摘要:
我国快速的经济发展带来了城市化的发展,尤其是在我国的岩溶山区。济南位于我国北部岩溶山区并且以断裂岩溶泉水而出名,其土地利用的空间形态已经被快速的城市化极大的改变了,并且城市的山体也面临变化。本文以济南岩溶山区为研究区域,利用RS和GIS技术,对济南岩溶山地土地利用变化状况进行了较深入的分析研究。济南岩溶山地土地利用类型分为6类,即:耕地,林地,草地,水域,城乡工矿居民用地和未利用地。研究结果表明,近20年来,济南岩溶山地土地利用景观格局发生了明显的变化,济南快速的城市化过程明显地改变了岩溶山地的空间格局。城市化始终对城市区域内的山地有着不利的影响。随着城市化的快速发展,济南岩溶山区诸如山体破坏、水土流失、土壤侵蚀、植被退化等环境问题,显得日益突出;这些环境问题将导致济南岩溶区发生滑坡、泥石流和山体崩塌等自然危害的潜在风险。
Abstract:
Rapid economic development has induced urbanization in China, especially in most of China’s karst geological mountain regions. Jinan City, belonging to the karst geological mountain region of north China and well known for its fractured karst springs, was investigated to assess land use change dynamics by the combined use of satellite remote sensing and geographical information systems (GIS), and to explore the interaction between these changes and the environment. Images were classified into six land-use types: cropland, forestland, grassland, water, urban or built-up land, and barren land. These results show that significant changes in land use occur within the whole karst mountainous region over the study period and cause severe environmental degradation, such as destruction of mountain body, soil and water loss, soil erosion, and degeneration of vegetation. These have resulted in the serious natural hazards in the karst mountainous region of Jinan City, i.e. mining landslide, debris flow, and mountain collapse.
1. 引言
从全球来看,陆地的15%是岩溶区[1] 。我国岩溶区分布广泛,其人类活动历史悠久。随着社会与经济的快速发展,人类的土地利用活动己经对岩溶环境造成了不同程度的负面影响,因此在我国及时开展土地利用/覆被变化对岩溶环境的影响研究是非常必要的[2] -[6] 。但在我国北方城市典型岩溶区的研究方面,相对薄弱;这也是我国北方岩溶研究的形势和任务很重要的一个方面。而近年来在我国北方岩溶区的大量研究,主要侧重于全面总结和归纳我国北方岩溶区地下水环境问题及特征方面[1] [7] [8] ,尽管有学者在北方岩溶塌陷风险方面进行过研究[9] ;但是大多没有考虑北方岩溶区水土资源开发利用的影响,更缺乏对城市化进程中北方城市典型岩溶区环境扰动所带来的生态风险的研究。
济南,是位于我国北方典型岩溶地区的主要城市之一,以泉水而闻名于世,以“泉城”而著称。济南城市岩溶区(泉域)作为泉水的重要水源涵养区,其生态与环境对济南市的可持续发展的重要性尤为突出。随着城市化进程的不断加快,特别是2009年全运会以来,济南城市的规模不断扩大,使得济南岩溶区的土地利用状况发生了深刻的变化,许多山地已经进入城市规划区和建成区范围,进而造成了岩溶山地环境的扰动和破坏,致使山地景观面临巨大的生态危机。济南城市岩溶区的快速城市化发展、大量商品房建设以及房地产的投资以及山地土层极其贫瘠,均使得山区许多泄洪通道被堵塞和建筑物占用,从而极易导致济南市更多的洪涝灾害。因此,济南岩溶区快速的城市化过程,导致了该区域深刻的土地利用变化,不可避免地会诱发基于土地利用变化的生态风险。
本研究以泉城著称的济南泉域岩溶区为研究对象,通过城市化过程中的人类活动过程分析,运用GIS和RS技术,研究济南岩溶山地土地利用/覆被变化、泉域山地破损状况以及地表景观生态和岩溶环境变化,进而分析研究区土地利用变化所带来的生态影响。这对于岩溶区恢复和建设良好的生态环境,实现区域的可持续发展,具有重大的科学理论和实践意义。
2. 研究区概况
济南地处北纬36˚14'36''~36˚53'51'',东经116˚30'47''~117˚22'31'',现辖历下、历城、槐荫、天桥、市中、长清6区,平阴、商河、济阳3县和章丘市。本文的研究范围为济南岩溶山区,主要包括西营、柳埠、锦绣川、仲宫、十六里河、党家庄、崮山、张夏、万德、高而、武家庄、马山、五峰山、归德、港沟等十五个乡镇。研究区具有典型的温带半干旱季风气候,四季分明,年平均温度14℃,年平均降雨量650~700 mm。济南岩溶山地总面积约为2615.6 km2。有关济南岩溶区地下水–地表水系–岩溶区变化相关性的分析,王琳等[10] 在这方面做了较深入的研究。
3. 数据来源与数据处理
本研究主要利用1987年、2000年和2009年遥感影像解译的土地利用现状数据;同时参考1:50,000济南2010年济南地形图以及来自《济南市统计年鉴》、以及济南市政府门户网、济南信息统计网等其他相关资料。数据处理主要是在GIS软件环境下进行。土地利用分类主要有耕地、林地、草地、水域、城乡工矿居民用地和未利用地6类。
数据处理主要应用ArcGIS和Microsoft Excel软件完成。研究区的边界从配准后的土地利用现状图中获得,在ArcGIS软件中对边界进行人工矢量化,利用该多边形文件切割裁剪,然后将1987~2005年adf格式的土地利用现状数据在ArcInfo Workstation中转换为shp格式土地利用数据,并在ArcGIS Desktop平台处理数据拓扑错误并重新计算面积。
4. 结果与讨论
4.1. 济南岩溶山地土地利用变化
1987~2009年间济南南部山区各土地利用类型中耕地一直占主导地位,所占比例接近50%,林地次之,约占25%,未利用地所占的比例最小,不到2%。耕地的面积比例变化最大,呈现总体减少的趋势;城乡工矿居民用地的面积比例变化次之,呈现逐年增长的趋势;水域的面积比例变化最小,基本持平;草地的面积比例变化不大,总趋势是减少的(表1)。
通过对1987~2009年土地利用变化情况可知,济南岩溶区域近20年来,1) 城乡工矿居民用地面积增加。随着社会经济快速发展,城市化步伐加快,城市的改造和扩建加速,城乡工矿用地的面积总体呈现增长趋势,1987~2009年间城乡工矿居民用地主要由耕地转化而来。2) 耕地面积减少。1987、2000和2009年的耕地面积分别占到研究区面积的50.363%、49.063%、35.371%,其中耕地的减少主要转为城乡工矿居民用地,20年间耕地转为城乡工矿居民用地的面积达269.22 km2;耕地其次转为了林地、草地

Table 1. Change of land use area in the karst geological mountainous region of Jinan in 1987-2009 (Unit: km2)
表1. 1987~2009济南岩溶山地土地利用变化(单位:km2)
和水域,说明近年来的退耕还林还草的工作效益明显。3) 草地面积呈总体减少趋势,而水域面积变化不明显。济南岩溶山区草地面积广阔,耕地、城乡工矿居民用地的相互转换较多,但是总的趋势是草地面积减少,1987~2009年间年草地主要是由耕地和城乡工矿居民用地转移而来,面积分别为86.8 km2、21.97 km2,草地主要转化为了耕地、城乡工矿居民用地和林地、面积分别为64.56 km2、3.36 km2和147.356 km2。水域与耕地、城乡工矿居民用地、草地之间的相互转换依次减少,转出和转入量基本持平。4) 林地面积呈现先减少后增加趋势,但面积总量是增加的。1987~2009年林地转为城乡工矿居民用地的面积逐年增加,转为耕地和未利用地的面积则是先减少后增加,说明人们对林地开发占用的同时也加大了造林育林的力度。1987~2009年主要是由草地和耕地转为林地,转移面积先减少后增加,但是面积总量是增加的。5) 未利用地面积增加。未利用地面积增加主要来源于耕地、林地和草地,人们对土地开发利用的同时也造成了大批土地的退化,荒地增多。
4.2. 济南岩溶山地景观变化的生态影响
自然环境的破坏和土地利用空间格局的变化,是最严重的环境质量恶化问题,特别是在脆弱的岩溶山区[2] [11] 。随着城市化的快速发展,环境退化问题显得日益突出。自从我国1978年实行改革开放以来,以泉水著称的济南市近三十年来,经济和社会发展方面取得了显著的成就。农业人口向城市中心地区迁移,并且城市规模仍在不断扩张。人口增长导致了城市中心区的快速发展,由此产生了一系列深刻的环境和社会经济后果。快速的城市化过程已经深刻地转变了城市土地利用的空间格局,济南市的南部山地也面临着同样的变化[12] [13] 。城市化过程一直对南部山区的土地有着不利的影响。随着济南城市化的快速发展,市区山地环境问题,例如山体破坏、水土流失、土壤侵蚀和植被退化等现象日益突出。相反,这些环境问题也会对济南泉水发源地的南部山区的健康和安全,产生不利的影响。
4.2.1. 济南的城市扩张趋势
从1978年我国改革开放以来的五十年中,济南的经济和社会发展有显著的突破,城市总面积已经达到了8117 km2。此外,建筑面积也已从1948年的23.2 km2增加到了2011年的310 km2(图1)。同时,伴随着济南城市化进程,济南岩溶山区大量建设商品房、过度投资房地产,居民住房条件得到改善(图2)。
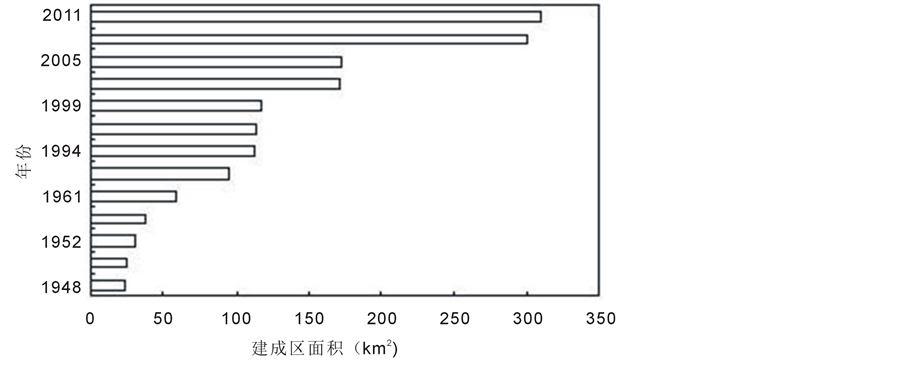
Figure 1. Urban area expansion of Jinan City in the past five decades
图1. 近50年来济南城市面积扩张趋势
4.2.2. 济南岩溶山地城市化发展的不利影响
城市化发展对济南市山地的主要影响就是造成山体的破损。岩溶山体破损的两种主要类型有:一种是由于城市化导致的山体破损(图3(a)),另一种是因采矿活动引起的山体破损(图3(b))。
另一方面,快速的城市化进程也给城市带来了洪涝灾害问题,威胁到了城市的可持续发展。济南城市岩溶区的快速城市化发展、大量商品房建设以及房地产的投资以及山地土层极其贫瘠,均使得山区许多泄洪通道被堵塞和建筑物占用,从而极易导致济南市更多的洪涝灾害(图4)。此外,城市化发展进

Figure 2. Urbanization status of construction and development in the karst mountainous region of Jinan City
图2. 济南岩溶山区城市化建设与发展现状

Figure 3. Urbanization (a) and quarrying and mining activities (b) induced destruction and breakage of hills in Jinan
图3. 济南城市化(a)与采矿活动(b)造成的山体破损情况

Figure 4. Impact of urban expansion on rapid flood passages of karst mountainous region in Jinan
图4. 济南城市化发展对岩溶山区泄洪通道的影响
程中不完善的基础设施,也是引起洪涝灾害不可避免的一个重要因素。
5. 结论
随着济南城市化的快速发展,城市居民的居住条件在不断改善,同时济南岩溶区山地景观也面临着根本性的改变,从而对城市岩溶山地环境造成的扰动也越来越加重,这反过来也对济南市人居环境的健康和安全存在着潜在的生态风险。
项目基金
水利部948项目(201103);山东省高等学校科技计划项目(J12LH04)。