1. 引言
寄生物与宿主协同进化的研究,不仅在种群生态学领域受到广泛关注,而且对农作物培育、畜牧养殖、致病细胞的过度复制等领域的预测研究有重要启示 [1] - [7] 。目前研究寄生物与宿主相互作用的经典模型都是基于寄生物将导致宿主种群减少的前提下建立的。然而,寄生物在很多情况下也会导致宿主种群的增长,如大肠杆菌和乳酸杆菌与其宿主的关系 [8] [9] 。若系统中寄生物与宿主之间既存在互惠关系也存在寄生关系,则可称该系统为互惠–寄生耦合系统。文献 [10] 在不考虑扩散因素的情况下,建立了互惠–寄生耦合模型,并研究了其动力学性态。事实上,扩散广泛存在于生物系统中,自然界各种生物通过扩散方式扩大栖居范围,以便获得更多的资源。本文拟在互惠–耦合模型的基础上,引入扩散因子,建立具有扩散项的互惠–寄生耦合模型空间模型,研究其斑图动力学性态,进而得出扩散对宿主与寄生物密度空间分布的影响。
2. 主要结果
2.1. 建立空间模型
首先给出互惠–寄生耦合模型 [10]
(1)
其中
分别表示宿主与寄生物的种群密度,
表示寄生物对宿主的固有促进水平,当系统内寄生物与宿主的数量之比不超过
时,寄生物对宿主具有促进作用;当该数量之比超过
时,寄生物对宿主具有抑制作用;其它参数的含义见表1。
注:这里的寄生物的固有增长率
是指其不受密度制约情况下的增长率,以上各个系数均为正实数。
由Fick法则我们假定个体的扩散是随机的,这导致如下的表达:
,
,
其中
是二维空间的Laplacian算子,
,
分别表示扩散系数,结合模型(1),可得如下空间模型:

Table 1. Definitions and the symbols used in model (1)
表1. 模型1中的符号及含义
(2)
其中
,
。从生物意义上考虑,假设这里的所有系数都是正的。
2.2. 空间模型的分支分析
设模型(1)存在唯一的均匀定态解
,即
与
满足
.
对均匀态解
作一个微扰,令
,
,代入方程(2),经泰勒级数展开并去掉高阶项,可得线性微扰方程
(3)
其中
,
,
,
.
将微扰变量在傅里叶空间展开,令
(4)
代入微扰方程(3)得特征方程
(5)
解特征方程(5)得如下色散关系:
其中
,
解色散关系得
.
由斑图动力学理论及(4)知,当所有的特征值
的实部都小于0时,微扰随时间衰变为0,因而系统是稳定的。而当系统有一个特征值
时,微扰变量将随时间不断增加,系统的均匀定态解
失稳。如果该反应扩散系统是有界的,由于系统的唯一均匀定态解失稳,它一定会向某种时空非均匀态转化,而这种转化必然伴随着系数的某种时空对称性破缺 [11] 。设
是系统控制参量
的函数:
,在临界点
,有
,
,则
是系统的一个动力学分岔点 [11] 。最常见的分岔有:跨临界分岔,Hopf分岔和图灵分岔。
下面,类似文献 [12] 的分析,给出三种分支临界线的表达:
1) 在跨临界分支中,非扩散模型的一个特征值消失。因此,解
,
,可得跨临界分支参数
的临界值表达式:
.
由于参数
的取值范围为
,故系统(3)不会出现跨临界分支。
2) Hopf分支不稳定的出现对应于下面情况:对于非扩散模型来说,当根从负到正跨越实轴时产生了一对纯虚根。从数学角度看,当满足下列条件:
,
.
在
系统产生了Hopf分支,即
,
.
方程两边同时乘以
得
,
,
即可得Holf分支参数
的临界值表达式:
.
3) 令
,
则
是关于
的二次多项式,它在某些
值处取得极小值。首先假设非扩散模型在平衡点处是稳定的(特别的
),且图灵不稳定的发生需满足下面两个条件:(a)
(如果这个条件不成立,对于所有的
,由
可推出
)是图灵不稳定的必要条件;(b) 图灵不稳定的充分条件是
,线性分析给出了图灵斑图产生的条件如下:
,
,
,
;
图灵分支产生的条件如下:
,
,
,
且波数
满足
.
由
得
其中,
,
,
即
,
整理得
由
得
,
整理
,
即
,
整理得
,
两边同时乘以
得
令
,
,
,
上式可变为
.
进一步,令
,
,
.
整理得
,
由此得图灵分支参数
的临界表达式为
.
根据
的取值范围,上述两个值里面取正,且要保证
。
下面我们将利用以上Hopf分支和Turing分支的临界表达式,确定出图灵斑图出现的区域,即Turing区域。由区域图可以清晰的看出系统的稳定与失稳区域。
在图1中,红线和黑线分别表Hopf和Turing分支线,参数空间中区域I表示稳定区域;区域II表示Hopf没有失稳,Turing失稳区域,即Turing区域;区域III表示Hopf和Turing同时失稳区域。参数取为
,
,
,
,
,
。
3. 数值模拟
一个具体的系统将会出现哪种斑图结构是斑图选择的问题,它基于比较难的非线性分析理论,故使用分析法或一般方法对空间模型的动力学性态进行研究是比较困难的。而借助于计算机进行数值模拟是解决该问题的一个有效方法。用计算机求解一个复杂的方程组,事实上就是将连续问题转化为离散问题。二维空间中定义的连续反应扩散系统的求解问题可以转变为由
格子组成的离散区域问题来进行求解。每两个格子间的空间距离定义为步长
。在离散系统中,描述扩散的拉普拉斯算子
用有限差分法进行离散,即导数是
上的差分逼近,当
时,差分与求导近似相等。同样时间演化也离散化,时间步长为
,可以用Euler法解决,下一个时间步长的状态依赖于前一个时间步长。
下面我们首先给出空间模型离散化后的差分格式,并进行数值模拟。模拟过程中采用零流边界条件(Neumann边界条件),离散区域为
个格子。此外,对于空间模型的数值模拟还依赖于下面两个初值条件:一种是种群密度随机分布,另一种是种群在水平空间呈不同的密度分布,而在垂直空间呈同一密度分布。在这里,我们选择第一种情况,种群密度随机分布。首先利用有限差分法给出模型(3)的差分格式:
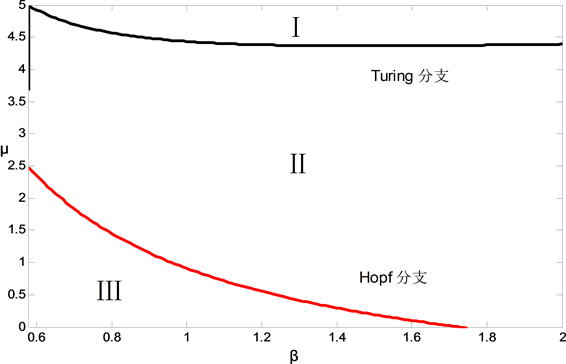
Figure 1. The parameter space of bifurcation
图1. 系统(3)的分支参数图
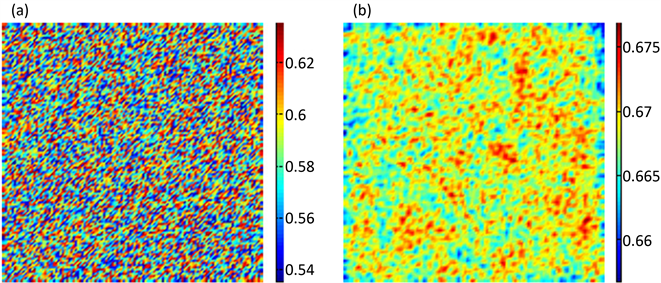
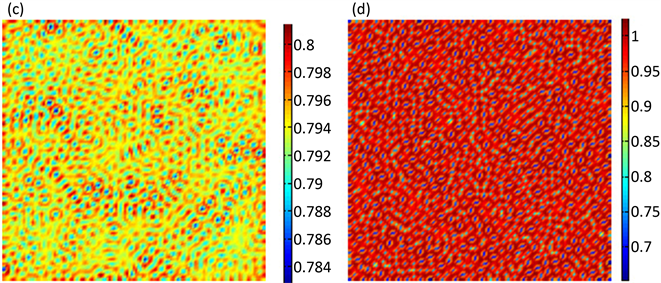
Figure 2. The time evolution of spatial pattern for parasitism
图2. 寄生物在空间分布的时间演化图
其中
.
零流边界条件离散为:
,
,
,
.
利用上述差分格式进行数值模拟,选取空间步长
,时间步长
。由于寄生物与宿主的空间分布很类似,在这里我们只给出寄生物的空间斑图。各图表示寄生物种群在空间状态下的分布,图中各颜色表示寄生物种群的密度(数量),不同的空间位置种群的密度不同,即图中呈现出不同的颜色。
图2给出了在迭代0,1000,10,000,100,000次时寄生物的斑图的空间演化,从图中可以看出初始不规则的斑图最终演化为规则的黑眼点状斑图,且动力学性态不再发生任何改变。模拟过程初始条件为正平衡点的小扰动,参数选取为
;
;
;
;
;
。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(31600299, 31560134);陕西省自然科学基础研究计划项目(2017JQ3020);陕西省高校科协青年人才托举基金(20160234);宝鸡文理学院重点项目(ZK2017021)。