
1. 引言
四川盆地是一个经历了多期次构造沉积演化,发育了多套烃源岩、多类型储集层以及多变的生储盖组合的叠合盆地,油气分布具有多层系富集、发育多个勘探“黄金带” [1] 的特点。自20世纪60年代以来,先后发现了震旦系威远、石炭系五百梯、二叠系–三叠系普光等大气田,并于近年在川中磨溪–高石梯地区寒武系发现了我国单体规模最大的海相特大型气田——安岳气田 [2] 。
川中地区的油气勘探可追溯到20世纪40年代,在经历“三上威远”后,终于在1964年发现了新中国成立以来的第一个大气田——威远气田。然而,其后的40年里,川中震旦系-寒武系油气勘探始终未取得重大突破,在经历了持续探索阶段(1965~2005年)、风险勘探阶段(2006~2011年),于2012磨溪-高石梯地区寒武系龙王庙组获得高产气流。截至2013年底,磨溪区块龙王庙组气藏探明储量为4404 × 108 m3,可采储量为3082 × 108 m3,含气面积达800 km2,气藏埋深为4600~5000 m,气层平均厚度为36 m,储量丰度为5.5 × 108 m3,开发井单井平均产量为172.57 × 104 m3/d,气藏具有气质好、开发效果好的特点 [3] 。川中地区寒武系龙王庙组气藏的勘探地位也逐渐由“兼探”转向主攻。
四川盆地寒武系发育比较完整,也是天然气开发的重点层位。笔者主要针对川中地区勘探“黄金带”,寒武系形成的安岳气田成藏特征及成控因素进行深入探讨。目前,学者对安岳气田的研究成果较多,提出的理论也较多,但是仍有一定的问题亟待解决,例如高–过成熟烃源岩如何继续大量生烃,古隆起现今构造斜坡及低部位能否规模富集等。笔者以戴金星院士提出的大气田成藏理论为指导,结合安岳气田的实际勘探情况,进一步总结其成藏特征,从成藏必备物质基础、关键成藏条件以及外界辅助因素综合分析大气田的成藏主控因素,以期提高对安岳特大型天然气藏形成规律的认识,为进一步勘探提供重要的理论指导。
2. 区域地质概况
川中地区位于四川盆地的腹部,地理位置上包括南充、遂宁和安岳等地,构造上位于川中古隆中斜平缓带 [4] (图1)。研究区寒武系保存较好,岩相变化具有规律性,自下而上分别发育麦地坪组、筇竹寺组、沧浪铺组、龙王庙组、高台组以及洗象池群 [5] 。下部麦地坪组和筇竹寺组主要为一套巨厚的暗色泥页岩;中部发育的沧浪铺组主要由砂岩及粉砂岩组成,龙王庙组则以灰色白云岩、粉砂质白云岩为主;而上部的高台组和洗象池组岩性组合与中部相似,分别发育红色碎屑岩和灰黑色结晶白云岩。同时,寒武系作为蒸发岩最重要的层位之一,在龙王庙组和高台组均有膏盐岩发育(图2)。
3. 大气田成藏特征
3.1. 低层生气中心
生气中心是指生气强度最大区,同时也是烃源岩厚度以及有机质类型、丰度和成熟度的综合体现。戴金星院士提出,高丰度的气源往往来源于生气中心及其周缘地区,且由于油气运移距离较短,可以最大程度地避免天然气的散失。根据生气中心烃源岩与储集层位的相互关系将其分为3类:① 同层生气中心,烃源层与大气田处于同一地层;② 低层生气中心,烃源层生成的天然气向上运移,聚集在上覆地层;③ 高层生气中心,天然气聚集在下伏地层中。从生储盖组合方式看,上述3类中心又可分别与自生自储型、下生上储型以及上生下储型组合相对应 [6] 。
川中寒武系安岳气田天然气主要源于麦地坪组和筇竹寺组。黄籍中等 [7] 统计下寒武统156块样品总有机碳质量分数(w (TOC))平均为0.97%,杜金虎等 [8] 统计筇竹寺组409个样品的w (TOC)介于0.5%~8.49% (平均为1.95%),有机质丰度高。相关钻井资料例如高科1井筇竹寺组黑色页岩w (TOC)为0.40%~1.58% (平均为0.99%),硫质量分数为0.93%~1.58% (平均为1.26%),两者均较高,适合生烃;高石17井麦地坪组烃源岩分析测试也表明w (TOC)较高,介于0.52%~4.00% (平均为1.68%),为较好烃源岩 [9] 。麦地坪组干酪根碳同位素分布在−36.4‰~−32.0‰之间(平均为−34.3‰) (图3),属于典型的腐泥型烃源岩;筇竹寺组烃源岩的显微组分也显示以腐泥型为主,但上述2套烃源层有机质成熟度均较高,处于高-过成熟阶段。整体情况表明,麦地坪组和筇竹寺组在盆地内具有分布广、厚度大、有机质丰度高的特点,是研究区的生气中心。
作为储集层的龙王庙组在沉积期整体位于水下隆起,处于古隆起高部位——斜坡地带,发育大面积的颗粒滩,储集空间以次生的孔、洞、缝为主,主要的储集类型有粒间(溶)孔、晶间(溶)孔、溶洞、溶蚀缝等 [10] 。由此可看出,麦地坪组与筇竹寺组生烃后,油气可向上运移到龙王庙组的优质储层得到保存,属于低层生气中心。
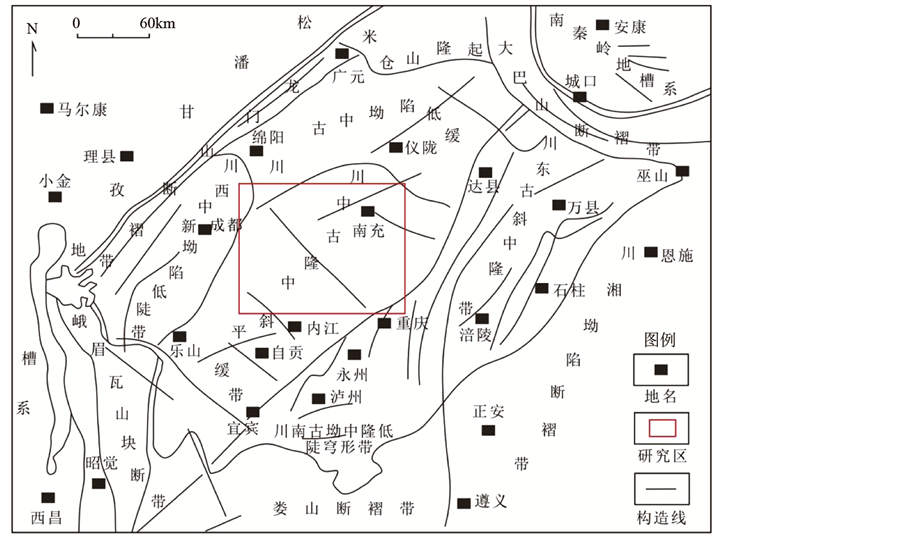
Figure 1. Tectonic location of central Sichuan Basin (according to the reference [4] )
图1. 川中地区构造位置图(据文献 [4] )

Figure 2. The column diagram of Cambrian stratigraphic division in central Sichuan
Basin
图2. 川中地区寒武系地层划分柱状图

Figure 3. The Cambrian geochemical section of Well Gaoshi 17 (according to the reference [3] )
图3. 高石17井寒武系地球化学综合剖面图(据文献 [3] )
3.2. 晚期成藏
晚期成藏对大气田的形成具有重要的作用,甚至优于大油田。从微观上来看,天然气的分子小、质量轻且易扩散 [11] ,因此,天然气形成后是不断向上运移和扩散的,如果在运移的过程中有很多扩散通道,储量会不断减少,甚至消失殆尽,使得大气田的形成更加困难。所以,成藏时间上越晚就会减少天然气的散失,相对于油田的形成来说,晚期成藏显得更为重要。
赵文智等 [12] [13] 提出,主生气期距今越近或者主要生气层位越新,对形成大气田更为有利。宏观上来看,四川盆地发生过多次大的构造运动,具有多旋回性。志留纪末期,川中古隆起定型,在古隆起的顶部地区,由于埋深较浅,热演化程度相对较低,Ro一般小于0.7%,处于未成熟–低成熟阶段,斜坡及凹陷区,Ro达0.9%左右,进入成熟阶段,有机质开始生成液态烃。随后,由于加里东期的抬升作用,烃源岩埋深变浅,生烃基本处于停滞状态。从二叠纪开始,下寒武统烃源岩再次开始生烃,古隆起顶部处于低成熟阶段,而斜坡及凹陷为生油高峰阶段。侏罗纪末,除古隆起顶部小部分区域处于高成熟阶段,盆地其他区域都进入过成熟生干气阶段 [8] (图4)。喜马拉雅期,四川盆地下寒武统烃源岩全部进入生干气阶段。总体看来,古隆起高部位烃源岩的热演化明显滞后于凹陷区,安岳气田的生气高峰在三叠纪,相对于烃源层和储集层要晚,生气层位较新,在一定程度上降低了多旋回性对天然气保存带来的损害。
3.3. 古构造聚气滞后
古构造聚气滞后是指聚气成藏作用发生在古构造运动之后 [14] ,安岳气田就是由该种方式形成的重要

Figure 4. The variation of organic matter maturity on the top and slope of the paleo-uplift in Central Sichuan Basin
图4. 川中古隆起顶部与斜坡凹陷有机质成熟度变化图
实例之一。川中古隆起圈闭位于成气区内,并且能够作为长期接受天然气聚集的有利场所。近年来,随着钻探井位的增加以及地震资料品质的提高,对古隆起的地质结构以及构造演化有了全新的认识。
通过对区域构造分析以及钻井、地震资料的深入研究表明,在四川盆地腹部的德阳-安岳大型克拉通内裂陷主要受张性断裂控制,呈NNW向展布,南北长320 km、东西宽50~300 km。克拉通内裂陷于震旦纪发生活化并于晚震旦世灯影组沉积期开始活动,早寒武世早期活动增强,区域拉张强烈,导致裂陷槽内部和两侧台地差异沉积,并于东侧台地发育高石梯-磨溪的古地貌高地,西侧发育威远-资阳古隆起,构成了川中古隆起的雏形。早寒武世沧浪铺期内裂陷逐渐消亡,与此同时,两侧隆起地貌合并成了一个统一的古隆起,并且规模不断扩大,一直持续到志留纪,古隆起定型 [15] 。之后志留纪末期,加里东运动使得地层抬升剥蚀,而聚气成藏作用主要发生在三叠纪,明显晚于成气区内重大地质构造运动之后,属于古构造聚气滞后型(图5)。
4. 大气田成控因素
大气田的形成并不是某一因素单独促进形成,而是多因素综合影响的产物,对于川中寒武系安岳气田来说,有学者从古裂陷或者古隆起出发,分析大气田的成控因素,也有提出比较综合的观点,例如:四古“古裂陷、古丘滩体、古隆起、古圈闭” [3] [15] 。笔者从大气田的必备物质基础、关键成藏因素以及外界辅助因素共同探讨了安岳气田的成藏条件。

Figure 5. The tectonic evolution of internal fractured depression and palae-uplift of central
Sichuan
Basin
(modified from reference [3] )
图5. 川中内裂陷、古隆起构造演化(据文献 [3] ,略修改)
4.1. 裂陷–隆起系统奠定必备的物质基础
大地构造从宏观上把控大气田的形成,古隆起和古裂陷的形成密不可分,属于一个整体的构造系统,为烃源层和储集层的形成奠定了重要的基础。
上述克拉通内裂陷强烈活动期时,内部沉积了2套厚度较大的优质烃源岩(麦地坪组和筇竹寺组),暗色泥页岩发育,控制了川中寒武系的生烃中心,是烃源岩层形成的重要前提。龙王庙期古隆起的高部位沉积了颗粒白云岩和晶粒白云岩,可以作为油气储层,由于后期加里东运动造成古隆起抬升剥蚀,溶蚀作用改善了储层的物性,发育了龙王庙组的优质储层。所以,古裂陷和古隆起的形成发育互为继承,裂陷-隆起的构造系统为大气田的形成奠定了必备的物质基础。
4.2. 生储盖层在时空上的有机配置是成藏的关键因素
安岳气田的生储盖组合在空间上属于下生上储型,下部巨厚且生烃潜力较好的麦地坪组、筇竹寺组暗色泥页岩与中上部沧浪铺组、高台组2套红色碎屑岩和龙王庙组、洗象池群2套厚层白云岩互夹发育,整体上构成良好的生储盖组合,并且辅以膏盐岩的高效封堵性,使得大气田在空间上具有良好的配置。
在时间上,大气田晚期成藏,于三叠纪到达生气高峰,而其后新生代发生的喜马拉雅运动使得川中古隆起西段发生强烈变形,但是东段高石梯–磨溪构造稳定,也是安岳气田得以保存的重要条件之一。
对于麦地坪组与筇竹寺组的优质烃源岩有机质成熟度均较高的问题,赵文智等 [12] [13] 在2005年提出有机质的“接力生气”模式,认为烃源岩进入“液态窗”规模排烃后,仍有相当数量的液态烃滞留于烃源岩内部,而当该部分尚未排出的分散液态烃再次达到生烃条件后会大量裂解生气,并且可能远远大于第一次干酪根降解形成的天然气。如果用时间线来解释,在凹陷和斜坡地区,麦地坪组与筇竹寺组烃源岩在志留纪末期进入低成熟阶段,开始生成液态烃,但之后由于加里东运动的抬升,使得生烃过程停止,烃源岩内滞留部分液态烃,接着古隆起一直埋深,直到二叠纪开始“接力生烃”,此后,构造稳定,形成大气田。
总体上,只有空间和时间上有机配置才是大气田成藏的关键因素。
4.3. 特殊的古环境有利于大气田的形成
寒武纪的气候变化影响海平面变化,具体表现在早寒武世早期,冰块迅速消融,海平面迅速上升,发生了寒武纪最大的一次海侵,在克拉通内裂陷槽内沉积了范围广、厚度大的麦地坪组和筇竹寺组海相泥质烃源岩。早寒武世中期,发生大规模海退,形成沧浪铺组碎屑滨岸相沉积和三角洲相沉积,可作为油气向上运移储集的通道。早寒武世晚期,龙王庙期发生第2次海侵,形成局限台地相、开阔台地相,发育颗粒滩等优质储层,并且此时海平面较低,海水咸度增加,加上气候干热,沉积物中的胶结物相对匮乏,孔隙得以大量发育,对储集层的形成多起到建设性的成岩作用,同时可形成部分膏盐岩沉积,作为良好的储盖层。中寒武世发生第2次海退,形成了高台组的局限台地相,砂泥坪扩大,膏盐岩继续发育,晚寒武世第3次海侵,形成洗象池群局限台地相,与龙王庙组类似,可以看出,油气运移和保存的场所增加,从而有利于形成大气田 [16] 。
4.4. 讨论
大气田的形成是多因素综合控制的,同样川中地区安岳气田的形成还有一些可能的影响因素,例如膏盐岩和古洋流的影响。
4.4.1. 膏盐岩对油气成藏的影响
膏盐岩层可作为优质的储盖层,从定性角度看,有利于形成异常压力封盖油气;又具有一定的流动性,不仅隆起过程中使周围岩石产生裂缝等作为油气运移通道,盐丘也可以作为油气聚集的场所,有利于大气田的形成;并且当膏盐岩被埋深到一定程度会脱水变成硬石膏,水中富有有机酸,具有一定的溶解作用,从而有利于次生孔隙的发育,改善储层的物性,但是如果硬石膏未能被溶解,堵塞在孔隙中,反而会使物性变差。有学者曾经提出,在蒸发环境中,水体盐度增加可以使生物大量死亡沉积在水底,膏盐岩迅速沉积有利于隔绝有机质,形成烃源层 [17] [18] 。但如果膏盐岩深埋脱酸可能会渗入烃源层对有机质产生腐蚀。所以,关于膏盐岩的形成机理及影响的定性理论较多,还需从定量角度加以佐证。
4.4.2. 古洋流对烃源岩的影响
上升洋流富磷、镁、铁等营养元素,会增加有机质的生产力。已有研究证明,现代洋流也是烃源岩发育的一个重要因素,但是上升洋流并不稳定,有时会变为下降流,对于古洋流的恢复就显得更加困难。虽然有通过古纬度恢复方法拟合烃源岩发育位置与上升洋流出现位置是否相当,但也仅是定性地证明上升洋流可能与烃源岩的发育有关 [19] 。
5. 结论
1) 川中地区寒武系大气田具有低层生气中心,晚期成藏以及古构造聚气滞后的特点,下部麦地坪组和筇竹寺组2套优质烃源岩生烃后向上部龙王庙的优质储层运移和扩散,由于盆地内多期次的构造运动,三叠纪到达生气高峰,聚气成藏时间明显晚于或者层位新于烃源层和储集层,且古隆起高部位区的生烃演化要滞后于凹陷及斜坡区。
2) 裂陷-隆起的构造系统为烃源层和储集层的发育提供良好的先决条件,德阳-安岳克拉通内裂陷与川中古隆起相继发育活动,裂陷槽内沉积麦地坪组与筇竹寺组烃源岩,古隆起高部位发育龙王庙组颗粒滩作为储层,并且加里东运动对古隆起的抬升使得储集层遭受溶蚀,从而进一步改善储集层物性。
3) 安岳大气田不仅在空间上具有良好的生储盖配置,在时间上晚期成藏,有机质得以“接力生烃”,同时避免油气因为构造运动的影响而逸散,从而保证了气田的产量。
4) 寒武纪初期气候干热、冰川消融、海平面上升,共发生3次海侵,分别为早寒武世早期、早寒武世晚期以及晚寒武世,进而控制了筇竹寺组、龙王庙组等沉积相的演化,对大气田的形成起到不可或缺的辅助作用。而关于膏盐岩对大气田的成藏目前还缺乏相关的定量证据,古洋流对于大气田的成藏是否起到明确的控制作用也还需要更多的证据加以佐证。
基金项目
国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05004-001-03)。