1. 引言
重水不但具有良好的慢化中子的能力,而且几乎不吸收中子。这点对于使用天然铀以及弱浓集铀的反应堆来说是非常重要的;对于使用高浓集铀的反应堆,这一点仍有其重要意义。因此,世界各国对重水的生产都极为重视。随着CANDU型重水堆的不断发展,重水的需求量随之不断增长,而且重水堆或以重水作反射层的实验研究堆在运行时,慢化剂重水中的氘原子俘获中子生成的氚会不断累积。据加拿大Chalk River实验室报道 [1] [2] ,每年CANDU堆慢化剂重水中氚产量约为1.4~2.0 kCi/MWe (1 Ci = 3.7 × 1010 Bq),CANDU-6堆慢化剂重水中氚的平衡浓度约为80~90 Ci/kg。以重水作为慢化剂的核电站,氚的放射性占整个放射性剂量的20%~35% [3] 。当含氚重水以液体或气体的形式泄漏时,不仅会增大运行人员的辐照剂量,而且会对周围环境造成危害。
水–氢液相催化交换是分离氢同位素的重要方法之一,该工艺在重水生产和重水升级、轻水或重水脱氚,以及热核聚变堆净化回收氚等方面有广阔的应用前景。加拿大、日本、印度、俄罗斯等 [4] [5] 已建立了液相催化交换和联合电解催化交换中试装置进行含氚重水或轻水脱氚实验研究。
因此,从提高重水产量与品质以及重水堆的运行人员安全、环境保护等角度考虑,需要开展重水除氚和重水升级即氢同位素水–氢交换方面的技术研究。
本工作基于建立的内径36 mm催化交换塔,以组内制备的新型柱形Pt-SDB憎水催化剂作为水–氢催化交换反应的催化剂系统研究高处理量下的水–氢交换工艺,为进一步开展这方面的研究打下基础。
2. 实验部分
2.1. 催化交换实验流程与参数
柱形Pt-SDB催化剂的水–氢交换工艺的实验流程如图1所示。T4中高纯氢气与T1储罐中已知浓度的原料重水(低浓)分别从塔底和塔顶进入催化交换塔S,在恒温条件下以气液逆流的方式进行氢同位素的催化交换反应。
主要实验参数:催化交换塔总高度约500 mm、有效填装高度约300 mm、内径φ1 = 36 mm,柱形催化剂1%Pt-SDB (SDB,聚苯乙烯–二乙烯基苯)、长度3~7 mm、粒径φ2 = 5 mm、孔隙率ε1 = 40.3%,填料

SP1-气体取样点(Gas sampling sites),
SP0-液体取样点(Liquid sampling sites),
T1、T2、T3、T4-液体储罐(Liquid storage tank),
E1、E2-热交换器(Heat exchanger),
B-恒温水浴槽(Thermostat-controlled water-bath),
D-硅胶干燥器(Silica gel dryer),C-冷凝器(Condenser),
F-质量流量计(Mass flow meter),
P-蠕动泵(Peristaltic pump),V1、V2-气阀(Valve),
低浓重水(Diluted heavy water),
氢气(Hydrogen gas), 水(Water)
Figure 1.Schematic flow diagram for the water-hydrogen isotope catalytic exchange experiments
图1. 水–氢同位素液相催化交换工艺实验流程图
与催化剂(固定催化剂单层高度10 mm)分层有序装填,操作压力0.2 MPa左右。
2.2. 柱形Pt-SDB憎水催化剂的流体力学性能实验与参数
填料的润湿:实验开始之前进行泡柱操作,将填料层预液泛,使填料层充分润湿。
填料层压降ΔP/Z测定:保持一定的液体喷淋密度,填料层压降的测试从某一较小的气速开始,逐步增加气速,测定在不同气速下填料层的压降。重复上述过程,测定结果具有可重复性。由填料层的总压降和填料层高度即可得到单位床层高度压降ΔP/Z,进而得到ΔP/Z与空塔气速u的关系。
泛点气速uF测定:在ΔP/Z的测定过程中可同时得到泛点气速uF。
持液量测定 [6] :在一定的气、液流速下,同时关闭气液进、出口后,收集填料层流出液体,其体积即为填料层的总持液量。
主要实验参数:催化交换塔总高度约500 mm、有效填装高度约300 mm、内径φ1 = 36 mm,柱形催化剂1%Pt-SDB(SDB,聚苯乙烯–二乙烯基苯)、长度3~7 mm、粒径φ2 = 5 mm、孔隙率ε1 = 40.3%,θ型不锈钢填料、长度4~5 mm、内径φ3 = 4 mm、孔隙率ε2 = 89.7%,填料与催化剂(体积比1:1、固定催化剂单层高度10 mm)分层有序装填,操作压力0.2 MPa左右。流体力学性能研究的实验测试范围:温度20℃,液体喷淋体积速度L为6.11~24.43 L/min;气体体积速度G为0~36.66 L/min。
2.3. 仪器及分析方法
DMA-500数字式密度计,奥地利Anton Paarl公司产品;MAT-253氢同位素气体质谱仪,美国Thermo公司产品。
低浓重水中的氘含量利用密度计分析,氢气中的氘含量利用气体质谱分析。压降测量采用液压差计,持液量体积采用量筒测量。
2.4. 水–氢同位素液相催化交换反应过程
水–氢液相交换反应体系实际上为气–液–固三相共存,是一个较复杂的传质–反应的串联过程 [7] ,主要包括了发生在亲水填料上的汽–液相间物理转化和发生在憎水催化剂上的氢同位素化学催化交换反应。具体过程如下:
汽–液相间转换:
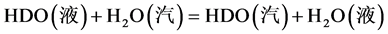 (1.1)
(1.1)
汽–气催化交换:
 (1.2)
(1.2)
总反应:
 (1.3)
(1.3)
2.5. 水–氢交换性能表征
水–氢交换性能可用传质效率来表示。传质效率主要有2种表示方法 [8] ,一是以理论级进行计算的表示方法,以每个理论级当量的填料层高度表示,即理论塔板高度(height equivalent of theoretical plate,简称HETP),或以每米填料相当的理论级数表示;另一是以传质速度进行计算的表示方法,以每个传质单元相当的填料层高度表示,即传质单元高度(height of transfer unit,简称HTU),或用传质系数Kya表示。工业生产上常以每单位容积(或质量)催化剂在单位时间内转化原料反应物的数量来表示,如每立方米催化剂在每小时内能使原料转化的质量数或体积数,一般称为催化剂的有效传质系数。传质系数Kya大,就意味着HETP值或HTU值低,或每米填料层所相当的理论级多,传质效率高。本文工作以HTU值和Kya值表征水–氢交换性能。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 填料层的持液量
填料层的持液量是指在一定的操作条件下,在单位体积填料层内所积存的液体体积,通常以(m3液体)/(m3填料)表示。实验对θ环填料与催化剂填装比例为1:1的动持液量HL进行了测定,在一定的液体喷淋密度下,填料层的动持液量HL与空塔气速u的关系如图2所示。
纵向比较可知,在一定的空塔气速u下,随着液体喷淋密度L的增加,动持液量HL增大;横向比较可知,在一定的液体喷淋密度L下,随着空塔气速u的增加,动持液量的变化分为3个阶段:开始阶段为恒持液量区,此时随着空塔气速u的增加,填料表面的液膜厚度不变,故动持液量HL基本维持不变;然后随着空塔气速u的增加,填料表面的液膜增厚,故动持液量HL增加,此阶段为载液区;最后空塔气速u稍有增加,但因填料层已积液,故动持液量HL急剧增加,此阶段为液泛区。
3.2. 填料层压降
在一定的液体喷淋密度L下,实验测定的不同气速下单位层高填料层压降△P/Z见图3。单位高度填
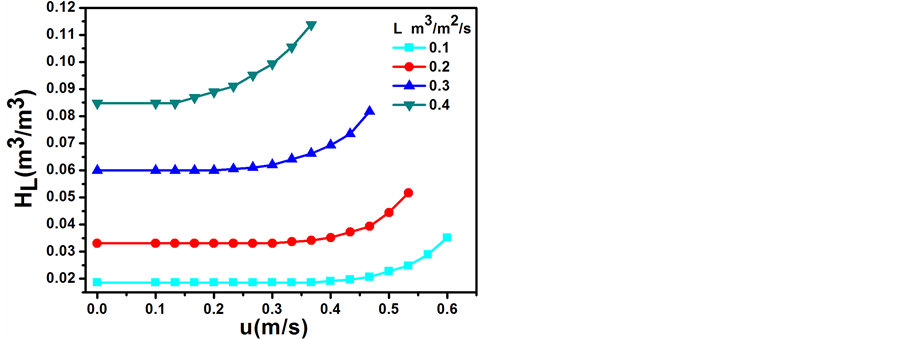
Figure 2. Relation of dynamic liquid holdup of packing layer HL and gas velocity in the empty tower u
图2. 填料层动持液量HL与空塔气速u的关系
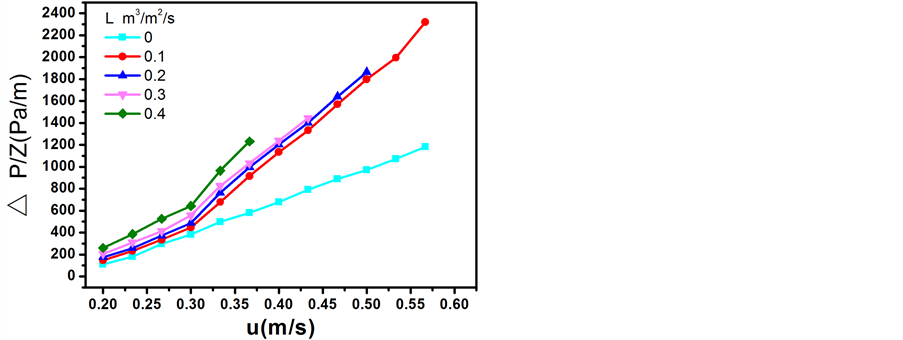
Figure 3. Relation between the pressure drop of packing bed ΔP/Z and the gas velocity in the empty tower u
图3. 单位高度填料层压降ΔP/Z与空塔气速u的关系
料层压降△P/Z与空塔气速u的关系,在载点以下,通常可用下式 [9] 关联:
 (2.1)
(2.1)
式(2.1)中,ρG为气体密度(查得常温常压下H2密度为0.0899 kg/m3),kg/m3;A、B为关联式常数。采用最小二乘法关联实验数据的结果列于表1。进而拟合可得到关联常数A、B与液体喷淋密度L的关系为
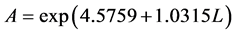 (2.2)
(2.2)
 (2.3)
(2.3)
其中关联常数A、B与喷淋密度L关系拟合公式的均方差分别为0.9265与0.9611。
将式(2.2)、(2.3)代入式(2.1)得:
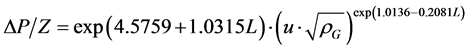 (2.4)
(2.4)

Table 1. Constants for correlation equations of the pressure drop
表1. 压降关联式常数
3.3. 填料的泛点特性
实验过程中通过观测发现,喷淋密度L较小时,塔壁处有向上移动的气泡出现。随着喷淋密度的增大,可以明显看出气体的通道从塔壁向填料中心转移。即液体的分布是随着喷淋密度的增大,从不均匀变到均匀,随后再到不均匀。同时,观察发现当填料内出现巨大气泡时,紧接着会发生液泛。
将泛点气速uF及气液速比Vg/VL随液体喷淋密度L的关系绘成曲线,如图4所示。
泛点气速是一个重要的设计参数,塔设备只有在泛点以下,才可能稳定地进行操作。
贝恩–霍根(Bain-Haugen)公式(2.5)是一个常用来预测泛点气速的关联式 [10] 。
 (2.5)
(2.5)
式(2.5)中:
A、B、a为系数;ε为孔隙率,m3/m3;
G、L分别为气体、液体质量流速,kg/h;
g为重力加速度,9.81 m/s2;uF为泛点气速,m/s;
ρG、ρL分别为气体、液体密度,kg/m3;
μL为液相粘度,mPa∙s。
代入数据化简得
 (2.6)
(2.6)
式(2.6)中A、B是与气液性质有关的系数。
泛点气速采用贝恩–霍根(Bain-Haugen)关联式表达,如图5所示,利用实验数据,可以回归出拟合公式
 (2.7)
(2.7)
拟合公式(2.7)的均方差为0.9835。
3.4. 填料与催化剂的填装比例对水–氢交换效率的影响
填料是催化交换塔内重要的组成部分之一,填料的性能对塔的操作性能及应用有很大的影响。填料选择应本着提高通量、减小压降、改善液体湿润性能、提高分离效率的宗旨。在实验过程中,先后采用了θ环填料、三角螺旋填料,最后经过测试比较和借鉴国外已有的经验 [11] ,选用了与柱形催化剂体型相近的θ环填料进行工艺实验。该填料的外形轮廓和主要特性参数分别示于表2。
当反应温度为65℃、氢气空速为0.3 m/s且气液比(G:L)分别为1:1、2:1、3:1时探究不同θ环填料与催化剂填装比例(V packing/V catalyst)对传质单元高度和传质系数的影响结果分别示于图6和图7。从图6

Figure 4. Relation of uF with Vg/VL and L
图4. uF和Vg/VL与L的关系
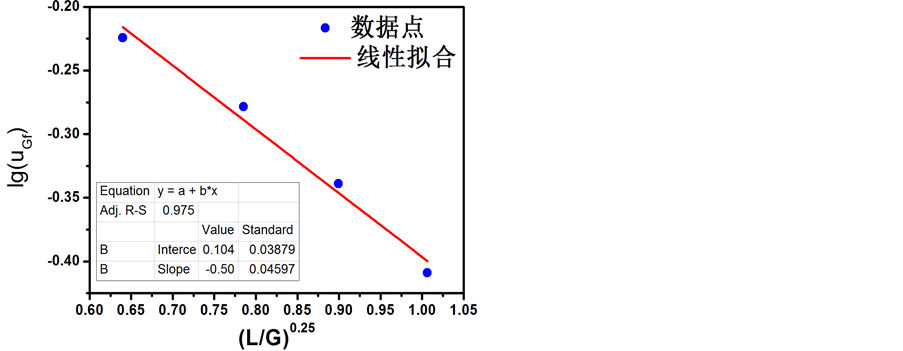
Figure 5. Bain-Haugen Relation of uF with L/G
图5. 泛点气速贝恩–霍根(Bain-Haugen)式的关联图
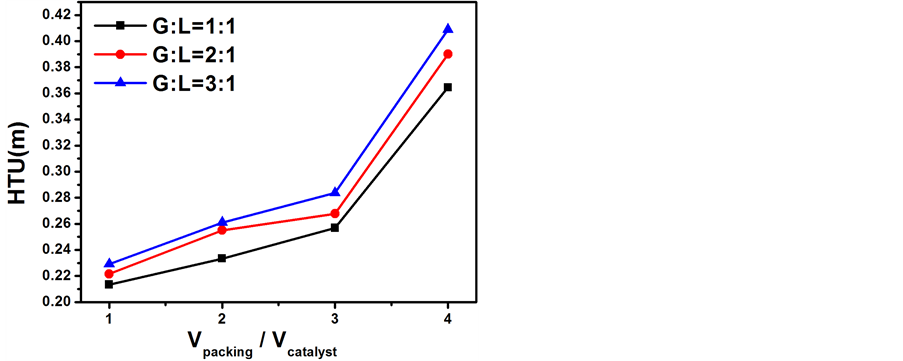
Figure 6. Influence of volume ratio of packing to catalyst on the HTU
图6. 装填比对传质单元高度的影响
表2. 柱形催化剂和θ环填料的特性参数
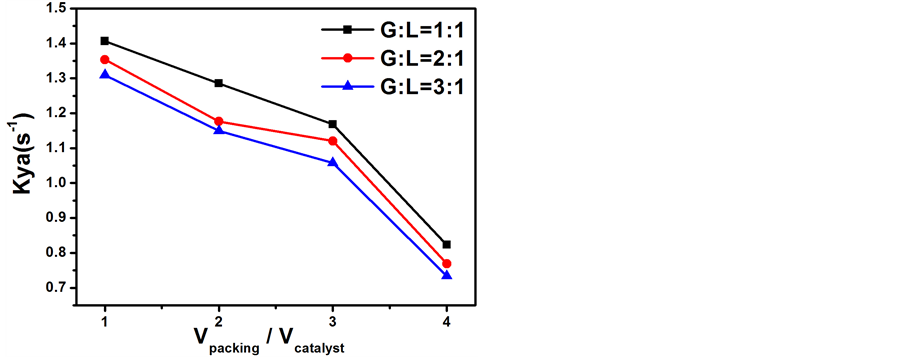
Figure 7. Influence of volume ratio of packing to catalyst on the Kya
图7. 装填比对传质系数的影响
和图7可以看出随着θ环填料与催化剂填装比例(V packing/V catalyst)的增加,传质单元高度不断增大,传质系数不断减小。这可能是因为所采用的新型柱形催化剂的催化活性较低(催化活性是同组内制备的小球Pt-SDB催化剂的1/3左右),这时发生在憎水催化剂表面上的汽气催化交换反应为总反应的速率控制步骤,填料的增加、催化剂的相对减少,虽然能促进亲水填料表面上的汽液相间质量转移反应,但由于整个交换过程是催化交换和相间质量转移的串联过程 [12] ,必然同时抑制在憎水催化剂上发生的催化交换反应,从而最终导致交换塔分离效率和传质系数的降低、传质单元高度高度的升高。
3.5. 反应温度对水–氢交换效率的影响
固定氢气空速0.1 m/s且气液比1:1、θ环填料与催化剂填装比例1:1时,考察了反应温度对水–氢催化交换反应效率的影响,不同温度下水–氢催化交换反应的传质高度和传质系结果示于图8。
从图8可知,应温度对反应总体积传质系数和传质单元高度影响显著。随着反应温度的升高,传质系数呈减速增长趋势,传质单元高度总体上呈减速下降趋势。因为无论是对憎水催化剂上的汽气催化交换反应还是对亲水填料上的汽液相间质量转移反应来说,升高温度均能提高反应的速率,所以塔的水–氢交换效率提高,传质单元高度下降。在实际工艺过程中,考虑到高温带来高能耗和水汽化量增加而影响交换效果,常常选择70℃~75℃作为水–氢催化交换反应的温度。
3.6. 气液比对水–氢催化交换反应效率的影响
氢气和低浓重水的流量之比,定义为气液比,用公式表示为:
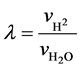 (2.8)
(2.8)
其中,λ为气液比; 、
、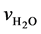 分别为氢气和低浓重水的流速。
分别为氢气和低浓重水的流速。
3.6.1. 氢气流速对水–氢催化交换反应效率的影响
当低浓重水流速为0.1 m/s、反应温度为65℃、θ环填料与催化剂填装比例1:1时,考察了氢气流速(气液比λ)对传质单元高度的影响,结果示于图9。
从图9可知,随着氢气流速的增大,即气液比的增大,传质单元高度上升。这可能是因为 ① 气体流速增大,其通过催化床的速度就越快,塔板上氢气与水的接触时间变短,反应深度降低,导致塔板交换效率降低; ② 气液流速越大,水汽挟带现象越严重,不利于水–氢同位素交换反应。
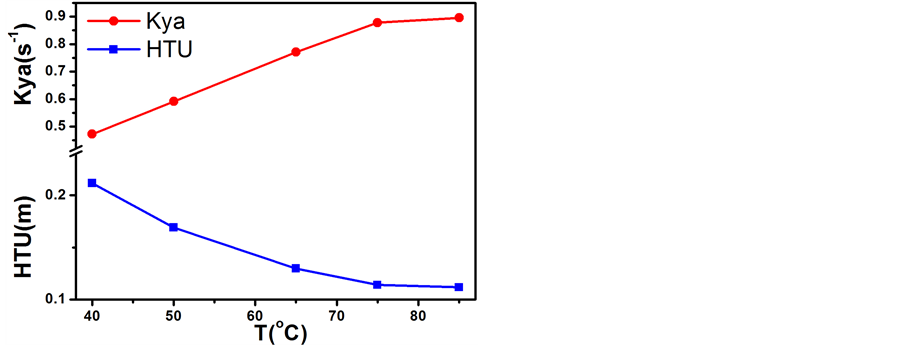
Figure 8. Influence of the experimental temperature on the W-H catalytic exchange reaction efficiency
图8. 温度对水–氢催化交换反应效率的影响

Figure 9. Influence of H2 flow rate on the HTU
图9. 氢气流速对传质单元高度的影响
3.6.2. 低浓重水流速对水–氢催化交换反应效率的影响
当氢气流速0.3 m/s、反应温度65℃、θ环填料与催化剂填装比例分别为1:1、2:1、3:1、4:1时,考察了低浓重水流速对传质单元高度和传质系数的影响,结果分别示于图10和图11。
从图10可知,随着低浓重水流速的增大,即气液比的减小,传质单元高度呈微弱下降趋势。这是由于,当催化床高度一定、氢气流量一定时,氢气与催化剂的接触时间是一定的,增大水流量即增大了反

Figure 10. Influence of the diluted heavy water flow rate on the HTU
图10. 低浓重水流速对传质单元高度的影响
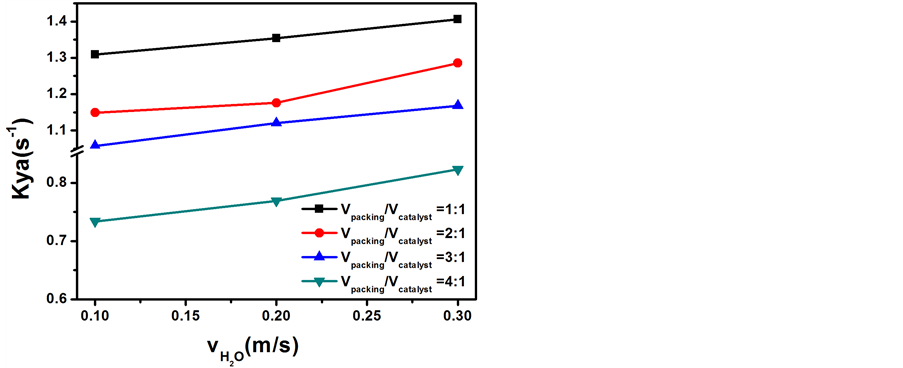
Figure 11. Influence of the diluted heavy water flow rate on the Kya
图11. 低浓重水流速对传质系数的影响
应器中水蒸气的量,使得在相同时间内氢气能够接触更多的水蒸气,促进塔板上水–氢交换反应。
如图11所示,随着低浓重水流速的增大,总体积传质系数随之增大但并不十分显著。重水流速的增加,增大了液体水到蒸汽的传递速率,使气液相传质面积增大,从而使总传质速率增加。增大趋势不明显是因为从总体积传质系数的计算公式可知,低浓重水流量的影响对总传质系数的影响较氢气体流量要小。
从工程角度考虑,对于一定的催化交换塔,希望处理氢气和低浓重水的流速越大越好,然而在一定的气液比范围内,氢气和低浓重水流速的增大,对塔的分离效率来说是一对矛盾,所以在实际工艺过程中,为了提升塔的处理量,一定会付出分离效率降低的代价。
3.7. 处理量对水–氢催化交换反应效率的影响
当气液比1:1、反应温度为65℃、θ环填料与催化剂填装比例1:1时,考察了空塔气速(处理量)对水–氢催化交换传质单元高度和传质系数的影响,结果分别示于图12和图13。

Figure 12. Influence of the air velocity of empty tower on the HTU
图12. 空塔气速对传质单元高度的影响

Figure 13. Influence of the air velocity of empty tower on the Kya
图13. 空塔气速对传质系数的影响
如图12所示,随着空塔气速的增大,水–氢交换反应的传质单元高度不断增大且增长趋势愈加明显,可见气速对于水–氢交换反应的影响强于水速对水–氢交换反应影响。而图13展示了空塔气速对水–氢交换反应传质系数的影响,即随着空塔气速的增大,传质系数不断增大但增长趋势逐步减缓,这是因为气速的增大虽然能提升塔内的传质效率,但是会降低反应的交换效率,综合效果就会表现为先增后减的变化。由2.3中泛点气速的研究可知,当空塔气速高于0.3 m/s时,交换塔内极易发生液泛现象,因此对于本实验,为最大限度提升交换塔的处理量,空塔气速应控制在0.3 m/s左右。
4. 结论
(1) 测定了柱形Pt-SDB憎水催化剂的θ环填料层压降ΔP/Z、泛点气速uF、持液量HL等流体力学性能;分别建立了ΔP/Z、uF与G、L的关联式。
(2) 组内制备的柱形Pt-SDB憎水催化剂的催化活性较传统的小球Pt-SDB憎水催化剂要低(约1/3);推荐的水–氢交换工艺条件是:选择体型接近的θ环填料,填料规格4 mm × 4~5 mm × 0.2 mm,填料与催化剂分层有序填装比例1:1,反应温度70℃~75℃,在推荐工艺条件下,当氢气空速0.1 m/s、气液比1:1时,水氢交换传质单元高度高度约13 cm。
(3) 在一定的气液比范围内,氢气流速会降低塔的分离效率而低浓重水流速会提高塔的分离效率,但是两者的影响效果不成比例,氢气流速的影响要远远强于低浓重水流速所产生来的影响。在实际工艺过程中,需根据处理量和分离效率的不同选择合适的气液比。
(4) 对于本文所采用的实验装置,为获得塔最佳处理能力,柱形Pt-SDB憎水催化剂水–氢交换工艺应选择:θ环填料与催化剂分层有序填装比例1:1,反应温度70℃~75℃,气液比1:1,空塔气速0.3 m/s。