1. 引言
百合(Lilium spp.)是百合科百合属的多年生草本球根花卉 [1] ,在观赏、食用、药用以及园林美化等方面都具有广泛的应用。随着近年来百合的栽种面积不断扩大,百合病害的发生也随之加重 [2] 。但研究发现,山丹百合对病害、低温胁迫、高温胁迫等方面都有着较强的抗性,是培育抗性百合的优良品种 [3] 。
MicroRNA (miRNA)是一群大小约21 nt的单链RNA,它们在生物体中通过与靶标基因mRNA配对而实现对靶标基因mRNA的剪切,或对其进行翻译抑制作用,进而调控转录后靶标基因的表达量 [4] 。研究表明,miRNA广泛存在于动植物中 [5] [6] ,可以同时控制多条代谢通路,在应对逆境胁迫时有很大的作用。miR396是在拟南芥中发现的一类miRNA小分子家族,是植物中公认的一类保守的miRNA [7] 。miR396家族调控它的靶标基因GRF,在叶片发育、根部发育以及花器官发育等多个方面都发挥着重要的作用,参与盐、低温、干旱、病原菌的胁迫反应 [8] [9] [10] 。
本课题组在做山丹的转录组测序时,发现在山丹中也存在着miR396,并得到了miR396a和miR396f前体序列,我们推测,山丹中的miR396和该品种的抗病性有着一定的关联。本试验旨在从山丹中扩增出miR396a和miR396f片段,并构建miR396a和miR396f的表达载体,转入适合侵染百合的EHA105根癌农杆菌中,为后续验证miR396基因家族在百合中的功能和培育具有抗性的百合奠定基础。
2. 试验材料及方法
2.1. 试验材料
2.1.1. 植物材料
本试验所用到的山丹材料来源于内蒙古蒙草生态环境(集团)股份有限公司抗旱植物研究所。
2.1.2. miR396a和miR396f前体序列
miR396a和miR396f前体序列是本课题组在做山丹转录组测序得到的,其中miR396a前体序列长度210 bp,miR396f前体序列长度为504 bp,具体序列见表1。
2.1.3. 表达载体
本试验所用到的UBI-pCANBIA1301表达载体购自于北京信诺金达生物科技有限公司,该载体的启动子为Ubi启动子,标记基因为GUS基因,抗性基因为卡那霉素抗性基因,植物筛选标记基因为潮霉素抗性基因。UBI-pCANBIA1301质粒图谱见图1。
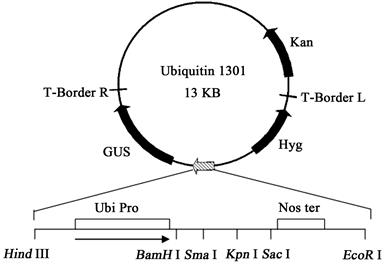
Figure 1. Plasmid profile of UBI-pCANBIA1301
图1. UBI-pCANBIA1301质粒图谱

Table 1. miR396aand miR396f precursor sequence
表1. miR396a和miR396f前体序列
2.1.4. 菌株
本试验所用到的农杆菌EHA105菌株来自于北京市农林科学院蔬菜花卉研究所西瓜课题组,大肠杆菌菌株T1购自于北京TaKaRa公司。
2.1.5. 试剂
DNA提取试剂盒、PCR所用的反应体系以及卡那霉素和氨苄青霉素均购自于北京TaKaRa公司,切胶回收试剂盒、酶切连接用到的试剂以及BamHI酶和KpnI酶均购自北京宝生物工程有限公司,琼脂糖凝胶回收试剂盒以及其他试剂则购北京自天根生化科技有限公司。
2.1.6. 培养基
LB液体培养基和固体培养基均是参照已有实验配方自行配制而成 [11] 。
2.2. 试验方法
2.2.1. 山丹总DNA提取
在无菌工作台中,取新鲜的山丹无菌苗的叶片,立即置于液氮中速冻,然后用DNA提取试剂盒,提取山丹叶片的总DNA。
2.2.2. miR396a和miR396f前体引物合成
引物设计运用DNAMAN,酶切位点确定运用VectorNTISuite7,参照UBI-pCAMBIA1301多克隆位点以及miR396a和miR396f前体的酶切位点,在基因片段的5'端引入BamHI酶切位点,在3'端引入KpnI酶切位点,并且在两端加保护碱基,交给华大基因合成引物,miR396a前体的引物扩增目的片段长度为227 bp,退火温度为60℃,miR396f前体的引物扩增目的片段长度为489 bp,退火温度为60℃,引物序列如下(大写字母部分为引入的酶切位点,划线部分为引入的保护碱基):
miR396a前体的正向引物:ataGGATCCggtccttcttgtattcttc
miR396a前体的反向引物:ggGGTACCggaatacaaaattgttaat
miR396f前体的正向引物:ataGGATCCttcaagaatttggagccaaag
miR396f前体的反向引物:ggGGTACCgagaaaacagaagttcaatt
2.2.3. 百合miR396a和miR396f前体克隆
以山丹总DNA为模板,加入合成好的引物,进行PCR反应。反应体系为25 μL,其中模板1 μL、引物各1 μL、Mix 12.5 μL、ddH2O 9.5 μL。PCR反应程序为:95℃预变性4 min;95℃ 20 s,60℃ 20 s,72℃ 30 s共30个循环,72℃延伸7 min;4℃保存。
反应结束后,PCR产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶检测及回收,电泳检测条带长度正确后,进行下一步试验。
2.2.4. miR396a和miR396f克隆载体构建
将切胶回收的miR396a和miR396f各取5 μL,分别与1 μL T1 Simple cloning Vector混合后,25℃反应5 min。结束后将此4 μL产物加入到100 μL的T1大肠杆菌感受态中,用冻融法进行转化后,加入250 μL室温的LB培养基,在37℃的条件下摇晃培养1 h。取8 μL 500 mM的IPTG和40 μL X-gal混合,均匀的涂在固体LB平板上,37℃放置30 min。然后将培养了1 h的转化后的T1大肠杆菌离心后取沉淀,涂在上一步制好的平板上,置于37℃下过夜培养12 h,进行蓝白斑筛选。
挑取白斑于10 μL的ddH2O中,取其中1 μL进行菌液PCR鉴定,其余9 μL加到具有抗性的500 μL LB液体培养基(含有氨苄青霉素50 mg/L)中,小摇6 h,取PCR鉴定中电泳条带长度为目的条带长度的菌液,进行测序鉴定miR396a和miR396f的单克隆载体构建成功。
2.2.5. miR396a和miR396f表达载体构建
双酶切连接时,先对T1-miR396a和、T1-miR396f和UBI-pCAMBIA1301质粒进行双酶切。双酶切体系为10× FastDigest Green Buffer 2 μL,质粒10 μL,FastDigest BamHI 1 μL,FastDigest KpnI 1 μL,加ddH2O到20 μL;配制好双酶切体系后混匀,37℃放置30 min,进行酶切反应,酶切后回收载体及目的片段。
再按照连接体系加入酶切产物,连接体系共20 μL,其中10× Reaction Buffer 2 μL,目的片段回收产物10 μL,UBI-pCAMBIA1301回收产物4 μL,T4 DNA Ligase 1 μL,ddH2O 3 μL,22℃反应60 min,进行连接转化。取出感受态细胞T1放于解冻后加入连接产物,用冻融法将连接好的载体转化到大肠杆菌中;每管加800 μL没有抗生素的LB液体培养基,37℃振荡复苏,离心1 min后涂布到抗性平板上;平板放置于室温吹干,倒置于37℃培养箱培养菌落。然后各选取8个菌落进行菌落PCR鉴定,确定条带大小是目的条带大小后,再选取前两个送去公司进行测序验证,验证结果正确,说明miR396a和miR396f表达载体构建成功。
2.2.6. UBI-pCANBIA1301-396a和UBI-pCANBIA1301-396f质粒转化农杆菌
首先制备农杆菌感受态,并提取构建好的质粒载体。活化待转化的农杆菌和含有表达载体质粒的大肠杆菌,当农杆菌菌液OD600约为0.6的时候,用常规的感受态制备方法进行农杆菌感受态制备 [12] 。当大肠杆菌菌液OD600约为0.6的时候,用质粒提取试剂盒对含有UBI-pCANBIA1301-396a质粒和UBI-pCANBIA1301-396f质粒的大肠杆菌进行质粒提取。
最后进行UBI-pCANBIA1301-396a质粒和UBI-pCANBIA1301-396f质粒转化农杆菌EHA105的感受态。取5 μL提取好的载体质粒DNA,加入到刚解冻的200 μL农杆菌EHA105的感受态中,用冻融法进行转化,然后在其中加入1 ml常温的LB液体培养基(含利福平50 mg/L),28℃振荡培养8 h;取100 μL涂于具有抗性的LB平板(含利福平50 mg/L和卡那霉素50 mg/L),28℃培养28 h。挑取单菌落于1 ml具有抗性的液体LB培养基(含有利福平50 mg/L和卡那霉素50 mg/L),小摇6 h;取小摇后的菌液做菌液PCR进行检测验证,将确认转化成功的菌液加入到5 ml的液体LB培养基(含利福平50 mg/L和卡那霉素50 mg/L)中,进行过夜摇菌,当菌液的OD600约为0.6的时候,保存于−80℃,以备后续试验所用。
3. 结果分析
3.1. 百合miR396a和miR396f前体克隆
以山丹总DNA为模板,进行miR396a和miR396f前体目的片段扩增,分别得到227 bp和489 bp大小的片段,和目的条带大小一致,如图2。
3.2. miR396a和miR396f表达载体构建
对含有miR396a和miR396f表达载体的大肠杆菌,各选8个菌落,以抗性菌落为模板进行菌落PCR鉴定,电泳显示的PCR条带长度和目的条带长度一致,如图3。
3.3. 表达载体转化农杆菌EHA105
用构建好的UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396和UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396f载体,转化农杆菌EHA105,转化后进行抗性菌落筛选和菌液PCR验证,确认目的基因转化正确,如图4。
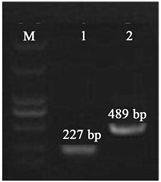
Figure 2. Electrophoretic map of the purpose gene. Lane M: DNA Maker of DL2000 (From top to bottom respectively 2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, 100 bp); Lane 1: miR396aprecursor fragments; 2: miR396fprecursor fragments
图2. 目的基因扩增电泳图。泳道M:DL2000的Maker (从上到下分别为2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, 100 bp);泳道1:miR396a前体片段;泳道2:miR396f前体片段
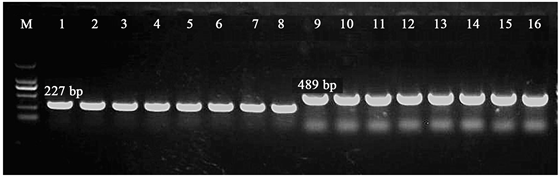
Figure 3. Colony PCR for rapid identification of positive clones. Lane M: DNA Maker of DL2000 (From top to bottom respectively 2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, 100 bp); Line 1 - 8: T1-miR396a colony PCR; 9 - 16: T1-miR396f colony PCR
图3. 菌落PCR快速鉴定阳性克隆。泳道M:DL2000的Maker (从上到下分别为2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, 100 bp);泳道1~8:T1-miR396a的菌落PCR条带;泳道9~16:T1-miR396f的菌落PCR条带
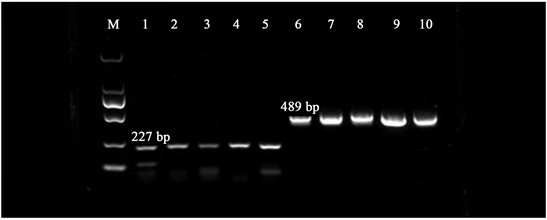
Figure 4. Recombinant UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396a/f Agrobacterium colony PCR identification. Lane M: DNA Maker of DL2000 (From top to bottom respectively 2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, 100 bp); Line 1 - 5: UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396a colony PCR; 6 - 10: UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396f colony PCR
图4. 重组载体UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396a/f农杆菌菌落PCR鉴定。泳道M:DL2000的Maker (从上到下分别为2000, 1000, 750, 500, 250, 100 bp);泳道1~5:UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396a的菌落PCR条带;泳道9~16:UBI-pCAMBIA1301-396f的菌落PCR条带
4. 讨论
构建表达载体时,选择合适的植物表达载体,对于目的基因在植株中的稳定遗传和高效表达有着至关重要的作用,表达载体中不同类型的启动子,对于外源基因的启动作用也有着很大的差异。启动子也称作顺式作用元件,选择合适的启动子,可以启动外源基因在受体植株中高效地转录和表达。玉米Ubiquitin基因是编码含有76个高度保守的氨基酸的玉米的泛素蛋白,Beer等人研究表明,在单子叶植物中,这个基因的Ubiquitin启动子有着较强的启动表达作用,并且可以同时对多种细胞功能起到调控作用 [13] ,而且当植物处于胁迫条件下的时候,Ubiquitin (Ubi)启动子的表达作用会增强 [14] 。因为本试验旨在为培育有抗逆性的百合奠定基础,而百合又属于单子叶植物,为使转入目的基因的百合,在逆境胁迫时,高效表达目的基因,从而使百合表现抗性,所以本试验选取具有Ubi启动子的UBI-pCANBIA1301载体作为miR396a和miR396f的表达载体。
在遗传转化试验中常常用到的农杆菌可分为章鱼碱型、农杆碱型和胭脂碱型三种类型,不同类型的农杆菌由于染色体背景不同,侵染能力也有很大的差别,不同的物种最适的农杆菌类型也不同 [15] 。在百合遗传转化中,常用到的农杆菌为GV3101、AGL0和EHA105菌株,EHA105菌株是一种超毒性菌株,张倩等人研究发现EHA105农杆菌菌株侵染百合的能力要优于GV3101和AGL0菌株 [16] ,所以本试验选取EHA105菌株作为侵染菌株。
miR396基因家族的靶标基因是GRFs基因 [17] ,GRF基因是一类植物特有的调控因子,它具有两个高度保守的结构域 [18] ,而且GRF基因在其他很多植物中都有研究报道,例如拟南芥、水稻、杨树、番茄、落叶松等植物,它在植物的根部发育、抗逆、花器官发育和叶片发育等多方面都有着调控作用 [19] ,所以在百合中很有可能也存在着GRF基因,所以构建miR396a/f对于后续培育抗百合枯萎病新品种百合有着深远的意义。
致谢
该试验可以顺利的完成,感谢北京农学院研究生科研创新项目(项目号5056516006/020)的支持。感谢我的师姐们对我提供的指导和帮助,感谢崔霞霞、张奋强等同学为我提供试验材料和帮助,感谢我的师弟师妹对我的试验提供的帮助,感谢内蒙古蒙草生态环境(集团)股份有限公司抗旱植物研究所为我提供山丹试验材料。
NOTES
*通讯作者。