1. 引言
图论起源于七桥问题,已经迅速发展到计算机科学,化学,生物学,物理等学科,化学中得到更加广泛的应用。在1985年,Klein和Randić [1] [2] 在研究分子共振结构时发现分子的一个凯库勒结构可以由固定的部分双键来确定,把所需的最少的双键的个数称作这个凯库勒结构的内自由度。Harary和Klein [3] 称其为图的完美匹配的强迫数。Adams [4] 等证明了在最大度为3的二部图中,它的一个完美匹配的强迫数是NP-完全的。Afshani等 [5] 证明了计算最大度为4的二部图的强迫数是NP-完全的。2004年,P. Adams,M. Mahdian和E. Mahmoodian [4] 定义了图G的强迫谱
,即图G的所有完美匹配的强迫数构成的集合。张和平,赵爽等 [6] 提出了强迫多项式的概念。1997年,李学良 [7] 研究了具有反强迫边的六角系统。2007年,Vhukičević和Trinajstić [8] 从匹配强迫的对立面出发,提出图的反强迫数。2015年,H. Hwang,H. Lei,Y. Yeh和H. Zhang [9] 介绍了图的反强迫多项式。2016年,雷洪川,叶永南和张和平 [10] 首次提出完美匹配的反强迫数的概念,并给出了图的反强迫谱。2017年,石玲娟,张和平 [11] [12] 给出了图的最大反强迫数的一个新上界,证明了(4,6)-富勒烯图的最大强迫数等于它的Clar数,最大反强迫数等于它的Fris数。邓凯等 [13] [14] 给出了图G的反强迫谱
的定义,即图G的所有完美匹配的反强迫数构成的集合。2018年,赵爽,张和平 [15] 计算了有强迫边的苯基系统和苯型平行四边形的反强迫多项式。姚海元、王杰彬、韩振云等 [16] [17] 得到了几类梯子图的反强迫谱和Lucas数列、Fibonacci数列之间的一些组合解释。2019年,赵爽,张和平 [18] 计算了
格子图和
格子图的强迫多项式和反强迫多项式。2021年,邓凯等 [19] 研究了芘系统,方格子系统的强迫和反强迫多项式。马聪聪 [20] 研究了C60的一个比较特殊的同分异构体和C70的完美匹配、强迫数和反强迫数,得到了它们的反强迫多项式,以及一些其它富勒烯图的反强迫多项式。王倩倩 [21] 研究了几类特殊图的反强迫多项式。2022年,刘雨童,马聪聪和姚海元 [22] 提出了图的双强迫多项式。刘雨童 [23] 给出了60阶富勒烯图的双强迫多项式。邓凯 [24] 计算了线性亚苯基系统的强迫和反强迫多项式,得到了它们精确的表达式。
本文主要研究几类梯状图的完美匹配与Hamilton圈的关系。
2. 预备知识
图G的完美匹配是指覆盖G中所有顶点的两两不交的边的集合。包含图G的每个顶点的路我们称为G的Hamilton路,类似地,G的Hamilton圈是指包含图G的每个顶点的圈。
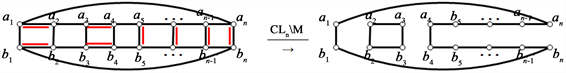
循环梯状图
是由圈
和路
的笛卡尔积
,也可以由梯子图通过添加边
和边
得到,如图1所示。
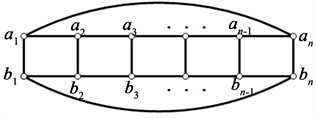
Figure 1. Cyclic ladder graph
图1. 循环梯状图
循环梯状图
中,我们把类似于的
边称为竖直边,类似于
的边称为水平边。设M是循环梯状图
的一个完美匹配,M中类似于
的边称为竖直匹配边,类似于
的边称为水平匹配边。
Möbius梯状图
是通过梯子图
添加边
和
,如图2所示。
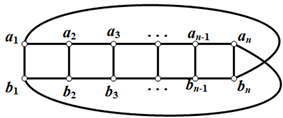
Figure 2. Möbius ladder graph
图2. Möbius梯状图
Möbius梯状图
中,把类似于的
边称为竖直边,类似于
的边称为水平边。设M是循环梯状图
的一个完美匹配,M中类似于
的边称为竖直匹配边,类似于
的边称为水平匹配边。
Hamilton圈是两个特殊完美匹配的不交并。设
是两个集合,A和B的对称差我们定义为
特别地,如果
,则
,即A和B的不交并。
下面给出计算循环梯状图
与Möbius梯状图
完美匹配个数的两个定理。
定理1 [25] 循环梯状图
的完美匹配个数
定理2 [25] Möbius梯状图
的完美匹配个数
定理1和2中,
为递推关系的Lucas数列,初始值
,它的第n项和
。当n为偶数时,循环梯状图
中,多了两个上下交错水平匹配边的完美匹配,在Möbius梯状图
中,这种情况出现在n为奇数。
3. 主要结论
3.1. 循环梯状图
与Hamilton圈
下面给出
的4个完美匹配(图3):
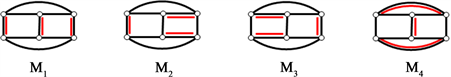
Figure 3. All 4 perfect matchings of cyclic ladder graph
图3. 循环梯状图
的所有4个完美匹配
分别删除各完美匹配的子图(图4):
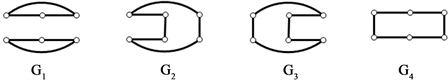
Figure 4. The graphs of deleting each perfect matchings of cyclic ladder graph
图4. 循环梯状图
分别删除各完美匹配的子图
下面给出循环梯状图
完美匹配与Hamilton圈的表示(表1)。

Table 1. Representation by perfect matching of 3 Hamilton-cycles of C L 3
表1.
3个Hamilton圈与完美匹配的表示
下面给出
的9个完美匹配(图5):
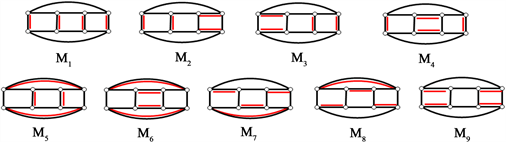
Figure 5. All 9 perfect matchings of cyclic ladder graph
图5. 循环梯状图
的所有9个完美匹配
分别删除各完美匹配的子图(图6):
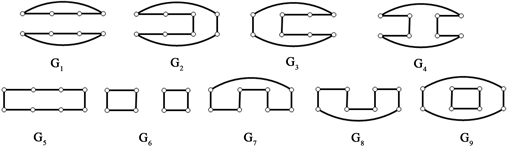
Figure 6. The graphs of deleting each perfect matchings of cyclic ladder graph
图6. 循环梯状图
分别删除各完美匹配的子图
下面给出循环梯状图
完美匹配与Hamilton圈的表示(表2)。

Table 2. Representation by perfect matching of 6 Hamilton cycles of C L 4
表2.
6个Hamilton圈与完美匹配的表示
下面给出
的11个完美匹配(图7):
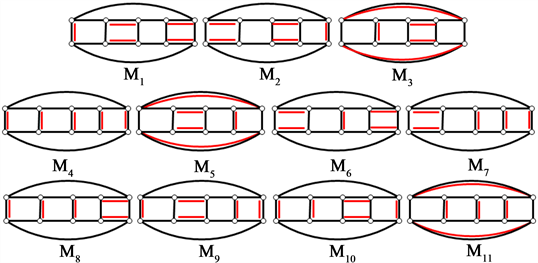
Figure 7. All 11 perfect matchings of cyclic ladder graph
图7. 循环梯状图
的所有11个完美匹配
分别删除各完美匹配的子图(图8):
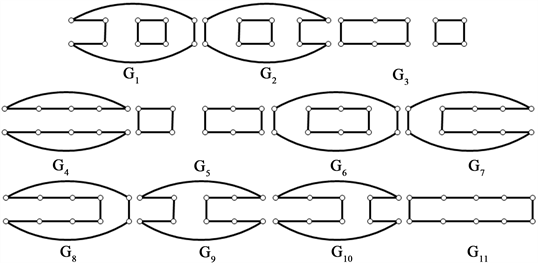
Figure 8. The graphs of deleting each perfect matchings of cyclic ladder graph
图8. 循环梯状图
分别删除各完美匹配的子图
下面给出循环梯状图
完美匹配与Hamilton-圈的表示(表3)。

Table 3. Representation by perfect matching of 5 Hamilton cycles of C L 5
表3.
5个Hamilton圈与完美匹配的表示
下面给出主要结论。
引理1 设M是循环梯状图
的完美匹配,若M含有至少2对水平匹配边,则
不存在Hamilton圈。
证明:首先,我们考虑n为偶数的情况。当n为偶数,我们根据水平匹配边的个数进行分类讨论。设p为M中成对水平匹配边的个数。
1) 当
时,即M中没有水平匹配边或是上下交错出现的水平匹配边。若M中没有水平匹配边,
在
后,存在两个不交的长度为n的偶圈,此时
不存在Hamilton圈;若上下交错出现的水平匹配边,
在
后,存在一个长为2n的Hamilton圈,不存在其它分支,因此
不存在Hamilton圈。
2) 当
时,即M中只含有一对水平匹配边,不妨设
,
在
后,如下图所示,删掉这对水平匹配边之后,顶点
和
之间没有边相连,此时通过外水平边
的路,因此
存在Hamilton圈且是一个长为2n的偶圈。

3) 当
时,即M含有至少2对水平匹配边,首先我们看
时的情况,如下图所示,不妨设
,删掉它的匹配边之后,至少会出现两个分支,且都是偶圈,因此不存在Hamilton圈,当随着成对水平匹配边个数的增加,出现偶分支的个数也随之增加。所以当
时,
不存在Hamilton圈。
综上可得,当n为偶数时,若M含有至少2对水平匹配边,则
不存在Hamilton圈。同理可得,当n为奇数时,引理成立。即证。
定理3 循环梯状图
的Hamilton圈的个数
为
证明:设M是循环梯状图
的任一完美匹配,由引理1及其证明过程可知,若M中含有上下交错水平匹配边(不成对匹配边)与含有一对水平匹配边(其余全是竖直匹配边),则
存在Hamilton圈。因此我们只对这2种情况进行讨论。设所有完美匹配中
有Hamilton圈的个数记作
。
1) 若M中含有上下交错水平匹配边,只有n为偶数时出现此类情况,这样的完美匹配有2个,它们互相平移可以得到。由引理1可知,
存在2个Hamilton圈,即
2) 若M中含有一对水平匹配边(其余全是竖直匹配边),不妨设第一个完美匹配中
,我们通过平移
这对水平匹配边,则可得到只含有一对水平匹配边的所有完美匹配。由引理1可知,
存在n个Hamilton圈。即
综上(1) (2)可得,
3.2. Möbius梯状图
与Hamilton圈
下面给出
的6个完美匹配(图9):
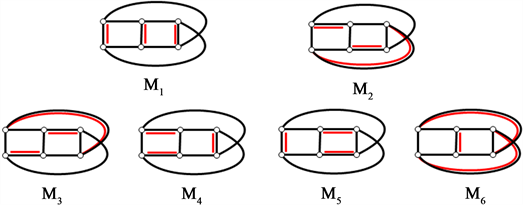
Figure 9. All 6 perfect matchings of Möbius ladder graph
图9. Möbius梯状图
的所有6个完美匹配
分别删除各完美匹配的子图(图10):
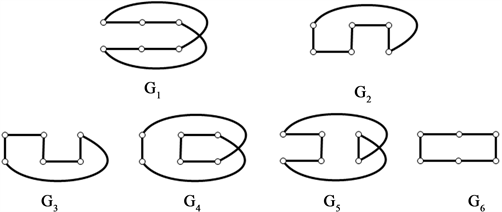
Figure 10. The graphs of deleting each perfect matchings of Möbius ladder graph
图10. Möbius梯状图
分别删除各完美匹配的子图
下面给出Möbius梯状图
完美匹配与Hamilton圈的表示(表4)。

Table 4. Representation by perfect matching of 6 Hamilton-cycles of M L 3
表4.
6个Hamilton-圈与完美匹配的表示
下面给出
的7个完美匹配(图11):
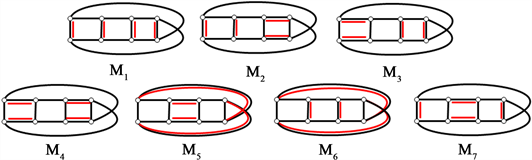
Figure 11. All 7 perfect matchings of Möbius ladder graph
图11. Möbius梯状图
的所有7个完美匹配
分别删除各完美匹配的子图(图12):
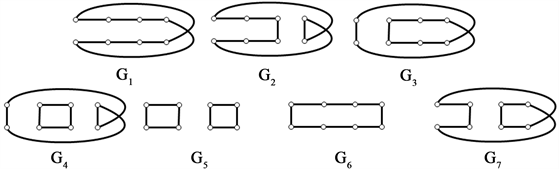
Figure 12. The graphs of deleting each perfect matchings of Möbius ladder graph
图12. Möbius梯状图
分别删除各完美匹配的子图
下面给出 Möbius梯状图
完美匹配与Hamilton-圈的表示(表5)。

Table 5. Representation by perfect matching of 5 Hamilton cycles of M L 4
表5.
5个Hamilton圈与完美匹配的表示
下面给出
的13个完美匹配(图13):
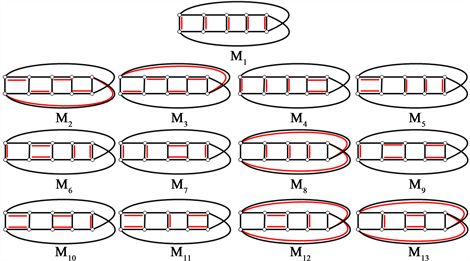
Figure 13. All 13 perfect matchings of Möbius ladder graph
图13. Möbius梯状图
的所有13个完美匹配
分别删除各完美匹配的子图(图14):
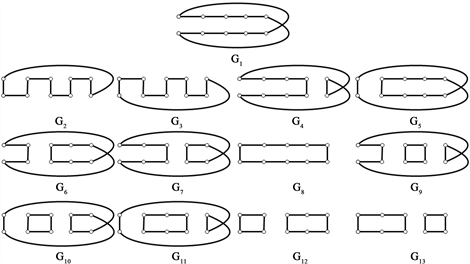
Figure 14. The graphs of deleting each perfect matchings of Möbius ladder graph
图14. Möbius梯状图
分别删除各完美匹配的子图
下面给出Möbius梯状图
完美匹配与Hamilton-圈的表示(表6)。

Table 6. Representation by perfect matching of 8 Hamilton cycles of M L 5
表6.
8个Hamilton圈与完美匹配的表示
引理2 设M是Möbius梯状图
的完美匹配,若M含有至少2对水平匹配边,则
不存在Hamilton圈。
证明:首先,考虑n为偶数的情况。当n为偶数,我们根据水平匹配边的个数进行分类讨论。设p为M中成对水平匹配边的个数。
1) 当
时,即M中没有水平匹配边,如下图所示,
在
后,存在一个长度为2n的偶圈,不存在其它分支,
存在Hamilton圈。
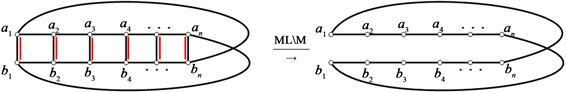
2) 当
时,即M中只含有一对水平匹配边,不妨设
,
在
后,如下图所示,删掉这对水平匹配边之后,顶点
和
之间没有边相连,此时通过外水平边
的路,因此
存在Hamilton圈且是一个长为2n的偶圈。
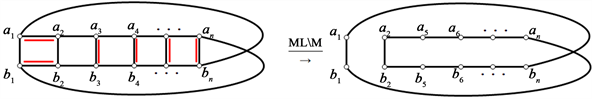
3) 当
时,即M含有至少2对水平匹配边,首先
时的情况,如下图所示,不妨设
,删掉它的匹配边之后,至少会出现两个分支,且都是偶圈,因此不存在Hamilton圈,当随着成对水平匹配边个数的增加,出现偶分支的个数也随之增加。所以当
时,
不存在Hamilton圈。
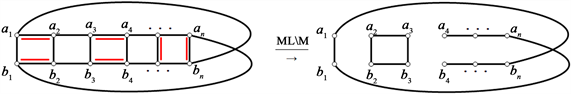
综上可得,当n为偶数时,若M含有至少2对水平匹配边,则
不存在Hamilton圈。同理可得,当n为奇数时,引理成立。即证。
引理3 设M是Möbius梯状图
的完美匹配,若M是全竖直匹配边,则
存在Hamilton圈。
定理4 Möbius梯状图
的Hamilton圈的个数
为
证明:设M是Möbius梯状图
的任一完美匹配,由引理2及其证明过程可知,若M中含有上下交错水平匹配边(不成对匹配边),含有一对水平匹配边(其余全是竖直匹配边)与全竖直匹配边,则
存在Hamilton圈。因此我们只对这3种情况进行讨论。设所有完美匹配中
有Hamilton圈的个数记作
。
1) 若M中含有上下交错水平匹配边,只有n为奇数时出现此类情况,这样的完美匹配有2个,它们互相平移可以得到。由引理2知,
存在2个Hamilton圈,即
2) 若M中含有一对水平匹配边(其余全是竖直匹配边),不妨设第一个完美匹配中
,我们通过平移
这对水平匹配边,则可得到只含有一对水平匹配边的所有完美匹配。由引理2可知,
存在n个Hamilton圈。即
3) 若M中是全竖直匹配边,由引理2可知,
存在1个Hamilton圈。即
综上(1) (2) (3)可得,
定理3与定理4也可以通过定理5证明得到。
定理5 梯子图
的Hamilton圈的个数
为
梯子图
只有唯一的一个Hamilton圈,即
当
与
不含上下交错边的完美匹配,其它完美匹配删除匹配边后是否有Hamilton圈,可由定理5证明。删除一个水平M-交错4-圈后,其子图若只含有竖直匹配边的完美匹配,则原图一定存在Hamilton圈。由定理3和4的证明过程即得。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金资助项目(12161081)。