1. 引言
随着社会经济的发展,我国水资源问题与水灾害问题得到了越来越多的关注。近些年来,由于气候变化与人类影响,湘江水系出现了不同程度的特枯水位及警戒水位现象,严重影响了湘江流域的水资源使用,产生了较多的水灾害问题,因此,精确模拟径流过程是有效进行水资源规划和水灾害防治的重要前提工作,而具有良好物理基础的分布式水文模型则成为了有效的工具。SWAT(Soil and Water Assessment Tool)作为美国农业部农业研究中心(USDA-ARS)开发的流域尺度模型,具备在不同土地利用和管理、不同土壤类型的大尺度复杂流域上,模拟预测流域内水文循环要素的长期变化,用以协调流域尺度的水资源管理利用的功能。
在我国,基于SWAT模型对于水量、非点源污染以及泥沙等方面的研究在近些年广泛展开。SWAT模型在汉江流域、黄河源区、淮河海河等地区的气候变化、土地利用变化对水资源的影响研究中取得了较好的效果[1] -[3]。本文以湘江流域为研究区域,收集了1991~2005年261个雨量站的雨量资料和5个水文站径流资料,利用DEM、土壤数据和植被数据构建SWAT模型的空间数据库,采用SUFI-2算法分区域对SWAT模型的参数进行敏感性分析和参数率定。在全球气候变化背景下,湘江流域水文循环规律发生了巨大变化,水资源时空分布不均的现象进一步加剧,水文气象等极端灾害事件越发频繁。因此,全面了解流域的自然情况,掌握气候变化规律,分析流域水资源的变化趋势,对于实现水资源的优化配置,流域的生态保护和经济发展具有重大的意义。本次水文模型的建立将为湘江流域的水资源规划与灾害防治提供科学支持与参考。
2. SWAT模型介绍
SWAT是由美国农业部农业研究中心开发的流域尺度分布式水文模型,具有在不同土地利用和管理、不同土壤类型的大尺度复杂流域上,模拟预测流域内水文循环要素的长期变化,以此来协调流域尺度的水资源管理利用的功能[4] 。模型主要由气象、水文、土壤、泥沙、作物生长、营养物、化学品以及管理模式八个部分组成,其中水文模块是整个过程最为基本、重要的一个环节,是其它模块的基础与驱动[5] 。
SWAT模型在具体应用时又发展出了许多新的改进模型。例如基于SWAT和MATSULA模型,并集成了GRASS模型的SWIM模型,在区域尺度上拥有更简便的操作性与更强的模拟能力[6] ;耦合了MODFLOW的SWATMOD模型,改良了SWAT在地下水模块的集总式处理[7] ;通过对SWAT模型中渗透和壤中流的计算修正,SWAT-G模型很好地应用到了山地地区[8] ;而集成了Qual2E的ESWAT模型,拥有更好的水质模拟功能[9] 。
3. 湘江流域SWAT模型数据库构建
3.1. 数据来源
本文SWAT模型构建采用的空间数据包括DEM、土地利用情况、土壤情况。所有空间数据都经过WGS-1984-UTM-Zone-49N平面投影处理。此外,还需要气象站点的实测气象数据、雨量站的雨量数据和水文站点的实测逐日流量,本论文广泛收集了上述资料,按照模型要求建立了各项数据库,见表1。
3.2. 空间数据库
空间数据库包括DEM、土地利用、土壤数据、生成的流域分区子流域、水系等空间特征数据等。
数字高程模型DEM是流域地形地貌的离散化数字表达。SWAT模型通过对DEM图的处理计算,对整个流域经行子流域划分、水系生成。图1为湘江流域初始DEM图以及ArcSWAT的处理结果,共划分出56个子流域。
本文的土地利用类型图采用湘江地区2005年比例尺为1:25万的土地覆盖数据。数据库构建中,通过转换,将其与SWAT2009土地利用属性表相匹配。根据流域实际情况对土地利用类型进行概化处理,重分类为10类,具体见图2。
本文的土壤类型图采用湘江流域1:100万土壤分布图,根据流域的实际情况进行概化处理,最终重分类出22类土壤类型,具体见图3。
我国已经完成的两次土壤普查中,分别采用苏联制和国际制计算土壤属性。而SWAT模型数据库采用美国制描述土壤质地。
3.3. 水文气象数据库
本文采用的11个气象站点,包括SWAT模型所需的日最高最低温度、平均相对湿度、辐射量、平均风速,由于这些变量的空间分布差异相对较小,且11个气象站空间分布相对均匀,本次论文直接使用。

Table 1. Input database for SWAT model
表1. SWAT模型输入数据库
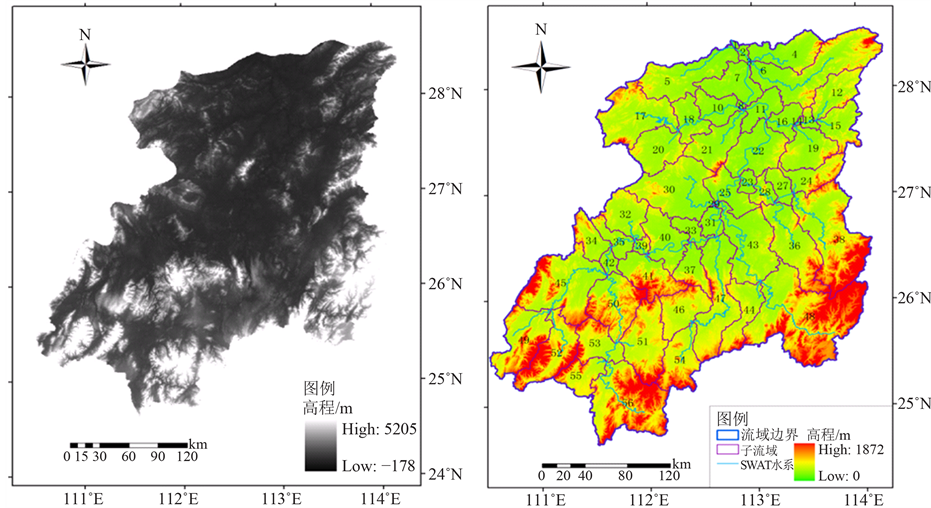
Figure 1. DEM map and digital stream and subbasin map of Xiangjiang basin
图1. 湘江流域DEM图及水系、子流域生成图
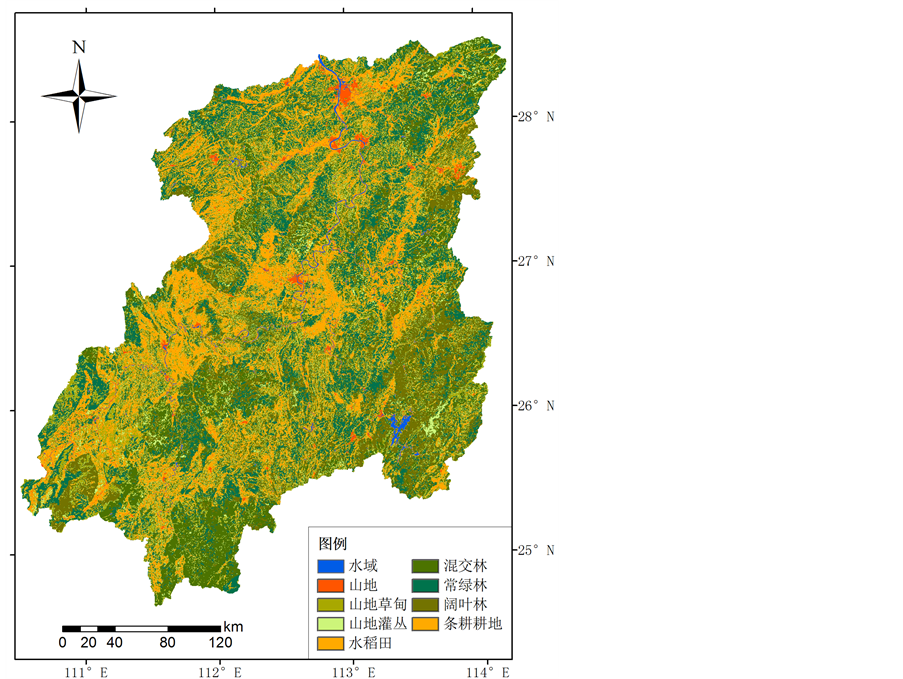
Figure 2. Landuse map in Xiangjiang basin
图2. 湘江流域土地利用图
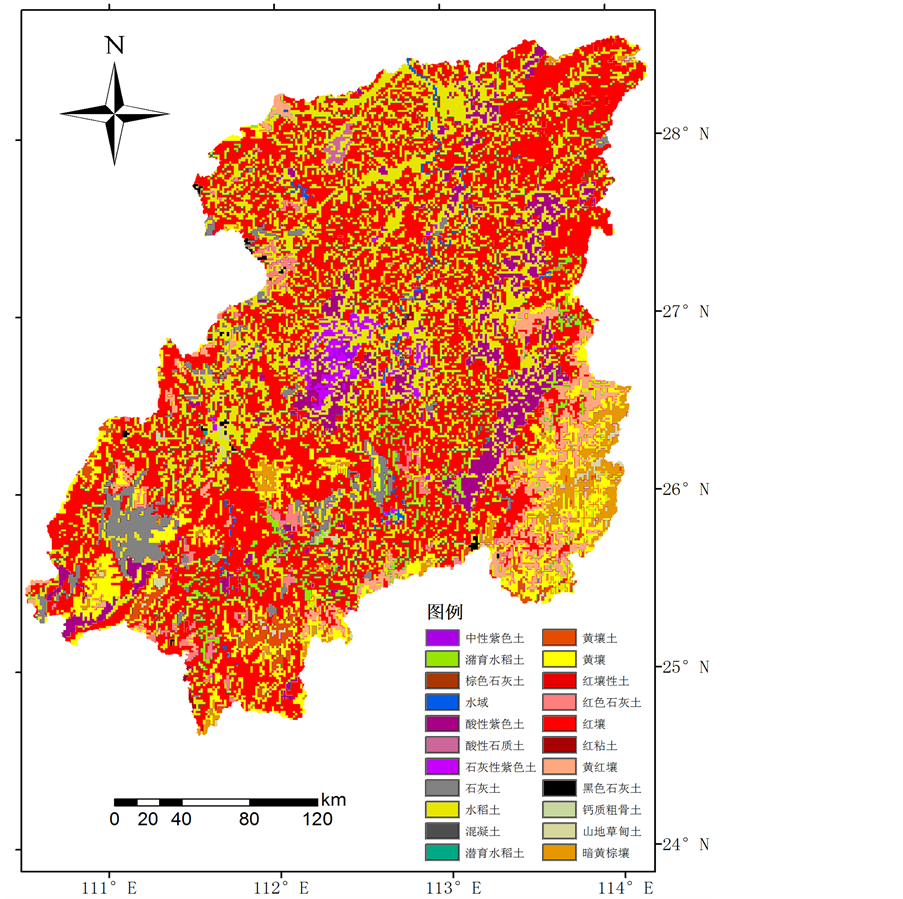
Figure 3. Soil map in Xiangjiang Basin
图3. 湘江流域土壤类型图
对于261个降雨站点,本次论文选取各个子流域以内以及周边靠近的若干雨量站点数据,通过SWAT内嵌的泰森多边形法插值得到子流域面的降雨,并制作相应的降雨数据库,水系及站点具体的分布情况见图4。
4. 湘江流域SWAT模型参数敏感性分析及率定
4.1. 流域分区划分方法
整理和收集了湘江干流衡阳、湘潭两个水文站以及湘江支流洣水、渌水及涟水各一个水文站的日径流资料。其中衡阳站以上流域、洣水、渌水以及涟水之间并无水力联系,可对各控制站以上的子流域进行合并,单独对这四个区域进行参数的敏感性分析及率定。最终保持这四个区域的率定参数不变,以湘潭站作为控制站,进行衡阳–湘潭区间的参数率定与分析。
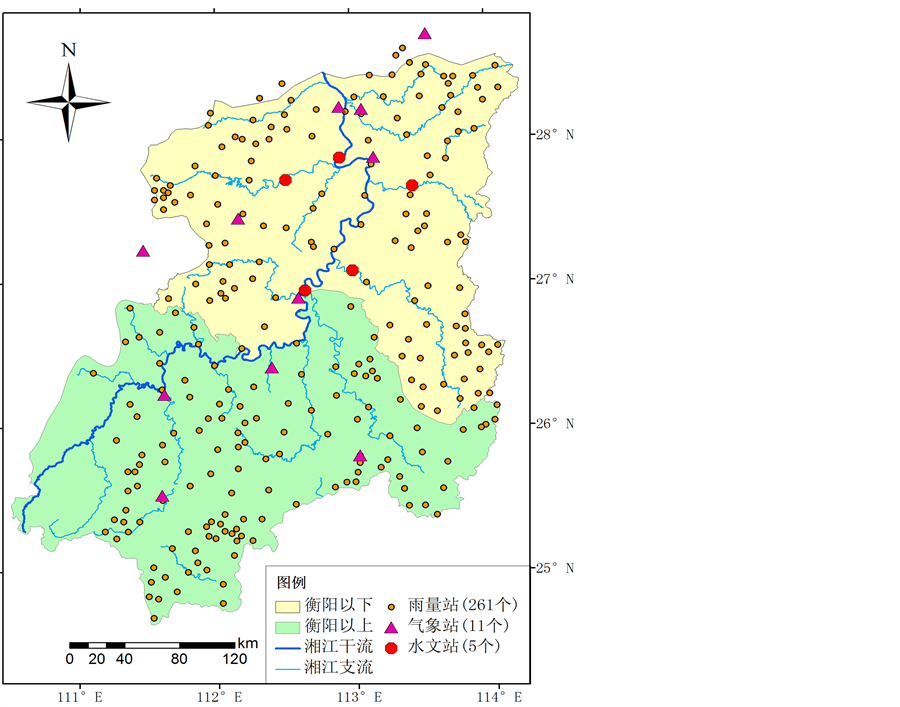
Figure 4. The stream of Xiangjiang basin and hydro meteorological stations location
图4. 湘江流域河流水系和站点分布图
4.2. SUFI-2算法参数优化
SWAT模型模拟过程涉及众多参数,在模型参数的率定检验过程中,部分参数对结果影响巨大,而部分则对结果的改进作用甚小。本次采用SWAT-CUP中的SUFI-2算法对湘江流域五个水文站的控制区域1991~2000年间进行敏感性分析。本次率定牵涉SWAT常用10个参数,根据SWAT-CUP中给出的初始不确定性范围,结合前人研究经验,对各区域均进行800次模拟,结果如表2所示。
在表2中,t值表示参数敏感性的大小,其绝对值越大,代表该参数在某一区域越敏感;p值表示该参数敏感性的置信水平,其值越接近0,代表该参数越重要。本文认为,在p值小于等于0.05的情况下,该参数比较敏感重要;而在p值大于等于0.3的情况下,该参数不敏感。
对于5个区域进行总体的分析发现,ALPHA_BF(基流回退系数)、CH_N2(主河道曼宁系数)、GW_DELAY(地下水的延迟系数)这三个参数普遍比较敏感。ALPHA_BF参数除了在洣水地区外,在其余地区皆为最为敏感的参数,这主要也是因为这些地区的汇流处高程落差明显较大,流速也明显较快,而ALPHA_BF反映基流的大小与快慢。在基础流速较大的情况下,ALPHA_BF的变化会对径流过程产生很明显的影响,故而该参数也最为敏感。CH_N2为主河道曼宁系数,在地表径流较大,河网密布的情况下会对产流产生较大的影响,而湘江流域地处南方湿润地区,降雨较为充沛,土壤的缺水率较小,汛期主要以类似蓄满产流的方式为主。在这样的情况下,曼宁系数会具有较高的敏感性。GW_DELAY代表地

Table 2. Parameter sensitivity of five controlled area in Xiangjiang basin
表2. 湘江流域5大控制区域参数敏感性
下水的延迟时间,对于枯水期的河道径流补给具有重要的意义,而湘江流域枯水期主要依靠地下水补给调剂,在这个时间段内地下水延迟时间对产流影响较大。同时,CN2(径流曲线数)参数在衡阳以上、渌水、涟水三个地区比较敏感。CN2值是SCS径流曲线法中反映降雨前期流域特征的无量纲参数。由于在本次SWAT模型中产流采用SCS径流曲线法,且降雨较为充沛,所以CN2对于地表径流的模拟起着至关重要的作用。说明在面积较小的区域上,下垫面的不透水性对径流的生成具有很强的影响。
对于不同地区的参数敏感性分析而言,在渌水、涟水两个地区,ALPHA_BF、CH_N2、GW_DELAY三个参数依次最为敏感。衡阳以上地区CH_N2参数不敏感,这主要是因为衡阳以上地区面积较大,但生成的河网较短,河网密度较低,从而使得曼宁系数对河道中地表径流影响降低,导致参数不太敏感。衡湘地区除了ALPHA_BF与CH_N2参数以外,其余参数均不敏感,这也是由于衡湘地区并不是水力独立的区域,受到其余四个区域入境水量的影响,自身产流相较于四个区域入境水量而言明显偏小,本身的水文过程功能被大大地弱化。所以反应基流大小与快慢的ALPHA_BF与影响河道流量的CH_N2可以调节所有水量,对最终径流结果产生影响,从而在该地区具有一定的敏感性,而其余参数基本不敏感。洣水地区ESCO(土壤蒸发补偿系数)最为敏感,这是由于洣水地区所在地区雨量站平均降雨量较其余地区降雨量小,蒸发量对洣水地区径流产生影响更加明显,从而导致ESCO参数更加敏感。
4.3. 湘江流域SWAT模型率定与检验
模型的率定就是寻找使模型的模拟值与对应实测值尽可能一致的参数。本文采用SWAT-CUP软件自带的SUFI-2模块进行参数的自动率定。各区域的率定检验期Nash-Sutcliffe效率系数如表3所示(率定检验期的第一年为模型预热),并给出了相应的径流总量相对误差系数RE。
表3表明,对于湘江干流两个区域的率定检验,日模拟效率系数均达到70%以上,而对于渌水、涟水、洣水等流量相对较小的湘江支流区域,日模拟效率系数也达到了60%以上。此外,5个控制区域率定检验期的径流总量相对误差系数均控制在10%以内。综上所述,湘江流域整体的日模拟率定取得了较好的效果。
4.4. 模型模拟结果比较分析
图5和图6给出了检验期湘潭站的模拟实测效果对比图,可以进一步比较SWAT模型径流过程模拟效果。

Table 3. Statistical index of daily simulation in calibration and validation period
表3. SWAT模型日模拟率定检验结果
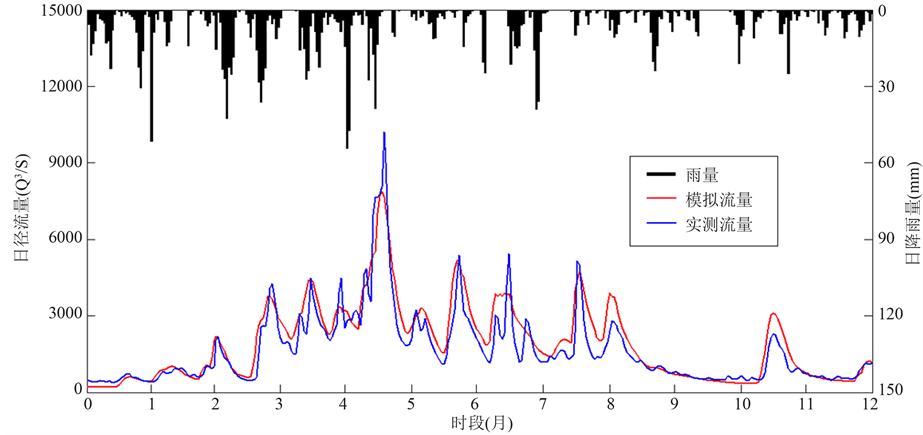
Figure 5. Daily flow in 2004 of validation period at Xiangtan station
图5. 湘潭站检验期2004年日径流过程线
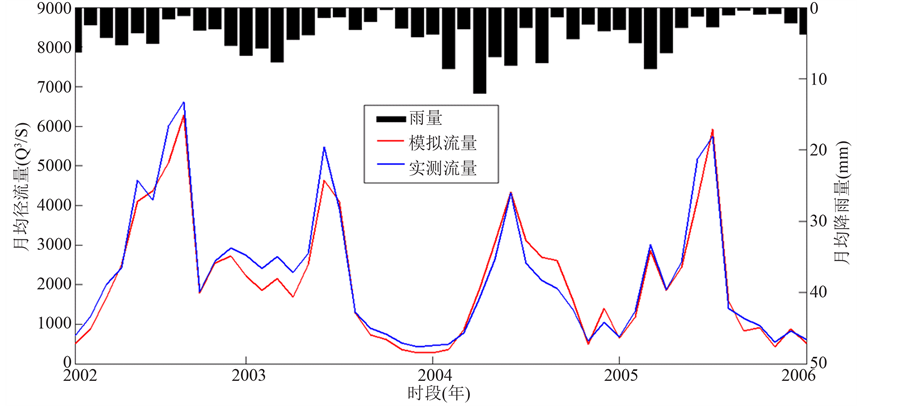
Figure 6. Monthly flow between 2002 and 2005 at Xiangtan station
图6. 湘潭站检验期2002~2005年月径流过程线
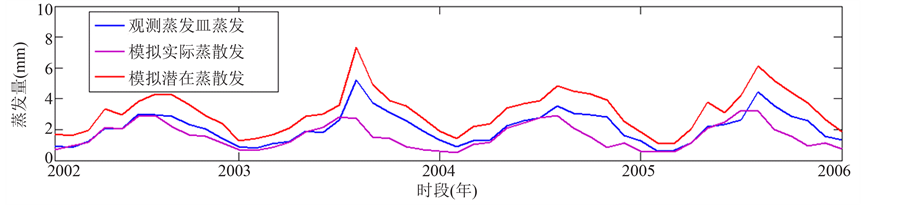
Figure 7. Comparison of monthly simulated evapotranspiration in Xiangjiang basin
图7. 湘江流域蒸散发月模拟效果对比
由于土壤含水量的实测资料较难获得,流域的水面蒸发较易获得,故统一对SWAT模型模拟的流域潜在蒸散发能力、实际蒸散发量与蒸发皿观测值进行对比,用以反映模型对于土壤植物水文过程模拟的合理性,如图6所示。
从图7可以看出,在大部分温度不高的月份,SWAT模型模拟的实际蒸散发量与观测的蒸发皿比较接近。而在7,8,9月的模拟精度则稍差,无法模拟出极值,论文认为这一现象的出现很可能是由于在高温月份,蒸发皿温度高于气温,进一步加速了蒸发皿内的水面蒸发速度,使得观测数据高于实际值。对这一部分的数据进行分析,可以发现尽管在高温月份模拟与观测数值相差较大,但是相关系数达到0.8以上,可以认为将这一阶段的实测数值乘以一个折算系数,才能真实地反映实际情况。此外,将观测数据与SWAT模型模拟的流域潜在蒸散发能力进行对比,相关系数达到0.9以上,也在一定程度上说明了模拟的合理性。因此可以认为,SWAT模型对于湘江流域土壤植物的水文过程模拟是比较正确合理的。
5. 结论
本文以湘江流域为研究区域,分析和讨论了SWAT模型建立过程中参数的敏感性以及模型在该区域径流模拟的精度,具体结论如下:
1) 相对于单一出口断面的径流率定,分区域多站点的率定模式更能反映模型的分布式特点,对提高最终流域出口断面的模拟精度也有一定的帮助;
2) 基流alpha因子、河道的曼宁系数在以径流模拟效率系数为目标函数的参数优化中,具有较强的敏感性;湿润条件下的SCS曲线数对于独立率定的小子流域较为敏感;
3) SWAT模型对于径流的模拟在汛期的极值模拟方面有一定的不足,但是水量误差整体效果好。
SWAT模型在该区域的日径流过程模拟是合理的,符合后续水资源评估的需要。

NOTES
作者简介:侯雨坤(1991-),男,江苏南京人,硕士研究生,主要从事气候变化对水文水资源影响研究。