1. 引言
SrTiO3(下简称STO)具有丰富而特殊的特性,STO具有典型的钙钛矿型结构所具备的特点,使其成为了一种具有广泛用途的电子功能陶瓷材料,它的优点有介电常数高、介电损耗低、热稳定性好等。在电子、机械和陶瓷工业上有着广泛地应用,在室温条件下,SrTiO3属于立方晶系,是一种典型的ABO3型钙钛矿复合氧化物。
STO晶体是一种具有宽禁带的半导体材料(带隙为3.25 eV [1] [2] ),光催化活性很好,并具有独特的电磁性质和氧化还原催化活性,被广泛的应用在光催化分解水制氢、光催化降解有机污染物和光化学电池等光催化领域。但是其较大带隙(3.25 eV)导致其只能吸收紫外光,限制了其对太阳光的有效利用。利用其产生的缺陷减小其带隙是使其具有可见光响应的有效手段,在STO中的氧缺陷可以形成亚带隙能级,亚带隙能级可以更多的响应可见光,更多的利用可见光能量,提高其光子利用率。
本文运用第一性原理计算对STO进行模拟计算,在计算过程中我们采用LDA + U [3] 方法对带隙进行修正。在此基础上对其电子结构以及光学性质进行研究。并本着提高其光子利用率为目标,重点研究氧缺陷时SrTiO2.875的光学性质。
2. 模型
本文所有计算由VASP软件包完成[3] [4] 。VASP是基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理量子力学程序。在密度泛函理论框架下,采用平面投影缀加波(projector augmented wave,PAW)处理价电子的相互作用[5] [6] ,电子关联相互作用采用基于广义梯度近似(GGA)的PBE泛函[1] 。本文将Sr的4p65s2,Ti的3p63d24s2,O的2s22p4电子视为价电子来处理。所有计算中选取平面波截断能为400 eV。对原子结构优化的标准为原子间的作用力不大于0.01 eV/Å。
无缺陷的STO晶体属于Pm3m空间群,为立方晶系,实验晶格常数为a = 0.39051 nm。如图1所示,在一个原胞中包含一个Ti原子,一个Sr原子和三个氧原子。其中Ti位于立方原胞中心,Sr位于立方顶点,O位于面心。本文经过原子结构弛豫后得到的晶格常数为a = 0.3905 nm,与试验吻合得比较好。
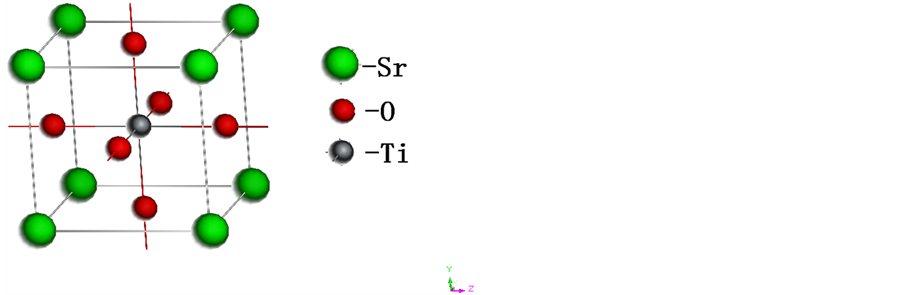
Figure 1. The cell structure of perfect STO
图1. 无缺陷STO单胞结构
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 具有氧缺陷的STO电子结构及光学性质的研究
在LDA + U方法下无缺陷单胞STO的禁带宽度和电子态密度都和实验值吻合很好,由此证明我们采用的LDA + U方法得当。且在STO的缺陷中,氧缺陷是最容易出现和存在的,所以下面我们只着重研究氧缺陷态STO的电子结构和光学特性。
为了减小缺陷带来的分子内部的相互作用,使计算更为准确,我们采取了如图2的2 × 2 × 2超晶胞结构进行研究。
采用2 × 2 × 2的包含40个原子的超晶胞模拟无限大的晶体,通过移去一个氧的办法产生相应的空位,形成SrTiO2.875体系。优化过程中选用paw-pbe赝势方法,截断能取400 eV,进行离子弛豫时,收敛标准为原子间作用力不大于0.01 eV/Å,布里渊区积分采用Monkhorst-pack型的k点网格。采用的高对称K点走向为X→R→M→G→R。
3.1.1. LDA + U方法下SrTiO3电子结构研究
首先用LDA + U方法计算无缺陷SrTiO3 (2 × 2 × 2)总态密度和能带图,如图3所示。
我们选取实验时的晶格常数a = 0.3905 nm,并用LDA + U方法进行计算,近似方式选择Dudarev近似方式。其中J = 0.64,并选取不同的U值对LDA + U方法进行测试[6] [7] 。随着U值得改变,带隙宽度接近实验值,带隙宽度为3.27 eV。与实验3.25 eV符合的比较好。故下面我们以此为基础来进行进一步分析。
下面我们将和具有氧缺陷时的能带结构作比较。
3.1.2. LDA + U方法下SrTiO2.875电子结构研究
我们从STO的电子结构出发,首先计算了有氧缺陷的SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2)态密度及能带图以及分波态密度,见图4-6。
由以上几幅态密度和能带图我们可以分析得到:
1) 与无缺陷的STO相比,氧缺陷的存在很明显的在禁带中出现了缺陷能级,它清楚地表现在能带图和态密度图中的0 eV附近。
2) SrTiO2.875体系的导带底主要是由Ti3d电子占据,价带顶主要由02p电子占据。
3) 由于O空位的存在,Ti的分波态密度在导带底费米能级附近有较大的变化。SrTiO2.875体系中费米能级进入了导带,O空位的存在使STO由绝缘性变成n型半导体。


Figure 2. The supercell structure of 2 × 2 × 2 STO: left is perfect STO model and right is SrTiO2.875 model
图2. 左图是perfect无缺陷模型 右图是氧空位模型

Figure 3. Density of states and band structure figure of perfect 2 × 2 × 2 STO supercell’s figure by LDA + U method
图3. LDA + U方法下SrTiO3 (2 × 2 × 2)的总态密度以及能带

Figure 4. Density of states of defect 2 × 2 × 2 SrTiO2.875 supercell’s figure by LDA + U method
图4. LDA + U方法下SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2)的总态密度

Figure 5. Band structure of defect 2 × 2 × 2 SrTiO2.875 supercell’s figure by LDA + U method
图5. LDA + U方法下SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2)的能带

Figure 6. Partial density of states of O defect STO’s figure by LDA + U method
图6. LDA + U方法下SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2)的分波态密度
4) 费米能级下方的缺陷能级主要由Ti原子的3d态电子占据,同时Ti的4s,3p态也有一定影响;氧原子2p态电子也有少量占据缺陷能级,但是贡献都较小,可以忽略[8] -[12] 。
3.2. LDA + U方法对STO光学性质的研究
3.2.1. LDA + U方法对无缺陷STO光学性质的研究
首先我们用LDA + U方法研究2 × 2 × 2的无缺陷的STO的光学性质,见图7。
图7左边是LDA + U方法研究的STO介电函数图,可以看出:当频率为零或很低时,介电函数的虚部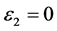 ,静态介电常数
,静态介电常数 ,随着频率增加,介电函数取复数形式(虚部不为0),对于STO来说,能量大于能隙3.27 eV后
,随着频率增加,介电函数取复数形式(虚部不为0),对于STO来说,能量大于能隙3.27 eV后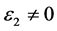 。
。
右图则是吸收系数与光子能量之间的关系曲线。从图可以看出,当光子能量在0~3.27 eV之间时,STO几乎不存在吸收;即STO仅仅只对紫外光有吸收,而对可见光没有吸收利用,其对光子的利用率较低,正是基于这样的结果我们下面引入氧缺陷,目的在于提高STO对于光子的利用率。
3.2.2. LDA + U方法对氧缺陷STO光学性质的研究
下面我们用LDA + U方法研究2 × 2 × 2的具有氧缺陷STO的光学性质,见图8。
可以分析得到:
图8(a):LDA + U方法研究的SrTiO2.875介电函数图,可以看出当频率为零或很低时,介电函数的虚部 ,静态介电常数
,静态介电常数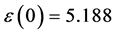 ,随着频率增加,
,随着频率增加,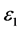 也快速增加,同时在1.47 eV处达到第一个峰值,介电函数取复数形式(虚部不为0),虚部
也快速增加,同时在1.47 eV处达到第一个峰值,介电函数取复数形式(虚部不为0),虚部 代表介质损耗,它是由于分子的电极化过程跟不上外场变化而引起的。对于SrTiO2.875来说,能量大于0.98 eV后
代表介质损耗,它是由于分子的电极化过程跟不上外场变化而引起的。对于SrTiO2.875来说,能量大于0.98 eV后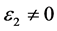 ,SrTiO2.875的吸收边为0.98 eV。介电函数虚部的主要的峰值出现在1.47 eV,3.43 eV,4.91 eV,7.86 eV,9.33 eV和22.11 eV,结合能带图和分波态密度图可以看出,第一个峰和第二个峰是缺陷能级的Ti3d和O2p电子向导带的跃迁,第三主要价带顶电子O2p电子到缺陷能级的跃迁,第四到第五个主要是O2p电子到导带Ti3d的跃迁,最后一个峰主要是Sr4p和O2s电子到缺陷能级的跃迁所致。由图可以看出它在低能量时多出了两个峰值。
,SrTiO2.875的吸收边为0.98 eV。介电函数虚部的主要的峰值出现在1.47 eV,3.43 eV,4.91 eV,7.86 eV,9.33 eV和22.11 eV,结合能带图和分波态密度图可以看出,第一个峰和第二个峰是缺陷能级的Ti3d和O2p电子向导带的跃迁,第三主要价带顶电子O2p电子到缺陷能级的跃迁,第四到第五个主要是O2p电子到导带Ti3d的跃迁,最后一个峰主要是Sr4p和O2s电子到缺陷能级的跃迁所致。由图可以看出它在低能量时多出了两个峰值。
折射率N = n + ik 与ε之间存在 ,
,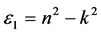 的关系。从图8(a)和图8(b)对应曲线来看,静态折射率为2.27,且在1.47 eV,3.43 eV处的峰值为缺陷所引起的。
的关系。从图8(a)和图8(b)对应曲线来看,静态折射率为2.27,且在1.47 eV,3.43 eV处的峰值为缺陷所引起的。
反射率与折射率n、k之间的关系如下: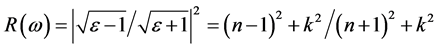 ,从图8(c)可看出,光子能量在0~0.98 eV之间,k接近0,R主要是由静态折射率引起的。R的第一个峰值出现在1.47 eV,R在1.47 eV和3.43 eV出现的峰值对应的n的峰值出现在1.47 eV和3.43 eV,此时反射率增加是缺陷带吸收了部分波长的光引起的[13] -[18] 。
,从图8(c)可看出,光子能量在0~0.98 eV之间,k接近0,R主要是由静态折射率引起的。R的第一个峰值出现在1.47 eV,R在1.47 eV和3.43 eV出现的峰值对应的n的峰值出现在1.47 eV和3.43 eV,此时反射率增加是缺陷带吸收了部分波长的光引起的[13] -[18] 。
为了更好地观察吸收系数,我们将上图d进行放大,见图9。
在吸收谱图9中可以看出该图是吸收系数与光子能量之间的关系曲线。当光子能量在0~0.98 eV之间时,具有氧缺陷的STO几乎不存在吸收;光子能量在0.98~3.93 eV,吸收系数的极大值出现在1.47 eV、3.43 eV附近。1.47 eV,3.43 eV处的峰值为缺陷所引起的。结合图8(a),可以知道这两个吸收峰是由缺陷能级Ti3d和O2p的电子向导带的跃迁引起的,而第三个4.91 eV处的峰是由价带顶O2p电子到缺陷能级的跃迁引起的,在3.93~15.23 eV之间的能量范围时,材料又出现明显的吸收过程,这个过程与无缺陷的分析基本一致,由此可知缺陷能级可以使得STO除了吸收紫外光还能更多的响应可见光,更多的利用可见光,使光子利用率提高。
4. 结论
本工作根据第一性原理运用LDA + U方法研究了STO材料的电子结构以及光学性质,对其能带、态密度、介电函数、折射率、反射率、吸收系数进行了分析。计算并得到了与实验值吻合的结果。并着重研究了具有氧缺陷的STO材料的电子结构和光学特性,发现无缺陷的STO只能响应紫外光,而具有氧缺陷的SrTiO2.875能够响应可见光。得到了氧缺陷的STO可以更多的响应可见光,更多的利用可见光能量,使光子利用率提高的结论。例如在基于STO的光催化分解水制氢、光催化降解有机污染物和光化学电池等光催化领域,可以通过在STO中引入氧缺陷提高光催化分解制氢效率、光催化降解效率及光电转化效率等。

Figure 7. The left figure black and red lines represent our calculated real and imaginary parts of dielectric function ε(ω) respectively of perfect STO (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method. The right figure is the adsorption coefficient I of perfect STO (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method
图7. LDA + U方法下纯STO (2 × 2 × 2)的复介电函数图
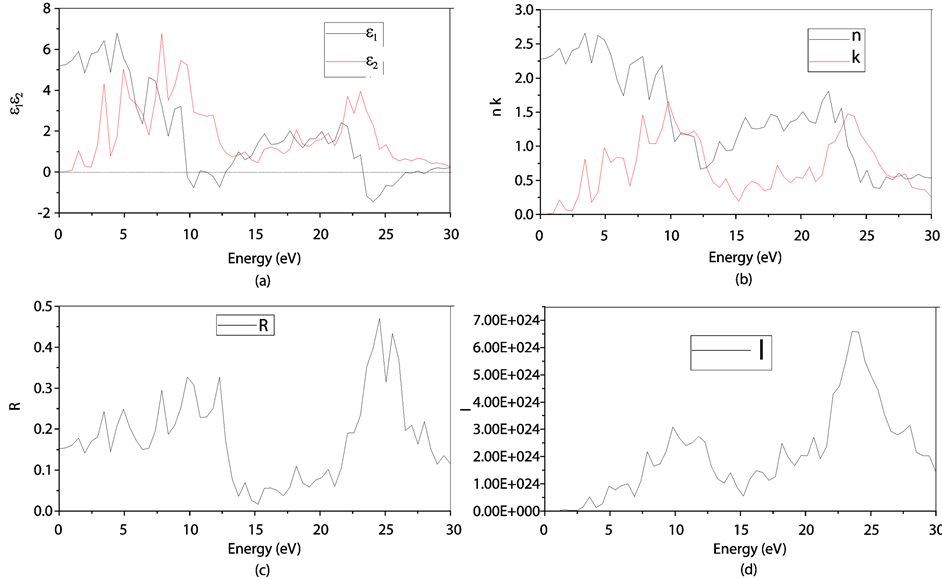
Figure 8. (a): The black and red lines represent our calculated real and imaginary parts of dielectric function ε(ω) respectively of O defect SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method; (b): The black and red lines represent our calculated real and imaginary parts of refractive index respectively of O defect SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method; (c): Optical spectra of the reflectivity R of O defect SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method; (d): Optical spectra of the adsorption coefficient I of O defect SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method
图8. LDA + U方法下SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2)的介电函数(a)、折射率(b)、反射率(c)、吸收系数(d)

Figure 9. Optical spectra of the adsorption coefficient I of O defect SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2) by LDA + U method
图9. LDA + U方法下SrTiO2.875 (2 × 2 × 2)放大后的吸收系数图
致谢
本课题由国家自然科学基金(10804095,61066005,11164032)和教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划(NCET-12-1080)资助。感谢云南大学高性能计算中心的支持。

NOTES
*通讯作者。