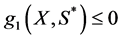1. 引言
传统布局设计研究大多简化成定型组件布局设计,即在布局设计过程中组件本身不产生形变,其本质上只是在系统设计层面上对布局组件的位姿进行调节,而没考虑组件结构因素影响,布局空间不一定是最优设计。如果某个或某几个对布局空间影响较大的组件在布局设计中可变形优化(称可变形组件,如车辆引擎盖下的水箱或油箱等),这种支持形变的布局紧凑度将大大提高,空间利用率得到合理提升。传统求解布局问题的方法有很多如线性规划、二次规划等[1] [2] ,但仅适用于特定问题的求解,且容易陷入局部最优。本文对复杂布局系统进行简化处理,将支持形变的空间布局问题分解为系统层优化和组件层优化,建立双层优化模型表达式,介绍双层模型的循环迭代过程,重点在组件层上对可变形物体建模分析、模型求解、运动分析和实时体积计算,为后续系统层优化提供支持。其流程图如图1所示。
2. 形变布局的双层优化模型
传统布局设计过程中,以各待布物空间位置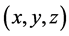 和方向
和方向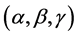 等作为优化指标,除了需要保证待布物体间不发生重叠干涉以及空间利用率外,还需要考虑各种性能约束,如动态特性、惯性、不平衡性、振动、连通性和相邻性等。对布局模型进行分解以达到简化处理,在引入可变形件形状参数S作为参考因素后,将空间布局优化模型分解为系统层和组件层两个层面进行处理,即双层优化,其数学模型为:
等作为优化指标,除了需要保证待布物体间不发生重叠干涉以及空间利用率外,还需要考虑各种性能约束,如动态特性、惯性、不平衡性、振动、连通性和相邻性等。对布局模型进行分解以达到简化处理,在引入可变形件形状参数S作为参考因素后,将空间布局优化模型分解为系统层和组件层两个层面进行处理,即双层优化,其数学模型为:
系统层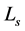
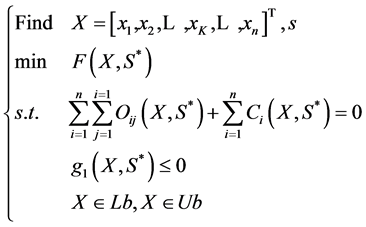
组件层

Figure 1. The flow chart of Bi-level optimized layout design
图1. 双层优化布局设计流程图
 (1)
(1)
式中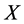 表示由各待布组件的空间位置和方向的矢量,
表示由各待布组件的空间位置和方向的矢量,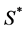 是可变形组件的初始外形参数如面积、体积等,
是可变形组件的初始外形参数如面积、体积等,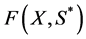 表示由
表示由 以及
以及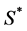 等参考指标决定的整体性能函数如动态特性、惯性、空间利用率等,
等参考指标决定的整体性能函数如动态特性、惯性、空间利用率等,
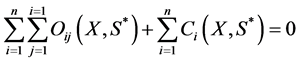 表示由固定件及初始状态下可变形件之间没有干涉重叠,
表示由固定件及初始状态下可变形件之间没有干涉重叠,