Abstract:
Objective: To explore the expression of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood in patients with re-fractory immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and the association between them. Methods: 21 patients with refractory ITP and 21 health controls were studied. The expressions of CD4
+CD25
+ cells and CD4
+CD25
+Foxp3
+ cells were detected by flow cytometry. Statistical analysis was carried out with regard to data in two groups. Results: The ratios of CD4
+CD25
+ cells and CD4
+CD25
+Foxp3
+ cells/ CD4+ cells in patients with refractory ITP decreased significantly compared with those in the con-trol group ((4.52 ± 2.95)% vs (6.33 ± 2.93)%, P < 0.001; (2.30 ± 0.72)% vs (4.17 ± 1.23)%, P < 0.05). There was no correlation between platelet counts and Treg cells. Conclusions: Detection of Treg cells in patients with refractory ITP can induce the hyper auto-reactive activation and more damages of platelets, but they don’t have relations, which may be one reason of refractory ITP.
1. 引言
免疫性血小板减少症(immune thrombocytopenia, ITP)是一种自身免疫性出血性疾病,其发病机制目前主要认为与自身免疫反应有关[1] 。当前ITP的治疗方法包括糖皮质激素、脾切除等均主要针对血小板免疫破坏环节,即通过抑制体液或细胞免疫而发挥疗效。历经皮质激素及脾切除治疗无效的难治性ITP其免疫功能异常紊乱主要与免疫调节异常有关[2] 。调节性T细胞(regulatory T cells, Treg)是具有免疫调节功能的T细胞群体,在维持自身内环境稳定和自身免疫耐受方面起到关键作用。其数量减少、免疫抑制功能减弱可能是导致ITP患者免疫调节机制紊乱的一个重要机制[3] [4] 。本文主要采用流式细胞术检测Treg细胞表达,探讨其在难治性ITP发病机制中的作用。
2. 对象和方法
2.1. 研究对象
选取我院于2011年7月至2012年9月住院诊断明确的难治性ITP患者21例,所有病例均符合难治性ITP诊断标准[5] 。其中男性4例,女性17例,平均年龄53.6 ± 14.3岁,对照组为健康自愿者21例,男性5例,女性16例,平均年龄49.4 ± 12.3岁。
2.2. 试刺与仪器
FITC标记的抗人CD4,APC标记的抗人CD25,PE标记的抗人Foxp3,PerCP标记的抗人CD45,均购自BD公司;流式细胞仪为BD公司BD FACSCanto II。
2.3. Treg细胞检测步骤
1) 取外周血静脉2 ml,肝素抗凝,每个试管内加入20 μl PerCP标记的CD45直标抗体,并分别加入FITC、PE、APC标记的不同抗体l0 μl,再加入100 μl全血,轻轻混匀 室温避光放置30分钟;2) 加入BD公司生产的稀释后的溶红细胞液2 ml,混匀后避光,室温放置20分钟;3) 1500转/分离心5分钟;4) 弃上清,加入0.5 ml破膜剂,充分混匀后避光放置20分钟;5) 用带有BSA的PBS 2 ml洗涤后加入胞浆Foxp3抗体,加入0.5 ml PBS混匀后上机检测。以SSC-A、CD45 PerCP-A射门分析。
2.4. 统计学处理
使用SPSS13.0软件,所有数据均用均数 ± 标准差(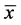 ± s)表示,两组资料之间的比较采用独立样本t检验;两变量之间的相关性分析采用Pearson相关分析;以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
± s)表示,两组资料之间的比较采用独立样本t检验;两变量之间的相关性分析采用Pearson相关分析;以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
3. 结果
3.1. Treg细胞比例
21例难治性ITP患者外周血中CD4+CD25+细胞比例(4.52 ± 2.95)%、Treg占CD4+细胞比例(2.30 ± 0.72)%均明显低于正常人,两者分别为(6.64 ± 1.42)%、(4.17 ± 1.23)%,差异具有统计学意义,详见表1。
3.2. 与血小板的相关性
难治性ITP组中CD4+CD25+细胞比例及Treg细胞比例与血小板计数均没有相关性,P值均 > 0.05,详见表2。
4. 讨论
调节性T细胞属于机体重要的免疫调节细胞,具有免疫应答低下和免疫抑制两大特征,通过“主动”的方式抑制免疫系统对自身和外来抗原的应答,在维持机体免疫耐受和免疫应答稳态方面具有非常重要的作用。它属于CD4+T细胞亚群中一个独立的T细胞亚群,过去常用CD4+CD25+T细胞来标记调节T细胞,但后来研究发现人CD4+CD25+T细胞上的CD25表达数量或荧光强度可分为阴性、弱阳性、强阳性三个等级,呈连续性低表达状态,这种连续性表达使得采用CD4/CD25分子确定Treg细胞比例很困难[6] -[10] 。由于缺乏特异的表面标记物来识别,针对它的研究和应用一直存在障碍。叉头状/螺旋状转录因子p3 (forkhead transcription factor p3, Foxp3)对调节性T细胞的发育和功能至关重要,实验研究发现Foxp3

Table 1. Expression of CD4+CD25+ and Treg in patients with RITP and controls
表1. 难治ITP组与正常对照组CD4+CD25+及Treg细胞比例的比较(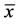 ± s)
± s)
注:与对照组比较比较,*P < 0.001;△P < 0.05。

Table 2. Correlation analysis between CD4+CD25+, Treg and platelet counts in patients with RITP
表2. 难治性ITP组中CD4+CD25+、Treg细胞比例与血小板值相关性比较
基因敲除或突变的小鼠体内CD4+CD25+Treg细胞数量减少,调节功能缺陷,可诱发严重的自身免疫反应;并且Foxp3在自然发生的调节性T细胞表面特异性表达,因此作为Treg细胞内的特征性标记物已得到公认[11] [12] 。
研究表明免疫性血小板减少性紫癜患者体内存在自身反应性T、B淋巴细胞,它们能识别和应答自身抗原,产生抗血小板抗体,导致血小板持续性减少。而调节性T细胞数量减少和功能异常能诱发自身免疫性疾病。一系列临床观察发现ITP患者存在T淋巴细胞亚群及功能异常。国内伏瑞祥首次发现CD4+CD25+T细胞比例在ITP发病患者中与正常人相比较明显减低,经治疗好转后其细胞比例可显著增加[13] 。吕学文通过检测急性特发性血小板减少性紫癜儿童体内调节性T细胞的变化发现,CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞数量减少,并且Foxp3 mRNA表达降低。大量研究还发现经应用糖皮激素或丙种球蛋白等治疗后,调节性T细胞数量增多、免疫抑制功能增强[14] 。
但临床上还存在一类对糖皮质激素、脾切除术以及免疫抑制剂等治疗反应很差或毫无反应,且外周血小板持续减少的难治性ITP患者,这群患者体内调节性T细胞数量的减少是否与疾病存在明显相关性尚未得到确认[15] 。目前关于难治性ITP的诊断标准主要争议在于是否一定要脾切除无效或有效后复发才可以称为难治性ITP,在我国由于实施脾脏切除术者较少,故糖皮质激素治疗无效,或激素依赖,血小板数量不在安全范围内也可归为难治性ITP[16] 。本研究观察了21例健康自愿者、21例难治性ITP患者外周血中调节性T细胞的表达情况,发现难治性ITP患者CD4+CD25+、CD4+CD25+Foxp3+的比例均低于正常对照人群,差异具有统计学意义,说明在难治性ITP患者中,调节T细胞数量和功能明显下降,导致体内自身反应亢进,引起血小板破坏增加。但是Treg细胞下降比例与血小板计数之间却没有相关性,这也可能是造成ITP难治的原因,需要进一步的研究。如何提高难治性血小板减少症患者中T细胞数量进而提高其治疗效果,已经成为目前临床研究的热点,我科长期从事于难治性血小板减少症的临床研究,验证了芪龙颗粒、益髓颗粒等临床有效制剂,希望在以后的研究中能明确中医药治疗难治性ITP效应机制,尤其是对免疫调节功能中的影响,Treg细胞可以作为一个良好的研究靶点。
基金项目
国家重点基础研究发展计划(2013CB531705)。

NOTES
*通讯作者。