1. 引言
量子点是一种三维空间受限的量子结构,量子效应非常明显,如量子尺寸效应,表面效应,库伦阻塞效应等 [1] [2] [3] [4] 。量子点有其特殊的物理性质和物理效应,其荧光稳定性,生物相容性,荧光寿命长等特性可以应用于生物荧光标记,使得量子点在生命科学等领域有广泛的应用。但是在实际应用中很难避免杂质的掺入,掺入的杂质能够影响量子点的能级结构、电学和光学性能 [1] [2] [3] [5] 。因此,在量子点的应用中不得不考虑杂质的影响。
电子被限制在量子点中,可以看成电子被囚禁在一个无限深的势阱中。而GaAs材料导带底具有抛物特征,电子受限于球形GaAs材料可以看成是受到抛物势场限制 [6] 。因此,早期Xiao Z等人 [7] 利用变分方法研究了球形量子点中抛物效应对类氢杂质基态束缚能的影响。之后,Varshni Y P等人 [8] 提出了一个简单的波函数来讨论球形量子点中抛物效应对类氢杂质基态束缚能的影响,获得的结果精度明显比Xiao Z等人的结果好。本文将利用有限差分方法研究此相关问题 [9] [10] [11] [12] 。有限差分法就是一种基于差分原理的数值方法,主要求解思路是:求解偏微分方程时将定解区域离散化,用网格或节点来代替,然后,将每一处的节点的导数用差商公式近似替代,用泰勒级数展开可以求出节点附近的数值,这也就相当于把求解连续的偏微分方程的问题转换成求解离散的代数方程的问题。
有限差分能够给出精度更好的计算结果,并且可以对系统激发态能级加以分析和讨论。本文重点通过有限差分的方法计算球形量子点中类氢杂质基态束缚能,探讨杂质基态束缚能的影响因素。研究结果表明:球形量子点中类氢杂质基态能级和束缚能与量子点的半径和导带抛物势参数有关。对于小半径量子点,束缚能随量子点半径的增加变化明显,当半径增加到一定时,量子点半径的变化对束缚能影响很小,趋于不变的趋势,但是对于大半径的量子点,杂质基态束缚能受抛物势参数的影响很大。
2. 理论推导
在有效质量框架下,球形量子点中受限电子可以看成受到阱宽为R的无限深势阱限制,然而GaAs材料导带底具有类似抛物的特征,可以看成受到抛物势场限制。因此,在GaAs量子点中心受限类氢杂质的系统哈密顿算符可以表示为:
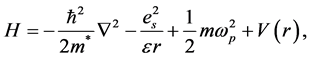 (1)
(1)
其中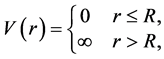
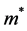 表示有效电子质量;
表示有效电子质量;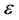 表示介电常数;
表示介电常数; 是谐振子的频率;
是谐振子的频率; 是约化普朗克常数;
是约化普朗克常数;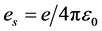 为约化的电子电量,
为约化的电子电量, 为真空介电常数。在球坐标系下,方程(1)可以满足
为真空介电常数。在球坐标系下,方程(1)可以满足
 (2)
(2)
其中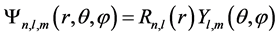 ,
,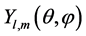 为球谐函数,量子数n,l,m分别表示径向量子数、轨道量子数和磁量子数。由于系统具有旋转对称性,因此系统能级可以通过轨道量子数l进行分类。我们定义
为球谐函数,量子数n,l,m分别表示径向量子数、轨道量子数和磁量子数。由于系统具有旋转对称性,因此系统能级可以通过轨道量子数l进行分类。我们定义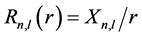 ,并代入方程(1)和方程(2),可以得到
,并代入方程(1)和方程(2),可以得到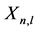 满足如下方程,
满足如下方程,

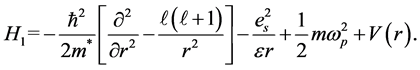 (3)
(3)
在分析过程中,我们引入无量纲参数。令长度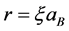 ,
,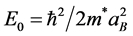 ;
; 为波尔半径,
为波尔半径,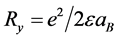 为里德堡能量,
为里德堡能量,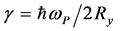 为抛物势场参数。方程(3)可以简化为
为抛物势场参数。方程(3)可以简化为
 (4)
(4)
令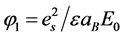 ,
,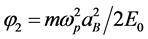 ,
,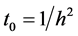 和
和 ,我们可以简化方程(4)为
,我们可以简化方程(4)为
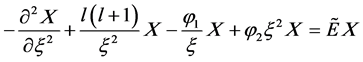 (5)
(5)
利用有限差分法,对受限量子点区域进行离散化,令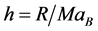 ;
;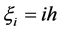 ,将方程(5)离散化:
,将方程(5)离散化:
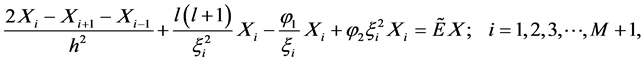 (6)
(6)
考虑到边界束缚条件: ,方程(6)可以矩阵化:
,方程(6)可以矩阵化: ,令
,令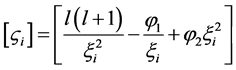 ,我们可以写出
,我们可以写出 的表达式为
的表达式为
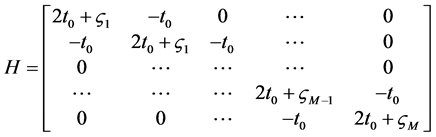 (7)
(7)
其中,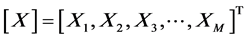 。
。
对方程(7)进行矩阵对角化,可同时得到系统能级和对应的波函数。至此,将求解能量本征方程的问题转化求解矩阵的本征值和本征矢的问题。球形量子点中处于中心的类氢杂质基态束缚能可以定义为 [7] [8] :
 (8)
(8)
其中,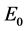 为杂质不存在时系统基态能量,
为杂质不存在时系统基态能量,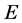 是系统中杂质基态能量。
是系统中杂质基态能量。
3. 结果与讨论
在本文中,我们采用波尔半径和里德堡能量作为系统长度和能量单位。对于GaAs材料而言,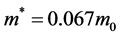 ,
,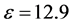 ,因此我们可以计算出
,因此我们可以计算出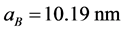 ,
,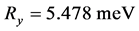 。本文主要讨论杂质的基态束缚能,因此,在计算过程中,我们选择
。本文主要讨论杂质的基态束缚能,因此,在计算过程中,我们选择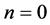 ,
, 和
和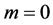 。
。
表1、表2和表3分别给出了γ = 0.2,0.3和0.4时球形量子点中类氢杂质基态束缚能。结果表明和文献 [7] [8] 数值计算结果变化趋势是一致的。由以上三个表可以看出,在γ取值一定时,球形量子点杂质
表1. 当γ = 0.2时球形量子点中类氢杂质基态束缚能
表2. 当γ = 0.3时球形量子点中类氢杂质基态束缚能
表3. 当γ = 0.4时球形量子点中类氢杂质基态束缚能
基态束缚能随着R的增大而减小,有限差分解误差也在越小。在量子点半径R一定时,随着γ的变大,杂质基态束缚能在变大,有限差分解误差是在越小。计算过程当中,我们发现有限差分格点数目越多,计算结果越精确,但是计算时间也更长。这里我们选择M = 1000,从表中可以看出,计算精确均小于1%,计算结果优于文献 [7] 的结果,略不如文献 [8] 中的结果。
图1是球形量子点在γ = 0.0、0.5、1.0、2.0和5.0时的基态束缚能随R的变化示意图。从中可以看出,当γ分别是0.0、0.5、1.0、2.0和5.0时,球形量子点的束缚能都随半径的增大而减小,主要原因在于随着R的增加,量子阱对电子的的限制减弱,导致库伦作用势场减弱,因此束缚能随R的增加是减小的。对于小半径量子点,束缚能随R的增加变化明显,当半径增加到一定时,量子点半径的变化对束缚能影响很小,趋于不变的趋势,主要原因在于量子点半径过大,阱的限制可以忽略不计,此时主要受到抛物势场限制的原因。此外,我们可以看出对于小半径的量子点,杂质基态束缚能随γ的影响不大,但是对于大半径的量子点而言,杂质基态束缚能随γ的影响很大,这是抛物势场限制宽度与量子点阱宽两个特征长度相互竞争的结果。当量子点的半径R很小时,抛物势场限制宽度相对过大,对杂质基态的影响较小,但是当量子点半径很大时,尤其是抛物势场宽度可以和量子点阱宽相比拟时,抛物势场的影响不能够忽略,抛物势场能进一步使得电子受限在一个更小的区域,从而使得库伦势场变大,因此我们可以看到在半径较大时,随着γ的增加束缚能是增加的。
图2是球形量子点在R = 0.2、0.5、1.0、5.0时杂质基态束缚能随γ的变化示意图。从图中可以看出,当R取值太小,比如R = 0.2、0.5、1.0时球形量子点杂质基态束缚能随着γ变化并不明显,尤其在R = 0.2、0.5其束缚能几乎不随γ的变化而变化。当R = 5.0时其束缚能随γ的变化较为明显,并且随γ的增大而增大。为了解释图2中束缚能随γ的变化规律,在图3中,我们分别给出了量子点半径R = 0.2,1.0和5.0时,球形量子点中杂质基态径向位置几率分布示意图,其中γ分别选择0.0,5.0和10.0。从图3中很容易看出:当量子点半径很小时(R = 0.2),此时量子点阱宽限制起决定性作用,球形量子点中杂质基态径向

Figure 1. Curve: The relation between the ground binding energy of the hydrogenic impurity and the radius of spherical quantum dots
图1. 球形量子点中杂质基态束缚能与量子点半径的关系示意图
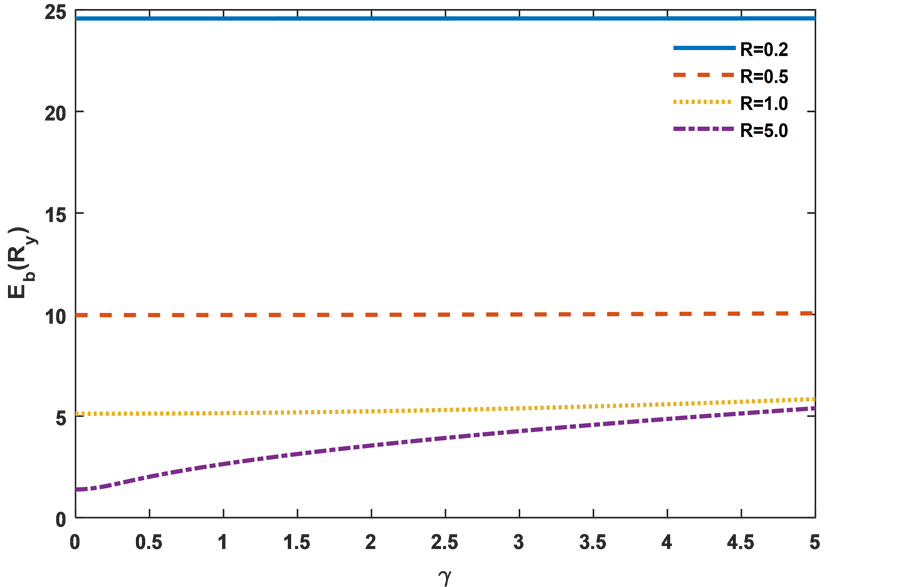
Figure 2. Curve: The relation between the ground binding energy of the hydrogenic impurity and the parabolic potential parameter
图2. 球形量子点中杂质基态束缚能随抛物势参数变化关系示意图
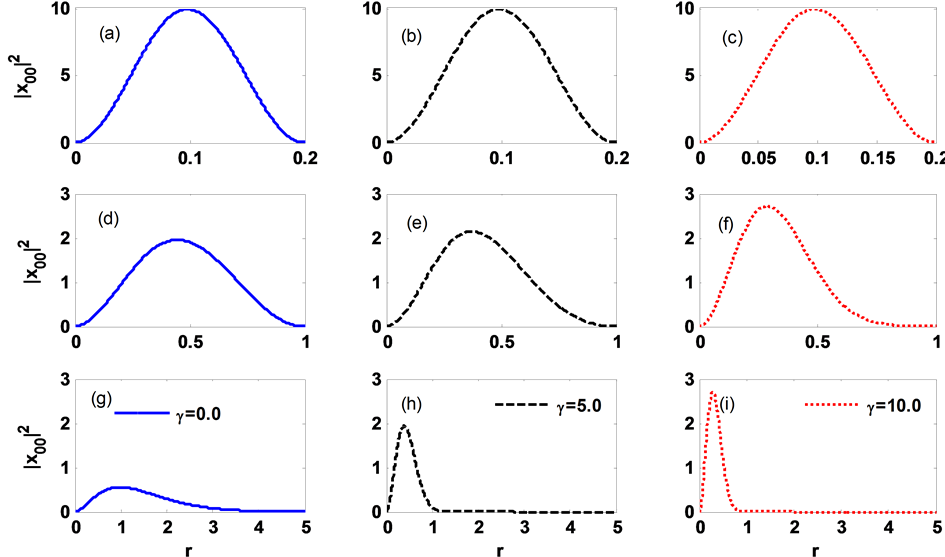
Figure 3. Curve: The ground state radial location probability distribution of hydrogenic impurity in spherical quantum dots with different radius
图3. 不同半径的球形量子点中杂质基态径向位置几率分布示意图
位置几率分布随着γ的变化几乎是不变的(如图3(a)~(c)),即使是取较大的γ值杂质基态束缚能随着γ的变化也是极其不敏感(如图2中R = 0.2);但是当量子点半径较大时(R = 5.0),杂质基态束缚能随γ值的增加在变大,但是随着γ值的增加这个变化趋势在减弱(如图2中R = 5.0)。原因是当量子点半径较大,此时量子点阱宽限制较弱,对电子的束缚较小。一方面,当引入抛物势场后,较小的抛物势场就能够对电子施加一个额外的阱宽限制,随着抛物势场的增加,这种额外的阱宽限制越是明显,电子被限制在一个更小的区域,因此束缚能会变大。另一方面,当抛物势场变得很大时,量子点阱宽效应就可以忽略,此时主要受到抛物势场的限制,电子运动被限制,并向着量子点中心靠近,但是这种趋势随着γ值的增加逐渐趋于缓慢(如图3(g)~(i)),因此,随着γ值逐渐增大,杂质基态束缚能变化逐渐趋于缓慢(如图2所示)。
4. 总结
本文利用有限差分方法研究GaAs球形量子点中心杂质基态束缚能。我们发现量子点尺寸大小和导带底抛物性对杂质基态束缚能有明显的影响。研究结果表明:在γ一定时,GaAs球形量子点中杂质基态束缚能随半径的增大而减小,同时随着半径的增大,其束缚能减小趋势越小,最后达到不变。在量子点半径R一定时,杂质基态束缚能随γ的增大而有所增大,尤其是对半径较大的量子点,势场参数γ的影响较为明显。从球形量子点中杂质基态径向位置几率分布的图形可以看出,在小半径范围内,由于抛物势场限制宽度远大于量子点半径,抛物势场的影响可以忽略,量子点阱宽限制起决定性作用,球形量子点中杂质基态径向位置几率分布几乎不随γ的变化而变化。当量子点半径较大时,量子点阱宽对电子的限制减弱,随着抛物势参数γ变大,几率中心位置明显向量子点中心移动,但是随着抛物势参数γ的增大,这种移动趋势逐渐减小。
基金项目
本文获得基金项目支持:国家自然科学基金(No. 11604289; 6147503),广西自然科学基金(No. 2016 GXNSFBA380017),广西高校科研项目(No. KY2015LX046)。