摘要:
以上海滨江森林公园为研究对象,按照公园空间分布特征和功能区域划分,将研究区域划分为香樟林、广玉兰林、特色植物观赏区、西南区和东南区5个片区,对每个片区的土壤层进行分层取样(0~10、10~20、20~30、30~50、50~100 cm),使用等离子电感耦合质谱仪(ICP-MS)分析土壤中重金属元素镉(Cd)的元素含量在园区内的分布状况,根据单项污染指数法对各片区的污染状况进行了评价。研究结果表明:滨江森林公园各片区的表层土壤0~10 cm重金属元素Cd的含量分别为香樟林0.351 mg/kg,广玉兰林0.321 mg/kg,特色植物观赏区0.327 mg/kg,西南区0.317 mg/kg,东南区0.309 mg/kg。随着土层深度增加,土壤中Cd元素含量呈逐渐下降趋势。该地区的土壤各层(0~10、10~20、20~30、30~50 cm) Cd元素含量均值分别为0.323 mg/kg、0.267 mg/kg、0.244 mg/kg和0.210 mg/kg。该地区土壤中Cd元素背景值为0.261 mg/kg,与国家土壤环境质量标准相比,该地区Cd 含量处于国家土壤质量II类标准范围。单因子污染指数法的计算结果表明,该地区Cd元素含量与上海市土壤重金属Cd含量背景值相近,处于污染临界值。
Abstract: Shanghai Binjiang Forest Park was investigated as the main study area based on the characteristics of distribution and divisions of functional area. This area was divided into 5 districts which were Cinnamonum campora stands, Magnoliagrandiflora stands, Ornamental plants, Southwest area and Southeast area. We used ICP-MS to analyze the Cadmium (Cd) concentrations, and analyzed the data with SFPI (Single Factor Pollution Index methods) to evaluate the pollution situation of the heavy metal Cd in the soil of these areas .The results showed that the soil concentrations of Cd at 0 - 10 cm in C. campora stands, M. grandiflora stands, Ornamental plants, Southwest area and Southeast area were 0.351 mg/kg, 0.321mg/kg, 0.327 mk/kg and 0.309mg/kg, respectively. The values of Cd concentrations gradually declined with the depth of soil raised. Compared with the national standard of soil quality category, the background values (0.261 mg/kg) of soil Cd concentrations in Binjiang forest park were at the range of national standard of soil quality II which indicated that there were no significant effects on vegetation and environment. The results of SFPI showed that these areas were at the contaminative critical state compared with the Shanghai background level.
1. 引言
随着我国城市化水平的不断发展,土壤重金属污染日趋严重。重金属污染物一旦进入土壤就难以降解排除,并且在土壤中滞留的时间较长,导致农作物的可食用部位积累过量后经食物链直接威胁到人类的生存健康问题[1] [2] 。因此,关于土壤中重金属元素的累积问题逐渐成为科学家研究的热点问题之一。森林是城市自然生态系统的重要组成部分,森林乔木层生物产量高,占有的空间大,巨大的根、茎、叶面积对污染物有一定的吸收、转化和累积作用,使污染物在短期内不释放到环境中,而其自身生长良好,又能充分发挥其改善环境的生态功能[3] -[5] 。
上海是我国经济最发达的城市之一,人口密度大,工业发展水平高,土壤重金属污染情况亦不容乐观。有关研究表明,上海世博园区内浦东工业区0~5 cm的表土层中砷、镉、镍、铜、铅、锌的浓度均高于土壤的背景值。其中镉的生态毒性最高的,其生态风险达到严重及以上级别的区间比例达86.5%(李胤等人于2008年的研究)。林啸等人测定了上海市区(浦西)0~2 cm的表层土壤中铬、铜、铅、锌的含量。结果表明,杨浦区和普陀区的东部及北部的铬含量相对较高,为背景值的10~50倍。铅和锌的污染浓度显著高于铬,在杨浦区东部和延安路与轨道交通二号线附近的浓度为背景值的100~500倍。土壤中铅的潜在生态危害指数为244.69,达到中等生态危害水平[6] -[8] 。根据庞金华等人持续十几年对于上海土壤中的Cd等8种元素的研究,Cd等7个元素基本上处于稳定状态,年际变化不大,但同时Cd是威胁上海土壤的主要污染元素[9] [10] 。史贵涛等人对于上海市区公园土壤重金属含量的研究表明,浦东新区的外环线内9家公园灰尘中Cd的含量平均值为1.75,超过背景值5.5倍[3] [11] 。
上海滨江森林公园位于浦东新区高桥镇,于上世纪50年代采取吹泥成陆的办法围垦形成。公园总面积约2000亩,是上海森林覆盖率最高的郊野森林公园。近年来,随着公园开发力度和人为干扰程度的增加,园区土壤受到重金属污染的状况还未有研究[12] [13] 。本文的研究目的是通过对上海滨江森林公园土壤重金属元素Cd的含量分布特征及污染状况进行研究,为掌握该园区土壤污染状况提供数据支撑,也为今后上海地区土壤重金属污染修复提供科学依据。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 样品布点与采集
本研究以上海滨江森林公园为研究对象,通过设置调查区域、采集土壤样品(按0~10、10~20、20~30、30~50、50~100 cm进行分层采集)进行室内测定分析了解该区域Cd元素分布特点。根据滨江森林公园功能区域分布以及植被的差异,将公园分为5个片区进行布点采样,即香樟林,广玉兰林,特色植物观赏区(杜鹃观赏区),西南区和东南区。每个区域按照网格法,分别设置8至10个取样点,每个取样点分按层次划分进行取样,一般每层土壤样品取500 g左右,将每个取样点的同层次样品混合后,得到每个区域每个层次的土壤混合样品,共得到土壤样品25个。
2.2. 样品测试与分析
土壤样品在采集完成后,带回实验室,在实验室自然晾干,过0.149 mm土壤筛,并装入自封袋中保存。样品过筛后,采用酸溶法(HNO3-HF-HClO4)在电热板上加热消解。消解后的样品定容后,在等离子电感耦合质谱仪ICP-OES (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA)上测定Cd元素含量。为了加强实验过程的质量控制,每批样品做一个试剂空白和一个标准样品进行样品含量校准。
2.3. 评价方法
对于污染状况的评价,本文采用农业部《农田土壤环境检测技术规范》对于所获得的测定数据(0~100 cm土层数据)进行了相应的统计、分析以及评价[14] 。其中对于土壤重金属Cd的污染评价,采用单因子污染指数法来进行。单因子污染指数法计算公式:
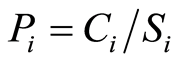 (1)
(1)
式中,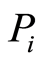 为土壤环境中污染物i的单项污染指数,
为土壤环境中污染物i的单项污染指数,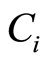 为土壤环境物i的实测数据,
为土壤环境物i的实测数据,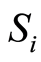 为污染物i的评价标准值。如果计算结果
为污染物i的评价标准值。如果计算结果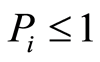 为非污染,
为非污染,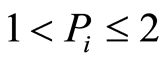 为轻污染,
为轻污染,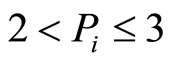 为中污染,
为中污染,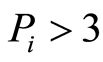 为重污染。
为重污染。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 不同功能区土壤Cd元素含量
表1为滨江森林公园不同功能区土壤不同层次Cd元素含量。由表1可知滨江森林公园各区域的土壤表层重金属Cd元素含量香樟林0~10 cm含量最高,为0.351 mg/kg,而0~10 cm土层中西南区土壤Cd含量最小,为0.317 mg/kg。随着土壤深度加深,土壤Cd含量呈逐渐下降趋势。以香樟林土壤Cd元素变化为例,在土壤10~20 cm中,Cd元素含量为0.277 mg/kg;20~30 cm土层中Cd元素含量为0.251 mg/kg;30~50 cm土壤深度时,Cd元素含量仅为0.224 mg/kg;由于土壤50~100 cm的Cd元素含量在测定检测限以下,未检出,因此表1中无此土壤层数据。
香樟林、广玉兰林和特色植物区的0~10 cm土层中Cd含量略高于西南区和东南区,可能是由人为干扰剧烈造成的,并且0~10 cm土层植物根系的生长对于土壤表层重金属Cd镉的迁移有一定的影响。在香樟林,广玉兰林,距离园区中心较远,开发程度相对较低,且人为活动相对较少,区域内林分栽植密度
较大,导致地上部分地被植物较少,土壤0~10 cm层次中植物根系不多,因此土壤表层的土壤状况较为稳定,Cd的迁移受到环境影响不大。而在西南和东南区域,采样点设置在公共草坪,因此人的活动对于土壤的稳定性的影响较大,而且由于草坪的浅根系的吸收和迁移作用,可能对于土层的Cd在土壤中的含量产生了的影响。
在不同的区域中,种植不同的植物品种,对不同土壤深度的Cd含量的影响也不同。根据表2的结果,可认为由于香樟和广玉兰的根系对于Cd的吸收和迁移的作用,因此,在10~50 cm的土层中,香樟和广玉兰林下的土壤中的Cd小于其他区域,以10~20 cm的土层最为显著。而由于根系分布深度的不同,香樟林下的土壤在20~50 cm的深度的Cd含量减小程度大于广玉兰林下的土壤。
3.2. 滨江森林公园土壤Cd元素含量分布特征
图1为滨江森林公园土壤各层Cd元素含量均值。由图1可知,随着土壤深度增加,土壤Cd元素含量逐渐减小。Cd元素水平在土壤空间垂直分布无显著差异,并且基本符合上海市土壤背景值(0.261 mg/kg)[15] ,处于污染临界值。
3.3. 滨江森林公园土壤Cd污染指数
通过单因子污染指数法分析,得到表3。表3数据表明,滨江森林公园不同功能区污染指数大小不一。该地区Cd元素含量都处于轻微污染或污染状态临界。其中广玉兰林污染指数最小,为0.97,而香樟林由于林分生长旺盛,乔木根系庞大,土壤表层0~10 cm的 Cd元素含量较高(0.351 mg/kg),因而对于土壤重金属积累作用强烈,其污染指数最大,达1.06。与上海市土壤重金属Cd含量背景值相比,滨江森林公园的土壤Cd元素含量处于污染临界值。

Table 1. The soil concentration of Cd (mg/kg) by depth and function areas in Binjiang Forest Park.
表1. 滨江森林公园不同功能区不同深度土壤Cd元素含量(mg/kg)
*表示土壤Cd元素含量在检测限下,未检出。

Table 2. The soil concentration of Cd (mg/kg) by depth and function areas in Binjiang Forest Park.
表2. 不同土壤深度Cd含量相对于0~10 cm土层的百分比(%)
*50~100土壤Cd元素含量未检出。
Figure 1. The background soil concentration of Cd in Binjiang Forest Park.
图1. 滨江森林公园土壤Cd元素背景值

Table 3. The soil concentration of Cd (mg/kg) in different function areas in Binjiang Forest Park.
表3. 滨江森林公园不同功能区域土壤Cd元素含量(mg/kg)
4. 结论
本文根据单因子污染指数法的计算结果表明,该地区Cd元素含量与上海市土壤重金属Cd含量背景值相近,与国家土壤环境质量标准相比,该地区Cd含量处于国家土壤II类标准范围,说明该地区土壤质量基本上对植物和环境不造成危害和污染。
随着土壤深度的加深,Cd含量均呈现出逐层降低的趋势,在50~100 cm未有检出,这个状况也说明了本地区土壤重金属Cd污染状况不明显。
通过与史贵涛等人对于浦东新区外环线以内9家公园的灰尘中Cd的含量的研究相对比(平均值为1.75 mg/kg)[3] [11] ,本文在滨江森林公园内的土壤Cd含量测定数据小于上述研究数据。分析其原因,可能是由于在史贵涛等人的研究中,土壤取样点在公园门口靠近道路边缘,因此受到人为干扰、浮尘和汽车尾气等外来因素的影响较大,而本文研究的取样点均位于公园的中心地带,受到周边环境影响较弱,导致数据差别较大。
5. 研究展望
通过本文研究,获得了滨江森林公园中土壤重金属Cd在公园的空间分布特征、垂直分布规律以及土壤重金属Cd的污染状况一手数据。这对于了解滨江森林公园的土壤Cd的背景值调查和分布规律,并且对于今后该地区基于土壤污染防护的森林经营具有重要意义。同时,本文仅对滨江森林公园的土壤Cd元素污染状况进行了调查研究,但是基于林分防污染隔离机制的相关研究仍是本文今后的重点研究方向。
项目基金
上海市科技兴农重点攻关项目(沪农科攻2010第6~1和沪农科攻2011第1~6)和上海市绿化和市容管理局局管项目G141208资助。