1. 引言
随着人们生活水平的提高和诊疗技术的进步,患有髋关节处疾病的患者多数都愿意接受手术来缓解甚至解除病痛。与此同时,我国正迈入人口老龄化阶段,将会有越来越多的老年病患被关节炎、骨质疏松造成的股骨颈骨折等髋关节疾病所困扰,髋关节处的医疗服务需求呈现迅速增长趋势 [1] [2] [3] 。人工关节置换术被公认为是治疗髋关节疾患最理想的方法,其诊疗技术也逐渐走向成熟,并且越来越受到医生和患者的认可 [4] [5] 。但是新世纪的精准医疗理念对髋关节置换技术也提出了更高的要求,在进行人工髋关节置换术时,股骨与假体之间的精确配合对手术的成功及假体的使用寿命至关重要,而股骨颈干角在精准医疗中具有重要地位 [6] 。颈干角可以增加下肢的运动范围,并使躯干的力量传达至较宽的基底部,颈干角的异常会使髋关节周围力学关系发生变化,图1为股骨颈干角示意图。“Wolff定律”表明骨骼在不同力学刺激下将会发生不同形式的生长及结构转变 [7] [8] ,因此,进行髋关节颈干角参数变化对髋关节应变分布影响的研究在全关节置换术、先天性髋关节脱位及股骨颈骨折等髋关节疾病治疗方面有重要的意义。本文建立了不同颈干角的髋关节模型,从而研究不同颈干角对髋关节应变分布规律的影响。
2. 建立三维模型
本研究采用逆向工程的方法对髋关节的股骨和骨盆进行建模。将扫描好的人体骨骼CT图导入逆向工程软件中,经过前期处理,建立髋关节的散点模型,去除模型周围的体外散点和非连接点,生成髋关节的外表曲面。新生成的曲面存在凸起、凹坑以及孔洞等缺陷,如图2(a)中的股骨模型,需要进行表面处理去除这些缺陷使模型表面更光滑,同时也能起到简化模型的作用,表面处理后的模型如图2(b)中的骨盆模型。髋关节的假体部分较为规则,用三维软件UG对假体进行建模,建好的髋关节假体如图2中(c)-(f)所示。将处理过的完整股骨模型在小转子上方1 cm处截断股骨颈,大转子保留,生成置换后股骨三维模型,再将绘制好假体的装配到置换后股骨上,该过程在也UG中进行。装配好的髋关节模型如图2(g)所示。

Figure 1. Femoral neck angle and anteversion
图1. 股骨颈干角示意图
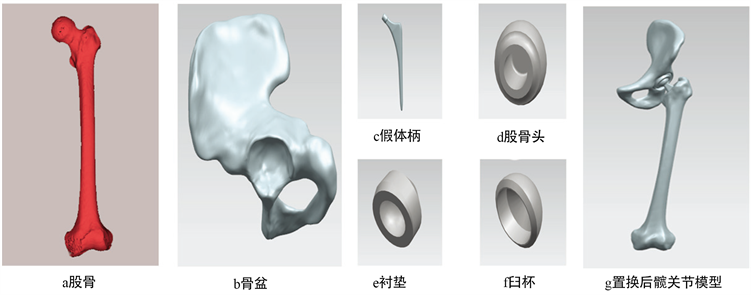
Figure 2. The established 3D hip joint and prosthesis
图2. 建立好的三维髋关节模型
3. 三维模型准确性验证
建立好的三维模型不可以直接进行数值模拟计算,需要验证模型的准确性。本研究采用有限元分析软件ANSYS对模型进行数值模拟计算,然后用电测实验的方法验证数值模拟结果的准确性,从而验证三维模型的准确性。本研究中由扫描建立的髋关节模型颈干角为132˚,因此在模型验证过程中装配的角度也为132˚。
3.1. 数值模拟
3.1.1. 定义单元类型和材料属性
人体骨骼的骨质存在差异,皮质骨和松质骨的弹性模量存在较大差异,股骨和骨盆上各部分的骨质密度也都不相同,而且随着年龄的变化骨质密度会逐渐减小。为了简化模型将股骨和骨盆的材质做了整体等效,由于电测实验使用的模型材料为高分子材料(PVC),在验证过程中的数值模拟部分中也赋予高分子材料的材料属性 [9] 。本研究中选择的单元类型为Solid 45,髋关节各部分单元类型和材料属性见表1。

Table 1. Element type and material properties
表1. 单元类型和材料属性
3.1.2. 网格划分与边界条件设置
为置换后各部分赋好单元类型和材料属性后,对髋关节各部分采用自由网格划分,网格类型为四面体,尺寸为5 mm。划分好网格后,在股骨头与衬垫之间的接触位置进行非线性接触设置。完成设置后在骨盆上端面上施加位移全约束,在股骨髁底端面上施加沿Z轴正方向的位移(对应300 N载荷的位移量)载荷,如图3所示。
3.1.3. 计算求解与测点选取
在数值模拟过程中涉及接触非线性的应用,需要对股骨头和衬垫的接触位置进行非线性计算设置。设置最终载时间为10,子步数为50,在“Nonlinear”中设置迭代次数为50,收敛准则为位移收敛准则,点击OK,完成非线性设置。计算完成后读取与300N载荷对应位移载荷的Von Mises应变结果(颜色由蓝到红为逐渐增大,下同),如图4所示。
从图中可以看出,置换后的髋关节模型应变较大的位置主要分布在股骨干内外两侧和假体柄的颈部上下两侧。根据数值模拟的结果在股骨髁中间位置建立坐标系,选取应变值较大的位置和几处应变值较低的位置作为电测实验中的贴片位置。如图所示,测点1、2、3、4、5、6和9为图中应变值较大的位置,测点7为股骨中段过渡位置,测点8和10为应变值较小位置。
3.2. 电测实验
3.2.1. 实验加载
仿照数值模拟中的模型制备电测实验模型。将制备好的模型在WDW-10微控电子万能力学实验机(长春新实验机有限责任公司生产)上进行压力实验,将10个应变贴片粘贴在图5中所选的测点上,另一端与DH3818-X10多测点应变显示仪(江苏东华测试股份有限公司生产)连接。仪器调零,然后以0.2 mm/min的速度进行加载至300 N,测出各测点的应变值,各测点应变值将在仿真与实验结果对比中给出,实验加载如图6所示。
3.2.2. 数值模拟和电测实验结果对比
在数值模拟中读取的Von Mises 应变数据不能与电测实验中应变测试系统中读取的数据直接进行对比,需求出数值模拟结果的线应变分量。分别查询10个测点的应变分量,则过任意线段|MN|的线应变都能求出。设无限小线段|MN| = r,则沿r方向的线应变为:
(1)
式(1)中
,
,
为通过该测点线段|MN|在X、Y、Z三个方向的方向余弦 [10] 。各测点数值模拟和电测实验的应变对比如图7所示,各测点得出的线应变分量以及电测实验中各测点的应变值已在对比图中给出。

Figure 4. The Von Mises strain of the hip model
图4. 髋关节应变分布Von Mises云图

 电测实验加载图 WDW-10 微控电子万能试验机控制软件界面
电测实验加载图 WDW-10 微控电子万能试验机控制软件界面
Figure 6. Experimental loading
图6. 实验加载

Figure 7. The strain of simulation and experimental
图7. 各测点仿真和实验应变结果对比
从图7中可以看出,数值模拟和电测实验的应变结果在方向上保持一致,由于置换后假体柄的弹性模量远高于股骨弹性模量,所以测点1和测点2的应变值明显低于其他测点在数值模拟和电测实验中都能得到验证。在髋关节应变分布Von Mises云图中应变较高的位置在电测实验中也表现出较高的应变(除测点9)。虽然电测实验的应变值在多数的测点位置都要高于数值模拟,但从整体上来看成一定的比例性,作者认为造成这种结果的原因是由于实验加载过程无法做到与仿真完全一致造成的,如果实验条件允许,可以实现应变结果更加相似。通过以上分析,作者认为建立的数值模拟模型具备准确性要求,可以进行进一步的参数研究。
4. 角度参数数值模拟与分析
髋关节股骨的颈干角在个体之间存在着很大的差异,正常人的髋关节颈干角在110˚~140˚之间,与此同时还与年龄、性别及人种等因素相关。在验证过模型准确性后,分别选取国人男性和女性中最常见的颈干角值和选取的样本中角度平均值 [11] [12] ,同时考虑到临床中使用较多的假体柄的角度,最终选取的颈干角度数分别为125˚、127˚、130˚、132˚及135˚。将装配好的不同颈干角有限元模型的材料参数赋予正常人骨的参数并在ANSYS中进行数值模拟,其过程与模型验证中的数值模拟过程一致。
4.1. 应变分布分析
由于在数值模拟过程中,骨盆和假体股骨头、衬垫等零件的应变分布只与接触位置相关,受髋关节的颈干角参数影响不大,因此不对这些部分进行应变分布规律分析。图8为不同角度模型股骨和假体柄Von Mises应变分布云图。由图8(a)各角度髋关节股骨模型Von Mises应变云图能够看出,股骨上最大应变位置会随着颈干角的改变而发生转移。随着颈干角的增大,股骨上的应变最大值从小转子下方的压应变转移到股骨底端外侧1/3处,而当颈干角增大到135˚时,最大应变值又会由股骨底端外侧1/3处的压应变转移为股骨中段内侧。
由图8(b)各角度髋关节假体柄Von Mises应变分布图中可以看出,各角度假体柄最大应变主要分布在假体柄柄颈内外两侧,随着颈干角的增大,假体柄最大应变值由假体柄柄颈内侧转移到假体柄柄颈外侧拉应变。此外由各角度假体柄应变分布云图可以看出,除应变最大值出现在柄颈外,应变有向假体柄锥部下移的趋势。
4.2. 应变值变化分析
图9为各角度模型股骨和假体柄应变最大值折线图。从图中可以看出,随着颈干角的改变股骨和假体柄上应变最大值也会随之发生改变,总的变化趋势为先降低后升高。在颈干角为132˚时股骨出现应变最低值(相对于5个最大应变值而言,下同),在颈干角升为135˚时应变值最大;假体柄上的最大应变值也会随着颈干角的改变而发生变化,在颈干角为130˚时出现应变最低值,在颈干角升为135˚时应变值变为最大。股骨和假体柄上出现应变最低值所对应的颈干角不同,因此在髋关节置换过程中不能只关注髋关节原有的角度参数,更要兼顾置换后髋关节各部分的受力情况。
5. 讨论
在数值模拟过程中,在假体柄与股骨交界处偶尔会产生较大的应变集中,这是由于交界处股骨边缘处理不得当,比较锐利造成的,在数据采集过程中应将其剔除。由于股骨不同位置骨质密度,难以精确的赋予不同位置骨质的材料属性 [13] ,出于简化的目的,将股骨和骨盆的材质做了整体等效处理,因此会在数值模拟过程中产生误差。在数值模拟过程中对模型施加载荷时,由于无法在髋关节处精确施加载荷,选择在骨盆上半部分面上施加位移全约束,在股骨髁底部施加位移载荷,而在电测实验加载过程无法做到与仿数值模拟完全一致,也是造成数值模拟和电测实验结果误差的重要原因。在电测实验过程中,由于股骨内部和假体柄的锥部无法进行贴片,因此无法测得内部的数据,影响结果的全面性。在对股骨颈干角角度选取过程中,由于颈干角的范围较大,不能也不必要所有角度都研究到,只选取了几个角度进行研究,不一定都具有代表性。
6. 结论
本文采用逆向工程方法建立了髋关节置换后带有骨盆的三维模型并对其进行生物力学研究。在经过数值模拟和电测实验验证过三维模型准确性后,对置换后不同颈干角参数的三维髋关节模型进行数值模拟,研究了角度参数对髋关节置换后各部分应变分布的影响。研究结果表明,随着髋关节颈干角的改变,股骨和假体柄上的应变分布规律也会随之改变,而最明显之处在于最大应变值及其位置会发生变化。由此说明,颈干角是影响髋关节应变分布和髋关节受力状态的重要因素,在髋关节置换过程中选择合适假
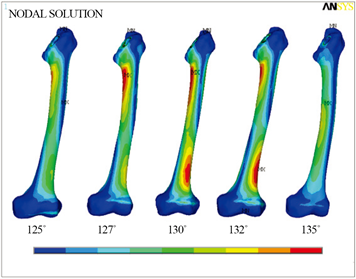 (a) 各模型股骨应变分布
(a) 各模型股骨应变分布 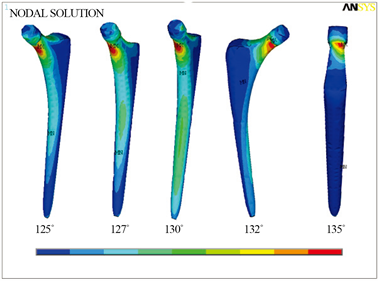 (b) 各模型假体柄应变分布
(b) 各模型假体柄应变分布
Figure 8. The Von Mises strain diagram of each angle model
图8. 各角度模型Von Mises应变图

Figure 9. The maximum strain value of each angle model
图9. 各角度模型应变最大值折线图
体类型和角度对手术效果和假体使用寿命至关重要。同时,在对股骨和假体柄上应变最大值的比较过程中,也提醒医生在进行手术的时候不仅要考虑病人原有的髋关节角度,更要考虑置换后髋关节的受力状态,以便更好地发挥换后假体的性能。
基金项目
天津市科技特派员项目(16JCTPJC49900);国家自然科学基金(11372221)。