1. 引言
“水包油”油藏是世界罕见的块状边顶底水油藏的俗称,二十世纪七十年代首次在辽河曙一区馆陶组发现,后相继在辽河H623块、Q12块、D239块以及辽东湾地区旅大5-2北油田发现该类油藏。边顶底水油藏类型特殊,四周均被水包围,油水关系复杂,其成因机制众说纷纭,但多数学者认为油藏顶部油水界面以上发育一套相对低渗的物性隔层而形成有效圈闭 [1] 。少数学者则认为原油运移过程中自身性质改变、地层温度低于原油凝固点形成自身封堵的“自凝结型油藏”。该类油藏多为超稠油油藏,以辽河D84块馆陶油藏为例,随着SAGD技术规模实施,蒸汽腔距离顶水越来越近,面临顶水下泄倒灌进油藏的风险,而油水交界处是否存在特殊物质,蒸汽腔扩散至油藏顶部能否抑制顶水下泄避免油藏过早水淹,成因机理研究成为当务之急。本文以辽河D84块馆陶油藏为例,利用钻井、录井、测井、取心分析等资料,对油水界面处储层特征进行系统研究,详细阐述油藏外部稠化带特征,提出特殊油层(“沥青壳”和“高阻层”)封堵油气的成因机制,而非盖层封堵油藏或自身封堵的“自凝结型油藏”。
2. 石油地质特征
D84块馆陶油藏构造上位于辽河断陷西部凹陷西斜坡中段,区内断层不发育。油顶埋深530~640 m。油层平均有效厚度105 m,平面上呈西厚东薄、南厚北薄的特点,纵向上主要分布在馆陶组下部,各油层组油水界面不一致 [2] 。20℃密度平均为1.0071 g/cm3,50℃粘度平均为23 × 104 mPa.s,原油属超稠油,油藏外层原油粘度高、密度大,油藏内部原油粘度相对较低、密度相对较小。油层和顶水之间没有泥岩隔层或物性盖层遮挡 [3] (图1)。
3. 成因机理探讨
3.1. 物性盖层封堵原证据有误
上世纪八十年代,先后两次在馆陶组油层进行常规取心,受当时取心分析技术所限,砾径太大而无法获取物性数据,S31-152井在馆陶组油层全井段取心,取样20块次均未获得常规岩心分析物性数据。
因此,早期物性盖层主要依据为岩性和电性。据当时47口电测资料,在馆陶油层上部水层的声波时差小于350 μs/m,远低于馆陶油层顶部450 μs/m~500 μs/m。S31-152取心井认为馆陶油层上部水层为泥质含量较高、物性差的泥质中–细砾岩,厚度在10~20 m左右,含油产状较差,多数未见含油显示,少数为油迹。据此认为该套岩性较差、电性特征区别于下部正常油层的砂砾岩层构成相对的物性盖层封堵油气,形成D84块馆陶油藏。
依据目前7口系统取心井428.7 m岩心资料、1184口井电性曲线证实,馆陶组砂体呈旋回变化,即砾岩和物性较差的泥质中–细砂岩互层(图2)。早期取心井S31-152油水界面以上正好为细粒旋回处,岩性为泥质中–细砂岩,电性为低时差,而其它井区油水界面上下岩性和电性无此特点。同时,后期取心井分析油水界面上下粘土矿物含量,油水界面以上为4.2%,油水界面以下为4.1%,含量基本一致。因此不存在所谓的砂岩物性盖层。
3.2. 自凝结成藏说不成立
自凝结成藏主要依据为早期D67井油层深度625 m时所测凝固点为36℃,当时处于勘探开发初期,含油面积仅0.4 km2,井数仅40口,油藏顶界深度530~630 m,油层温度32.9℃~35.8℃,低于凝固点温度,形成自身封堵的油藏——自凝结型油藏 [4] 。但随着勘探开发程度提高,工区含油面积增大到1.92 km2,完钻井数近1200口,油藏顶界埋深511~748 m,地层温度32.4℃~39.3℃,而原油凝固点平均为27℃(表1),油层温度高于原油平均凝固点,存在“开天窗”现象,因此自凝结成藏说不成立。
3.3. 特殊油层(“沥青壳”和“高阻层”)封堵油气
3.3.1. 特殊油层特征
通过大量取心井分析,油藏顶部发育一套特殊油层,该油层粘度呈上稠下稀、外稠内稀特征,最外层“沥青壳”和相邻“高阻层”共同构成“稠化带”,其孔隙度和水平渗透率与其它含油层段相差不大,但其垂直渗透率、含油饱和度、导热率与下部油层段不同。“稠化带”垂直渗透率较低,垂向渗透率与水平渗透率比值(Kv/Kh)较低,含油饱和度较高,导热率高(表2),“稠化带”沥青质含量较内部正常油层高出约10%,起到了封堵油气的作用。
“沥青壳”是油藏最外部直接与水层接触的特殊油层,饱和烃含量低,最高仅20%,而正常油层一般30%~50%;“沥青壳”遭受严重生物降解,C30-降霍烷含量可达1600,而正常油层不超过600;同时,“沥青壳”沥青化严重,沥青质含量一般30%~43%,而正常油层一般3%~22% (图3)。“沥青壳”实际岩心为饱含油砂岩,颜色黑而干,摸之不污手,质地较硬,用手掰不动,锤之可碎,油味淡,多数为油

Figure 2. The lithology profile of Guantao reservoir
图2. 馆陶油藏岩性剖面示意图
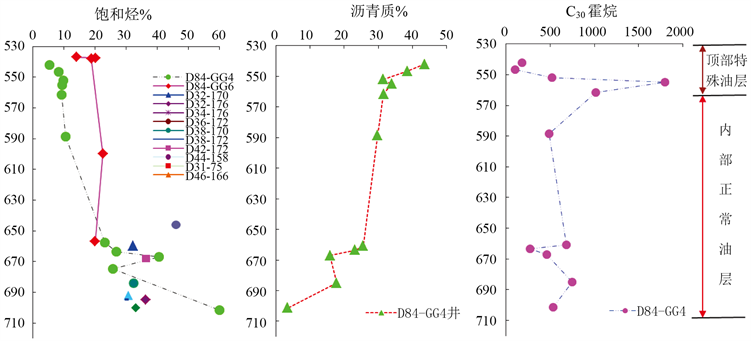
Figure 3. Longitudinal distributions of polar components of Guantao formation
图3. 馆陶组油层极性组分纵向分布特征

Table 1. Comparison table of solidifying point and the oil layer temperature of D84
表1. D84块凝固点与油层温度对照表

Table 2. Parameter table of “thickening zone” segment physical property
表2. “稠化带”物性参数表
浸–油斑级别,荧光呈深褐色~红褐色,厚度为0.5 m~2 m,深电阻率60~150 Ω∙m,局部达到300~350 Ω∙m,自然电位负幅度差,是其他含油层段的12倍,为原油沥青化所致,室内实验测得重轻比(S2/S1)大于14。
“高阻层”是位于“沥青壳”与正常油层之间的特殊油层,其含油饱和度比正常油层段高(图4),电阻率也较正常油层大,故称“高阻层”。岩心观察呈黑~黑褐色,含油性非常饱满,为饱含油-富含油级别,其颜色最深,油味重,摸之污手,烧之可燃,荧光呈深黄褐色~黄褐色,厚度10 m~25 m,深电阻率一般400~500 Ω∙m,远高于正常油层电阻率(平均200 Ω∙m),室内实验测得重轻比(S2/S1)一般12~14,较内部正常油层重轻比值(<12)略高。
3.3.2. “稠化带”分布特征
通过岩心观察,“沥青壳”厚度一般0.4~1.5 m;高阻层稳定分布,厚度较厚,一般10~25 m。纵向上,自上而下,依次为水层、“沥青壳”、“高阻层”、正常油层,部分区域“沥青壳”不发育(图5)。
3.3.3. 特殊油层封堵机理
研究区馆陶组油源主要来自沙四段烃源岩,其次为沙三段。烃源岩生油后,油气通过断层、不整合面以及连通砂体初次运移到本区下伏兴隆台油层成藏,此时原油已被稠化,粘度达50,000~160,000 mPa∙s。受构造运动影响,兴隆台油藏遭受破坏,超稠油二次运移到上覆馆陶组储层。由于超稠油运移动力小,仅在油源逸出点附近聚集成藏,而馆陶是湿地冲积扇,具有特高孔、特高渗特征,孔喉半径大、渗透性好储层中的水优先得到排替,随着能量逐渐消耗,当油驱水达到动力平衡时,在油水交界处,由于生物降解和氧化作用,使原油粘度和密度进一步增大,与地层水接触位置在油藏外部形成具有良好封闭性的“沥青壳”和“高阻”油层,它们既是油藏的一部分,又对原油继续运移起到封堵作用,从而形成具有边、顶、底水的“水包油”油藏 [5] [6] [7] [8] 。
曙光油田原油成熟度较高且降解较严重,稠油以次生作用为主,低熟原生成因不明显。稠油的次生作用主要包括生物降解、水洗、氧化等作用,其中生物降解是关键;而活跃地下水是微生物生存、生物降解有利条件;氧化化用是微生物新陈代谢的方式,三者相辅相成。其中细菌生物降解是致使原油稠变最重要因素 [9] [10] 。
从原油的饱和烃质量色谱图来看,研究区馆陶原油具有以下几个特征:链烷烃损耗或匮乏较为严重,原油的αααR甾烷的碳数分布具有w(C29) > w(C28) > w(C27)的特征、呈“反L型”(图6),出现生物降解标志化合物C25-降藿烷系列(图7),依据Peters和Moldowan1993年提出分级标准,馆陶原油遭受过严重的生物降解,降解程度达6级以上 [11] 。
4. 特殊油层封堵能力评价及石油地质意义
常规油气藏必须具备能够封隔储集层使其中的油气免于向上逸散的保护层,对油气聚集的封堵物可以是盖层本身的弯曲变形,如背斜,也可以是另外的封堵物,如断层、岩性变化等。常规油气封堵能力评价方法主要评价封堵物遮挡油气能力,如断层封闭性、不同岩性的物性封闭性、异常压力封闭性等。而本区油藏没有传统意义上的盖层对原油形成遮挡作用,位于油藏顶部的“稠化带”厚约10~27 m。馆陶油藏开发方式采用蒸汽吞吐转SAGD开采,蒸汽吞吐阶段油藏压力持续下降,动用部分的油藏与周边水体之间形成压差,容易破坏原始平衡状态,弄清稠化带的承载能力,从而选择对应的开发方式,对于该类水包油特殊油藏具有重要的石油地质意义。
4.1. “稠化带”封堵能力评价
“稠化带”垂直渗透率低于正常含油层段,流体不易垂向串流,对油气有一定的阻挡作用,即油气在此很难向上运移。而油藏由下至上,随着突破压力逐渐增大,小孔隙含量也逐渐增加,说明“稠化带”有一定的封隔能力(表3)。

Figure 4. Histogram of permeability-oil saturation
图4. S30-143井渗透率–含油饱和度柱状图
Figure 5. Profile diagram of special oil segments in Guantao reservoir
图5. 馆陶油层特殊油层段剖面示意图
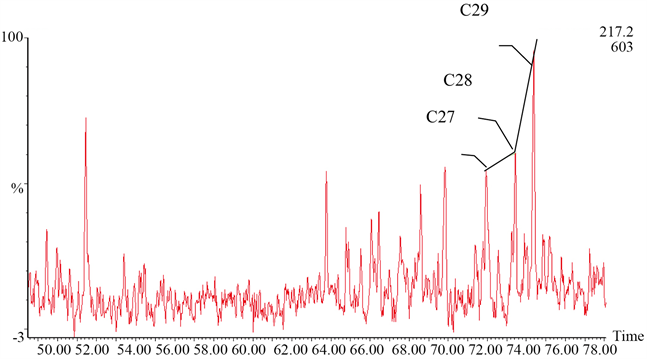
Figure 6. Mass chromatogram of saturated hydrocarbon m/z217 in D84-GG4 well at 701.39 m
图6. D84-GG4井701.39 m饱和烃m/z217质量色谱图
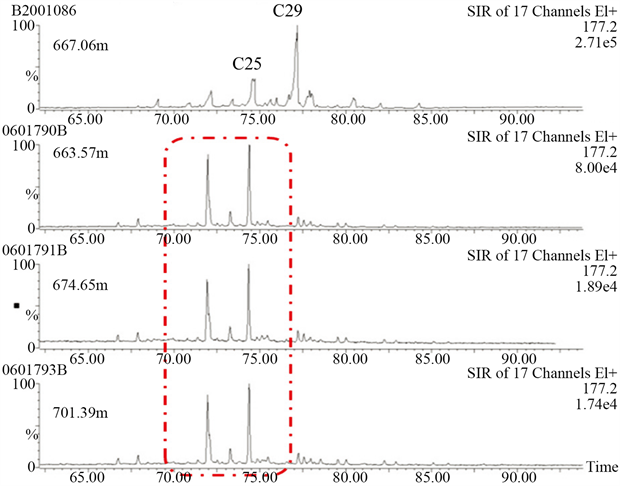
Figure 7. Mass chromatogram of saturated hydrocarbon m/z177 in D84-GG4 well at various depths
图7. D84-GG4井馆陶油层不同深度段饱和烃m/z177质量色谱图

Table 3. Quantitative parameter table of thickness zone (asphalt shell + high resistance layer)
表3. 稠化带(沥青壳 + 高阻层)定量参数表
4.2. SAGD蒸汽腔扩展对“稠化带”的影响
通过室内物模实验,温度和压力是评价馆陶油藏“稠化带”封堵能力的关键因素。相同温度条件下高阻层先软化,“沥青壳”后软化;温度越高“稠化带”流动性越强,“沥青壳”80℃稍有软化,120℃软化,160℃具有流动性,230℃易于流动。通过压力物模实验,80℃热水驱,注入压力高达10.97 MPa,回压0.52 MPa;130℃热水驱,注入压力14.97 MPa,停止注入,压力保持稳定,回压0 MPa,说明“稠化带”没有流动。160℃热水驱,进出口压差曲线趋近于零,表明压力已经突破“稠化带”(图8)。因此,原始油藏状态下,“稠化带”可有效封堵油藏,而SAGD持续200˚以上的高温,“稠化带”封堵能力遭受破坏。
4.3. 顶水泄漏界限研究
数值模拟研究表明,顶水能否突破“稠化带”,主要影响因素有“沥青壳”厚度、温度、油水界面上下压力差三个方面。三者的匹配关系直接影响顶水泄漏界限(图9)。
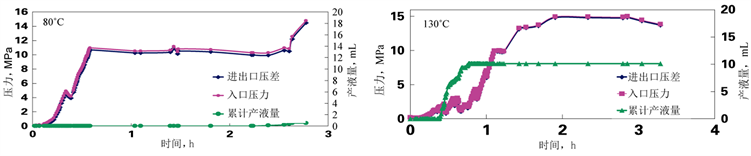
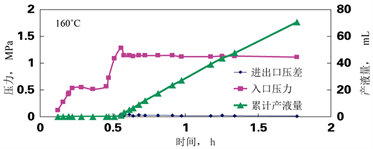
Figure 8. Experimental curve of Guantao oil layer flooding in D84 block
图8. D84块馆陶油层驱替实验曲线图

Figure 9. Relation curves of top water leakage technology parameters
图9. 顶水泄漏技术参数关系曲线图
综合物模和数模研究结果,馆陶油层“稠化带”封闭性稳定范围为:温度低于80℃,油水界面内外压差小于2 MPa。
4.4. 顶水泄漏的预防措施
馆陶油层经过长时间SAGD生产,蒸汽腔已形成连通的大腔体。局部汽腔高度达70~90 m,D84-GG4井附近汽腔距离油层顶界仅29 m,顶水泄漏风险很大(图10)。通过物模研究表明,当“稠化带”温度由33℃升到138℃,“稠化带”粘度由885 × 104 mPa∙s下降到8 × 104 mPa∙s,顶水将突破“稠化带”封堵。为预防顶水突破“稠化带”泄漏进入油藏内部,延长馆陶SAGD稳产时间,采用间歇注汽方案可控制汽腔上升速度,汽腔可保持在安全范围内。

Figure 10. Temperature profile of Guantao SAGD steam chamber
图10. 馆陶SAGD蒸汽腔温度剖面图
5. 结论
1) D84块馆陶油藏为下伏兴隆台油层遭到破坏后二次运移至馆陶组,边运移边稠化的次生超稠油油藏。曾遭受过严重的生物降解作用,油水交界处原油发生沥青化,为多因素控制形成的沥青封堵油藏,四周被水包围,油水关系复杂。
2) 油藏最外层由“沥青壳”和“高阻层”共同构成“稠化带”,其岩心、电性、物性以及地球化学特征有别于下部油层。
3) SAGD蒸汽腔温度高于200℃,汽腔波及“稠化带”时将破坏其原有的封堵能力,控制蒸汽腔与“稠化带”的安全距离,是防止馆陶油藏顶水下泄的关键。
基金项目
国家科技重大专项“辽河、新疆稠油/超稠油开发技术示范工程”(2016ZX05055)。