1. 引言
除了在大暴雨时有一小段时间内路基处于饱和状态外,路基和道基在大部分时间里是处于非饱和状态的[1] [2] 。道路土基的土是土壤的一种特殊形式,具有高压实特点,压实度在90%到98%之前,大部分时间处于非饱和状态。它主要由土颗粒骨架、水及气体三相体(有人把水膜作为第四相而称为四相体)组成[3] 。由于基质吸力的影响,使非饱和土的物理力学特性变得十分复杂[4] 。道基土被道面覆盖,并且与土跑道和平地区的土壤相连接。在外界环境的影响下,其含水量产生迁移,改变初始路基含水量,使土壤工程性质发生改变。随着中西部地区经济发展,高等级公路和飞机场发展迅速,使得越来越多公路和机场穿越黄土覆盖地区,因此,黄土成为这些地区主要路(道)基材料。
地下水对道路基础的影响,其本质是非平衡基质势与毛细效应引起水分迁移后土体强度发生了弱化[5] 。因道路土基大都属于非饱和土,土中基质吸力使道基中存在毛细作用,毛细水源源不断的浸润路基,增加了路基含水量,尤其地下水位上升,缩短了毛细作用路径,加快了毛细作用对路基土水的补给。含水量的增加将降低道路土基强度,给道基带来危害[6] [7] 。因此,了解高压实条件下土壤非饱和水运动规律是有效分析和治理道路土基病害的根据。
2. 压实度对土水特征曲线的影响
驱动非饱和流的动力是土水势梯度[8] ,毛细运动时非饱和流的一种特殊形式,毛细水的上升高度即为此高度处的重力势与基质势的平衡高度[9] 。基质势是由土壤基质对水分的吸附作用引起的,通常用基质吸力来表征。土壤水的基质势或基质吸力随土壤含水量而变化,其关系曲线称为土壤的土水特征曲线,一般由试验得出。
2.1. 试验方法
解析形式的水分特征曲线经验公式目前已得到广泛的应用[10] [11] ,按照其数学形式,描述水分特征曲线的经验公式可以分成4类[11] ,即指数型、幂函数型、多项式型和误差函数型。
目前,测量非饱和土壤土水特征曲线的主要方法有三种,负压计法、压力膜仪法和离心机法[4] [12] 。负压计法操作简单,成本较低,但测试精度和范围较小;压力膜仪和离心机法测试成本较大,但测试精度很高。文献[13] 和文献[14] 通过离心机法测试土壤在不同容重状态下土壤特征曲线的变化规律,证明密实程度对土水特征曲线有很大的影响力。
目前的方法主要有对经典模型参数进行干密度的相关性分析,得出拟合公式[14] [15] ;以及通过两条已知初始孔隙比的土–水特征曲线为基准,预测具有任意初始孔隙比土体的土–水特征曲线[16] [17] 。
滤纸法测量土壤基质吸力具有成本低,精度高和操作简单等特点[18] ,本次试验基于滤纸法来量测非饱和压实黄土的基质吸力。操作图见图1。
试验使用的土壤是西安市灞桥区白鹿塬脚下的黄土(E108˚59’; N34˚10’)。根据《公路工程土工试验规程》要求,采用联合液塑限仪、烘箱和重型击实法进行了相关指标的测定,测定结果如表1所示。
试样是按设计的含水率计算所需的加水量,将无气水均匀地喷洒在风干土样中,充分拌合,配置成不同水分状态的散状土样密封在多层塑料袋中,在恒温恒湿条件下放置不少于2d,以便土中水分充分运移、混合均匀,然后按照设计的干密度将散状土料压密而成的。试验所用滤纸采用杭州新华造纸厂的“双圈”牌No.203型滤纸,该滤纸的主要技术指标如下:直径为70 mm;灰分为0.000035 g/张,占质量百分比0.01%;滤速为慢速。其率定方程为[18] :
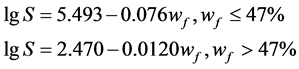 (1)
(1)
试验时,先将烘干的滤纸放入称量盒内,一次放3张,中间的一张滤纸用于量测吸力,另外两张滤纸主要用于保护中间滤纸不受来自土的污染。为了保证土样和滤纸的充分接触,将制备好的土样以及完成剪切过程的土样放在滤纸上面,土样放好后立即盖好盒盖并用透明胶带将称量盒密封,然后将密封好的称量盒放入恒温器内等待平衡。只要平衡期间的温度变化保持很小,滤纸法的结果基本上不受周围温度的影响。为了保证滤纸和土样之间的水量迁移达到平衡,平衡的时间均不少于10 d(平衡10 d后滤纸的含水率基本稳定)[18] [19] 。平衡期间终了时,倒出土样,用镊子取出中间的那张滤纸称其质量。为了减少滤纸与周围大气接触而发生水分变化,这一过程均尽量在30 s内完成了。根据滤纸的干质量和湿质量之差,便可计算出滤纸的平衡含水率。根据滤纸的平衡含水率,可从率定方程求得平衡吸力值。
2.2. 结果分析
试验时对压实度为93%、95%和98%,即干密度为1.767、1.801和1.862 g/cm3的土样进行测试,部分测试结果如表2所示。对含水率小于12%的部分才用插值得到。
从表2可以看出,基质吸力随含水量的变化是非常显著的,随密度的变化也比较明显,因此,基质吸力的确定应该同时考虑含水量和密度两种因素。对于密度一定的土体,国内外学者已经给出很多拟合公式来表述基质吸力随含水量的变化规律[12] ,这些公式基本上是针对特定的土壤得到的,并不是普遍适用的。由于土质和密度的区别,采用这些公式拟合本文测试结果效果很差。为了探讨密度一定的压实黄

Figure 1. Measurement of soil water characteristic curve
图1. 测量土水特征曲线

Table 1. The soil properties
表1. 土壤性质

Table 2. The volume of the moisture content corresponding to the suction of the soil under different compaction condition
表2. 不同压实条件下土壤的吸力值对应的体积含水率
土土基质吸力随含水量的变化规律,对干密度分别为1.767、1.801和1.862 g/cm3西安黄土的测试结果进行了拟合分析[20] ,得到基质吸力的计算公式形式如式(2)所示。三种密度的拟合结果如式(3)、(4)和(5)所示;拟合曲线如图2所示。
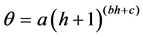 (2)
(2)
式中:θ——体积含水率;h——基质吸力;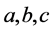 ——拟合参数。
——拟合参数。
(1) 压实度为93%时:
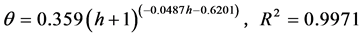 (3)
(3)
(2) 压实度为95%时
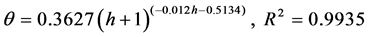 (4)
(4)
(3) 压实度为98%时:
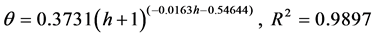 (5)
(5)
3. 压实度对非饱和土导水能力的影响
由于非饱和土水是通过其占据的孔隙空间而发生流动的,所以在流动中水占有的孔隙空间是影响渗
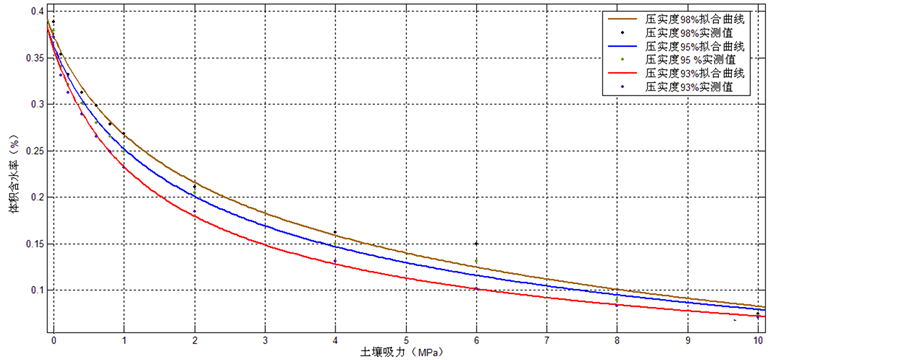
Figure 2. Soil water characteristic curves under different compaction conditions
图2. 不同压实条件下的土水特征曲线
透系数的一个重要因素,即非饱和土渗透系数不是常数,它随含水率变化而变化。因此,常把非饱和土渗透系数表达为饱和度或体积含水率的单值函数[21] 。目前,国内外学者已经给出很多数学模型[10] -[22] 。
3.1. 试验方法
由于非饱和土水是通过其占据的孔隙空间而发生流动的,所以在流动中水占有的孔隙空间是影响渗透系数的一个重要因素,即非饱和土渗透系数不是常数,它随含水率变化而变化。因此,常把非饱和土渗透系数表达为饱和度或体积含水率的单值函数[21] 。目前,国内外学者已经给出很多数学模型[10] -[22] 。
土基的土壤,由于压实导致了土壤孔隙结构的改变。因此,要想正确认识压实土壤的水分迁移规律,就有必要分析压实黄土的非饱和导水率。传统的测量方法有:(1) 根据土壤水分的再分布过程推求土壤的导水参数;(2) 水平土柱法测定土壤水分扩散率D(θ);由水分特征曲线推求导水率K(θ);(3) 利用水分特征曲线,根据垂直土柱蒸发的实测水分动态过程计算土壤的导水参数;(4) 瞬时剖面法测定导水率K(θ)。这些方法需要消耗大量的时间,而且测量精度较低。本文采用水平入渗法,水平入渗法是非稳定流法,最早由Bruce和Klute提出的。
图3所示为水平土柱法试验装置实物图和示意图,土柱壁由有机玻璃圆筒组成,直径9 cm,每2 cm设有一刻度线,在刻度线的上开一小孔,用于实验结束后取土测含水率。土柱首末加有挡板,并用螺杆紧固。土柱全长100 cm。在进水边界处(x = 0),为保证土壤含水率为饱和含水率但又不产生重力水流,在进水室与土柱之间装设低气泡压力和高传导率的多孔板或滤网。马氏瓶为供水平水之装置,用以控制水平土柱的作用水头和测量进水量。
3.2. 结果分析
试验使用风干土,过2 mm圆孔筛。试验测试压实度为91%、93%、95%和98%(干密度为1.729、1.767、1.805和1.862 g/cm3)的压实土的扩散系数。由于压实要求较高,填土前将风干土配制成含水率为8%的土样。填土采用分层压实,每1 cm填装土壤,通过填装质量来控制压实度。试验结果如图4所示。
从图4可以看出,随着压实度的增加,相同体积含水率条件下,土壤的扩散能在减弱。这和导水率的变化趋势是一致的。也就是说,土壤的压实可以有效减缓土壤水分的传播能力。为了探讨密度一定的压实黄土土基质吸力随含水量的变化规律,对干密度分别为1.710、1.767、1.801和1.862 g/cm3西安黄土的测试结果进行了拟合分析,得到基质吸力的计算公式形式如式(6)所示。三种密度的拟合结果如式(7)、
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 3. A horizontal infiltration testing
图3. 水平入渗试验
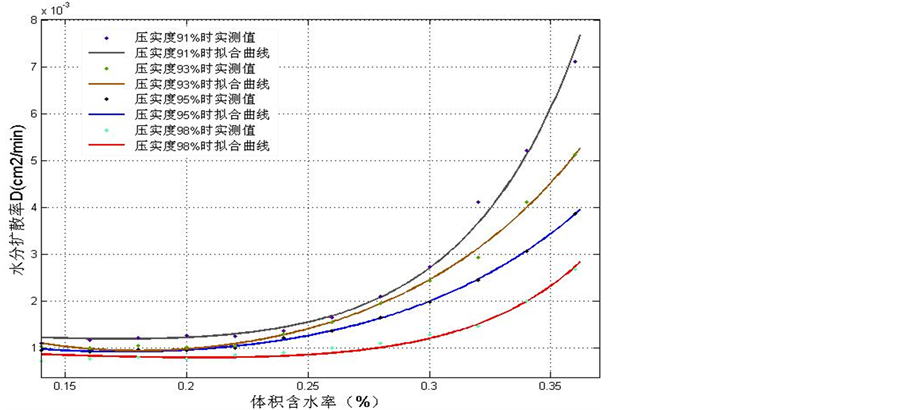
Figure 4. Soil water diffusivities under different compaction conditions
图4. 不同压实条件下水分扩散率
(8)、(9)和(10)所示;拟合曲线如图4所示。
 (6)
(6)
(1) 压实度为91%时:
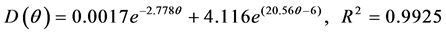 (7)
(7)
(2) 压实度为93%时:
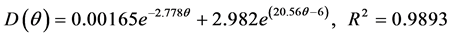 (8)
(8)
(3) 压实度为95%时:
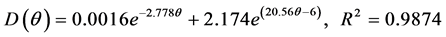 (9)
(9)
(4) 压实度为98%时:
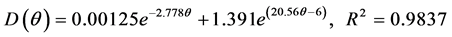 (10)
(10)
4. 毛细水上升试验
目前毛细水上升高度室内试验方法主要有竖管法和负水头法[23] [24] 。竖管法直观、准确、可靠,对各种土都适用,但耗时较长、费用高,特别是对黏性较大的土壤。负水头法比竖管法方便简捷,费用低,试验周期短,虽然工程人员用的较多,但局限性很大。鉴于实际条件,本试验采用自行设计的仪器进行竖管法观测,试验使用的土壤是西安市灞桥区白鹿塬脚下的黄土(E108˚59ꞌ; N34˚10ꞌ)。
4.1. 试验方法
试验采用竖管法,配合高清摄像头(动态像素1000万,150帧/秒)进行观察。其示意图和实物图如图5~图6所示。水箱提供足够的水源。水槽液面保持水平,并和土柱地面接触。土壤根据压实要求分层填充在内径为10 cm,壁厚7 mm,长100 cm的有机玻璃管中。分层压实/1 cm,严格通过质量控制压实度,初始含水率为7%。毛细水润湿锋的上升观测采用摄像头实时监控,历时105天。
4.2. 结果分析
将记录下来的毛细水上升视频通过截图的方法进行分析,以土壤颜色变化为毛细水润湿峰前进标志(如图7)。将实测数据放在以时间和高度为坐标的直角坐标系中(如图8所示)。使用Matlab将高度对时间
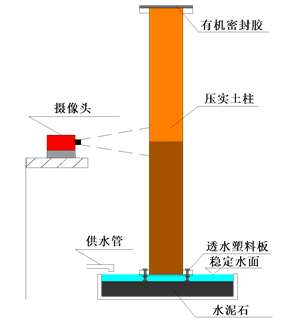
Figure 5. A schematic diagram of capillary water rise test
图5. 毛细水上升试验示意图

Figure 6. A real figure of capillary water rise test
图6. 毛细水上升试验实物图


Figure 7. Measurement of capillary water rise
图7. 毛细水上升观测
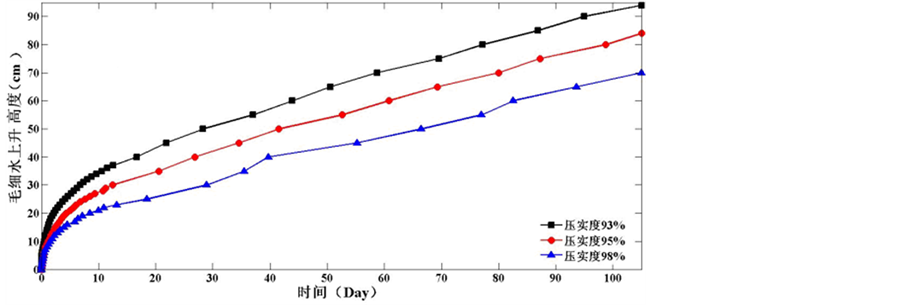
Figure 8. Rising heights of capillary water different compaction conditions
图8. 不同压实条件毛细上升高度
求导,得到毛细上升速率(如图9)。
图8可以看出,对于西安黄土来说,压实度越大,毛细水上升速度越慢,上升高度越小。压实度为98%、95%和93%的压实土柱,在105天后毛细上升高度分别为74 cm、80 cm和94 cm。主要原因式在粘性土中弯液面周边的表面张力的合力,尚需克服孔隙中结合水的阻力后,水柱才能达到一定高度,因而粘性土的毛细上升高度不服从孔隙愈小、毛细高度愈大的规律。
从图9中可以看出,毛细水上升速率在前5天里,是随着压实度的升高而快速降低;但在以后的时间里,毛细水的运动速率和压实度关系并不是很大。
将试验至105天的土柱,以每2 cm的距离进行钻孔取样,测出其含水率与高度的关系,如图10所示。三种压实度下的含水率与高度关系如图11所示。
5. 毛细水上升模拟计算
毛细水运动的土壤特征曲线模型可以本质是非饱和土水运动的Richard方程针对非饱和水上升的特殊形式。一维土柱非饱和水分迁移的基本方程为Richard方程,写成含水率为因变量的表达式为:
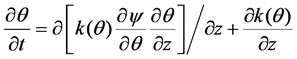 (11)
(11)
式中,θ为体积含水率;ψ为基质吸力;z为位置水头,向上为正。
(1) 初始条件:
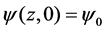 (12)
(12)
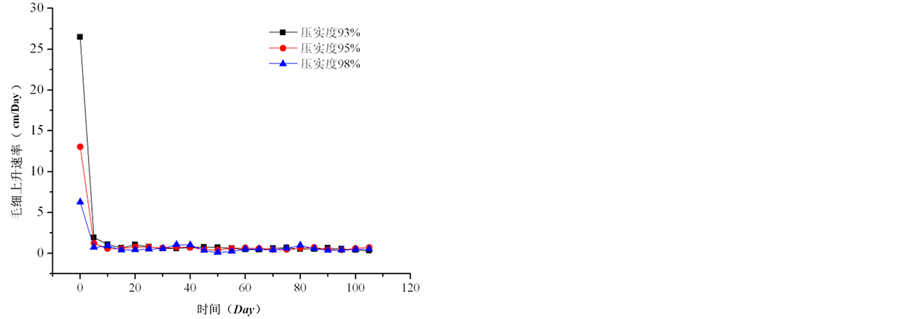
Figure 9. Rising velocities of capillary water under different compaction conditions
图9. 不同压实条件下毛细上升速率

Figure 10. Drilling sampling
图10. 钻孔取样
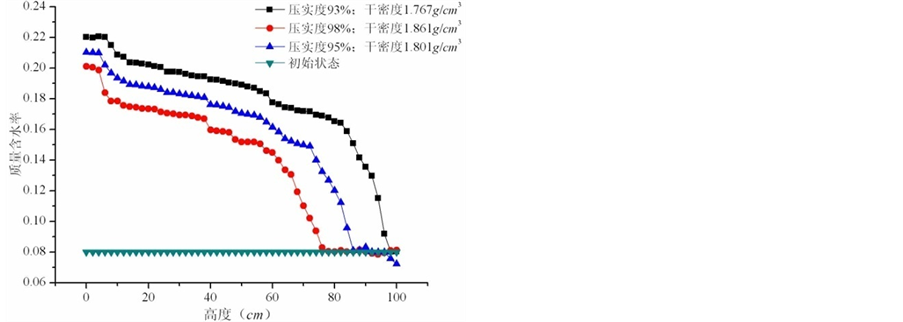
Figure 11. The final moisture content distribution
图11. 最终含水率分布
(2) 边界条件为
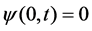 (13)
(13)
对上述偏微分方程可以通过数值方法进行求解。本文使用Geostuido中的SEEP/W模块进行有限元建模。土柱模型的单元划分如图12所示。
土水特征曲线使用前文两组试验得到的压实度为98%、95%和93%的数据;非饱和导水率通非饱和导税实验得到的非饱和水分扩散率D(θ)和ψ(θ)对θ求导后的乘积得出。
以93%压实土柱为例,将105的实测值和模拟值进行对比,可以看出模拟效果很好。并对其余时段的含水率分布进行模拟值计算,模拟结果如图13所示。
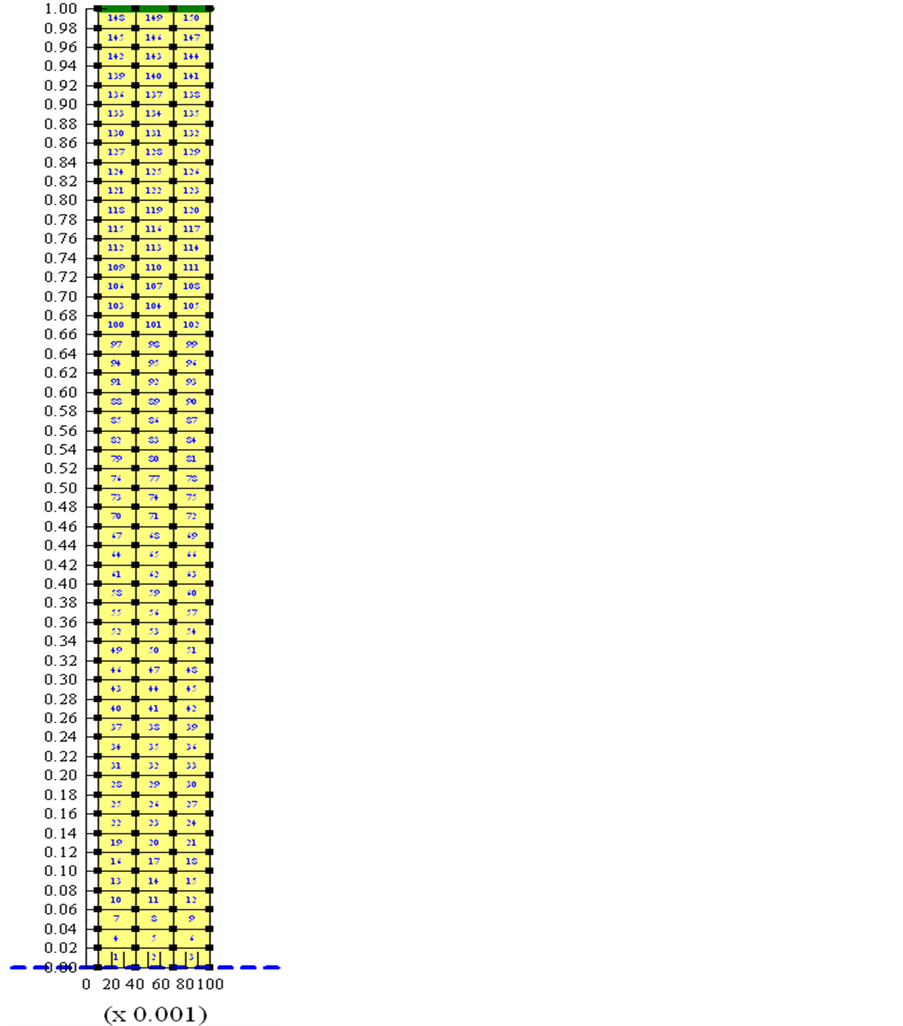
Figure 12. The finite element unit division
图12. 有限元单元划分
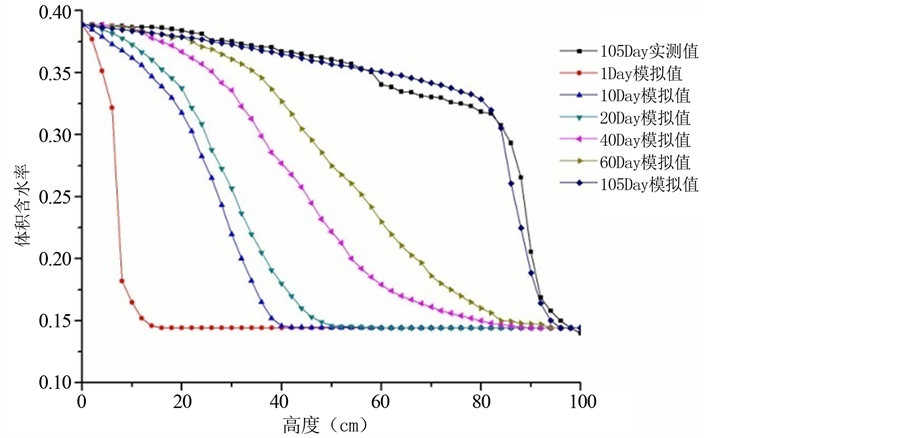
Figure 13. A contrast of measured and simulated values (93%)
图13. 实测值与模拟值对比(93%)
6. 结论
(1) 土水特征曲线是反应土壤基质吸力和含水率的重要关系曲线。压实度是反应土壤孔隙结构的物理指标,孔隙结构的改变将改变土壤的非饱和土持水特性。因此,压实度对土水特征曲线有很大的影响。通过滤纸法对压实度为98%、95%和93%的西安黄土的土水特征曲线进行了测量。结果表明,由于压实程度的不同将改变土壤孔隙的结构特征,对土壤的持水特性有较大的影响。
(2) 由于土壤压实将改变土壤的孔隙结构,这种结构的改变会直接影响土壤的导水性能。
使用水平土柱入渗法测定了压实度为91%、93%、95%和98%的西安黄土非饱和土水扩散率。随着压实度的增加,相同体积含水率条件下,土壤的扩散能在减弱。其变化特点和非饱和渗透系数相似。含水率较低,即吸力较大时,土壤水分扩散能力由吸力控制;相反时,由土壤孔隙结构控制。
(3) 通过室内试验,测试了初始含水率为8%,压实度为98%、95%、93%的西安黄土土柱毛细水上升时间和高度的关系。证实了粘性土由于结合水膜的阻力,随着压实度的增加,毛细现象得到减弱。从压实度为98%、95%和93%的压实土柱,在105天后毛细上升高度分别为74 cm、80 cm和94 cm。提高压实度可以缓解毛细水对道路土基的入侵,但不能完全避免,实际工程中要通过其他方法来阻隔毛细水对道路土基的入侵。
另外,使用有限元模拟软件,对压实度为93%的土柱,105天含水率分布情况进行了模拟,从模拟结果来看,模拟效果很好,该方法可以用于毛细水上升的模拟。

NOTES
*通讯作者。