1. 引言
工业革命以来,大气中的二氧化碳浓度从280 ppm增加到2010年的398 ppm,并仍以近2.0 ppm/a的速度在继续增长。加上其他一些温室气体也在缓慢增加,大气成分和辐射发生改变,气候系统的能量平衡遭到破坏,气候的变化将改变全球水循环的现状,从而引起水资源在时空上的重新分配,并对降水、蒸发、径流、土壤湿度等造成直接或间接的影响。河流湖泊作为全球水循环的重要载体,首当其冲受到气候变化的影响。研究气候变化在流域尺度上的影响,对维护流域健康生命,保障流域水资源可持续利用,保证流域社会经济可持续发展具有重要的现实意义[1] 。
太湖流域面积约3.69万km2,地处长江三角洲核心区域;北依长江,南濒杭州湾,东临东海,西以茅山、天目山为界,行政分属江苏、浙江、上海、安徽三省一市。太湖流域地形呈周边高、中间低的碟状分布;西部为山区,中部河网密布,湖泊棋布;太湖位于流域河流水系的中心,多年平均水面面积为2338 km2。太湖流域属于典型的亚热带季风气候区,受到西太平洋亚热带高压和东南季风的双重影响,气候特征复杂多变;流域年平均气温14.9℃~16.2℃,自北向南递增;多年平均降水量为1177 mm,其中60%的降水集中在5~9月。降水年内年际变化较大,最大与最小年降水量的比值为2.4倍;年径流量年际变化更大,最大与最小年径流量的比值为15.7倍。
本文应用统计降尺度方法分别建立表征气候变化信息的大尺度气候因子与太湖流域气象站点日降水、日气温之间的统计学关系,预测分析太湖流域未来降水和气温的变化趋势,为未来太湖流域防洪抗旱及水资源管理提供参考依据。
2. 数据选取
气候变化研究中一般需要三类数据:气象站点实测地面气象数据、大尺度气候因子观测数据以及全球气候模式(GCM)模拟得到的大尺度气候因子在当前和未来气候条件下的输出数据。本文选取太湖流域内常州、溧阳、东山、徐家汇、天目山、杭州、平湖等7个国家气象站点的日平均降水和平均气温数据作为实测地面气象数据;其中徐家汇站和天目山站分别采用1961~1998年和1961~1997年的数据系列,其余站点采用1961~2001年的数据系列。将美国环境预报中心(NCEP)全球再分析日数据(1961~2001年)作为观测的大尺度气候数据,其空间分辨率为3.75˚ × 2.5˚。在与NCEP数据相同的空间分布中,采用全球气候模式HadCM3在温室气体高排放(A2)和低排放(B2)情景下输出的模拟数据作为当前(1961~2001年)和未来(2010~2099年)大尺度气候因子的模拟数据[2] [3] 。气候因子输出数据格网基本覆盖整个太湖流域,选择格网范围为:117˚30'00''E~121˚15'00''E,30˚00'00''N~32˚30'00''N。本文采用的NCEP全球再分析日数据和全球气候模式HadCM3数据包含海平面气压、地面气温、500 hPa和850 hPa位势高度场、500 hPa和850 hPa湿度等26个大尺度气候因子(详见表1),并且经过同化处理,使得两种数据能够匹配。太湖流域位置及气象站点分布见图1。
3. 模型建立
3.1. 统计降尺度模型
全球气候模式(GCM)是目前研究气候变化与气候变异最重要也是最可行的方法。但是由于GCM的水平网格分辨率一般在104~105 km,缺少足够的区域尺度下的气候过程,地形情况以及海陆分布情况等因素,所以将其直接应用到区域尺度是非常困难[4] 。为了弥补GCM在区域气候预测中的不足,水文气象学家提出了尺度降解技术,即将GCM输出的大尺度、低分辨率信息转化为区域尺度的地面气候要素信息。降尺度技术主要包括统计降尺度法和动力降尺度法两种。其中,统计降尺度法以其计算量小,节省机时,可以很快地模拟出百年尺度的区域气候信息,可以很容易的应用于不同的GCM模式,可以将大尺度气候信息降解到站点尺度上等特点在国内外得到广泛应用[5] -[10]。本文采用自动统计降尺度模型ASD (Automated Statistical Downscaling model),将GCM输出的大尺度、低分辨率的信息转化为区域尺度的地面气候要素信息。由于篇幅限制,ASD模型的原理详见参考文献[11] 和文献[8] ,这里不再赘述。

Table 1. The atmospheric variables for predictors from NCEP and HadCM3
表1. NCEP和HadCM3输出大尺度气候因子
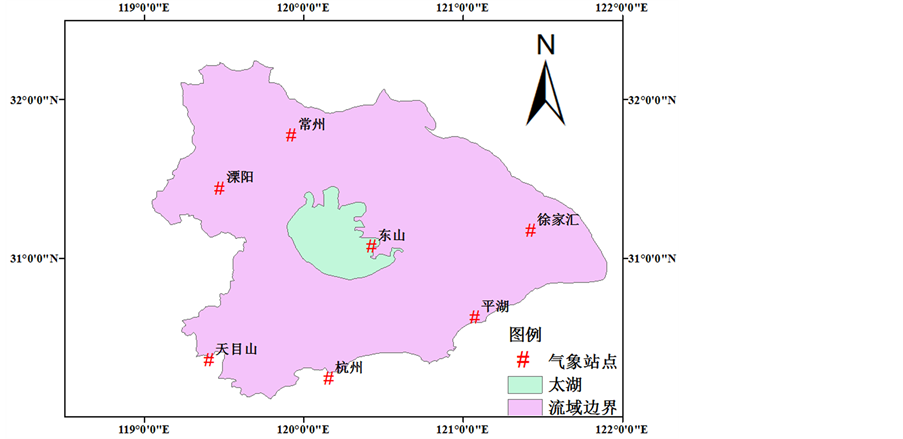
Figure 1. Location of the Taihu Basin and the meteorological stations
图1. 太湖流域位置及气象站点分布
3.2. 因子选择
本文选择站点所在网格包含如海平面气压、地面气温、500 hPa和850 hPa位势高度场、500 hPa和850 hPa湿度等26个因子作为备选因子与每个站点降水、气温分别建立统计降尺度关系(备选因子如表1所示)。降尺度预报因子的选择在统计降尺度中是很关键和重要的一步。通过因子选择不仅可以降低预报因子数据集的维数,避免维数灾,提高计算效率,而且可以筛选出代表大尺度气候场的重要物理过程和气候变率,以及与地面气候变量有很强相关性的气候因子。通过因子选择发现,与各站点降水、气温关系比较显著的气候因子一般为风向场、湿度场及风速场等。这也印证了太湖流域地处季风区,降水、气温多受西太平洋亚热带高压和东南季风影响的气候特性。
3.3. 模型率定与检验
利用太湖流域7个国家气象站的日降水、气温资料,以及经过因子选择后的NCEP大气环流因子,分别建立大尺度环流因子与各气象站日降水和气温之间的统计关系,其中各站均已1961~1990年作为率定期。除徐家汇站和天目山站分别以1991~1998年和1991~1997年作为检验期,其余站点均已1991~2001年作为检验期。
为了对ASD模型的模拟效果优劣性进行评价,针对降水和气温,本文分别选择5个统计指标进行分析。降水系列统计指标包括:日降水系列均值(Mean)、日降水系列标准差(Std)、90%分位数日降水量(Percentile90)、日降水量 ≥ 1.0 mm天数所占比例(Wet)、最大连续干旱天数(Cdd);气温系列统计指标包括:日气温系列均值(Mean)、日气温系列标准差(Std)、90%分位数日平均气温(Percentile90)、最高日平均气温(Max)、最低日平均气温(Min)。在此基础上,选择模拟系列与实测系列各统计指标的相对误差RE,均方根误差(RMSE)和均方根误差变差系数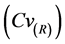 3个评价指标来评定ASD模型所建立的统计关系的优劣性。其中
3个评价指标来评定ASD模型所建立的统计关系的优劣性。其中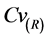 是一个用来衡量两列数据之间相对变化程度的统计量,定义如下:
是一个用来衡量两列数据之间相对变化程度的统计量,定义如下:
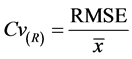 (1)
(1)
式中: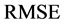 为模拟数据系列相对于实测系列的均方根误差,
为模拟数据系列相对于实测系列的均方根误差,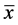 为实测系列的均值。
为实测系列的均值。
表2和表3分别列出了利用NCEP数据模拟太湖流域7个测站降水、气温的结果。表2结果显示,
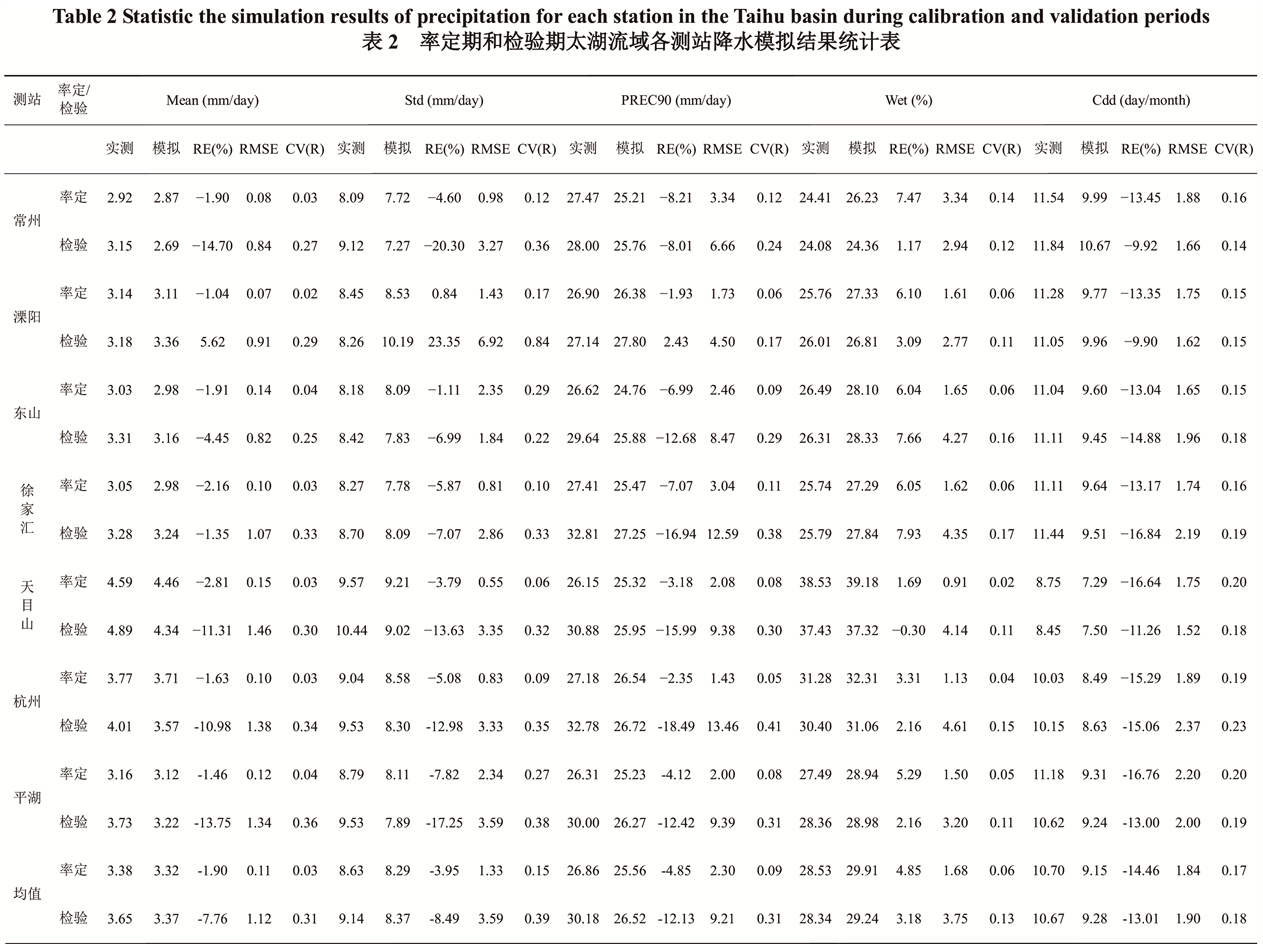
Table 2 . Statistic the simulation results of precipitation for each station in the Taihu basin during calibration and validation periods
表2.率定期和检验期太湖流域各测站降水模拟结果统计表
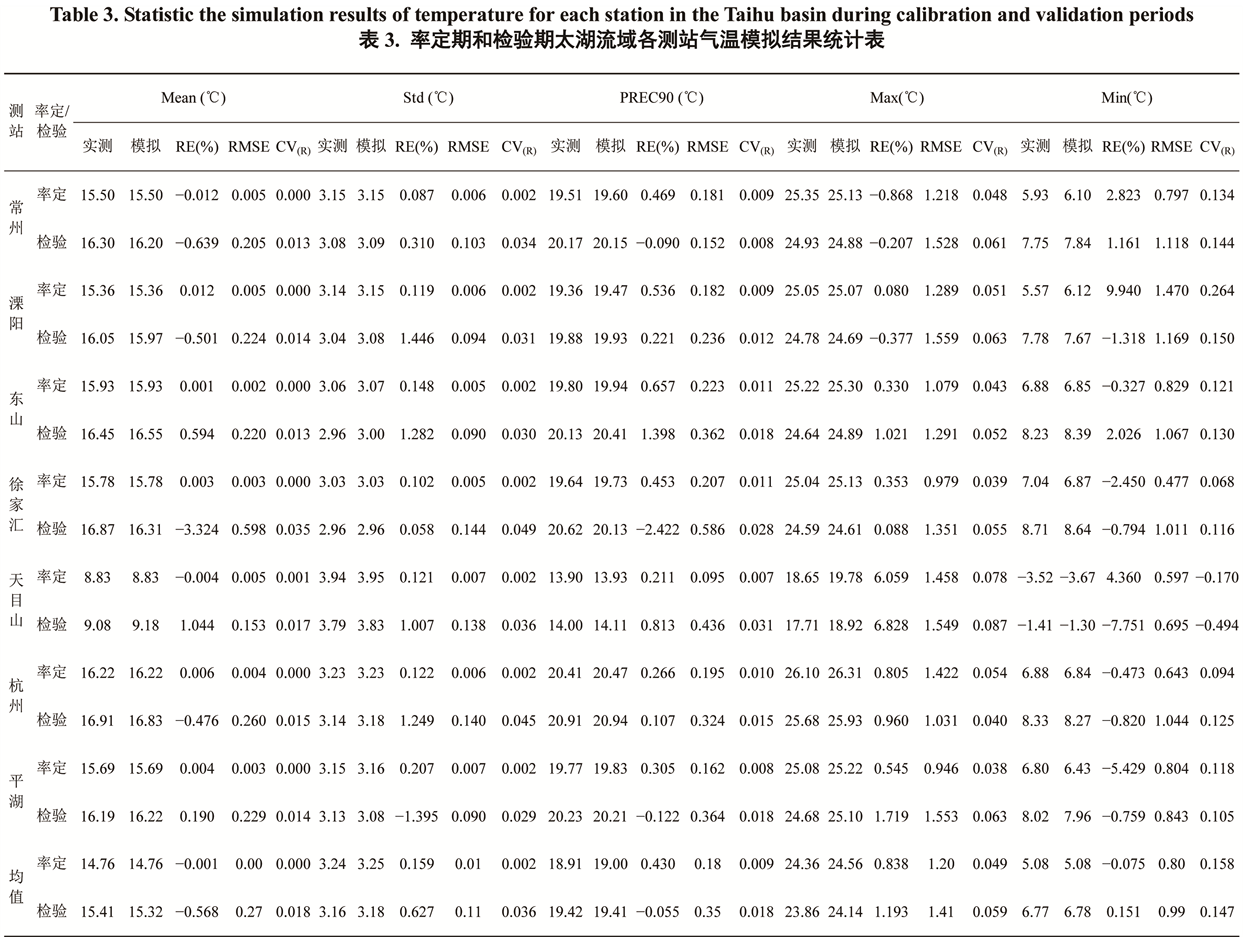
Table 3 . Statistic the simulation results of temperature for each station in the Taihu basin during calibration and validation periods
表3.率定期和检验期太湖流域统计表
率定期和检验期,除去Cdd统计指标以外,各测站其余降水统计指标的模拟相对误差(RE)基本在±10%以内;率定期各测站降水统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均在3.5以内,均方根误差变差系数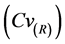 均在0.3以内;检验期各测站降水统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均大于率定期,均方根误差变差系数
均在0.3以内;检验期各测站降水统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均大于率定期,均方根误差变差系数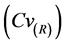 控制在0.9以内。表3结果显示,率定期和检验期,各测站气温统计指标的模拟相对误差(RE)基本控制在±5%以内;率定期各测站气温统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均在1.5以内,均方根误差变差系数
控制在0.9以内。表3结果显示,率定期和检验期,各测站气温统计指标的模拟相对误差(RE)基本控制在±5%以内;率定期各测站气温统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均在1.5以内,均方根误差变差系数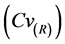 除最低日平均气温(Min)以外均控制在0.1以内;检验期各测站气温统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均大于率定期,除最低日平均气温(Min)以外均方根误差变差系数
除最低日平均气温(Min)以外均控制在0.1以内;检验期各测站气温统计指标的均方根误差(RMSE)均大于率定期,除最低日平均气温(Min)以外均方根误差变差系数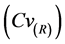 也均在0.1以内。
也均在0.1以内。
通过以上分析可以看出,由NCEP大尺度气候因子率定的降尺度统计关系能够较好地反映太湖流域降水和气温的特征,比较客观的模拟太湖流域降水和气温的变化过程,其中气温模拟结果优于降水。
4. 太湖流域降水和气温预测分析
为了分析未来太湖流域面均降水和气温的变化情况,以1961~1990年作为基准期,将未来气候分为3个时期:2020s(2010年~2039年)、2050s(2040年~2069年)以及2080s(2070年~2099年)。应用全球气候模式HadCM3输出的A2和B2气候情景,输入经过验证的ASD统计降尺度模型,分别生成太湖流域7个测站的降水和气温序列。通过对以上降水、气温面均系列分析来研究未来太湖流域的气候变化情况。
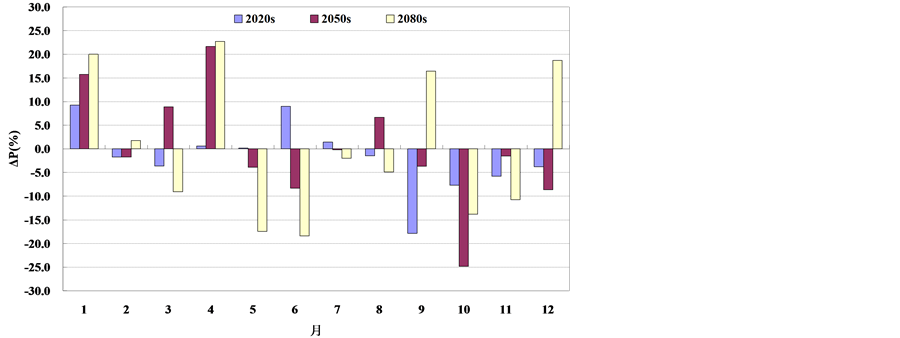
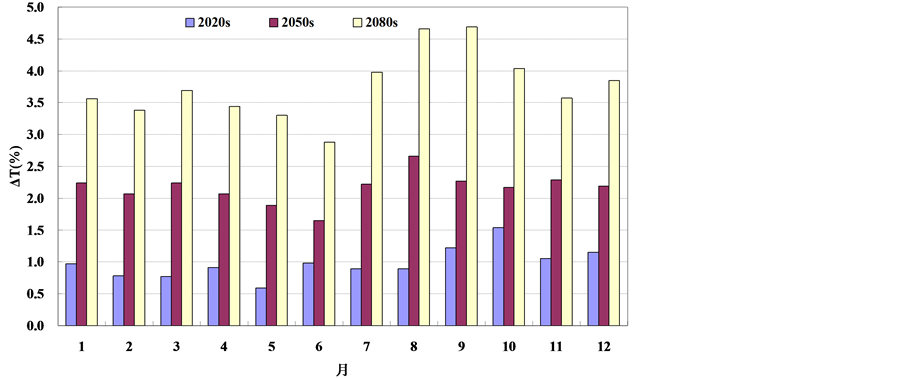
图2和图3分别给出了未来3个时期的年内降水、气温相对于基准期的变化情况。为了消除模型系
 (a)
(a)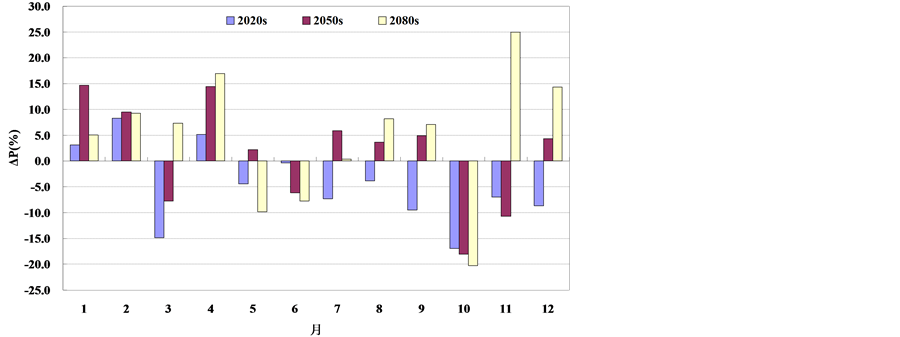 (b)
(b)
Figure 2. Relative changes of the areal-averaged monthly precipitation corresponding to the base period and future periods in the Taihu basin; (a) A2 Scenario; (b) B2 Scenario
图2. 太湖流域未来面均月降水相对基准期变化情况;(a) A2情景;(b) B2 情景
 (a)
(a)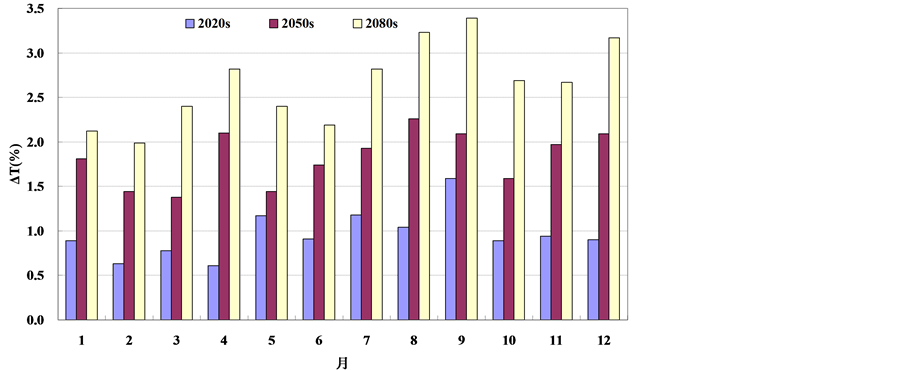 (b)
(b)
Figure 3. Relative changes of the areal−averaged monthly temperature corresponding to the base period and future periods in the Taihu basin; (a) A2 Scenario; (b) B2 Scenario
图3. 太湖流域未来面均月气温相对基准期变化情况;(a) A2 情景;(b) B2 情景
统误差,使得基准期和未来降水、气温能在相同的模型误差下进行比较,本文基准期的降水量、气温均采用GCM资料模拟成果。由图2可知,在A2情景下,未来3个时期太湖流域月降水量在1、4月以增加为主,其余月份以减少为主;B2情景下,未来3个时期太湖流域月降水量在1、2、4、7、8、9和12月等7个月份以增加为主,其余月份以减少为主。图3结果显示,两种气候情境下未来3个时期太湖流域各月平均气温均呈增加趋势;其中A2情景和B2情景的月最大增加幅度分别为4.7℃和3.4℃,均发生在2080s时期的9月份。比较两种情景下月内气温变化情况可以看出,A2情景基本大于B2情景,可见A2情景气温变化更加剧烈。
表4列出了A2、B2情景下太湖流域未来3个时期多年平均面均降水量、气温及其相对于基准期的变幅。降水变化预测中,A2情景下,2020s、2050s和2080s时期年均降水量分别比基准期减少2.24%、0.38%和1.20%;B2情景下,2020s时期比基准期减少5.00%,2050s和2080s时期分别比基准期增加1.06%和3.78%。从3个时期降水变化趋势看,A2情景下,太湖流域降水是先增加后减少趋势,2050s时期达

Table 4. The prediction results of areal-averaged precipitation and temperature under A2 and B2 scenarios
表4. A2、B2情景下太湖流域未来面均降水、气温预测结果
注: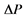 为与基准期降水模拟值相比的相对变幅;
为与基准期降水模拟值相比的相对变幅;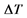 为与基准期气温模拟值相比的变幅。
为与基准期气温模拟值相比的变幅。
到峰值;B2情景下,太湖流域降水呈增加趋势。气温变化预测中,A2情景下,2020s、2050s和2080s时期年均气温分别比基准期增加1.0℃、2.2℃和3.7℃;B2情景下,2020s、2050s和2080s时期分别比基准期增加1.0℃、1.8℃和2.7℃;两种气候情景下,未来3个时期气温总体呈上升趋势,其中A2情景比B2情景升温更加显著。
5. 结论
本文利用太湖流域的7个国家气象站实测降水、气温数据和NCEP再分析大尺度气候因子数据,建立了太湖流域降水、气温统计降尺度ASD模型,在此模型基础之上,采用A2和B2情景下的HadCM3输出数据,预测太湖流域未来降水、气温变化情况,主要结论如下:
1) ASD统计降尺度模型能够较好地抓住太湖流域降水和气温特征,比较客观的模拟太湖流域的降水和气温变化过程,其中气温模拟结果优于降水。
2) 降水模拟结果显示,A2情景下,未来3个时期太湖流域降水呈先增加后减少趋势,2050s时期达到峰值;B2情景下,未来3个时期太湖流域降水呈增加趋势。
3) 气温模拟结果显示,两种气候情景下,未来3个时期气温总体呈上升趋势,其中A2情景比B2情景升温趋势显著。
4) 由于全球气候模式、气候排放情景及尺度降解技术均存在不确定性,因此本文预测的降水、气温变化结果,仅作为相关决策的参考。

NOTES
*作者简介:郭靖,男(1982-),博士,高级工程师,研究方向:气候变化下水资源开发利用研究。