摘要:
目的:分析376例心脏瓣膜置换手术EuroSCORE预测死亡风险和实际死亡率的变化趋势,评价心脏瓣膜置换手术对重症心脏瓣膜病患者的治疗价值。方法:回顾性分析本中心2007年3月至2012年12月376例心脏瓣膜置换手术的临床资料,对比全组病例欧洲心脏手术危险评估系统(EuroSCORE)平均值与手术死亡率的逐年变化趋势。同时将病例分为两组,符合重症心脏瓣膜病诊断标准的纳入重症组,其余患者纳入普通组。统计两组病例的EuroSCORE分值的平均分、手术死亡率、呼吸机辅助时间及并发症发生率(包括围术期心梗、脑卒中、恶性心律失常、急性肾功能衰竭及呼吸功能不全等),进行组间比较。结果:全部病例EuroSCORE评分平均值从2007年的1.9上升到2012年的5.7,手术死亡率由2007年的3.1%下降至2012年的2.3%。EuroSCORE平均值逐年上升,而手术死亡率略有下降。重症组与普通组EuroSCORE平均值、手术死亡率、并发症率、呼吸机辅助时间等方面比较,差异均有统计学意义(p < 0.05),但是两组手术死亡率均显著低于预测死亡率。结论:随着手术适应症的不断扩大,我院心脏瓣膜病患者EuroSCORE平均分逐年上升,手术死亡率略有下降。EuroSCORE预测死亡风险显著升高的重症心脏瓣膜病患者经过充分的术前准备、手术技术的完善和发展及严密的围术期监护和治疗,可以降低手术死亡率,改善高预测风险患者的预后。
Abstract:
Objective: To analyze the relationship between EuroSCORE high prediction risk and low operation mortality in 376 cases of cardiac valve replacement, and evaluate the value of heart valve re-placement in the treatment of patients with severe heart valve disease. Methods: 376 cases of heart valve replacement form March 2007 to December 2012 were analyzed retrospectively in our center. The yearly change trends of the average value of the European heart operation risk assessment system (EuroSCORE) and operation mortality were contrasted. Then, the patients were divided into two groups. The severe group was divided with severe heart valve disease diagnosis standard, the remaining patients into common group. The average EuroSCORE, operation mortality, ventilation time, and the incidence of complications (including preoperative myocardial infarction, stroke, malignant arrhythmia, acute renal failure and respiratory insufficiency) of the two groups were compared between two groups. Results: The average EuroSCORE increased from 1.9 in 2007 to 5.7 in 2012; operation mortality decreased from 3.1% in 2007 to 2.3% in 2012. The average EuroSCORE was increasing year by year and the operation mortality declined slightly. The differences of the average EuroSCORE, operation mortality, ventilation time, and the incidence of complications between severe group and common group were statistically significant (p < 0.05). But the operation mortality of the two groups of was significantly lower than predicted mortality. Conclusion: When the operation indications continue to expand, the average EuroSCORE of the pa-tients in our hospital with heart valve disease increased year by year, operation mortality declined slightly. After the improvement of sufficient preoperative preparation, operation technology and strict preoperative care and treatment, the operation mortality of patients with severe heart valve disease can reduce. The prognosis of patients with high risk prediction can improve.
1. 引言
欧洲心脏手术风险评估系统(European System for Cardiac Operative Risk Evaluation, EuroSCORE)模型是目前心脏外科领域应用最为广泛的术前风险预测模型。该模型依据来自 8个欧洲国家128个心脏中心1995~1999年的成人心脏外科手术数据建立,最初用于预测心脏手术患者术后30天死亡情况[1] [2] 。随着心脏外科手术及围术期处理技术的不断改进和提高,部分临床研究发现EuroSCORE模型过高地估计了成人心脏手术的死亡率[3] 。本研究回顾性分析了南京医科大学附属淮安第一医院2007年3月至2012年12月376例心脏瓣膜置换手术EuroSCORE高预测风险和实际手术死亡率的变化趋势,评价了瓣膜置换手术对高预测风险重症心脏瓣膜病患者的治疗价值。
2. 资料和方法
2.1. 临床资料
376例行心脏瓣膜置换手术患者中男性171例,女性205例,平均年龄58.2 ± 7.6岁。符合重症心脏瓣膜病诊断标准[4] 的纳入重症组,其余患者纳入普通组。重症组113例,其中男性55例,女性58例,平均年龄58.1 ± 6.9岁;普通组263例,其中男性122例,女性141例,平均年龄60.5 ± 6.8岁。具体手术方式详见表1。
2.2. 方法
采用EuroSCORE官方网站所提供的软件,参照EuroSCORE模型中相关的危险因素和其定义标准,收集纳入患者的相关危险因素、心脏相关危险因素及手术相关危险因素,然后按additive EuroSCORE评分方法对入选患者进行评分并计算预测死亡率[5] 。同时逐年统计全组患者实际手术死亡率、呼吸机辅助时间、并发症发生率(包括围术期心梗、脑卒中、恶性心律失常、急性肾功能衰竭及呼吸功能不全等),对重症组和普通组的上述指标进行组间对比。其中手术死亡率是指手术期间至手术后30 d内因为心脏手术引起死亡患者所占比例。
2.3. 统计学分析
计量资料采用均数 ± 标准差(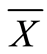 ± s)表示,计数资料采用百分比表示。计量资料统计采用t检验,计数资料统计采用χ2检验,p < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。统计分析应用SPSS软件16.0版(SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA)完成。
± s)表示,计数资料采用百分比表示。计量资料统计采用t检验,计数资料统计采用χ2检验,p < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。统计分析应用SPSS软件16.0版(SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA)完成。
3. 结果
全组患者EuroSCORE评分平均值从2007年的1.9上升到2012年的5.7,手术死亡率由2007年的3.1%下降至2012年的2.3%,具体变化趋势见图1。普通组死亡4例(1.5%);重症组死亡6例(5.3%),高于普通组,差异有统计学意义(p < 0.05)。普通组与重症组实际手术死亡率均低于预测死亡率,差异有统计学意义(p < 0.05),详见表2。
普通组与重症组在手术死亡率、呼吸机辅助时间、并发症发生率、EuroSCORE平均值方面差异均有统计学意义(p < 0.05),详见表3。
4. 讨论
手术风险分层评分系统可以通过个体的手术风险与获益之间的权衡以客观评估手术风险,准确的风险预测对患者的选择、患者的术前教育和知情同意、手术相关危险因素的识别及不同中心手术疗效的比较均有重要意义[6] 。1995~1999年由欧洲多中心的心脏内外科医师前瞻性收集13,302例心脏手术患者的术前和术中危险因素,共同确立了心血管手术危险因素评分系统EuroSCORE。该系统通过对三个种类、合计18项高危因素进行量化,对每个危险因素赋予分值,术后院内死亡影响越大的危险因素被赋予的分值越高。每一个患者首先收集该患者所具备的EuroSCORE危险因素, 将患者全部危险因素评分累加,即得出该患者风险评分。EuroSCORE计算简单,利用其官方网站提供的软件可方便地计算出Logistic评分,因此得到了快速的推广。

Table 1. 376 Heart valvular replacement cases report
表1. 376例心脏瓣膜置换病例手术资料

Table 2. Operative mortality rate comparing predicative mortality rate
表2. 手术死亡率对比预测死亡率

Table 3. Comparison of normal group and surgical critical care
表3. 普通组与重症组相关资料对比
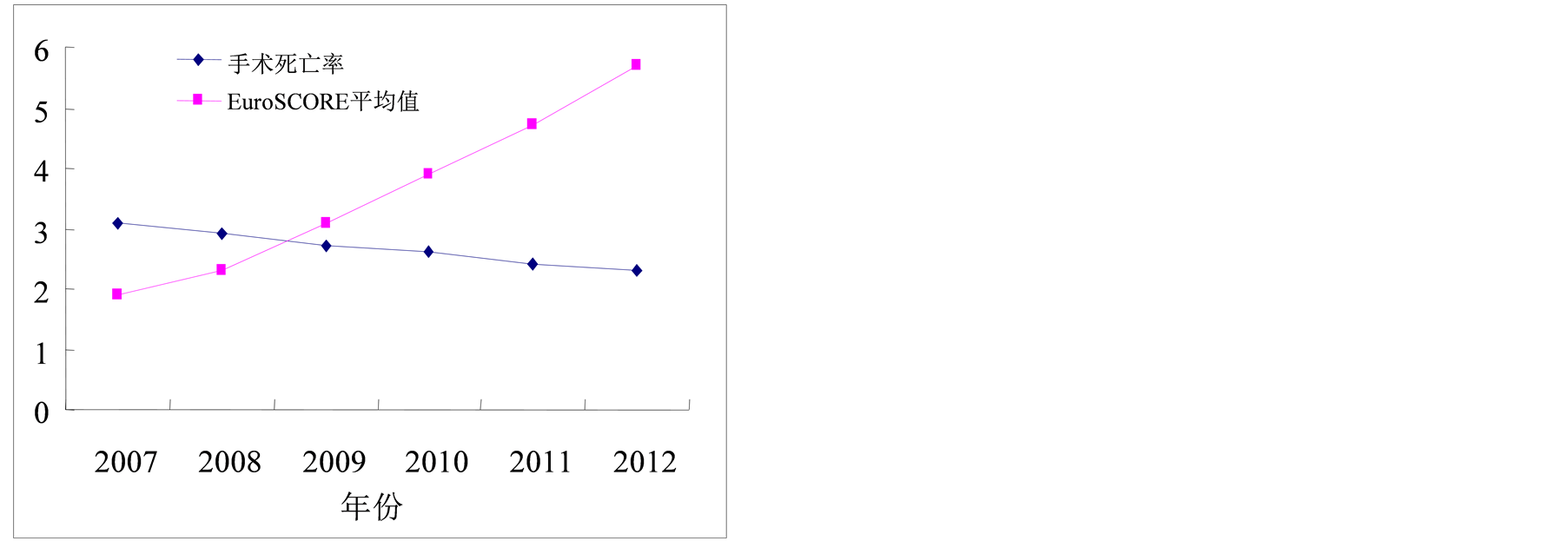
Figure 1. Variation tendency of EuroSCORE data and operative mortality rate
图1. EuroSCORE评分与手术死亡率逐年变化趋势
本研究结果显示,2007年至2012年期间我院心脏瓣膜置换手术EuroSCORE评分逐年增长(1.9到5.7),全组患者预测死亡率均高于实际手术死亡率,差异有统计学意义。EuroSCORE评分增长及预测死亡风险较高原因主要为以下几点:1) 我国已经开始步入老龄化社会,高龄患者的数量上升迅速,冠心病、高血压、慢性阻塞性肺病以及外周血管病等伴随疾病增多。2) 随着我院心脏外科的快速发展,重症瓣膜病患者逐年增加,多数重症患者左心功能较差,射血分数(EF) < 0.5,左室明显增大,左心功能低下的部分患者术前就需应用呼吸机辅助呼吸。目前认为左心室舒张末期内径(LVEDD) > 70 mm的巨大左室是影响心脏瓣膜手术疗效的高危因素之一[7] 。3) 较大比例的心脏瓣膜病患者合并心律失常、肺动脉高压。4) 一定比例的重症瓣膜病患者术前合并肝肾功能不全、冠心病、不稳定性心绞痛。
不同国家的多项研究均显示,心脏瓣膜手术术前预测风险在不断增加,然而手术死亡率却在不断下降。本组病例分析结果显示,2007年至2012年间尽管EuroSCORE评分增加3倍,然而手术死亡率却略有降低,普通组与重症组实际死亡率均低于预测死亡率,差异有统计学意义。EuroSCORE预测的高风险与低手术死亡率之间的矛盾可能与以下几点有关:1) EuroSCORE数据库预测系统是基于1995~1999年欧洲心脏手术病例数据而建立的,而最近10年心脏瓣膜手术技术及相关器械的不断进步和完善,娴熟的手术操作及麻醉技术的快速发展,导致EuroSCORE系统过高的评价了心脏瓣膜手术风险。2) 先进的血液超滤净化技术、连续肾脏替代治疗、IABP及ECMO的应用使高龄、合并有巨大左室、小左室、冠心病、严重肾功能损害的病例可以安全的度过围手术期、降低了手术死亡率[8] 。3) 心脏瓣膜病相关病理生理基础理论研究的不断深入,也可以更好的指导临床治疗。
文献报道,我国重症心脏瓣膜病的病死率为9%~14% [9] 。本组病例中,虽然重症组手术死亡率、呼吸机辅助时间、并发症发生率均高于普通组,但是重症组手术死亡率明显低于EuroSCORE预测死亡率,也显著低于文献报道的病死率。可以认为,对于重症心脏瓣膜病患者,正确的评估病情、选择合适的手术方式、良好的心肌保护及严谨的围手术期处理可以降低手术死亡率,改善高预测风险患者的预后。

NOTES
*通讯作者。