1. 引言
科学计算可视化(简称科学可视化)已成为科学研究和工程技术人员感知、分析和理解科学计算数据中蕴含的物理现象和规律不可或缺的重要手段。传统的科学可视化普遍采用后处理模式,先将高性能计算机数值模拟计算产生的海量结果数据保存在外存磁盘中,当需要可视化处理时通过网路或介质将外存磁盘中的数据传递到外置的科学可视化平台或可视化服务器进行可视化处理。由于存在网络传输与磁盘I/O瓶颈问题,使用这种传统的处理方式,用户不能及时对数据进行可视化处理,因此不能及时发现数值模拟计算中的问题进行改进优化,降低了整个问题求解的效率。随着高性能计算机技术的飞速发展,科学计算的能力不断提高,科学计算数据规模不断扩大,由GB级、TB级发展到PB级,甚至EB级,可视化后处理模式存在的瓶颈问题越来越突出。
原位(in-situ)可视化是在高性能计算机上使数值模拟计算和可视化过程并发进行,充分发挥高性能计算机的资源优势,及时对数值模拟计算数据进行高效并行可视化处理,显著提高海量数据的可视化效率。近十年来,国际上对原位可视化技术的研究与应用取得较大进展。2006年Yu. H等人开发了一个针对特定大规模地震模拟数据的原位可视化系统[1] ,取得良好的应用效果。在已有并行可视化软件平台上开发原位可视化框架也是当前原位可视化领域的主要趋势。2011年著名开源并行可视化软件ParaView实现远程、交互式的原位可视化[2] ,同时著名开源并行可视化软件VisIt与模拟程序集成,实现了Client/Server模式的原位可视化[3] 。欧洲瑞士国家超算中心为当前不同数值模拟应用开发了一套完整、通用的原位可视化接口框架ICARUS[4] 。实际上,原位可视化技术面临诸多挑战,至今还没得到广泛使用。本课题组提出在原位可视化已有研究成果基础上,面向多用户远程可视化的应用需求,充分发挥高性能计算机的资源优势,构建基于高性能计算机的高性能并行可视化服务器。既可实现基于高性能计算机的高效大规模科学数据的高效并行可视化服务,克服传统后处理模式科学可视化存在的效率低等问题,又可实现基于web的多用户远程交互可视化,使传统原位可视化技术的发展进入一个新阶段,得到更加广泛的应用。
并行可视计算的任务调度与资源分配对高性能并行可视化服务器的服务质量和可视化效果有重要影响。本文首先简要介绍课题组正在开发的高性能并行可视化服务器的功能和组成结构,然后,重点论述研究提出的基于任务属性选择的并行可视计算资源分配算法和基于线性回归方法的任务属性的自适应维护算法。模拟实验结果表明,所提出的资源分配算法可靠有效,任务属性自适应维护算法提高了资源分配的准确性和效率,可保障大规模科学数据并行可视计算的高性能。
2. 高性能并行可视化服务器功能与组成结构
在高性能计算机上构建高性能并行可视计算服务器的主要目的是面向高性能计算数据原位可视化和远程可视化的应用需求,发挥高性能计算机的超强计算能力和超大规模存储能力,为多用户可视化请求提供高性能并行可视化服务。下面简要介绍高性能并行可视计算服务器的功能与组成结构。
2.1. 主要功能
2.1.1. 主要服务功能
1) 基于web的多用户远程交互可视化服务:提供地理分散位置用户的全图形操作、交互和分析服务。允许桌面计算机、笔记本用户使用可视化方法和技术,理解和分析大规模高性能计算数据,通过为用户提供基于web的方便的使用方式实现随时随地的可视化。
2) 原位可视化服务:在超级计算机上对数值模拟计算结果数据直接进行高效可视化处理,生成图像或文本可视化结果,传送到客户端。
3) 传统后处理可视化服务:将数值模拟计算结果数据先存入磁盘,需要可视化时,从磁盘读取数据在高性能计算机上进行并行可视化处理。
2.1.2. 主要管理功能
1) 多用户请求管理:响应用户请求,管理多用户权限,解释用户命令。
2) 可视化任务管理:根据用户命令的解释,确定可视化任务及属性,规划多任务执行顺序。
3) 可视化资源管理:根据可视化任务及属性,配置和优化可视化资源。
4) 可视化数据管理:管理数值模拟计算产生的可视化源数据,以及可视化服务器输出给客户端显示的图像数据。
2.2. 硬件组成结构
并行可视化服务器配置在高性能并行计算机(比如天河-1号)上运行,输出的是经绘制处理的图像信息。为了保证并行可视化服务器的可视化效率,并行可视化服务器需相对独立的占用高性能计算机部分节点资源,专用于数据存储、I/O通讯、图形绘制、资源管理等。其硬件结构如图1所示。
并行可视化服务器内部使用高速内网来完成数据和命令的传输,服务器和客户端之间通过高速互联网相连。客户端是远程可视化的人机交互界面,各节点通过I/O节点访问磁盘。为了保障并行绘制效率,并行可视化服务器配置多个绘制节点,每个绘制节点需要配置1~2个硬件GPU图形加速处理器。并行可视化服务器配置多个数据节点用于缓存数值模拟计算的结果数据,配置多个I/O通讯节点用于外存磁盘数据的访问,以及通过高速互联网与客户端交换数据。资源管理节点根据多用户综合可视化的任务需求,与高性能计算机作业管理系统协同对数据存储、I/O通讯、图形绘制节点资源进行配置和优化,使其既能够高效完成可视化任务,又对高性能计算机上运行的其它计算任务的影响最小。
2.3. 软件组成结构
考虑到可视计算任务一般数据量巨大,不同类型算法的并行性也有较大差异,因此服务器应当将用
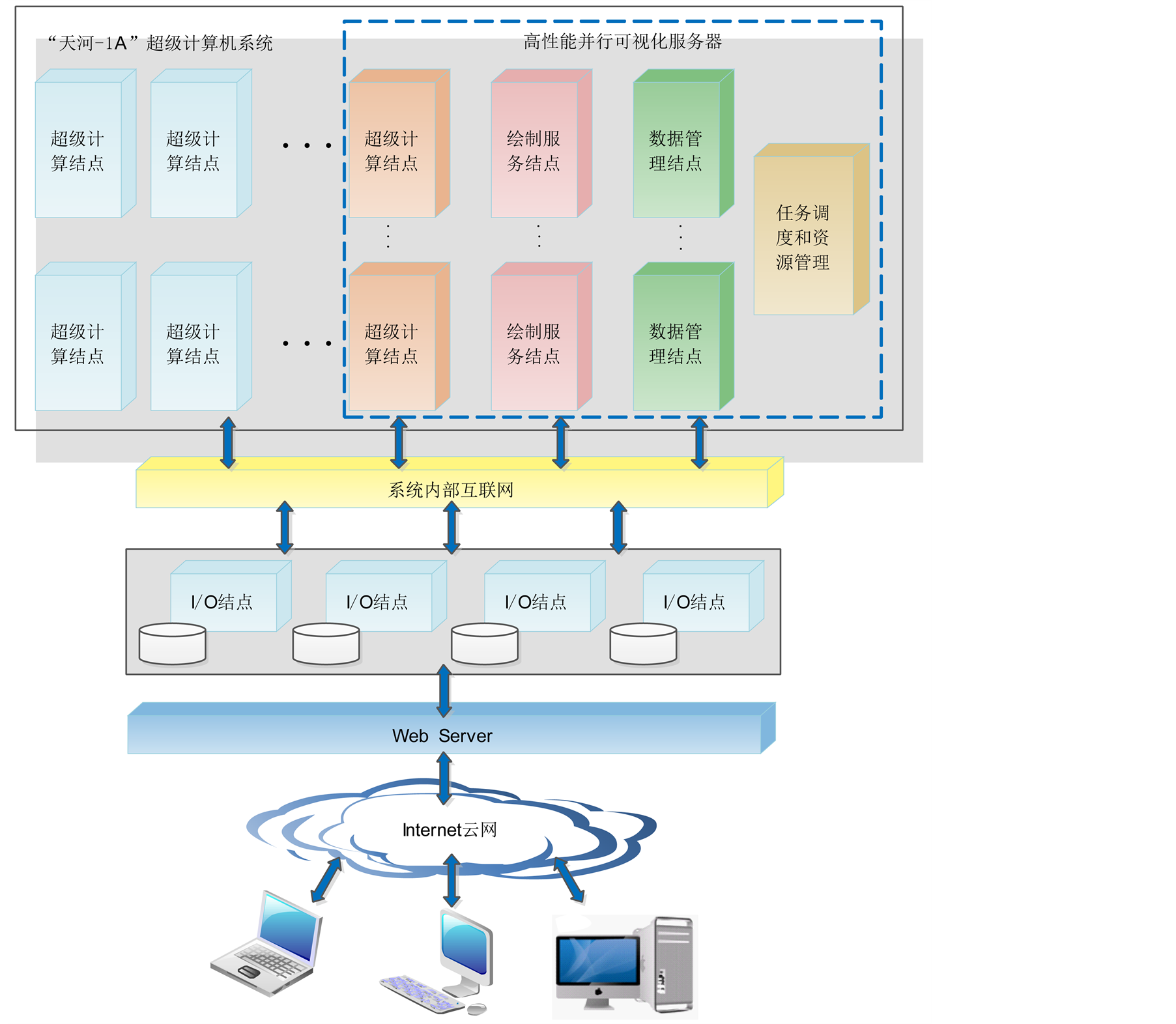
Figure 1. High performance parallel visualization server hardware structure
图1. 高性能并行可视化服务器硬件结构图
户使用的可视计算工具和算法在服务器的每个结点上安装好,以便用户远程调用,并维护所存储的算法信息,以便在同类型任务下次到来时,能够更加准确的估算出其预估时间,所需结点数等信息,帮助服务器更加精确地进行任务调度和资源分配。
其软件组成结构如图2。
3. 高性能并行可视化服务器的资源管理
高性能并行可视化服务器的资源管理是为用户请求完成的可视化任务配置和分配资源,资源管理的正确性和效率直接关系到整个服务器的服务质量和可视化效果。国内外许多科研人员,对高性能计算机的资源管理技术做了深入研究。不仅提出了多种任务调度和资源分配算法,例如,通过阀值结合min-min和max-min的任务调度和资源分配算法[5] ,基于资源属性选择的任务调度和资源分配算法[6] ,基于资源记账统计的资源管理方法[7] 等,而且开发了多个开源的高性能并行计算资源管理工具,例如SIum[8] 、IBM系统中的LoadLeveler[9] 、TORQUE[10] 等。但是,已有的资源管理算法主要针对科学计算和数值模拟并行计算效率的提高,对于任务属性的特点考虑较少,不完全适应高性能并行可视化服务器的资源管理。
本文基于Slurm高性能并行计算机系统作业管理工具,根据高性能并行可视化任务的特点和规律,
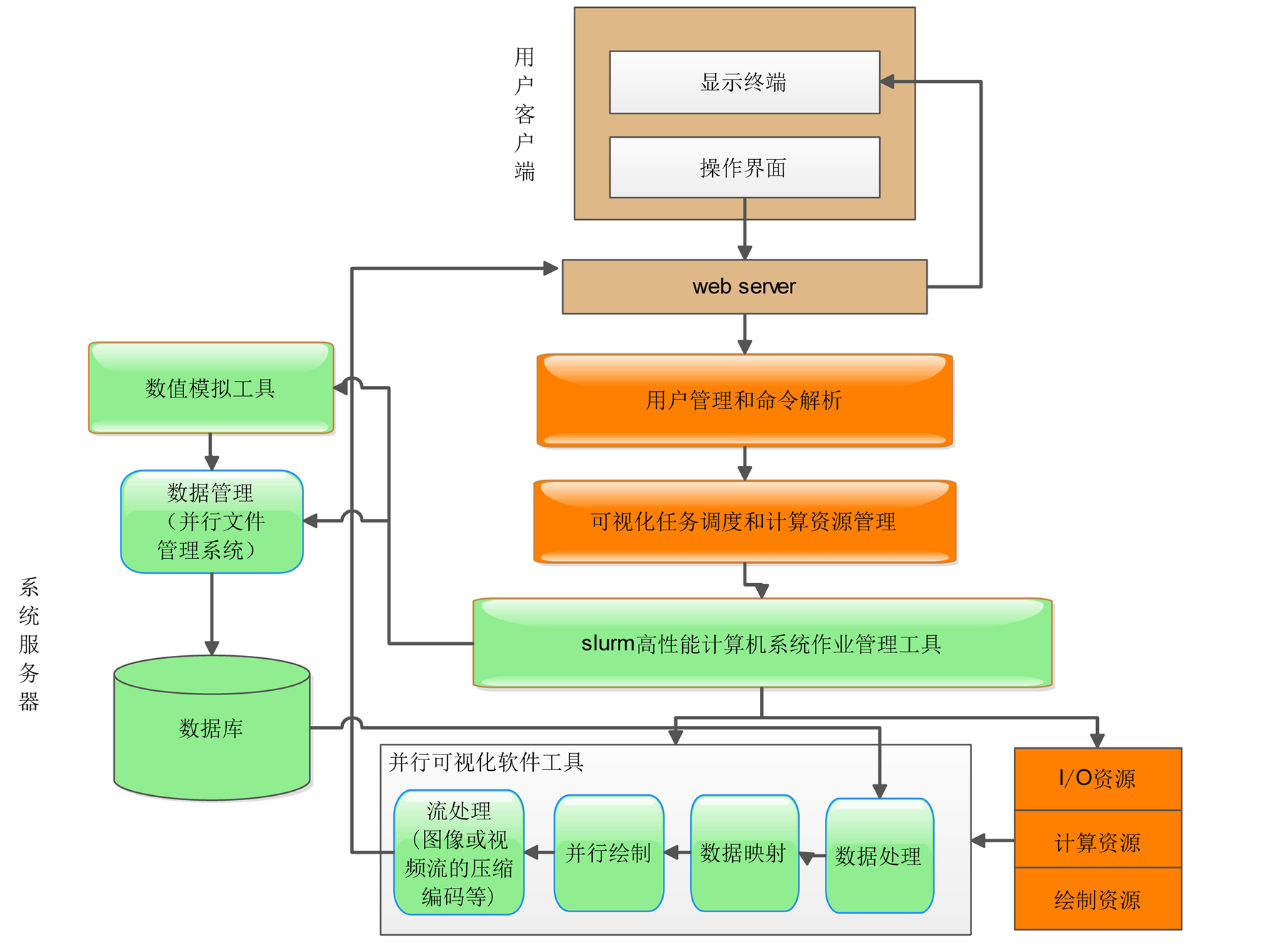
Figure 2. High performance parallel visualization server software structure
图2. 高性能并行可视化服务器软件结构
提出了基于任务属性的资源管理策略,并在此基础上,提出了基于线性回归方法的任务属性的自适应维护算法。
3.1. Slurm及全局并行文件系统简介
Slurm是一个由LLNL(Lawrence Livermo National Laboratory)和Linux Network X等机构共同合作研发的,能够兼容各种UNIX系统开源集群管理系统工具,具备容错功能和良好的可扩展性。可用完成各种集群和大规模并行处理系统任务调度和资源管理。其主要包含了3个功能:第一、以独占或共享两种方式分配结点资源;第二、提供一个作业启动、运行和监控的框架;第三、根据作业调度算法和资源分配策略管理资源的访问。Slurm支持多种不同插件(支持动态调用的函数库)完成某一个模块,运行时根据配置文件选择具体的一种实现提供服务。例如记账,作业调度,资源预留等功能模块都可由用户使用现有的或自己实现的不同的插件完成。此外Slurm为用户提供了一个(静态)函数库,包括了支持各种功能的API,用户可以使用这些API获取系统信息,编写自己的作业调度和资源分配策略。
对于数据的管理,可视化服务器和“天河1-A”高性能计算机系统一样,采用全局并行文件系统对磁盘阵列及其中的数据进行管理。全局并行文件系统由三个分区构成,每个分区作为独立的全局目录空间,创建用户时在每个分区上均创建私有目录,其中HOME分区为高可用SAN存储设备,可靠性好但存储规模小,建议存放项目代码和文本,WORK分区采用了大规模高速盘阵配置,具有大容量、高带宽和高可扩展性的特点,适合存放大规模作业处理和输出的数据文件。
3.2. 资源的定义
根据并行可视计算服务器服务对象的特点,本文所讨论的资源包括了四类:数据资源、计算资源、存储资源和工具资源。通过对这四类资源的定义及分析,确定服务器分配给任务的资源的类型及数量。针对高性能并行可视化服务器的服务功能和特点,我们将可视化计算结点资源分为计算结点、存储结点、绘制结点、I/O结点四类,将可视化服务资源分为可视化数据、可视化工具二类分别进行定义:
可视化计算结点资源定义如下:
1) 计算节点:专门用做计算的高性能计算机计算结点。
2) 绘制节点:配置有GPU的高性能计算机计算结点。
3) 存储节点:专门用做存储可视化数据的计算结点。
4) I/O节点:专门用做访问磁盘数据和与负责客户端通信的结点。
可视化服务资源定义如下:
1) 可视化数据:由科学计算产生的,需要进行可视化处理的中间或结果数据。
2) 可视化工具:专门用于对可视化数据进行可视化处理与交互软件工具。
这些资源,我们借助“天河-1A”中的Slurm软件,通过/etc/slurm/partition.conf系统配置文件中的PartitionName=...参数对可视化服务器占用的结点进行分区,以便统一管理使用。主要配置细节为:PartitionName:分区名字;Nodes:分区中的结点;Default:是否为默认分区;RootOnly:是否仅root可访问;AllowGroups:允许访问分区的用户组;MaxNodes:提交到此分区的作业所允许分配的最多结点数;MinNodes:提交到此分区的作业所允许分配的最少结点数;MaxTime:提交到此分区的作业所允许的最长运行时间(分钟);State:分区是否可用。例如:PartitionName=long Nodes=cn[4~51] DisableRootJobs=YES MaxTime=10080 MaxNodes=32 Default=NO AllowGroups=all。我们的可视化服务器初步分区情况如表1。
3.3. 基于任务属性选择的计算结点资源分配算法
可视化服务器依托“天河-1A”高性能计算机,基本的资源管理模式采用slurm开源并行集群资源管理软件实现,包括用户登陆,任务调度和管理,资源的配置和监控,以及全局的并行文件系统管理。我们在此基础上进行了资源节点分配算法的优化,提出了基于任务属性的结点资源分配算法。资源配置和管理功能模块流程如图3。
3.3.1. 任务属性的定义
考虑到可视计算任务中,影响任务调度及执行时间的要素主要有:应用算法、数据规模、数据类型和并行程度。任务属性由系统任务管理模块接收用户提交的任务申请中的信息表,经过任务管理模块查

Table 1. High parallel visualization server resources partition table
表1. 高性能并行可视化服务器资源分区情况表
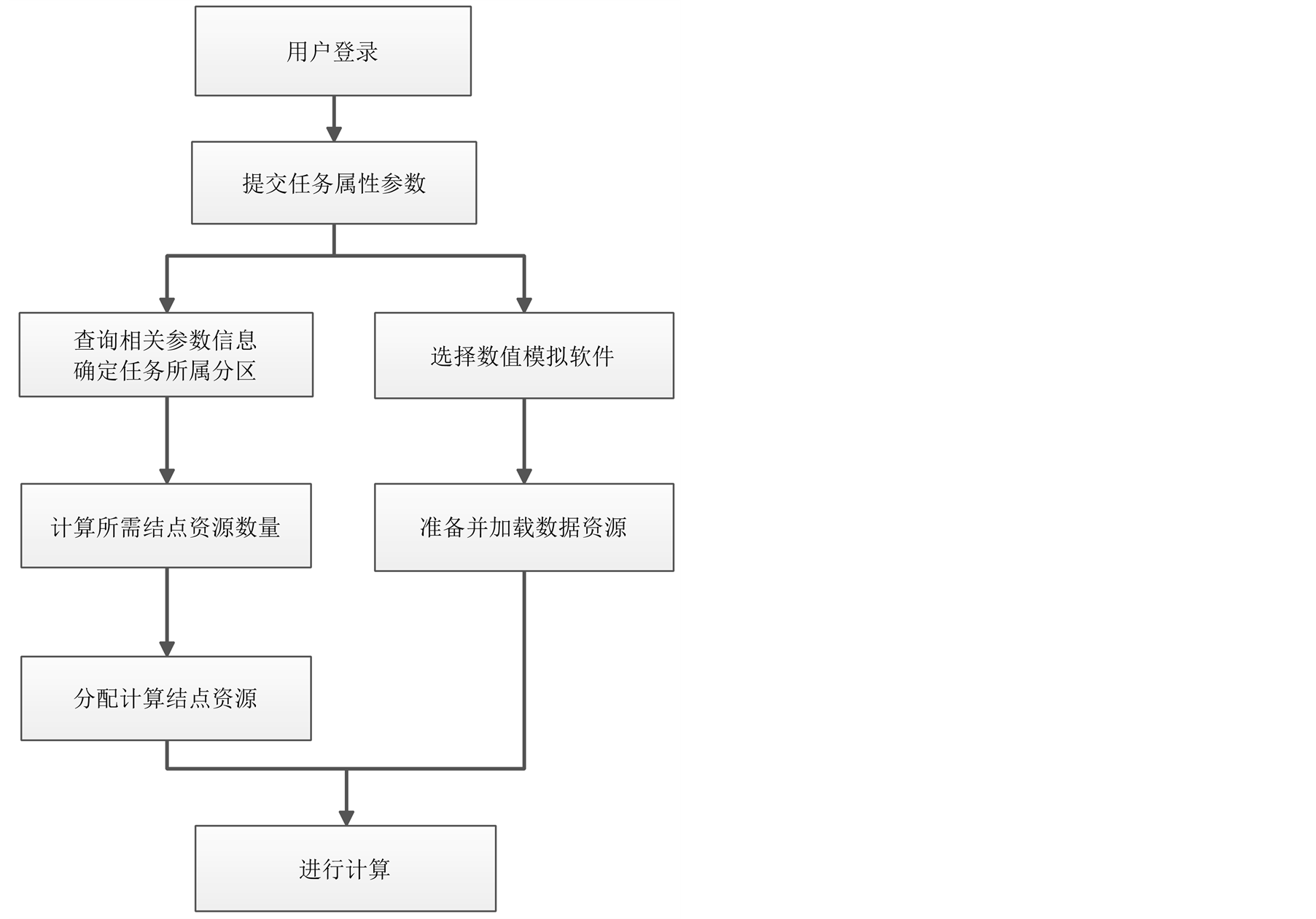
Figure 3. Resources management and allocation design
图3. 资源配置和管理功能模块设计
询或者计算之后得到。任务属性应当由一个六元组来表示:ID, Algorithm, DataScale, DataType, ParallLevel, DNodeNum。
1) 任务ID:在系统中唯一标识这一个任务的ID编号,以便维护唯一的任务会话
2) 应用算法(Algorithm)
不同用户的服务申请往往使用不同的算法来对不同的或者相同的数据进行处理,而不同的算法在处理数据上其所需的运行时间、并行性、不同结点数下运行的加速比都不尽相同,而这些信息直接影响到资源的分配和系统服务的效率。应用算法元素用于查询服务器中维护的算法信息,这些算法信息以表单的形式被维护在系统中的任务调度和资源管理结点中,以便计算出将要启动任务的综合并行度和所需结点资源的种类和数量。
3) 数据规模(Data Scale)
数据规模大小直接关系到任务所需的处理时间的大小,显然,数据规模越大,任务所需的计算和处理时间越长,反之越小。对于可驾驭式任务而言,原始数据的大小往往也意味着中间计算步结果数据的大小,从而决定着其所需的额外存储资源间以存储这些中间步的计算结果,以便于用户对科学计算和可视化结果进行分析。
4) 数据类型(Data Type)
科学计算可视化研究的对象一般是科学计算产生的数据和科学测量产生的数据,这些数据是具有一定的空间几何分布的数据场,同时也具有一定的时间属性。通常分为:标量数据场、矢量数据场和张量数据场、以及完整场景和模型数据。
5) 并行程度(Parallel Level)
基于高性能并行计算机的可视计算服务器对于科学计算可视化应用来说无疑提供了一个很好的硬件平台,但由于科学计算可视化领域,许多应用在数值模拟过程本身存在明显的数据相关性,其并行程度受到其算法本身的极大局限,许多应用在多结点上并行运行时,由于数据相关性存在大量的数据同步和时间上的互相等待,其效果反而不如在单节点上运行效率高。因此,任务的并行程度将会是分配计算资源的一个重要因素。
6) 用户申请结点数(DNodeNum)
考虑到服务器用户一般为与任务相关的专业领域研究人员,对数值模拟过程的算法熟悉,因此熟悉其并行性和并行过程,在申请结点时具有一定的经验。在计算资源充足的情况下,额可以尽可能的满足用户申请的结点数,以便达到最好的用户体验。但考虑到用户的自私心理,其为了确保自身应用程序尽早完成很可能在申请过多的结点,造成计算资源的浪费,因此申请结点数元素一般只在算法初次使用时发挥作用。本文主要考虑所需算法均在服务器中所有结点安装好,并使用过多次,具有一定维护信息量的情况。
3.3.2. 多用户下资源管理策略
高性能并行可视化服务器用户需要特定的账号名和密码在登陆结点登陆服务器,用户登录后方可选择所需的应用类型,算法,数据等任务的属性参数,请求服务。在启动一个新任务并为他分配必要的资源之前系统必须清楚其请求的服务与之前已经在运行的任务之间有何种关系,由于可视计算服务器用户往往对本领域专业性很强,对某一领域专业性数据进行访问的用户数量相对不多,同领域中大多数用户极有可能会访问相同的数据,因此,许多任务之间都会存在直接或者间接地关系,不论使用什么算法,只要处理的数据不同就必须为任务分配计算资源,因此需考虑以下两种情况:一是多个任务使用同一可视化方法对同一数据进行访问:这情况下,多个任务都用同样的方法访问数据,因此在分配资源时只需为这些任务中的一个进行分配即可。在计算完成后将结果传递给每一个用户;二是多个任务使用不同可视化方法对同一数据进行访问:这种情况下,如果可视计算任务是对同一块数据进行驾驭式交互处理,存在对数据的修改和交互,则在对数据进行处理时需进行权限认证,只有具有交互修改权限的任务才能够继续运行。对于每一个用户在Slurm管理系统中的每个任务和用户是关联的,这就方便了系统对所有用户和任务进行统一的管理。
3.3.3. 具体算法介绍
算法基本思想如下:
1) 数据规模函数决定存储空间资源占用的大小
针对可视计算服务器面向的任务需求,我们采用全局文件系统来管理数据资源。统一使用一部分数据结点来存储所有任务可能使用到的原始数据以及任务结果的输出数据,用文件名加以区别,方便检索,用户可根据自己的权限,登陆服务器并访问部分数据空间。数据空间的大小根据该用户申请服务中的应用算法需求,按照如下公式确定:
S = F(DataScale) = K·DataScale + C
其中Data为原始数据大小,K和C为常数,往往由系统根据用户应用算法决定。根据以往执行此类任务时的经验数据由线性回归方法计算得到,系统应为每个应用算法维护一个信息表,用来记录该类型任务在服务器中的运行情况和历史记录,并动态更新。在使用一次该算法之后,其所用到的存储空间和数据规模会被自动保存起来,利用这些信息,经过线性会给计算得到一个线性回归方程,用于下次同一算法被用户申请时估算存储空间使用。
2) 应用算法的综合并行度决定资源分配的顺序
主要考虑结点个数对任务执行效率的影响,并行程度一般由服务器执行该类任务的历史信息计算得到。记任务运行时间为t,使用结点为N = 1, 2, 3 得到运行时间t1, t2, t3,
得到运行时间t1, t2, t3, 。单机运行时间为T,则可以得到加速比在不同的结点数下为b1, b2, b3
。单机运行时间为T,则可以得到加速比在不同的结点数下为b1, b2, b3 ,可以得到该任务并行情况下的最大加速比B,此时的结点个数可以认为最佳并行结点数。
,可以得到该任务并行情况下的最大加速比B,此时的结点个数可以认为最佳并行结点数。
考虑到可视计算服务器一般维护的都是专业领域的可视化算法,一般情况下用户对同一算法的使用往往会有多次重复提交的情况。这里我们考虑,服务器上的算法应当将这些重复申请的任务运行信息统一保存管理起来,或者对于某一在不同数据规模下使用不同数量的结点所获得的加速比进行测试并保存。很多算法针对不同数据反复应用,所以对算法的使用情况,服务器应当建立数据结构来保存,以便于及时更新任务使用算法的属性信息,更好的对用户任务存储开销和并行性进行预估。
算法在系统中维护的信息表单所包含的内容如下:主要由两张表维护,表2为主要信息表,表3为算法使用历史信息表,主要用于自适应的维护用户使用该算法存储资源开销的预估计算和对某一数据规模的数据进行处理时单结点运行时间的预估计算。
考虑到系统的实用性,计算出来的结点个数并不能够直接分配,还应该考虑到任务运行的时间问题,比如说,如果一个任务在单机运行时需要1秒,1000个结点并行运行只需1/1000秒,其加速比1000,但1秒本身时间已经很短了,并不影响用户体验,因此在分配结点时没有必要为了加速比为其分配1000个计算节点,造成不必要的资源浪费。
为了解决这个问题,我们自然地考虑到,当任务在单结点下运行时间越长,其加速比对于任务运行效率的贡献就越大,反之越小。因此设计一种标准来对加速比对任务运行效率和用户体验的贡献进行量化评价。一般来讲,不同于网站交互和游戏程序的交互设计,可视计算服务器面向的应用一般都是基于庞大数据集合的科学计算可视化。数据和算法具有特殊性,主要用于科学研究和气象海洋等空天预测,大规模流场模拟等,对系统的是实时性要求并不像网络游戏人机交互等应用那么高。一般来讲许多应用单机运行的事件一般都在十几到几十个小时以上,甚至有的应用在高性能计算机上的运行时间都有可能达到十几天以上考虑到单机运行时间越久,其加速比产生的贡献就越大,节约的时间就越多,因此更应该考虑优先为这样的应用分配较合适的结点。
定义3.1. 可视化计算任务时间尺度:
Level0:单节点运行时间以0至1小时的应用。

Table 2. Algorithm main information table
表2. 算法主要信息表

Table 3. Algorithm using history information table
表3. 算法使用历史信息表
Level1:单结点运行时间在1至24小时的应用。
Level2:单结点运行时间在一天至三天的应用。
Level3:单结点运行时间在三至十天的应用。
Level4:单结点运行时间在十天以上的应用。
为每一个时间尺度等级定义一个权重如下:
Level0: 1;Level2: 2;Level3: 4;Level4: 8
定义3.3:任务综合并行度:P = Levelx∙T∙B即任务时间尺度∙单节点运行时间∙最大加速比。
系统优先满足当前任务池中综合并行度高的任务{Pmax}。
算法流程:
步骤1:用户通过客户端提交任务,服务器接收任务,维护任务列表,进行任务调度。对当前执行的任务进行初始化,生成任务信息表。
步骤2:根据任务属性查询所需数据,计算任务综合并行度。
步骤3:将要启动的任务按照任务并行度从大到小排序:P1 > P2 > P3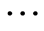 > Pn。
> Pn。
步骤4:优先为综合并行度较大的任务分配计算资源。
步骤5:若当前结点数不能满足该任务的需求,则挂起任务i,并返回任务管理模块,继续为下一任务分配结点,直到所有任务分配完毕。
步骤6:有任务结束之后将节点释放,更新结点信息返回任务管理模块。
步骤7:检查是否能够满足当前存在的挂起等待任务,若能满足分配资源启动任务,否则返回步骤1,接收新任务。
3) 基于线性回归的算法信息自适应维护算法
在上面的算法中的主要参考元,应当基于大量科学计算可视化算法的历史记录信息。这些统计信息决定了算法的效率以及算法所需存储资源的预估和在处理不同规模数据的情况下单结点运行时间的预估值的准确性,我们采用线性回归[11] 的方法,将服务器上的算法运行历史记录有效利用起来,计算出预估值的回归函数,利用回归函数来为下一次该算法的启动预估存储开销和单节点运行时间。
①线性回归模型简介
回归(regression)一词来源于英国著名人类学家和气象学家高尔顿,1885年在其《身高遗传中的平庸回归》一文中提出,用来阐述遗产学上人类身高邮箱平均值靠拢的趋势,现在通常用在科学计算中考察某些因素对我们所关心的某个指标的影响。模型简介如下:
设自变量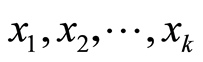 是影响因变量
是影响因变量 的
的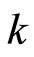 个因素,假定他们之间具有如下线性关系
个因素,假定他们之间具有如下线性关系
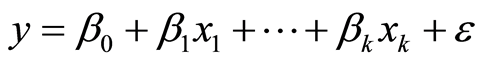 (1)
(1)
其中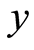 是可观测的随机变量,
是可观测的随机变量, 是未知参数,称为回归系数,
是未知参数,称为回归系数,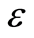 是不可观测的随机误差,且
是不可观测的随机误差,且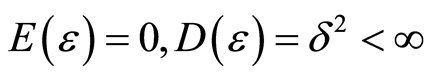 ,其中
,其中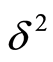 是未知参数,自变量
是未知参数,自变量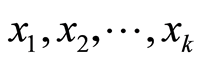 常称为回归因子或预报因子,简称为因子。取因子n组不同的值
常称为回归因子或预报因子,简称为因子。取因子n组不同的值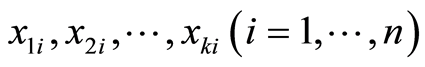 分别进行n次独立实验,得因变量y的n个独立观测值
分别进行n次独立实验,得因变量y的n个独立观测值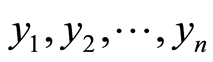 ,称为一个样本,由式(1)有
,称为一个样本,由式(1)有
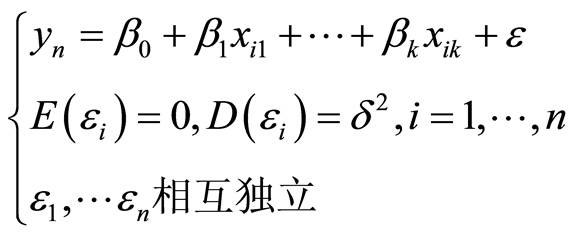 (2)
(2)
在应用中,通常将上式表示为向量和矩阵的形式。记为

则线性回归模型可以表示为(3)
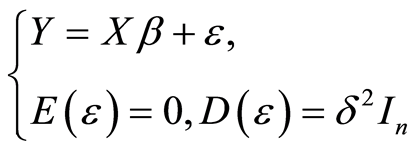 (3)
(3)
我们称多元线性回归模型即式(2)或者式(3)所构成的模型。对于线性回归模型,首先要解决的问题就是求位置参数向量β。根据矩阵的运算可以推出向量β有唯一最小二乘估计:
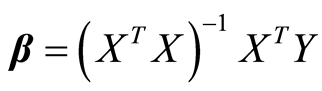 .
.
即可令
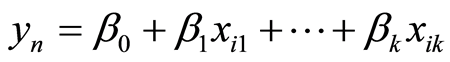 (4)
(4)
在实际应用中,我们通常称式(4)为经验回归方程或回归方程。
②基于线性回归方法的自适应维护算法
在基于任务属性选择的资源分配算法中,为应用程序分配资源时往往需要使用存储空间和该数据规模下的单节点运行时间的预估值,对于一个特定算法历史信息中的存储规模作为影响存储开销的因子X,对应的数据规模下,算法使用的存储开销历史信息作为已知的观测向量Y,假设 ,其中观测误差
,其中观测误差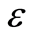 满足
满足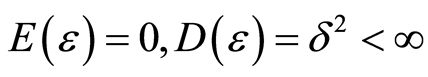 ,每当得到一组x值,即可利用上一小节的计算公式得到
,每当得到一组x值,即可利用上一小节的计算公式得到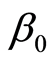 ,
,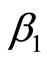 的参数值。历史记录信息越多,则得到的参数值越准确,为下一次算法分配存储空间时的值也越精确。考虑到估计值如果比实际使用的空间小,则可以在计算出的结果上乘以一个大于1的权值
的参数值。历史记录信息越多,则得到的参数值越准确,为下一次算法分配存储空间时的值也越精确。考虑到估计值如果比实际使用的空间小,则可以在计算出的结果上乘以一个大于1的权值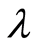 ,确保算法正确完成,这里先暂定为
,确保算法正确完成,这里先暂定为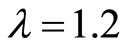 。则实际分配值为
。则实际分配值为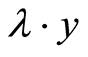 。
。
同理,在某一特定算法对于不同规模的数据在单一节点的处理时间预估上,可以采用同样的方法得到预估函数。
算法每次服务完毕后,其运行信息按照表3的格式添加到该算法的历史信息表中,并根据线性回归模型计算得到新的预估函数,对表2的主要信息中的预估函数进行更新。
3.4. 算法实现与模拟实验结果分析
采用模拟测试程序在Linux系统下进行实验。先根基可视化服务器的实际需求,对“天河-1A”分配给可视化服务器的结点进行分区。采用Slurm官方网站提供的在线配置工具SLURM System Configuration Tool生成配置文件,并拷贝到每个结点,以便对资源进行有效管理。使用yhi-1命令查看分区状态如图4。
1) 基于任务属性选择的资源分配算法实验
为了考察尽量多的情况,我们根据该算法思想,首先编写了模拟程序对算法的有效性进行了测试,测试的算法包括三维云景的可视化,大规模流场可视化,大规模场景绘制,等值面提取等算法,其中算法信息都由实际试验收集得到,测试的任务集以.xml文件形式输入,其属性参数如图5。
任务管理和调度程序根据任务属性查询算法信息,用数据规模作为参数,根据算法时间预估函数计算单节点运行时间预估值,并根据算法最高加速比结点数来计算综合并行度。按照综合并行度从大到小为JobID排序如下:1217,1218,1216,1213,1211,1215,1219。根据排序和任务属性,按照天河-1A系统使用的slurm作业提交格式提交作业,使用yhq命令查看作业运行情况如图6。
其中作业1219由于资源不足不得不使用少于最优结点数的方式运行,否则也可由用户在申请服务时在这种情况下选择挂起等待。如果此时又有任务需要使用normal分区的资源,则必须挂起等待之前的任务运行结束之后释放资源,再启动运行。实验结果表明基于任务属性选择的资源管理算法能够根据可视化任务的不同需求有效为用户分配资源。实际系统安装调试结果也与模拟实验结果基本一致,用户体验的效果也好于直接使用slurm自带的先来先服务加回填机制。
2) 算法自适应维护实验
以时间预估函数为例。针对基于气象预报数据的三维云景可视化算法[]为例。当数据规模采用27 km数据尺度,原始网格数为100万时可以得到渲染用时10.0 s,根据线性回归模型,简单确定时间函数满足T = 0.1∙D,其中D为原始数据规模即多少万个网格数。由此可以推算当采用原始网格数约为380万的9 km数据尺度的数据进行计算时,渲染用时为38 s,实际测试得到的渲染用时为32.1 s,误差为5.9 s,为实测值的18%。将两组数据合并考虑计算时间预估的回归函数得到T = 2.11 + 0.079D,用更新过的函数预估使用3 km尺度的数据约2960万个初始网格数据的运算时间为236.1 s,实际测试得到的数据为240.0 s,

Figure 4. High performance visualization server partition
图4. 高性能并行可视化服务器分区情况
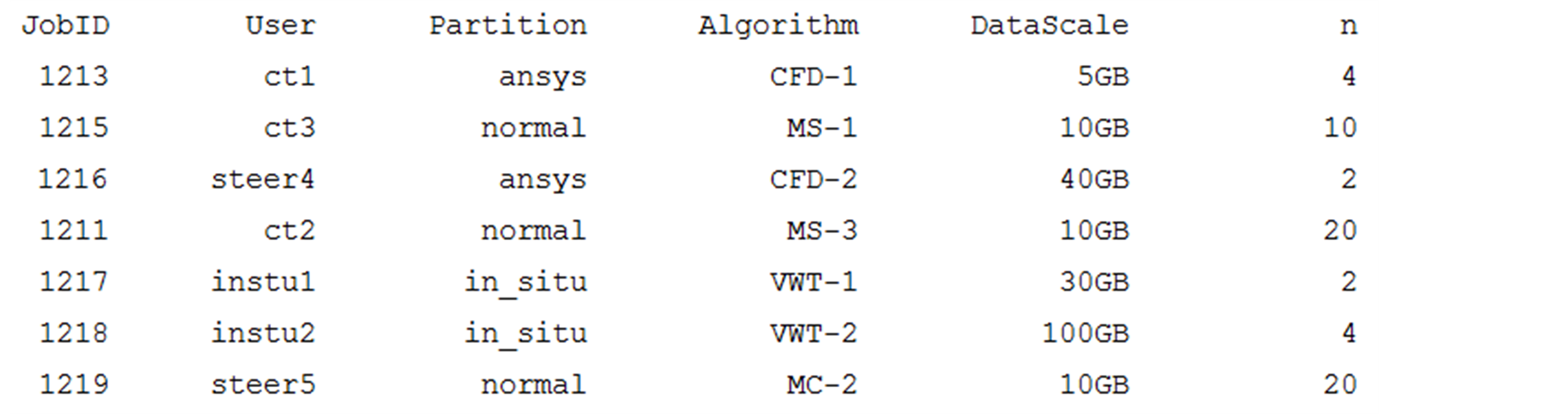
Figure 5. Attribute parameters of the test tasks for the algorithm
图5. 算法模拟测试任务集属性参数

Figure 6. Status of the running tasks
图6. 作业运行状态
误差为实测值的1.6%。单纯就该算法看来,随着系统掌握算法运行历史信息的增加,线性回归模型能够得到越来越准确的时间预估函数从而更好得为调度服务。
4. 总结和展望
本文针对高性能计算系统在为科学计算可视化提供服务时面临的诸多挑战,提出了针对可视化计算任务的高性能可视计算服务器的概念,并重点研究了针对科学计算可视化算法特点的资源管理技术,借鉴之前的研究成果,提出了基于任务属性选择的资源分配算法,提出了综合并行度来衡量算法的并行性,并作为资源分配先后的重要参考。同时提出了基于线性回归方法的算法信息和预估函数的自适应位数算法。资源管理策略,综合考虑了数据规模,运行效率,并行性能和运行时间等多方面因素。但对于实际应用的服务器来说还有一些缺陷,实验作为下一步研究和改进的方案:在存储空间的分配上通过大量实验确定合理的λ值,确保算法正确运行,或者研究出更好的策略,确保不会出现存储空间不足的情况。在资源节点分配上,对于时间尺度权重常量(Leveli)的确定需要通过大量实验进一步确定更加合理值,以确保计算结点分配的有效性。同时可将线性回归方法应用在算法的并行计算的时间预估上,以使用结点数和数据规模作为参数因子,算法运行历史时间作为观测值,计算得到预估运行时间的函数,来作为服务器任务调度的重要参考。
致 谢
感谢李思昆老师的悉心指导和参与讨论和设计的同学们。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(No. 61272009,61202335)。