1. 引言
空气与人们的生活密切相关,近年来,由于我国经济飞速发展,城市化进程不断加快,城市人口持续增长,人类活动使原本保持稳定的空气遭到越来越严重的污染。城市中大量的车辆和人口引发的汽车尾气以及居民生活和取暖等问题使空气质量开始逐渐恶化,严重威胁着城市居民的日常生活和人体健康,破坏城市生态。空气中含有的一些污染物如果超过一定浓度极有可能对人体产生健康威胁,引起各种各样的疾病。全面掌握城市空气污染源的排放数据,了解污染分布情况,完成对于空气质量监测、分析以及城市空气质量评价的研究,掌握城市空气质量在空间的分布,对城市规划与建设、污染控制、环境管理有重要的理论意义与实用价值。现今国内外都在进行环境质量评估相关工作,到现在为止,有很多评价空气质量的方法,比如模糊聚类法、层次分析法和人工神经网络法。空气本身涉及到众多的参数和复杂的数学模式,这些评价方法具有一定的局限性,很难对空气质量进行准确的评价。本文针对空气质量指数监测数据中存在的不确定性等问题,以PM2.5、PM10、SO2、CO、NO2、O3六类主要空气污染物作为指标,建立自组织竞争网络模型(self-organizing feature map),在保证数据的模糊性和随机性的基础上,对湖北省13个主要州市空气质量指数监测数据进行分析,得到湖北省城市空气质量在空间的分布情况。
在进行环境污染治理时,针对性地消除空气中的污染物、了解污染物之间的相关性有助于提高环境治理工作的效率。关联规则是描述数据库中的数据项(属性、变量)之间所存在的(潜在)关系的规则。2012年我国环保部批准发布的《环境空气质量标准》(GB3095-2012)明确规定了PM2.5、PM10、SO2、CO、NO2、O3六类主要污染物的浓度限制和分级标准 [1] 。本文以湖北省空气监测数据为依托,应用经典关联规则数据挖掘算法Apriori算法发现主要污染物之间的关联规则,找到他们的相关性。
2. 数据来源及数据预处理
选取2015年1月~2017年4月湖北省13个州市(武汉市、黄石市、十堰市、宜昌市、襄阳市、鄂州市、荆门市、孝感市、荆州市、黄冈市、咸宁市、随州市、恩施自治州)6个空气质量指标:PM2.5、PM10、SO2、CO、NO2、O3,相应指标数据来自中国空气质量在线监测分析平台。
选取的六个指标具有不同的量纲和量纲单位,为了消除指标之间的量纲影响,采用最大最小法对数据进行标准化处理,使结果值映射到[0,1]之间。各指标平均值标准化数据见表1。
3. SOM网络模型在湖北省空气质量分析中的应用
芬兰学者Kohonen提出自组织竞争网络模型(SOM),他认为,一个神经网络在接受外界输入模式时,

Table 1. Standardized data for average value of each index
表1. 各指标平均值标准化数据
可以对输入信号特征进行自适应学习,从而自组织形成对输入模式将具有不同的响应特征的不同区域。在输出空间中,这些神经元形成一张功能相同的神经元靠得较近、功能不同的神经元分得较开的映射图,因此叫做自组织特征映射网络,通过竞争学习完成 [2] 。
当接受一种输入模式后,其输出层其中一个神经元得到最大限度的刺激从而竞争获胜,同时也因侧向相互作用使获胜神经元附近的一些神经元得到较大刺激。然后,修改这些神经元和输入神经元之间的连接权值,二维平面上获胜的输出神经元会随着输入模式改变发生相应改变。
SOM网包括可以模拟感知外界输入信息的视网膜输入层以及模拟做出响应的大脑皮层两层,输出阵列见图1。
本文根据自组织竞争网络具备的自组织、自适应的数据压缩、特征抽取等特点,以PM2.5、PM10、SO2、CO、NO2、O3作为指标体系,建立SOM网络模型。应用SOM网络进行空气质量评价分类的步骤如下 [3] :
1) 选取标准空气质量样本;
2) 对每一种标准空气质量样本进行学习,学习结束后,对具有最大输出的神经元标以记号;
3) 将待分类数据输入到SOM模型中。
运用MATLAB软件编写程序,建立SOM网络,按照SOM算法步骤,设定学习率在前1000步训练中从0.5线性下降至0.04,接着在训练到10,000步时减小至0。优胜领域半径初值设定为2个节点,1000个训练步时减至0。然后将表中的数据样本进行归一化处理,输入网络并进行训练,依次进行5、20、50、100步数训练。当训练步数为5时,城市空气质量被分为4类,此时网络已经对数据进行了初步的分类。当训练步数为50时,分类更加细化,大多数都是单独被划分为一类,这时如果继续提高训练步数,已经不具备实际意义。根据实际情况选取5步训练结果,湖北省城市分类结果见表2。
根据上述结果,以绿色颜色深浅表示城市的空气质量情况(绿色颜色深表示级别越高,城市空气污染度成都低,空气质量好),绘制湖北省城市空气质量级别评价图,表征湖北省城市空气质量的空间分布特征,见图2。

Table 2. Results of urban classification in Hubei province
表2. 湖北省城市分类结果
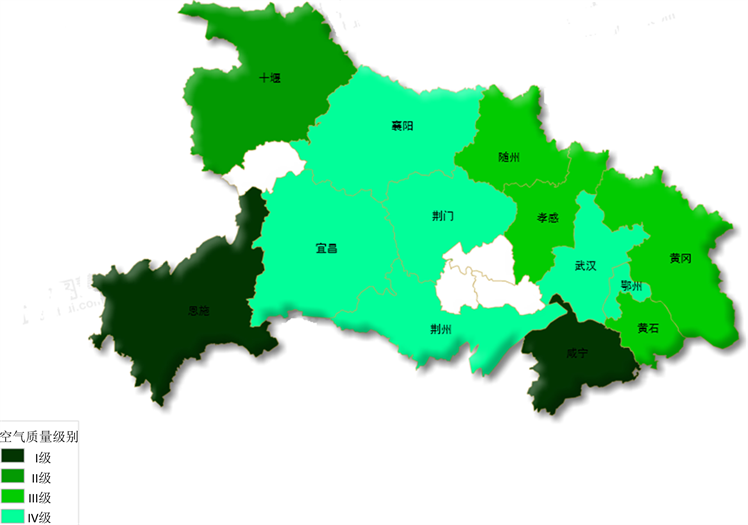
Figure 2. Urban air quality evaluation of Hubei province
图2. 湖北省城市空间质量级别评价
由图可知,湖北省城市空气质量在空间上由外围向中心变差,空气污染程度加剧。绿色最深的城市是恩施自治州和咸宁市,分别位于湖北省西南部及东南部,空气质量最好;其次为十堰市,位于湖北省西北部,空气质量较好;位于湖北省东北部的黄冈市、孝感市、黄冈市、黄石市绿色颜色较浅,城市空气质量较低,空气污染程度较低;荆门市、鄂州市、宜昌市、武汉市、荆州市、襄阳市位于湖北省内部地区,绿色最浅,是省内空气质量最差的区域。从基于SOM模型分析湖北省13个主要州市空气质量数据得到的结果来看,从总体来看,大部分城市都处在程度不同的环境污染问题当中,需要得到及时治理。
4. 关联规则挖掘空气污染物相关性
关联规则由Agrawal等人于1993年首先提出用于挖掘顾客交易数据库中项集间的联系,最成功的应用之一是超市的购物篮研究 [4] 。设数据集为
,
为一个项目的集合,事务
表示项目子集
,而每个子集都有唯一的标识
。
是由项目子集构成的集合,叫做项集。当且仅当
时,我们才认为事务
是包含项集
的。另外,当项集
包含
个项目时,项集
称为
项集 [5] 。
关联规则是形如
的逻辑蕴含式,其
中且
。而关联规则
指的就是事务数据库D的支持度,表示的是项集X在整个数据集D中所占的百分比 [6] 。支持度作为衡量关联规则强弱的重要标准,描述的是挖掘出来的规则在整个事务库中出现的频率。在挖掘过程中,用户可以根据实际需要来设定自身所需的支持度的阈值,通常称为最小支持度,记为min_sup。
(1)
(2)
置信度是关联规则中对挖掘出来的关联规则正确率的评判标准,取值范围是[0,1]。与支持度一样,用户可以根据实际需要来设定相应的置信度阈值,称为最小置信度,记为min_conf,其中
。
(3)
关联规则的挖掘算法中最经典的是Apriori算法 [7] ,Apriori算法是1994年Agrawal提出的挖掘完全频繁项集中最具有影响力的算法。算法有两个关键的步骤:一是发现所有的频繁项集;二是生成强关联规则。该算法简单明了,易于实现,目前仍是使用最广泛的关联规则挖掘算法。关联规则按照变量类型分为布尔型关联规则和数值型关联规则,布尔型关联规则主要处理离散、种类化的数值类型,算法相对比较成熟。数值型属性的取值范围较广,在进行关联规则挖掘时通常将之转换成布尔型关联规则挖掘问题,即将属性取值划分为若干个区间,然后将每个区间映射为一个布尔型属性。
湖北省六种基本空气污染物监测数据为数值型数据,本文根据《环境空气质量标准》中规定的空气污染物浓度限值和分级标准(见表3),将指标数据映射为布尔型数据,得到364条记录,映射数据部分记录见表4,各指标映射结果见图3。
由上图可知,在记录中PM10、SO2、CO区间几乎没有变动,反映出这三种污染物在本文研究区域内基本相同,因此本文选取PM2.5、NO2、O3指标,利用Apriori算法探寻这三种主要污染物的相关性。
Apriori算法主要是通过产生一组更小的候选项集,根据阈值对产生的候选项集进行必要剪枝,以此来减少候选项集个数,最后由剩下的候选项集产生频繁项集,得到对用户有用的结果。运用Python软件编写程序,实现Apriori算法,设定min_sup为50,min_conf为0.8,最终得到以下关联规则:
规则1:6-I&1-II→5-Iconf:0.8384;
规则2:5-I&1-III→6-Iconf:0.8824;
规则3:6-II&1-II→5-Iconf:0.9107;
规则4:5-II&1-III→6-Iconf:0.9545。

Table 3. Air pollutant concentration limits and classification standards
表3. 空气污染物浓度限值和分级标准(单位:mg/m3)

Table 4. Partial record of mapping data
表4. 映射数据部分记录
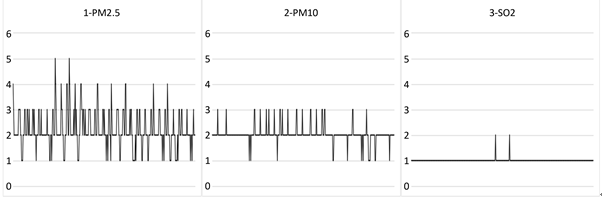
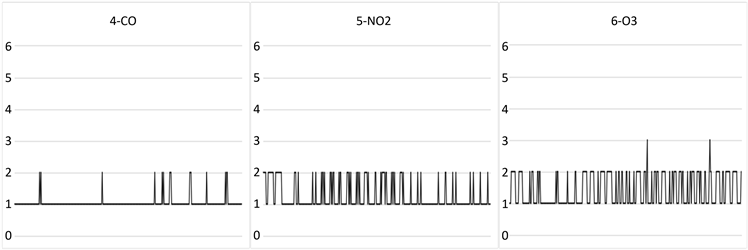
Figure 3. Mapping results of each index
图3. 各指标映射结果
分析规则我们发现PM2.5、NO2、O3这三种污染物之间存在很强的相关性,当O3I级、PM2.5I级时,NO2为I级的置信度为83.84%;当NO2I级、PM2.5III级时,得到O3为I级的置信度为88.24%;当O3为II级、PM2.5II级时,NO2为I级的置信度为91.07%;当NO2II级、PM2.5III级时,O3为I级的置信度为95.45%。
5. 结论
1) 利用神经网络中的自组织(SOM)神经网络进行湖北省13个州市空气质量评价,建立SOM网络模型,将13个州市分为四类,发现在空间分布上湖北省呈现从外围到中心空气质量降低的特征。评价结果与实际相符,从实践上证明了神经网络用于城市空气质量评价的优越性,SOM模型的建立解决了BP神经网络的精度低的缺点,大大提高了数据分类的精度,为人工神经网络在城市空气质量评价领域提供了新的途径。
2) 应用经典关联规则Apriori算法发现PM2.5、NO2、O3三种主要污染物之间的强关联规则,找到他们的相关性,有助于我们了解污染源,以便制定相应环境治理措施。