1. 引言
我国人口数量日益增加,耕地面积却在不断缩减 [1] [2] ,地少人多,迫使我们不得不增加粮食的产量。影响粮食产量的因素有很多,其中施用化肥是作用速度最快、作用结果最有效的一个增产措施 [3] 。但是长期以来,盲目施肥和过量施肥不仅造成肥料的浪费,肥料利用率降低,而且带来农业面源污染。目前,国外肥料利用率为50%~55%,我国一般只有30%~35% [4] ,其中的氮肥利用率仅25%~35% [5] 。
化肥中的氮素进入土壤后,从一级配比到二级配比之间会有大量的损失,易发生 -N的淋失、NH3挥发以及硝化–反硝化脱氮而导致氮素损失 [6] 。这些过程,导致只有少部分氮素能够在作物需要时迁移至土壤耕作层,供植物吸收利用,从而使得氮素的利用率很低。
-N的淋失、NH3挥发以及硝化–反硝化脱氮而导致氮素损失 [6] 。这些过程,导致只有少部分氮素能够在作物需要时迁移至土壤耕作层,供植物吸收利用,从而使得氮素的利用率很低。
土壤中氮素的形态可以分为两种,一种是可以被植物直接吸收或是很容易经过转化被植物吸收利用的形态,统称为速效氮,包括水溶性有机态氮、水解性有几台氮、交换性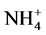 、水溶性
、水溶性 和
和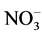 ;另一种是很难或是不能转化为可被植物吸收利用形态的氮,包括非水解性有机态氮、固定态铵和气态氮。各种形态的氮在一定条件下可以相互转化。
;另一种是很难或是不能转化为可被植物吸收利用形态的氮,包括非水解性有机态氮、固定态铵和气态氮。各种形态的氮在一定条件下可以相互转化。
微生物在氮素转化的过程中起着重要的作用。其中包括生物固氮,在固氮酶的催化作用下将N2转化为NH3;硝化作用,硝化细菌在有氧条件下,将NH3或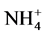 氧化形成硝酸盐;反硝化作用,反硝化细菌在缺氧条件下,将硝酸盐还原成分子态N2或N2O;氨化作用,将有机态氨降解成为NH3等。
氧化形成硝酸盐;反硝化作用,反硝化细菌在缺氧条件下,将硝酸盐还原成分子态N2或N2O;氨化作用,将有机态氨降解成为NH3等。
锰在自然界中广泛存在,是植物生长中的必需微量元素。锰与作物的光合作用、氮、碳和脂类代谢有密切关系。适宜浓度锰处理(Mn2)为大豆高产提供坚实的保障,过高浓度锰(Mn3)处理在不同程度上使酶活性降低,不利于大豆氮代谢 [7] 。较高或较低浓度锰,限制了棉花对氮养分的吸收;而土壤锰在一定浓度范围内能促进棉花根系对氮养分吸收,和地上部对氮养分的积累 [8] 。
微量元素锰也能够影响氮素形态的转化。杨维等 [9] 研究发现高含量锰的水样中发生硝酸盐还原作用使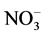 -N向
-N向 -N转化,较低含量的锰对硝化作用有抑制作用。陈建平等 [10] 研究发现在120 cm深度土层中,可滤态锰和氨氮呈显著正相关,和亚硝酸盐氮呈极显著正相关,和硝酸盐氮呈极显著负相关。
-N转化,较低含量的锰对硝化作用有抑制作用。陈建平等 [10] 研究发现在120 cm深度土层中,可滤态锰和氨氮呈显著正相关,和亚硝酸盐氮呈极显著正相关,和硝酸盐氮呈极显著负相关。
本文将研究土壤中微生物和微量元素锰对氮素迁移规律的影响,期望优化化肥养分在土壤中的传递过程,防止养分流失,为保护地土壤合理施肥提供依据。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 试验材料
实验土壤取自四川省彭州市郊区大田,采用标准法随机取样,取样深度为地表以下0~20 cm。土样收集后于实验室自然条件下进行风干、除杂等预处理,然后过2 mm筛,保存实验备用。土壤样品的基本理化性质如表1所示。
2.2. 试验方法
实验所用装置由上、中、下三段相同规格(Φ10 cm × 11 cm)有机玻璃柱连接而成,其中:上、中段玻璃柱无底面,最下段玻璃柱下底面开有均匀小孔,以利于径流水分的顺利排出。
土柱的装填依次由下至上顺序进行,每段填土前在柱底或者段间用纱布隔开,以防止土壤外漏。每段土柱的填土参数由黄壤土的容重(1.4 g/cm3)计算得出:填土高度为10 cm,填土质量为1100 g (中、下段);填土高度4 cm,填土质量为450 g (上段);填土高度1 cm,填土质量为105 g (表层)。其中,表层填土材料为微量元素锰(MnSO4∙H2O)、肥料(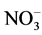 -N态)、微生物菌剂和土壤混合材料,均匀混合后散铺于土柱表层。全部土样装填完毕,向土柱表层不断加蒸馏水,维持水层高度2 cm左右,使土样一直处于淹水状态。最后,将实验装置置于20℃室内通风实验台进行培养,以得到实验样品。土柱做每组做3次平行实验。
-N态)、微生物菌剂和土壤混合材料,均匀混合后散铺于土柱表层。全部土样装填完毕,向土柱表层不断加蒸馏水,维持水层高度2 cm左右,使土样一直处于淹水状态。最后,将实验装置置于20℃室内通风实验台进行培养,以得到实验样品。土柱做每组做3次平行实验。
表层混合材料具体含量配比为:(表2)。
2.3. 数据分析
实验培养共计25天,分别于第5天、第10天、第15天、第20天、第25天进行五次取样,取样深度为表层以下5 cm、15 cm两处。使用碱解扩散法测定不同耕作层深度速效氮的含量。数据采用Microsoft excel 2016软件处理数据,采用origin作图。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 微生物菌剂对速效氮迁移规律的影响
不添加微量元素锰,微生物菌剂对速效氮迁移规律的影响如图1。
单施肥料后0~5天,溶解在水中的氮素随水分的快速入渗,以对流扩散的形式不断从土壤表层向下扩散,施加化肥中氮素形态以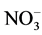 -N为主,
-N为主,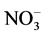 -N很少被土壤胶体吸附,易随水分向下迁移,氮素土壤中各截面处速效氮含量均快速增加。施肥后5~25 d,土壤表面水分已经饱和,化肥中的养分溶解在水中,只能靠浓度梯度推动下的分子扩散作用传递。在此阶段,肥料中的氮素已完全溶解在水中,随着水分向下迁移,导致5 cm处速效氮的含量减少,15 cm处速效氮含量缓缓增加。
-N很少被土壤胶体吸附,易随水分向下迁移,氮素土壤中各截面处速效氮含量均快速增加。施肥后5~25 d,土壤表面水分已经饱和,化肥中的养分溶解在水中,只能靠浓度梯度推动下的分子扩散作用传递。在此阶段,肥料中的氮素已完全溶解在水中,随着水分向下迁移,导致5 cm处速效氮的含量减少,15 cm处速效氮含量缓缓增加。
菌剂和肥料混施后0~10天,氮素逐渐溶解在水中随水分向下迁移,但在5 cm处氮素增加速率满足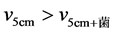 。因为菌剂和肥料混合施入土壤后,增加了土壤中活性微生物的含量,这些菌能发生硝酸盐还原作用使
。因为菌剂和肥料混合施入土壤后,增加了土壤中活性微生物的含量,这些菌能发生硝酸盐还原作用使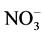 -N向
-N向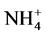 -N转化,而
-N转化,而 -N在迁移过程中易被土壤固定,因此向下迁移的速度减慢。施肥后10~25 d,化肥中的养分完全溶解在水中,只能靠浓度梯度推动下的分子扩散作用传递,同样导致
-N在迁移过程中易被土壤固定,因此向下迁移的速度减慢。施肥后10~25 d,化肥中的养分完全溶解在水中,只能靠浓度梯度推动下的分子扩散作用传递,同样导致

Table 1. The basic physical and chemical properties of the soil sample
表1. 土壤样品基本理化性质

Table 2. The experimental scheme of Soil column
表2. 土柱实验设计方案

Figure 1. Effect on the available N in different section when add microbial agents
图1. 施加微生物菌剂对各截面处速效氮含量的影响
5 cm处速效氮的含量逐渐减少,15 cm处速效氮含量缓缓增加。并且混施条件下5 cm和15 cm处速效氮的含量均显著高于单施肥料,因为混施增加的固氮菌能够将大气和土壤空气中的N2还原为NH3,最终转化为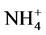 -N,增加了土壤中速效氮的含量。并且第5天后,混施在15 cm处的速效氮含量更高,说明混施不但有利于土壤中氮素的增加,而且有利于氮素的向下迁移。
-N,增加了土壤中速效氮的含量。并且第5天后,混施在15 cm处的速效氮含量更高,说明混施不但有利于土壤中氮素的增加,而且有利于氮素的向下迁移。
3.2. 不同C/Mn比对速效氮迁移规律的影响
添加不同含量的微量元素锰与微生物菌剂对速效氮迁移规律的影响如图2。添加锰元素后,各截面处速效氮含量的趋势基本与空白组一致。施肥后0~5天,氮素以对流扩散的形式随水分的快速向下扩散,氮素土壤中各截面处速效氮含量均快速增加。施肥后5~25 d,在分子扩散作用下,5 cm处速效氮的含量减少,15 cm处速效氮含量缓缓增加。
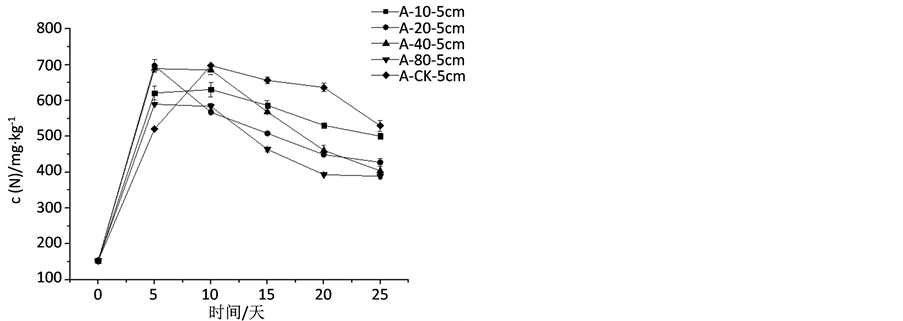
Figure 2. Effect on the available N in different section in different C/Mn conditions
图2. 不同C/Mn比对各截面处速效氮含量的影响
锰元素对于氮素的循环有着密切的关系。在5 cm处,加入锰元素的各组的速效氮含量低于空白组;在15 cm处,加入锰元素的各组的速效氮含量均高于空白组。在好氧环境下,还原性锰离子会参与氨氮的氧化过程,即把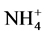 -N氧化成
-N氧化成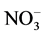 -N或
-N或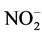 -N。而相比于
-N。而相比于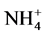 -N在迁移过程中易被土壤固定,氧化形成的
-N在迁移过程中易被土壤固定,氧化形成的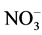 -N则容易向下迁移,导致5 cm处速效氮减少,15 cm处速效氮含量增加。
-N则容易向下迁移,导致5 cm处速效氮减少,15 cm处速效氮含量增加。
当C/Mn = 40时,15 cm处含量最高,说明这种条件下速效氮迁移速率最快,即速效氮的存在以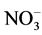 -N为主。在C/Mn = 10和C/Mn = 20的高锰含量条件下,发生硝酸盐还原作用使
-N为主。在C/Mn = 10和C/Mn = 20的高锰含量条件下,发生硝酸盐还原作用使 -N向
-N向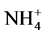 -N转化,
-N转化, -N含量增加,易被土壤固定,因此速效氮迁移速率小于C/Mn = 40。当C/Mn = 80的低锰含量条件下,锰对硝化作用有抑制作用,抑制了
-N含量增加,易被土壤固定,因此速效氮迁移速率小于C/Mn = 40。当C/Mn = 80的低锰含量条件下,锰对硝化作用有抑制作用,抑制了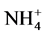 -N向
-N向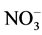 -N的转化,
-N的转化,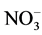 -N含量的减少同样减小了速效氮向下迁移的速率。
-N含量的减少同样减小了速效氮向下迁移的速率。
4. 结论
1) 微生物菌剂和肥料混施的过程中,增加了土壤中能使 -N向
-N向 -N转化的活性微生物,由于
-N转化的活性微生物,由于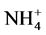 -N在迁移过程中易被土壤固定,因此向下迁移的速度减慢。此外混施增加的固氮菌能够将大气和土壤空气中的N2还原为NH3,最终转化为
-N在迁移过程中易被土壤固定,因此向下迁移的速度减慢。此外混施增加的固氮菌能够将大气和土壤空气中的N2还原为NH3,最终转化为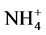 -N,增加了土壤中速效氮的含量。所以微生物菌剂和肥料混施不但有利于土壤中氮素的增加,而且有利于氮素的向下迁移。
-N,增加了土壤中速效氮的含量。所以微生物菌剂和肥料混施不但有利于土壤中氮素的增加,而且有利于氮素的向下迁移。
2) 锰元素对于氮素的循环有着密切的关系。在本实验中,加入锰元素的各组的速效氮含量均远远高于空白组,最佳锰离子浓度为C/Mn = 40。氮元素在好氧环境下,适量浓度的还原性锰离子会参与氨氮的氧化过程,即把 -N氧化成
-N氧化成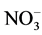 -N或
-N或 -N,则氮素更容易向下迁移。在高锰含量条件下,发生硝酸盐还原作用使
-N,则氮素更容易向下迁移。在高锰含量条件下,发生硝酸盐还原作用使 -N向
-N向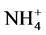 -N转化;低含量的锰对硝化作用有抑制作用减弱
-N转化;低含量的锰对硝化作用有抑制作用减弱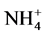 -N向
-N向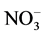 -N转化,结果都会抑制速效氮向下传递。
-N转化,结果都会抑制速效氮向下传递。