图
入点,也就是扩音器所在的位置。
通过对计算整个系统振动的动能和势能的方法可以得到空杯子的共振频率为 [13]
(2)
其中
为杨氏模量,
为所装液体的密度
为杯子的密度,当添加部分水之后,共振频率可以由下式得到 [13]
(3)
其中
是一个常数与振幅有关,取决于酒杯本身。添加部分水的液体可以由空酒杯的共振频率得到
(4)
可见,酒杯中的水的高度是主要影响因子,这种特性使控制加水量的不同而控制音调进而制成乐器成为可能。
2.3. 多极共振模式
事实上,在玻璃酒杯共振中并不是只有的四极振动模式,还存在其他的振动模式 [14] ,在玻璃酒杯上形成的驻波的表达式可以表示为
(5)
其中νF为应力波的传播速度,如果同样假设玻璃酒杯的厚度为常数a,则应力波的速度就会由声波的速度νL相联系
(6)
其中有关系
,
,则
(7)
由此连续圆周上的频率与n不是呈整数倍上升,而是呈二次方关系,例如,n = 3时的频率是n = 2时的9/4倍,n = 4时的频率是n = 3时的16/9倍。当n = 3,4,5时所对应的六极、八极、十极振动模式如图7所示,T. D. Rossing用全息干涉测量验证了这个结论 [6] ,同时,因为水的存在不会改变系统的共振结构 [8] ,所以可以相信,在略低于高阶振动模式的频率下可以看到多极水面振动波纹。
3. 实验结果与分析
图8为实验装置的示意图,用扩音器使装有水的玻璃酒杯产生共振,连接在显示屏上的摄像机实时记录产生的现象,这样可以更好地观察实验现象和寻找共振频率,虽然观察法存在实验误差,但其值处在 ± 0.2 Hz之内,共振频率都在102~103 Hz数量级,同时对于频率随其影响因素的变化趋势而言,这种误差可以忽略。下面将从液面高度、液面密度、液体黏度、液体温度和酒杯尺寸五个因素对共振频率的影响进行探究。
3.1. 液体高度对频率的影响
取容积为350 ml的酒杯,这种酒杯是市面上比较常见的玻璃酒杯,由于酒杯无刻度线所以控制酒杯
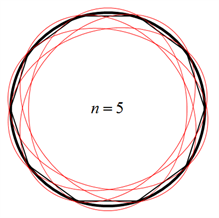
Figure 7. Figure of high-order vibration modes
图7. 高阶振动模式图
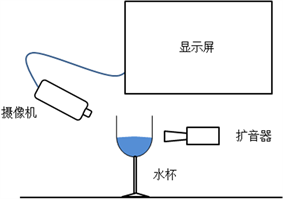
Figure 8. Diagram of experimental device
图8. 实验装置示意图
的高度具有较大难度,且精确度通常不高,在此使用10 ml针管每次抽取相同体积的液体来控制高度的变化。详细的实验步骤如下:
· 取干净的350 ml酒杯,并倒满蒸馏水但注意不要溢出,控制水面的最高处恰好到达杯口位置;
· 调节扩音器输出音频的频率,直至在显示屏上观察到最大振幅的共振现象,并记录此时频率fd;
· 测量水面高度h,并从玻璃酒杯中用针管抽取10 ml水,重复1、2步骤;
从前面的理论推导中可以得到
(8)
其中,实验测得酒杯的密度为3.57 g/cm3,蒸馏水的密度取为1 g/cm3,空杯时的共振频率为783 Hz,酒杯的有效高度为100 mm,玻璃酒杯的厚度和半径分别为0.35 mm和39.8 mm,用软件对所得数据进行拟合,并回归出系数β,结果如图9所示。
图中点为实验数据,曲线为理论曲线,得到的β = 0.4971,可以看出当液面酒杯中的液面升高时,其共振频率降低,且实验结果与French能量模型结果基本吻合。由于实际的R并非是恒定的,在趋于杯颈处的半径逐渐减小,这可能是造成误差的主要原因。
3.2. 液体密度对频率的影响
液面的高度会对共振频率产生较大影响,所以质量分布对共振频率起到关键作用,下面探讨液体的密度对频率的影响。将10、20、30、40、50、60、70、80、90 g食盐分别溶入350 ml蒸馏水中,制得不
同浓度的溶液,再将其转到酒杯中,为更好控制水面高度不变的,每次添加溶液时使水面最高处刚好到达玻璃酒杯上沿,值得注意的是,在转移溶液后要在液面静止时再进行测试,在Matthieu Courtois的研究中,搅拌的液体对玻璃酒杯的共振频率也有影响 [7] 。由(3)式可得
(9)
将实验测得的ρl与(f0/fd)2进行拟合,拟合的结果见图10,可见(f0/fd)2与ρl基本满足一次关系,再次验证理论的准确性。
3.3. 液体黏度系数对频率的影响
实验采用葡萄糖溶液与食盐溶液进行对比,比较在密度相同的情况下,两者的共振频率是否一致。将10、20、30、40、50、60、70、80、90 g葡萄糖分别溶入350 ml的蒸馏水中,得到具有不同浓度不同黏度的溶液,分别测得其共振频率并与食盐溶液进行对比,结果如图11所示。
随着葡萄糖溶液的密度的升高,其黏度也在升高,葡萄糖曲线与食盐曲线的之间的差距也越来越大,可见当酒杯内液体的黏度增大时,酒杯的共振频率也将降低。
3.4. 液体黏度系数对频率的影响
在实验中发现,不同环境下(比如温度不同),酒杯的共振频率也是不一样的。将液体加热至沸腾,然后转移至酒杯中,直至水面最高处刚好到达玻璃酒杯上沿,使其自然冷却,每隔2分钟调频率使其共振并记录此时温度,实验结果与拟合曲线如图12所示。
可以看出,当酒杯中的液体温度升高时,其频率会相继降低,在实验中还发现不同型号的酒杯对温度的灵敏度不同,即在DT相同的情况下,不同类型的杯子对应的Df是不同的。取相同形状的210 ml、350 ml、540 ml三种容积的酒杯进行温度实验,实验结果如图13所示,210 ml的频率改变量不明显,350 ml较为明显,540 ml的酒杯明显大于以上两者,可见,容量大的酒杯对温度的灵敏性强。
3.5. 杯子尺寸对频率的影响
不同尺寸的杯子对温度的灵敏性不同启发我们,探讨相同形状下,杯子的尺寸对共振频率的影响。
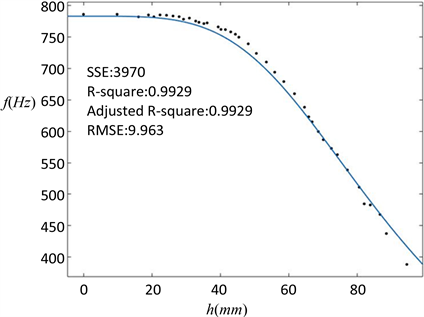
Figure 9. Fitting result of liquid level-frequency
图9. 液面高度–频率拟合结果
对三种形状相同,容积分别为210 ml、350 ml、540 ml进行高度–频率实验,实验结果如图14。
当水位较低时,杯颈对酒杯振动的约束能力较强,三种酒杯都无明显变化,当水位逐渐升高时,低容量的杯子变化幅度较大,中容量次之,高容量对高度变化量最小,这种现象可以归因于大酒杯的高度较高,即公式(8)中H较大,对水面高度的变化Dh反应较弱,故变化较小,小酒杯则相反。可见,由于频谱更宽,小酒杯显然更加适合用来演奏。另外,在相同水面高度下,容积越小频率越高。
将其数据根据能量模型拟合,即可得到不同尺寸下β的值,结果如表1所示,β取决于振幅,其值可能与杯壁和颈部连接处的厚度变化有关。
4. 结论
采用臂力棒模型可以形象地解释应力波在玻璃酒杯中传播的微观机制,由于酒杯特有的圆形结构与弹性,使其具有多种振动模式。在实验操作中,本文得到了以下结论:1) 液面高度、液体密度与酒杯的共振频率呈负相关,且实验结果与理论符合较好;2) 液体的黏度系数越高,酒杯的共振频率越大;3) 液
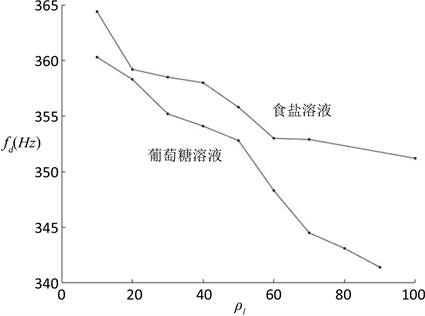
Figure 11. Relation of liquid density-frequency
图11. 液体黏度–频率关系

Figure 13. Relation of temperature-frequency of different size glasses
图13. 不同酒杯温度–频率关系
表1. 数据拟合结果
体的温度越低酒杯的共振频率越低,且形状相同的情况下,酒杯的容积越大对温度变化的敏感度越高;4) 对与同种形状的杯子,容积越小的酒杯频谱越宽,频率总体越高。对酒杯进行圆柱形简化可以较好解释共振现象,但由于没有考虑与杯颈部分连接处的影响,使得计算结果并不完全与实验相符,而且此部分结构较为复杂,需要进一步深入研究。
基金项目
成都理工大学优秀创新团队项目资助(No. KYTD201704)。