摘要:
本文立足于旅游地理学的基本理论,利用flickr图片分享网站与去哪网、马蜂窝、携程网站中共享的含地理位置的照片信息和信息文本,结合百度地图拾取系统作为数据源,采集了2008年至2017年中2000张照片中筛选的403张照片。并运用GIS10.3中空间分析法作为主要方法进行可视化表达。绘制了山西省游客空间分布的相关图件,分析表明山西省游客的空间分布格局呈现三个明显特征:第一,山西省游客主要集聚在山西中部北部,空间形态上呈现集中于太行山、吕梁山之间的纵贯全山西省中部的盆地地区。东、中、西三大纵列地形带,游客分布表现出明显的空间差异。第二,呈现沿交通线与知名景区的重叠区域是游客分布的重心区。第三,山西省游客空间过度集中于太原市、大同市、忻州市、晋中市为依托的周边地区,并刨析影响游客分布格局的因素。研究结果还表明临汾市、运城市不是游客空间分布重心,并分析导致该布局的原因提出对应旅游营销策略解决这一问题,对整体上完善山西旅游产业转型升级有一定参考意义。
Abstract:
This paper uses Flickr pictures and text message which has shared from the where to go, the hor-net’s nest, CTRIP and Mafengwo Website. Combining Baidu maps pickup system as a data source, 403 photos of 2000 photos screened from 2008 to 2017 were collected and used GIS10.3 in the spatial analysis method as the main method for visual expression. The spatial distribution pattern of tourists in Shanxi province was summarized. First, the overall pattern of Shanxi province is the main tourist gathering in north central Shanxi, space form has concentrated between in Taihang mountain and the central region of the province of Lvliang mountain basin. There are significant spatial differences in East, Middle and West three vertical terrain belts. Second, the overlapping area along the traffic line and the famous scenic area is the center of distribution of tourists. Third, the spatial distribution of tourists in Shanxi province too concentrated in the Taiyuan, Datong, Xinzhou and Jinzhong. Research demonstrates that Linfen City and Yuncheng City are not popular tourist destination among all cities. Analyzing the factors affecting tourists’ distribution, corre-sponding reasons and marketing strategies to solve this problem also is instrumental in the transformation and upgrading of the tourism of Shanxi province as a whole.
1. 引言
2012年被定为大数据元年,在大数据时代下游客的空间分布特征成为旅游地理研究领域非常重要的课题。随着移动互联网、社交媒体、智能手机等电子产品的快速发展使基于用户地理位置的服务(location based service)应用于生活。如今游客出行到旅游目的地都会拍摄大量照片,其中有些会留下地理位置痕迹,像这样的含有地理位置的数据大量的出现,为研究山西省游客的空间分布提供了的新的数据收集与研究方法。通过把在社交媒体上含有山西地理标记照片收集起来,针对山西省特定区域,采取空间分析方法完成山西省游客空间分布可视化表达,并阐述产生这样格局的文化与地理原因是本文的独特之处。研究山西游客空间分布规律特点最终可以为科学指导山西旅游目的地旅游规划、旅游营销提供依据。
在国内外前人做出的研究成果中,有研究使用过这样的研究方法而且取得很大成果,主要集中研究了旅游空间结构客源地市场结构 [1] 、游客的空间行为 [2] 等方面。但是没有针对山西省这一独特的区域进行游客空间分布研究,本文针对这一空白进行研究。李春明等利用地理标记照片分析了在景区尺度上的游客时空行为和旅游热点区域上的优势 [3] 。杨兴柱收集Panoramio这一媒体含有地理位置的南京市游客信息数据结合地理信息系统的运行发现了城市内部的游客路径轨迹模式并通过Getis-Ord Gi分析了城市中旅游景区中的核心热点区 [4] 。黄震方收集7年游客统计资料采用K-Means聚类法对盐城麋鹿生态旅游区游客的时间和空间变化规律进行总结 [5] 。胡英浩使用核密度推估法计算野柳湿地公园可能的游客空间分布 [6] 。在游客的地理位置数据获取方法上Abdul Majid的研究是基于社会化媒体的数据挖掘技术并从中提取有用的信息,推荐合适的旅游景区 [7] 。Masato Naka利用现实社交媒体twitter上超过800万条数据地理位置信息进行数据的时空挖掘,预测个体移动模式 [8] 。国外学者Girardin通过地理标记的数据获取、进行地理可视化表达研究旅游流的分布 [9] 。Snepenger研究了游客季节性分布特点和旅游需求时间变化提出了研究游客分布的另一个思路 [10] 。Shoval和Isaacson从以色列古城游客的旅行数据发现了游客的旅游轨迹 [11] 。Yin也采用从Flickr中浏览照片获得地理位置数据分析游客游览位置提出代表性游览模型轨迹。Kisilevich认为信息技术的发展数据的储存获取更为便利,提出密度阈值、自适应密度两种密度聚类算法分析的概念 [12] 。
研究者研究方向集中于游客空间行为,分析旅游流流动规律,发现游客路径存在不同的路径轨迹模式。较少以地理标记照片来研究游客空间分布。虽然目前基于地理标记照片分析游客分布方面已经取得一定的进展,还存在一些问题。如限于数据的信息处理量大、空间关系复杂多变等问题,研究相对全面但不够深入,理论提升不足。基于上述分析,国内外研究集中在一个城市或者一个景区空间范围内游客的时空分布、游客的空间行为、游客路径轨迹模式。因此本文把研究一个山西省游客空间分布格局并揭示背后的文化地理因素从大的格局去认识游客空间布局作为切入点,以山西省作为研究区域。基于Flickr图片分享网站和旅游社交网站中的用户分享的带地理标签的图片、文本信息作为基础数据,用空间核密度方法、分析山西游客的空间格局特征。结合山西地理环境特征和区位条件,分析游客的空间分布与时间特征,文化与地理环境对其影响提出与山西旅游时空结构对应的发展措施与游客最佳的游览路线。在研究方法上,前人研究大多从定性分析中获取资料,较少采用定量方法提取空间信息。本文分析方法是利用新地理信息技术获取游客空间数据,数据来源新颖,地理标记照片来源分为国内游客和国外游客,使游客旅游偏好选择更为客观研究结果更加真实。分析游客分布规律影响因素时结合山西自然条件气温、地形、水资源和景区分布、经济状况、交通分布综合考虑,这也是本文分析方法的优势。
2. 研究范围与方法
2.1. 研究范围
山西省地理范围110˚14'~114˚33'E和34˚34'~40˚43'N,东西跨290公里,南北跨550公里。东西两边有两大山脉纵贯穿全境分别是太行山、吕梁山并形成了太行山大峡谷、晋陕大峡谷;横向有恒山、中条山、霍山等。全省境内山地丘陵面积占80%,河间谷地、盆地内平原占20%,被誉为“表里山河”地势从东北向西南倾斜。境内有海河水系黄河水系其中汾河是山西的母亲河。山西地处中国内陆属于温带大陆性季风气候,冬季寒冷干燥,夏季气温较全国来说是清凉宜人的。山西旅游资源在全国突出,有6家5A级景区有地面不可移文物3.7万多处,各级文物保护单位6068处,全国重点文物保护单位271处被称为“地上博物馆”。18个国家级森林公园,5个国家级自然保护区,9个地质公园,12个风景名胜区。国务院正式印发《“十三五”旅游业发展规划》将优化空间布局,构筑新型旅游功能区。山西省旅游业迎来了千载难逢的机会。2015年,全省实现旅游总收入3447.5亿元,同比增长21.11%。共接待国内游客3.6亿人次,同比增长20.22%;入境过夜旅游人数59.38万人次,同比增长5.14%;旅游外汇收入2.97亿美元,同比增长5.83%。可以看到山西省旅游业发展增速潜力大,因此把到访山西作为研究区域有可行性。
2.2. 数据处理
Flickr是属于雅虎公司注册用户可以将拍摄的照片上传到服务器同时记录下拍摄照片地理位置包含纬度、经度、海拔、时间、相机型号,用户可按照自己的喜好对照片进行分类同时填写照片描述。Flickr网站有严格规定会审核一些非风景照片将其删除,这样就给照片浏览者提供了便利,搜索时可以输入山西省这个关键词,搜索该照片会出现拍摄地理位置、时间、游客姓名等基本信息。另外,本文还通过马蜂窝、携程网、去哪网中游客的旅游游记作为数据来源,这些网站都是国内游客经常使用的,他们会上传自己去旅游景点的风景照片。通过筛选他们上传的干扰照片例如一些美食照片、个性写真、软文宣传等等。将国内网站上搜索出的到访山西游客照片结合百度拾取系统确定这些照片的经纬度。最后将2000照片筛选出401张位于山西省这一空间范围的图片,将文本、图片信息处理成为Excel数据库(如表1),将Excel中的数据导入到Arcgiss10.3中,将山西省行政区域作为底图进行配准。将照片经纬度进行定位,建立shapefile格式的文件,把Excel中数据库导入Arc-GIS,坐标相同的点则互相叠加,最终生成到访山西游客的地理标记照片空间分布(见图1)。
2.3. 研究方法
记录、分析和展示空间信息并进行可视化表达的工作是地理学大多数任务的核心 [13] 。基于这些空间数据采取空间分析可以从大空间上发现山西游客的分布格局。空间分析是基于地理对象的位置和形态特征的分析和建模的系列技术,目的是为获取和传输空间信息,一直以来是作为地学研究的主要技术工具受到广泛关注 [14] 。因此本文采用核密度分析,核密度分析工具用于计算要素在其周围邻域中的密度。此工具既可计算点要素的密度,也可计算线要素的密度。核密度分析用于计算每个输出栅格像元周围的点要素的密度。使用核函数根据点要素计算每单位面积的量值以将各个点或折线拟合为光滑锥状表面。要想深入了解来到山西的游客的具体分布情况,引入一维核密度估计法。该方法假定点状地理要素可不同的概率分布在任意空间位置。点状地理要素在聚集区域和分散区域分布概率不同,前者大,后者偏小。
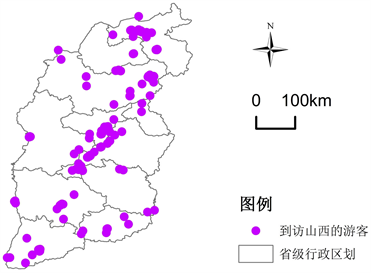
Figure 1. Shanxi, geographical indications, photos, spatial distribution
图1. 山西地理标记照片空间分布
表1. 照片定位部分数据
在计算过程中,利用核函数,以圆为邻域,绕每一个栅格点产生一个平滑曲面,落入搜索范围内的点状地理要素将被赋予不同的权重值,靠近格网中也,权重值越大,密度值越高,向外围减少,当距离格网中也一定阔值范围处密度值降为0。本文采用Arcgiss 10.3的核密度分析方法,研究山西游客的热点分布区域把山西省省级行政区划作为底图,通过自然断开点分级法将结果分为4个等级分别为游客集中极高区、高值区、低值区、极低区即可以代表游客分布空间分布程度。极高区游客分布最广,极少区不代表没有游客分布,高值区、低值区也会有游客分布(见图2)。接下来就要分析游客分布的地理特征,试图发现这样分布原因。
3. 分析游客空间分布特征
山西游客分布格局总体上呈现局部地理集中性,分布广泛形成了独特“Z”型结构。图2中分析得出地理标记照片分布区域其中北部大同市、朔州市、忻州市一共有135张地理照片其中是以大同市为核心区域有84张地理标记照片;中部太原市、阳泉市、晋中市、吕梁市地理标记照片一共有207张,其中晋中市占到114张;南部临汾市、长治市、晋城市、运城市一共有53张,临汾有25张;总之这些地理标记照片空间分布不同,呈现以大同、晋中、为核心向外扩展布局。游客空间分布与交通线和景区分布高度吻合。交通密度和旅游收入进行对比交通条件与旅游经济水平间有较强的正相关性,也就是说交通越发地区游客分布越集中 [15] 。通过将到访山西省游客地理标记照片与山西省国道交通线路、布局结合分析生成图片(见图3)。研究发现海南山西省游客分布中部地区呈以太原和为端点向周围延伸,南部以运城为端点延展,北部以大同为起点延伸形成了横贯山西中部盆地的带状分布格局。
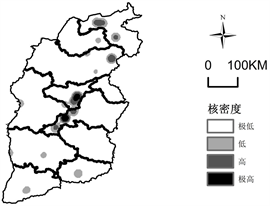
Figure 2. Shanxi geographical hotspots map spatial distribution
图2. 山西地理标记照片热点空间分布
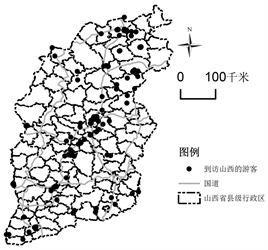
Figure 3. Shanxi state highway main line and spatial distribution of tourists
图3. 山西主要国道线路及游客空间分布
4. 结论
通过对地理标记照片的研究及其影响因素分析得出以下结论:
1) 山西省旅游线路客观上存在东纵、中纵、西纵三条主要线路中,其中中部线路游客分布量占很高比例,是旅游最发达的部分。形成这种游客分布的原因第一是中部是山西省经济最为发达,人口最稠密的地区。第二,交通网络便捷,是山西的交通枢纽。中纵的公路从新荣得胜口至垣曲古城732公里,机场从北往南依次为大同云冈机场、忻州五台山机场、太原武宿机场、临汾乔李机场、运城关公机场。第三,中部纵向上旅游资源集中,分布有山西的王牌旅游景区。从北向南依此有云同石窟、五台山、恒山、平遥古城、乔家大院、介休绵山、洪洞大槐树、尧庙、运城盐池等著名景区。而且山西省打造的核心旅游产品晋商文化游区、佛教文化游区贯穿中部纵线。总之,随着经济发展旅游资源的重要性有可能下降,但其仍是促进旅游经济发展和造成旅游经济空间差异的重要基础 [16] ,旅游资源禀赋的空间差异对山西省游客空间格局产生重要影响。
2) 山西省游客空间布局受到地理环境影响。从游客分布格局的纵向上看,游客分布数量上西部是到访的最少区域,东部为太行山区,西部是吕梁山区。这两个地区地势较高,沟壑纵横,水资源短缺,大部分地区生态环境不如中部,这些天然形成得自然地理环境会制约着游客的到访。中部纵线为山西省内部地势最为优越的地区有着串珠状的盆地平原,这里同时是游客分布的集中带区。本文将收集到的402地理标记照片按照季节进行整理得出冬季照片占8%、春季占24%、夏季占45%、秋季占23%,还有一个原因是山西气候导致,山西属于温带大陆性气候冬季寒冷相对漫长,夏季南方气温低,春秋两季时间较短。气候舒适度会影响游客出行。近50年来山西省旅游气候舒适度发生了较大的变化,从空间表现上看温湿指数在西南–东北一线上升趋势明显,今后更利于游客在这一线分布 [17] 。
3) 本文旨在运行地理学空间差异思维,结合地理信息系统方法研究山西游客空间分布格局。山西作为煤炭资源大省今后必须转型发展,未来旅游业是其重点。本文从大格局出发研究山西游客空间格局。采取数据的方式更为准确、科学、方便,可以为今后研究山西游客内部流动模式提供数据支持和新的思路。有助于山西今后旅游规划特别是旅游线路、旅游产品的设计,为旅游基础设施、景区开发、旅游市场营销提供科学依据,未来山西省东部太行山区、西部吕梁山区纵向特色旅游产品旅游线路开发,会使得游客分布越来越向这两个区域集中。目前很多研究者已经关注了地理数据的获取但还有一些问题要解决,随着地理信息的大爆炸人们的隐私也引起关注。基于Gis和地理信息在更大尺度上研究游客的流动性,及流动性的空间差异也要关注。