1. 引言
期权作为一种重要的金融衍生产品,在当前的金融市场中非常活跃。1973,F. Black和M. Scholes [1] 提出著名的Black-Scholes模型。但Black-Scholes模型忽略了一些市场特征,如市场跳跃和崩溃,而这些是应该考虑的重要事件。
1976,R. Merton [2] 将一个跳跃项添加到Black-Scholes模型中。相较于连续路径模型,跳扩散模型允许标的资产的价格发生大的突变。在文献 [3] 中,S.G. Kou介绍了具有对数双指数型分布的跳扩散模型。在更为一般的CGMY模型 [4] 中,标的资产价格是满足可能发生无限次跳跃的Levy过程。
跳扩散模型的解可以通过求解一个偏微分积分方程(PIDE)获得。求解PIED的直接数值法在文献 [5] [6] 中已有讨论。然而直接法通常是要解一个全矩阵,这需要大量的计算,因此,应考虑其他数值方法。D. Tavella和C. Randall [7] 描述了欧式期权定价模型的一种定常迭代方法。S. Salmi和J. Toivanen [8] 提出了跳扩散模型下美式期权定价的一种迭代方法。U. Ascher,S. Ruuth与B. Wetton [9] 介绍了随时间变化的偏微分方程的隐–显方法,包括隐–显三阶SBDF法。J. Frank,W. Hundsdorfer和J. Verwer [10] 分析了隐–显线性多步法的稳定性。S. Salmi和J. Toivanen [11] 讨论了跳扩散模型下期权定价问题的一些隐–显二阶方法。
在本文中,我们讨论Kou跳扩散模型下美式期权定价的隐–显三阶SBDF方法,并把零阶项表示成凸组合的形式,该思想在文献 [11] 中有过介绍;然后用傅立叶分析研究该方法的稳定性;最后用数值实验表明该方法的有效性。
2. Kou跳扩散模型下的美式期权定价
在风险中性测度下,标的资产价格
满足下面随机微分方程
, (1)
其中
是漂移率,
是波动率,
是标准布朗运动,
是标的资产从
跳跃到
所产生的脉冲函数,
,其中
表示期望算子,
是参数为
的独立泊松过程。
令
表示执行价格为
的美式期权价格。若定义
, (2)
则
可表示为如下偏微分积分互补问题的解
(3)
其中
是到期日,
,
,
,
是无风险利率,
是跳跃幅度的概率密度函数,并且满足
。本文中,我们讨论Kou模型。Kou模型下,
满足对数双指数分布
, (4)
其中
,
,
,
是赫维赛德阶跃函数。则
可表示为
. (5)
若考察美式看跌期权,则还需施加下面的边界条件
,
, (6)
其中
满足
。同时,
也应满足终值条件
, (7)
其中
为美式看跌期权的支付函数。
为了简单表示,我们把(2)式改写为如下形式
, (8)
其中微分算子
和积分算子
定义为
(9)
3. 时间步长法及稳定性
下面,我们引入参数
,使得(8)式的零阶项
形成一个凸组合,则(8)式改写为
, (10)
其中
是恒等算子。
当
时,我们可以引出隐–显三阶SBDF (semi-implicit backward differentiation formula)时间步长法,即
, (11)
其中
,
和
是(10)式空间离散所生成的矩阵。对于该方法的更一般情形请参考文献 [9] 。
参数
的引入,使得我们得到了一族隐–显三阶SBDF方法(每固定一个
,即得到一个确定的隐–
显三阶SBDF法)。对于空间的离散,我们采用有限差分法,关于具体的离散过程请参考文献 [8] 。
我们用傅立叶分析研究数值格式的稳定性。有限差分格式称为稳定的,如果初始误差不随着时间的推移而被放大。一个方法当
时是稳定的,则称该方法为(零)稳定的。这种方法的解在有限时间内保持有界。然而,在实际情况中,时间步长是固定大小的,为了获得最佳计算效率,人们通常希望选择最大可能的时间步长来获得所需的精度水平。零稳定是该方法的必要条件,但在实际计算中并不是充分的。满足稳定性所需的实际时间步长对于刚性问题或者拥有两个以上时间层次的方法尤其受限制。最坏的情况是,一个方法可以是零稳定的,但是对于任意固定的
都是不稳定的。
一个方法当
小于一个给定的正值时是稳定的,则称该方法是条件稳定的。这是一个更严格的要求,因为条件稳定的必然是零稳定的。但一个方法的稳定性区域往往难以精确找到。通常的方法是将该方法应用于线性试验方程,并分析其稳定性。对于隐–显方法,线性试验方程为
(12)
其中
和
分别表示显式部分和隐式部分的复特征值。
对偏微分积分方程(2)应用线性逼近法,我们得到常微分方程的半离散线性系统
,
. (13)
使用交换矩阵可以很容易把试验方程(12)的稳定性结果推广到线性系统中。文献 [10] 讨论了可交换框架下隐–显格式的稳定性分析。然而,
和
一般是不可交换的。更甚至,在许多实际应用中,基于线性测试方程时间步长的限制,即便在非可交换的情况下也可能是准确的(见文献 [12] )。下面,我们将应用线性测试方程(12)分析隐–显三阶SBDF格式(11)的稳定性。
3.1. 试验方程的稳定性
隐–显线性多步法的稳定性是由下列特征方程的根决定的
, (14)
其中
,
和
是隐–显方法的系数,
表示涉及到的前面节点个数(见文献 [10] )。该方法称为稳定的,如果所有的根满足
,并且当根为重根时不等式严格成立。我们采用文献 [10] 中的方法,对方程(14)两边同时除以
,并令
。则特征方程变为
, (15)
其中
,
和
为
,
,
. (16)
如果所有根满足
,并且重根时不等式严格成立,则稳定性成立。它的一个必要条件是
,
. (17)
除去模1存在多重根的可能性外,这也是一个充分条件。
对于隐–显三阶SBDF法(11),特征方程(15)中的各项为
,
,
. (18)
和
由下面两式得到
,
. (19)
令特征值
和
为
,
. (20)
则满足
,
. (21)
把(18)和(21)代入到特征多项式(15)中,有
. (22)
从上式中解得
. (23)
设
,代入到(23)式中,并令
在
间变化,我们可以得到
稳定区域的边界值。图1表示当
时,隐–显三阶SBDF方法的稳定性边界。图中绿球表明可能的特征值区域
。这表明隐–显三阶SBDF方法当
时,对于任意的
都是稳定的。
现在我们研究隐–显三阶SBDF方法的稳定性区域。我们假设
没有因为区间截断而产生误差。因此
为非负右随机矩阵。另一个选择是假设
有截断误差并且是非负定的。在这种情况下,可由Gershgorin圆定理得
成立。因此,模1的根是不存在的,并且即便
不是右随机的,下面的结论仍是成立的。我们假设
不存在截断误差。
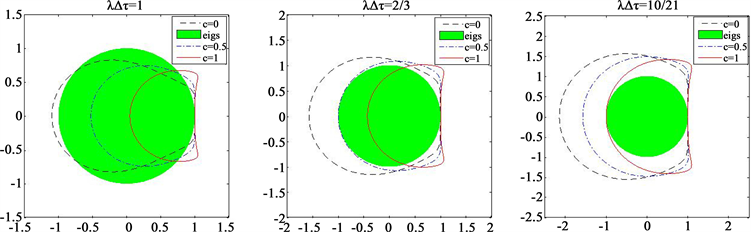
Figure 1. Stability boundaries for
under the IMEX third-order SBDF scheme with
and
(left),
(center) and
(right)
图1. 当
,隐–显三阶SBDF法对于
下的稳定性边界,左边图为
,中间图为
,右边图为
由文献 [11] ,我们得到如下引理
引理1:如果
是严格正定的,那么
成立并且模1的根是单根。
命题1:如果
是严格正定的,
,
,那么对于实数
,隐–显三阶SBDF法对于所有
和
是条件稳定的。
证明:特征方程满足(23)式,即
.
由引理1得
。假设
并且方程(23)式成立。下面我们将推导出矛盾。令
,
,
。方程(23)两边同时乘以
,得
. (24)
现在我们证明
,也就说明
。由(24)式可知,
由4部分组成,下面我们分别讨论参数
,
和
部分的实部情况。首先考虑
的系数
.
其实部
,
这说明
关于
是单调递增的。接下来考察
的系数
,
其实部
,
这说明
关于
是单调递减的。最后讨论
的系数,并令
,有
,
经计算,其实部
,
这说明
关于
是单调递增的。综合上面分析可得如下不等式成立
.
经计算,有
。
上述分析说明
,因此
。这导致
,即
,与引理1矛盾。因此,不存在
使得(23)式成立,这表明稳定性的必要条件(17)式是满足的。同时这也是充分的,因为引理1保证了模1的根都是单根。 □
在Kou模型下,
对于任意带正权的积分都是严格正定的。我们可以从命题1中得到以下推论。
推论1:如果
,那么隐–显三阶SBDF法在Kou模型下,对于所有
和
都是条件稳定的。
3.2. 隐–显三阶SBDF法的稳定性
在上面的分析中,我们假设
。特征值
为非正实数的一个充分条件是:
是三对角矩阵并且是M-矩阵。在
的情况下,M-矩阵的性质可以通过在模型中添加人工扩散来实现(见 [13] )。
我们分析了
情况下的稳定性。图2表示当
,
和
时隐–显三阶SBDF法的稳定性区域。对于任意实数
,稳定性区域都是增加的。这表明在适当的假设条件下,特殊情况
可以看作是稳定性条件满足的最坏情况。
4. 数值实验
本节中,我们讨论由隐–显三阶SBDF法计算所得的数值结果。我们应用文献 [13] 中提到的方法来
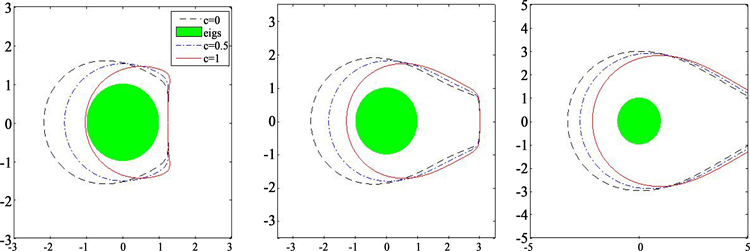
Figure 2. Stability boundaries for
under the IMEX third-order SBDF scheme with
,
and
(left),
(center) and
(right)
图2. 当
,
时,隐–显三阶SBDF法对于
下的稳定性边界,左边图为
,中间图为
,右边图为
计算美式看跌期权,并选取惩罚因子
。Kou模型下的美式看跌期权参数如下
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
.
这些参数也在文献 [6] 和 [13] 中使用过。我们使用 [13] 中描述的期权价格作为参考价格(见表1)。
我们把区间
作
等分,并令
。迭代的终止条件为
。计算空间节点
处的均方根误差(RMSE)。RMSE更准确的表示为:
,其中
和
分别表示在节点
处的参考价格和计算所得价格。先验选择的凸组合参数为
。
表2、表3和表4分别表示当
时的数值实验结果,类似的思想可见文献 [14] 和 [15] 。

Table 1. Reference prices used for numerical experiments
表1. 数值实验的参考价格

Table 2. Numerical results when c = 0
表2. 当
时的数值结果
表3. 当
时的数值结果

Table 4. Numerical results when c = 1
表4. 当
时的数值结果
5. 结论
我们讨论了(2)式中当
时所形成的偏微分积分方程的隐–显三阶SBDF方法,并引入其零阶项
的凸组合,使其形成一族算法。通过傅里叶稳定性分析,可知该方法对于所有
和
都是条件稳定的。数值实验表明,当
时该方法能得到最好的计算精度。因此,我们可以应用
时的隐–显三阶SBDF方法对Kou跳扩散模型下的美式期权进行定价。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(11571365, 11401162)。