摘要:
目的:探讨动脉血气分析在新生儿窒息中诊断中的临床价值。方法:选取2013年10月到2014年4月在我院产科出生的1分钟Apgar ≤ 7分的40例新生儿为窒息组,其中3 < Apgar评分 ≤ 7分者为轻度窒息组,≤3者为重度窒息组,同期选择Apgar评分 ≥ 8分者50例生后无窒息、病情相对稳定的新生儿为对照组,分别于生后1小时内行血气分析,并将与Apgar评分进行相关性分析。结果:窒息组与对照组相比,其PH、PO2、BE、HCO3、乳酸值降低,PCO2则升高,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义,而重度窒息组比轻度窒息组降低(或升高)更明显。结论:动脉血气分析联合Apgar评分有助于新生儿窒息的诊断及客观的反应新生儿缺氧缺血的性质及严重程度,并有利于预测新生儿预后。
Abstract:
Objective: To explore the clinical value of arterial blood gas analysis in the diagnosis of neonatal asphyxia. Method: Choose 40 infants born from October, 2013 to April, 2014 in our hospital with 1 min Apgar score ≤ 7 as asphyxia group, within which 3 < 1 min Apgar score ≤ 7 as mild asphyxia group, Apgar ≤ 3 as severe asphyxia group; at the same time, choose 50 infants with 1 min Apgar score ≥ 8 points, and without symptoms of asphyxia, relatively stable as contrast group. One hour after the infants born, we carry out an analysis of blood gas, and make a relevant analysis with Apgar evaluation. Results: The result comes out that compared with the contrast group, infants in asphyxia group have decreased value in PH, PO2, BE,HCO3 and Lactic acid, and have increased value in PCO2. While, severe asphyxia group has more obvious changes in values. Conclusion: Ar-terial blood gas analysis, together with Apgar evaluation can help to diagnose neonatal asphyxia. What’s more, they can reflect the quality and severity of HIE more objectively, and help to predict the prognosis of neonatal.
1. 引言
新生儿窒息是指由于产前、产时或产后的各种原因使新生儿出生后不能建立正常呼吸,引起缺氧并导致全身多脏器损害,是围产期新生儿死亡和致残的主要原因之一。目前国内对新生儿窒息的诊断方法仍为传统的Apgar评分,此方法敏感性比较高,但特异性低。本文对40例1分钟Apgar ≤ 7分的窒息新生儿的血气分析进行统计学分析,以探讨与其关系,并指导对新生儿窒息的诊断及判断预后。
2. 资料与方法
2.1. 一般资料
选取2013年10月到2014年4月潍坊市人民医院产科出生(已告知家属知情)的足月新生儿90例,男婴58例,女婴32例,按Apgar评分分为三组,各组在孕周、母亲年龄、分娩方式、性别、出生体重等方面比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。
2.2. 方法
2.2.1. Apgar评分
对所有新生儿生后均给予Apgar评分,1分钟Apgar评分 ≥ 8分者为对照组,≤7分 > 3分者为轻度窒息组,≤3者为重度窒息组。
2.2.2. 动脉血气分析及脏器损伤
生后1小时内对窒息组及对照组患儿均行桡动脉血气分析,血气分析仪为GEM3000型,分析项目包括PH值、PCO2(二氧化碳分压)、PO2(氧分压)、Na+、K+、Ca2+、Lac(乳酸)、Hct(红细胞压积)、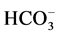 (碳酸氢根)、Be值(碱剩余)、Hb(血红蛋白),同时行血常规、肝肾功、心肌酶、大小便常规、胸片检查等,出现抽搐、前囟紧张、球结膜水肿等症状者行床边头颅彩超或头颅MRI等,以明确有无神经系统等脏器损伤。脏器损伤依据金汉珍等主编的《实用新生儿学》第4版有关诊断标准[1] 。
(碳酸氢根)、Be值(碱剩余)、Hb(血红蛋白),同时行血常规、肝肾功、心肌酶、大小便常规、胸片检查等,出现抽搐、前囟紧张、球结膜水肿等症状者行床边头颅彩超或头颅MRI等,以明确有无神经系统等脏器损伤。脏器损伤依据金汉珍等主编的《实用新生儿学》第4版有关诊断标准[1] 。
2.3. 统计方法
应用SPSS16.0进行统计学分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差( )表示,多组比较采用方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义。
)表示,多组比较采用方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义。
3. 结果
窒息组与对照组相比,重度窒息组与轻度窒息组相比,其PH、PO2、BE、 降低,PCO2、乳酸值则升高,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义。结果见表1,表2。
降低,PCO2、乳酸值则升高,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义。结果见表1,表2。
4. 讨论
1953年美国学者Virginin Apgar提倡用Apgar评分系统对新生儿窒息进行评估,50多年来一直是国际上公认的评价新生儿窒息最简捷使用的方法。但Apgar评分亦有不足之处,近年来不断提出质疑,因为其可受多种因素影响。如早产、某些先天性畸形、产妇分娩前及分娩中使用麻醉、镇静药物、产伤、宫内感染等都可使Apgar降低等。因此不能将其作为诊断窒息的唯一指标。近年来有人提出对窒息的患儿检测血气分析以增加诊断依据。两者结合可增加其准确性[1] 。美国妇产科学会和美国儿科学以及国际权威专著已经将血气分析列在诊断围生期窒息必不可少的指标之一[2] [3] 。
我院对入住新生儿重症监护室(NICU)的新生儿常规行血气分析检查,本研究资料表明,窒息组与对照组相比,其PH、PO2、BE、 降低,PCO2、乳酸值则升高,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义,而重度窒息组(Apgar评分 ≤ 3者)比轻度窒息组(Apgar评分 ≤ 7分 > 3分者)降低(或升高)更明显。证实Apgar评分与血气分析值在一定程度上成负相关,因此,血气分析可及时反应患儿窒息程度的变化,故临床上可以综合Apgar评分及血气分析,对窒息新生儿作出正确、及时的诊治。有研究表明,Apgar评分与血气分析均可作为评估新生儿出生缺氧状态的有价值的指标,尤其以血气分析分析客观性更强[4] 。
降低,PCO2、乳酸值则升高,P < 0.05差异有统计学意义,而重度窒息组(Apgar评分 ≤ 3者)比轻度窒息组(Apgar评分 ≤ 7分 > 3分者)降低(或升高)更明显。证实Apgar评分与血气分析值在一定程度上成负相关,因此,血气分析可及时反应患儿窒息程度的变化,故临床上可以综合Apgar评分及血气分析,对窒息新生儿作出正确、及时的诊治。有研究表明,Apgar评分与血气分析均可作为评估新生儿出生缺氧状态的有价值的指标,尤其以血气分析分析客观性更强[4] 。
窒息可引起器官功能损伤,尤以神经系统为著。分析原因为新生儿窒息可引起缺氧及酸中毒,体内

Table 1. Parameter comparison of three newborn groups’ blood gas analysis
表1. 3组新生儿血气分析各参数比较

Table 2. The relation of asphyxia newborn blood gas analysis and organ damages
表2. 窒息新生儿血气分析与脏器损害的关系
血液重新分配,即肺、肠、肾、肌肉和皮肤等非生命器官血管收缩,血流减少,以保证脑、心和肾上腺等生命器官的血流量。如低氧血症持续存在,可出现无氧酵解,从而使代谢性酸中毒进一步加重,导致生命器官供血减少,发生脑损伤[5] 。新生儿窒息后引起的神经系统表现主要为新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病(HIE),是反应短期预后的一种指标。由于Apgar评分的局限性,致使单纯Apgar评分难以准确反应发生HIE的可能性,而血气分析中PH值与胎儿窒息缺氧、缺血后HIE的关系密切[6] 。我国已将血气分析中PH < 7.0作为新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病的诊断标准[7] 。本研究中表2 PH ≤ 7.2的新生儿发生HIE的几率与PH > 7.20发生HIE的几率有显著差异性,可见,血气分析中PH值越低,引起新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病的几率越大。神经系统对缺氧的易感性较高,最易受损,故临床上应对窒息的新生儿,特别是PH值明显降低的新生儿,应及时复苏治疗,防止神经系统后遗症的发生。治疗上首先应清理呼吸道,保持呼吸道通畅,纠正缺氧,必要时应用CPAP辅助通气甚至机械通气,改善微循环及增加肾血流量,促进乳酸等代谢产物的排泄以达到就诊酸中毒的目的[8] 。
综上所述,血气分析可对不同程度窒息的新生儿进行评估,以了解患儿的缺氧及酸碱平衡情况,并预测新生儿发生多脏器损害的可能性,以及时给予治疗,因此,对生后存在窒息的新生儿应密切监测血气分析。