摘要: 目的:探讨寡糖链检测在乙肝相关早期肝细胞癌中的预警价值。方法:收集2020年7月至2022年2月青岛大学附属医院感染科就诊并符合纳入与排除标准的224例HBV感染患者的血清及相关资料,定量资料以中位数(四分位间距)表示,两组间比较采用Wilcoxon秩和检验;定性资料用百分比(%)表示,用卡方检验进行比较。按照寡糖链检测(Glycan-Test, G-Test)结果分为G-Test(+)患者58例,G-Test(−)患者166例,对其随访观察半年,通过半年内肝癌发生率比较评价寡糖链检测的预警价值。结果:随访观察半年,G-Test(+)患者中有12名诊断为肝癌,发病率为20.7% (12/58);G-Test(−)患者中则有6名诊断肝癌,发病率为3.6% (6/166);两组间差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。224例患者中AFP(+) 24例,G-Test(+) 58例,随访观察半年,AFP(+)患者中有6例发生肝癌,G-Test(+)患者中有12例发生肝癌,发病率分别为25.0%、20.7%,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。AFP(−)的200例患者中G-Test(+) 44例,G-Test(−) 156例,随访半年,44例患者中有8人发生肝癌,发病率为18.2%;156例患者中有4人发生肝癌,发病率为2.6%;差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。结论:对乙肝相关肝癌高风险人群行寡糖链检测能够提高肝细胞癌的早期发现,降低漏诊率。
Abstract:
Objective: To investigate the early warning value of Glycan-Test in hepatitis B virus-associated early hepatocellular carcinoma. Methods: 224 serum samples and clinical data were collected from the patients with HBV infection who met inclusion and exclusion criteria and were admitted to the Af-filiated Hospital of Qingdao University from July 2020 to February 2022. Quantitative variables were presented as median (25th-75th percentiles), median values of two groups were compared by the Wilcoxon test; qualitative variables were expressed as percentage (%) and compared by the chi-squared test. Among them, 58 cases were Glycan-Test positive patients, 166 cases were Gly-can-Test negative patients. For follow-up observation for half a year, the early warning value of Gly-can-Test was evaluated by comparing the incidence of liver cancer within six months. Results: After half a year of follow-up, 12 cases of the Glycan-Test positive patients were diagnosed with liver can-cer, with an incidence of 20.7% (12/58); 6 cases of the Glycan-Test negative patients were diag-nosed with liver cancer, and the incidence was 3.6% (6/166). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P < 0.001). Among the 224 patients, there were 24 AFP positive cases and 58 Glycan-Test positive cases. After six months of follow-up observation, there were 6 cases of liver cancer in AFP positive patients and 12 cases of liver cancer in Glycan-Test positive pa-tients, with the incidence of 25.0% and 20.7%, respectively, and the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). There were 44 Glycan-Test positive cases and 156 Glycan-Test negative cases in 200 AFP negative patients, and 8 of the 44 patients developed liver cancer with an incidence of 18.2%. Among the 156 patients, 4 cases developed liver cancer, with an incidence of 2.6%. The dif-ference between them was statistically significant (P < 0.001). Conclusion: The Glycan-Test can im-prove the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma, and reduce the rate of missed diagnosis in high risk population of hepatocellular carcinoma.
1. 引言
2020年,全球每年原发性肝癌发病率位居新发恶性肿瘤第六位,是全球第三大癌症死亡原因,在男性死亡率中排名第二 [1] 。而在中国,原发性肝癌新增与死亡病例分别占全球病例的45.3%与47.1% [2] ,承担着全球几乎过半的肝癌负担。日本有报道指出 [3] ,在所有初步诊断肝癌的病例中,62.5%是可根治的早期肝癌(巴塞罗那肝癌分期0期或A期),远高于亚洲其他地区或西方国家30%的治愈率。因此,在慢性乙肝人群中筛选出肝癌高危人群并定期随访监测,是提高我国肝癌早诊率的经济有效的方法。
而糖基化在人体多种生理和病理过程中起着重要作用,包括蛋白质折叠和转运、细胞分化、受精、免疫反应、肿瘤发生和转移等过程 [4] ;当糖蛋白成熟并穿过内质网,然后通过高尔基复合体到达细胞内外的最终目的地时,多糖会受到广泛的修饰。这些多糖被用作通用的“标签”,允许特定的凝集素和修饰酶在各种成熟的糖蛋白之间建立秩序 [5] 。同时糖基化改变是肿瘤细胞的共同特征,糖基化的复杂性增加了肿瘤分子的异质性,以及功能多样性 [6] 。肝癌发生时,肝脏的糖蛋白合成代谢将会有所改变,表现在寡糖结构和含量上的变化 [7] 。本研究通过对行寡糖链检测(Glycan-Test, G-Test)患者随访观察半年,评价寡糖链检测对于乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)相关性肝细胞癌(HCC)的预警价值。
2. 资料与方法
2.1. 研究对象
本实验共收集2020年7月至2022年2月青岛大学附属医院感染科就诊的HBV感染患者。
纳入标准:① 慢乙肝及肝硬化患者符合《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》(2019年中国版)诊断标准;② 新发肝癌患者符合《原发性肝癌诊疗规范》(2019年中国版)诊断标准;③ 年龄18岁以上;
排除标准:① 合并HCV、HDV、HIV感染者;② 合并其他肝病者,包括自身免疫性肝病、药物诱导的肝损伤、中重度脂肪肝及酒精性肝病等;③ 合并其他部位的原发性肿瘤;④ 怀孕或母乳喂养的妇女;⑤ 失访病人。
2.2. 研究方法
通过对患者血清样本中寡糖链含量进行检测,同时行甲胎蛋白测定,随访观察半年后应用统计学分析寡糖链检测对HBV相关HCC的预警价值;血清学标本送上海伯豪医学检验所,对样本进行毛细管电泳得到糖组学图谱,对检测的9个寡糖链组分的含量进行图谱分析,检测取寡糖组分的相对含量关系(G值)为5作为标准,≥5为阳性,<5为阴性。其余检测均在青岛大学附属医院检验科完成,AFP取≥20 ug/L为阳性。
2.3. 统计学分析
计量资料以中位数(四分位间距)表示,两组间比较采用Wilcoxon秩和检验;计数资料用百分比(%)表示,用卡方检验进行比较。采用ROC曲线进行诊断效能分析,采用z检验比较不同参数间AUC,相关分析采用Spearman秩相关。P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。采用SPSS26.0软件进行统计分析。
3. 结果
3.1. 研究对象的人口学特征
224例患者中G-Test(+)组58例、G-Test(−)组166例。男150例,女74例,年龄24~68岁。G-Test(+)组患者血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine aminotransferase, ALT)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase, AST)、γ-谷氨酰基转移酶(γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, GGT)、总胆红素(total bilirubin, TBIL)水平以及男性占比、中位年龄高于G-Test(−)组患者(P < 0.05);而白蛋白(albumin, ALB)、血小板(platelets, PLT)水平低于G-Test(−)组(P < 0.05) (表1)。
3.2. 血清中寡糖链组分含量相对关系与肝脏血清学指标的相关性分析
G值与ALB、PLT、TBIL、ALT、AST、GGT的相关系数分别为−0.410、−0.303、0.322、0.198、0.323、0.529;G值与ALB、PLT存在负相关关系,与TBIL、ALT、AST、GGT存在正相关关系(P均<0.05) (表2)。
3.3. 寡糖链检测与甲胎蛋白检测患者随访半年的肝癌发生结果
1) G-Test(+)患者随访半年共12名患者诊断为肝癌,发病率为20.7% (12/58);G-Test(−)则有6名诊断肝癌,发病率为3.6% (6/166);两组间差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05) (表3)。

Table 1. Clinical baseline data of the study population
表1. 研究人群的临床基线资料

Table 2. Correlation analysis between G value and liver metabolic and functional indexes
表2. G值和肝脏代谢与功能指标的相关性分析

Table 3. The incidence of liver cancer in 224 patients were observed for six months
表3. 224例患者随访半年肝癌发生情况
2) 224例患者中AFP(+) 24例,G-Test(+) 58例,随访观察半年,其中AFP(+)患者中有6例发生肝癌,G-Test(+)患者中有12例发生肝癌,发病率分别为25.0%、20.7%,差异无统计学意义(P = 0.668 > 0.05) (表4)。

Table 4. The incidence of liver cancer in AFP(+) patients and G-Test(+) patients were observed for six months
表4. AFP(+)与G-Test(+)患者随访半年肝癌发生情况
3) AFP(−)的200例患者中G-Test(+) 44例,G-Test(−) 156例,对其随访半年发现,44例患者中有8人发生肝癌,发病率为18.2%;156例患者中有4人发生肝癌,发病率为2.6%;差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.001) (表5)。

Table 5. The incidence of liver cancer in 200 AFP(−) patients were observed for six months
表5. 200例AFP(−)患者随访半年肝癌发生情况
3.4. 寡糖链检测与甲胎蛋白检测对肝癌的诊断效能评价
通过ROC曲线下面积计算,单独检测G-test (AUC = 0.732)或AFP (AUC = 0.757)诊断HCC的敏感性,未见明显统计学差异(P = 0.580) (图1)。进一步比较两者在HCC诊断中的灵敏度与特异度,并用Mcnemar检验分析两者之间的差异。在诊断灵敏度中,G-test的灵敏度为66.7%,AFP的灵敏度为33.3% (P > 0.05);特异度中,G-test的特异度为77.7%,AFP的特异度为91.3% (P < 0.05)。以上结果提示AFP的特异度高于G-test,但不能提示两者之间的灵敏度差异(表6)。
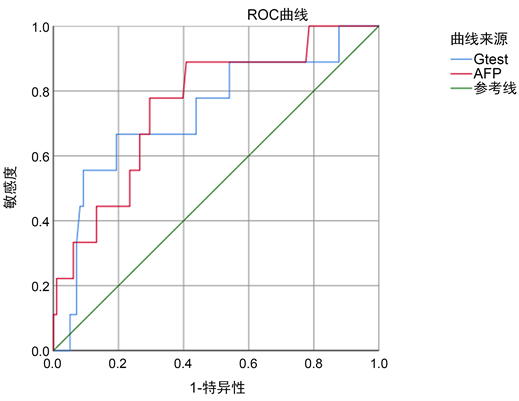
Figure 1. ROC curves of G-test or AFP for the diagnosis of HCC
图1. 独立检测G-test或AFP诊断HCC的ROC曲线

Table 6. Evaluation of the diagnostic efficacy of G-test and AFP single detection for hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 224)
表6. G-test、AFP单项检测对肝癌的诊断效能评价(n = 224)
4. 讨论
HCC的诊断主要通过B超、CT、MRI等影像学方法,但需相互补充,全面评判;肝穿刺是HCC确诊的金标准,因其为有创操作,且存在出血及针道种植的风险,有时难以被患者所接受。AFP是目前唯一被广泛用于HCC早期筛查、诊断和复诊的血清标志物;但仍有约30%的病例AFP并未升高,因而其敏感性、特异性和预测价值受到了一定质疑 [8] 。因此需要一种新的血清标志物及早发现HCC,提高早诊率,延长预后。
N-糖组是一种新的有效肝脏疾病血清标志物。大多数的血清N-糖蛋白是由肝脏和B淋巴细胞合成的,血清中总N-聚糖的变化可能反映了肝脏或B淋巴细胞的生理改变,糖链的改变常常反应出机体的异常改变 [9] 。有研究证实N-聚糖与肝癌密切相关 [10] ;LIU等人 [11] 发现,在慢性肝病患者与HCC患者血清中N-聚糖之间差异分析,有57种N-聚糖丰度发生显著变化。有研究发现 [12] ,在早期肝癌(early stage of HCC, EHCC)诊断前6个月或12个月,Glycomics-EHCC模型可以将潜在的EHCC患者与纤维化和肝硬化患者区分开来,敏感性和特异性分别超过90%和85%。国内多名学者通过对HCC患者和非HCC患者进行回顾性分析发现,G-test对HBV相关HCC患者的诊断效能优于AFP,与AFP联合的诊断效能优于单项检测 [13] [14] [15] ,提示G-test可作为AFP阴性HCC患者的补充标志物 [16] 。
本研究发现,G值与白蛋白、总胆红素、血小板、谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶、γ-谷氨酰基转移酶具有一定的相关关系(表2),提示寡糖链组分变化受肝脏的病理生理改变影响;白蛋白、总胆红素、血小板这3个指标在排除其他因素影响后与肝硬化程度相关,提示肝硬化可能影响G值;谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶、γ-谷氨酰基转移酶通常在肝脏炎症时有所升高,G值与这3个指标呈正相关关系,提示肝脏炎症可能影响G值变化。通过随访观察半年发现G-Test(+)结果能够预警半年内肝癌的发生(表3);G-Test(+)与AFP(+)患者随访半年相比,两组间肝癌发生率无统计学差异(表4),但G-Test能够预警AFP(−)患者中肝癌的发生(表5);说明G-Test与AFP相比,能够提高对HCC的早期发现,降低漏诊率。
但本研究尚且存在一些局限性:一是样本量比较少,随访时间相对较短,未能验证G-test的诊断能力优于AFP (取≥20 ug/L为阳性),所得结论有待于继续扩大样本量并延长随访时间进行验证;二是G-Test与AFP联合预警,能否进一步提高HCC的早期诊断率尚待进一步验证,且肝癌患者血清中寡糖链组分的相对含量水平变化与肝癌患者预后其复发风险之间是否存在关联等问题,需要进一步研究阐明。
NOTES
*通讯作者。