Abstract:
The distributed generators (DG) make the establishment of switch function extremely complex and slow searching when optimization algorithms are applied to locate the fault points. In order to make the location of fault points of distributed system with DG rapid and accurate, the model based on bilateral power flow is established in this paper, suited for not only single-source-single- fault situation, but also the situation of multiple distributed generators with multiple faults. A regional processing method for DG distribution network is raised, which divides the network into active trees and passive branches. The solution’s dimension is reduced by eliminating the passive branches free of fault current, so as to improve search efficiency. This method takes fault position as variable, so a large number of infeasible solutions are eliminated by limiting the fault number. It applies harmony algorithm on global optimization due to its speed and accuracy. The validity and rapidity are confirmed by example analysis.
1. 引言
分布式电源因清洁、经济及有效提高电力系统可靠性等特点而被广泛应用,但配电网的故障定位也因其接入产生了新的影响,主要为以下两点:① 传统配电网只由主变电源供电,因此故障电流为单向流动,但是含DG的配电网中故障电流为双向流动;② 传统配电网发生故障时,故障电流只存在于主变电源到故障点的路径中,含DG的配电网,每个DG都会向故障点提供故障电流,使得存在故障电流的线路数目大大增多。所以,通过优化算法进行故障定位时,开关函数的建立变得非常复杂,搜索速度也比较慢。
目前已存在的故障定位算法主要分为直接和间接两大类。直接算法主要为矩阵算法 [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] ,其特点是速度快,适用性和容错性通过学者们的努力亦加强不少。间接算法主要是神经网络算法和智能群体算法,遗传算法,粒子群算法和蚁群算法等是主流的群体智能算法,此类算法特点是容错性好,但是算法计算速度与进化参数的设置关联度大,若进化参数设置不合理,则算法容易陷入局部最优或难以收敛 [6] - [12] 。
多尺度量子谐振子优化算法 [13] 主要有以下优点 [14] :① 概念简单,容易实现;② 具有良好的自适应性和全局收敛性,能有效地适应规划求解问题,能够避免陷入局部最优解的情况从而获得全局最优解。因此,本文利用多尺度量子谐振子算法进行含分布式电源(DG)的配电网故障定位研究。本文提出一种适用于含DG的配电网分区域处理方法,以故障位置的为变量,利用故障个数来避免产生不可行解,以提升故障定位速度,并通过算例分析,验证了所提方法的正确性和实用性。
2. 多尺度量子谐振子优化算法的原理
2.1. MQHOA模型描述
MQHOA以量子理论为基础,模仿量子谐振子波函数从高能态多个高斯分布叠加向低能态单一高斯分布这一收敛过程的概率解释。谐振子通常被用来描述在平衡位置附近的振动,优化算法的解空间的搜索也可以近似被看作是在最优解位置附近的振动。在量子力学中,一维谐振子势能函数如式(1):
(1)
在谐振子势能条件下根据量子谐振子的薛定谔方程解得量子谐振子的波函数概率密度如式(2):
(2)
波函数概率密度随能级变化曲线如图1所示。量子谐振子的波函数从高能态向基态的变化是一个逐渐收敛的过程,这一过程描述了算法同一尺度下多个高斯采样区域在迭代过程的不断聚焦过程,通过引入多尺度优化函数二进信息高斯采样模型,使算法能在不同尺度进行不同精度的搜索聚焦同时保证不遗漏采样,从而获得所求解问题的全局最优解。
2.2. MQHOA算法的基本流程
MQHOA算法的基本过程如下(一维目标函数) [15] :
① 初始化k 、m 、σmin 在目标函数定义域范围内随机生成k 个初始采样中心位置ki ,并设定初始尺度σs = MAX-MIN,[MIN,MAX]为目标函数搜索定义域。
② 按k 个高斯分布
在目标函数定义域各生成m个采样位置,根据采样位置对应的目标函数值从新生成的k × m 个采样位置中选出k 个较优的采样位置更新ki 。
③ 如果k个较优采样位置ki 之间的标准差σk 满足
,则返回步骤②
④ 如果
,则尺度减半为
,并返回步骤②
⑤ 依据目标函数取 k 个采样中心位置ki中的最优位置为结果输出。
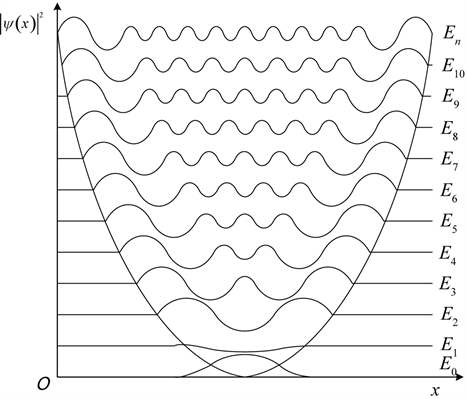
Figure 1. Variation of probability density of harmonic oscillator wave function with energy level
图1. 谐振子波函数概率密度随能级变化示意图
其中 k 为群体参数,m为采样参数。算法在初始化时通常将目标函数定义域作为初始采样尺度开始迭代,σs为s尺度下高斯采样的σ 值,它在进行尺度迭代时逐次减半,直到搜索尺度σs小于预设的最小尺度σmin时停止。σmin事实上就是求解精度,文中通常取为0.000001。迭代进行时当前k个较优解采样位置的标准差为:
(3)
MQHOA算法的收敛过程包含两个迭代步骤:一个是在同一尺度下的量子谐振子收敛过程(quantumharmonic oscillator,QHO收敛);一个是多尺度收敛过程(multi-scale,M收敛)。QHO收敛过程实现对搜索空间的逐步收缩定位,M收敛过程实现对采样精度的逐步提高。MQHOA算法从数学的角度也可以认为是一种多尺度高斯邻域采样群体算法。对高维函数进行优化时只需要对各个方向的坐标分别执行QHO收敛过程,待所有坐标方向上的QHO迭代都分别达到收敛条件后,再减小尺度进入下一轮QHO收敛过程。
3. 多尺度量子谐振子优化算法在故障定位中的应用
多尺度量子谐振子优化算法实现配电网故障定位的基本原理是根据FTU设备上传的故障电流信息,对开关故障电流信息和线路状态信息进行编码,并通过定义开关函数将线路状态信息转换成相应的开关故障电流信息,再利用目标函数来评价各个解的优劣程度,从而找出最优解,即为FTU信息对应的故障位置。
3.1. 编码方式
线路的故障状态采用0和1二进制编码方式,0代表无故障,1代表有故障,种群中解的信息即为线路状态信息。线路状态对应的开关电流信息用−1、0、1来编码,−1代表有负方向过电流,0代表无过电流,1代表有正方向电流。本文定义主变电源的潮流方向为正方向。因此,顺着主变电源潮流方向的过电流为正,逆着主变电源潮流方向的过电流为负。
3.2. 开关函数
配电网发生故障时,从FTU得到的信息是各个开关的故障电流越流信号,为实现故障定位,必须建立从线路的故障状态到开关设备故障电流信息的转换。本文假设DG的短路容量能覆盖系统总负荷。建立的开关函数包含两部分,第一部分为主变电源提供的故障电流,即主变电源到故障点通路所包含的开关电流,其越限电流方向为正方向;第二部分为各DG提供的故障电流,即DG到故障点通路所包含的开关电流,其越限电流方向由方向系数w决定。开关函数如下式
(4)
式中,
为第j个开关的开关函数,正常值为0,有正方向的故障电流为1,有负方向的故障电流为−1;I为主变电源到各故障点的通路所包含的开关集合;k表示分布式电源的个数;Nm为第m个DG到故障点的通路所包含的开关集合;I(i)为集合I中第i个元素所对应的开关;Nm(n)为集合Nm中第n个元素对应的开关;w为开关电流的方向系数,当过电流逆流时,w = −1;当过电流顺流时,w = 1。
如图2所示接有一个DG的简单馈线网络,当线路c发生短路故障时,CB及s1、s2的过电流由主变电源提供,故障电流为1;s3、s4的过电流由DG提供,且方向与正方向相反,故障电流为−1。

Figure 2. A simple feeder network with DG
图2. 含DG简单馈线网络
3.3. 目标函数
目标函数即评价函数,是优化算法能否成功进行故障定位的关键。目标函数的构造直接影响到故障定位的准确性、容错能力,以及算法的收敛速度。本文建立的目标函数采用异或运算,适应度函数值越小代表开关电流与FTU上传信息相似度越高,如下式
(5)
式中,Ij 为FTU上传的过流信息值;−1代表有负方向过电流,0代表无过电流,1代表有正方向过电流;
为开关函数得到的开关电流值,−1代表有负方向过电流,0代表无过电流,1代表有正方向过电流;xor为异或运算符,相同为0,不同为1。
如图2所示网络c处发生故障,开关电流
为(1 1 1 −1 −1),若FTU上传的信息为(1 1 1 −1 −1),则
,
,可得
。
4. 网络结构分区域思想的应用
考虑到配电网闭环设计、开环运行,呈辐射状的结构特点,以及DG接入后对配电网故障定位的影响,将配电网络看成一个有向图,将度(图中与某个顶点相关联的边的数目)为1且以电源点为顶点的连通图定义为有源树,除去有源树剩余的路径称为无源树枝,这样就把整个配电网络划分为一个有源树和若干个无源树枝。有源树包含网络中的所有电源,由于系统发生故障时各电源都会提供故障电流,所以在定位过程中有源树包含的所有开关都应予以编码,参与运算;无源树枝本身无电源,依靠有源树提供故障电流,若某个树枝无故障,那么整个树枝的节点都无故障电流,在定位过程中可以不予考虑,缩短算法中解的维度,从而提高定位效率。如图3所示。
该配电网接有4个DG,实线相连的网络结构为有源树,虚线相连的为无源树枝,图中共有6条无源树枝。假定F1发生故障,则FTU上传的故障电流信息中6条无源树枝均无故障电流,将无源树枝全部剔除,可以将解的维数由33维减少到14维,大幅度地提高了运算速度。
5. 算例分析
本文以图3所示的配电网结构作为算例,在MATLABR2015a环境下,处理器为2.3 GHz、内存为8 GB的PC上进行仿真,分析算法的合理性与有效性。多尺度量子谐振子算法参数设置如下:采样中心位置
,采样位置
,求解精度
。
5.1. 单故障与双故障算例分析
本文分别对单故障、双故障情况随机生成FTU信息进行100次仿真,其迭代次数、耗时与正确率统计结果如下表所示。本算法对于含DG配电网单故障和双故障定位的正确率为99%,几乎不会出现误判,且运用多尺度量子谐振子优化算法实现故障定位速度非常快。由表1可知,单故障与双故障的最小与最大耗时相差不大,但是平均耗时有较小差距。仿真结果证明了多尺度量子谐振子优化算法能够准确、高效的解决含DG配电网故障定位问题。

Table 1. Results for one fault and two faults simulation
表1. 单故障与双故障仿真结果
5.2. FTU信息畸变情况算例分析
本文设置的终止判据是相同最优解的连续代数,当连续代数超过一定值时跳出循环。判据代数的设置对畸变FTU信息的故障定位显得尤为重要,判据代数过小会降低正确率,过大会增大耗时。分析结果如图4、图5所示。由图4可知,随着代数由10增大到80,正确率迅速升高达到97%,但是当代数80增大到100时,正确率基本无变化。因此,只要判据代数设置合理,本算法对于FTU信息畸变情况的故障定位准确率可以达到很高,且并不是随着判据代数的增大一直增大,当判据代数达到一定值时,继续增大不再影响正确率。
由图5可知,随着代数的增大,消耗的时间基本呈线性增长。因此,综合正确率与耗时考虑,对于本算例,判据代数取80代最优,正确率高且耗时短。
6. 结论
根据所提出的含分布式电源配电网故障定位模型,针对FTU信息正常、FTU信息有畸变缺失、单故障以及多故障等情况,分别进行了定位仿真分析,通过算例验证得出如下结论:
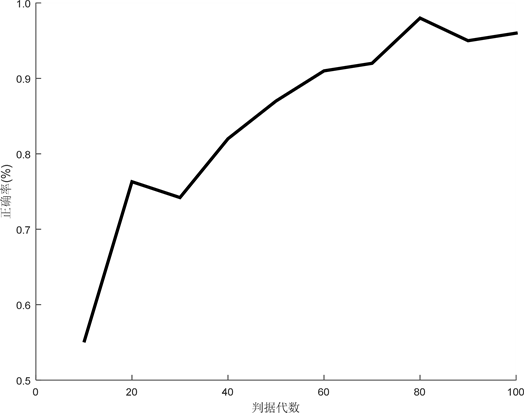
Figure 4. Curves of accuracy and criterion iterations under the situation of information distortion
图4. 信息畸变情况正确率与判据代数的曲线

Figure 5. Curves of time-consuming and criterion iterations under the situation of information distortion
图5. 信息畸变情况耗时与判据代数的曲线
1) 按照本文提出的开关函数与评价函数,通过多尺度量子谐振子优化算法进行求解,能够有效的实现不同情况下故障定位,而且速率与准确率都较高。
2) 仿真显示对于有畸变信息故障定位,判据代数存在一个最优值,使其既满足正确率的要求也满足时间的限制。