1. 引言
细胞生长和分裂是生命的重要特征之一,它是经过严密的时间调控和空间调控而得以完成的。严密的时间调控,使细胞通过细胞周期的各个时期,经过细胞核的一系列变化把遗传物质准确地平均分配至两个子细胞,完成核分裂。细胞分裂又通过严密的空间调控,精确地分割细胞质并分配细胞器,选择特定分裂位点进行胞质分裂,使每个子细胞有足够的细胞质开始自己的生命周期[1] [2] 。
机械力作为一种特定的物理刺激形式普遍存在于自然条件下植物所处的环境之中,应力与生长关系逐渐成为物理学家和生物学家所关心的课题。关于植物对应力刺激的生物学效应已由宏观水平逐渐深入到细胞和分子水平探讨其机理。1993年,Cosgrove教授系统地研究了植物细胞壁的力学性质,并阐述与细胞生长之间的关系。他首先从细胞壁的结构入手,然后进行了细胞壁的应力/应变率、蠕变和应力松弛实验,建立了植物细胞的生长模型[3] 。后来,人们逐步开始从分子机理探讨细胞如何感受力的信号。植物对环境信息的响应可以分为三个主要的阶段:植物体对刺激的感受,细胞信号转导(信号的产生、传递和转换),以及随后在下游生物化学过程方面的变化。动物细胞感受机械刺激的机制为植物的研究提供了参考模式[4] 。目前,许多人认为在植物中可能存在整合素或整合素的类似物,机械应力施加于这种细胞表面的粘附受体,活化细胞内的信号转导途径并诱导相应的基因转录。Nagpal和Quatrano(1999)用一种脊椎动物的抗β1整合素抗体筛选表达文库,从拟南芥中获得了Atl4a的完整cDNA,它编码一个43 kD的蛋白质,该蛋白部分地定位于细胞膜上并与整合素具有同源性。Laval(1999)等从拟南芥中找到了另一个包含β-整合素的cDNA克隆,它编码一个70 kD的蛋白质,它主要定位在质膜上[5] 。因此,人们逐渐相信,类整合素可能在植物对机械信号的转换中发挥了非同寻常的作用。钙离子(Ca2+)已被许多研究工作证实是植物细胞信号转导过程中重要的第二信使之一。近年来,在钙信号系统对机械刺激信号的传递和转化方面也取得了一些突破性的进展。多位研究者运用了转水母发光蛋白的烟草植株,观察了触摸和风吹等机械刺激过程中其幼苗的胞内Ca2+浓度的变化[6] -[8] 。另外,有证据显示CaM参与了机械信号的转导[9] [10] 。然而,这些数据过多基于植物的部分组织或器官而获得。
本研究已烟草BY-2细胞为材料,重点探讨应力大小,以及在恒定应力条件下施力时间与细胞定向伸长的关系。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 原生质体的分离与包埋
取对数生长期的转微管基因的烟草BY-2细胞置于酶液中,黑暗25℃条件下酶解4 h。酶液包含9%甘露醇、0.6%纤维素酶、0.5%果胶酶,pH 5.7。酶解后分离、纯化得到原生质体。将得到的原生质体与约15 ml的琼脂糖MS培养基(添加2,4-D 1 mg/L,6-BA 1 mg/L,蔗糖2%,低熔点琼脂糖0.6%)混合均匀,pH 5.8,最终细胞密度约为0.5 × 105/mL。琼脂冷却后制成尺寸为0.5 cm × 1.0 cm × 4.0 cm琼脂条。
2.2. 原生质体活力的测定
原生质体的活力测定用FDA荧光染色法。测定时FDA的工作浓度为1 μg/mL,蓝光激发下镜检。细胞显绿色荧光为有活力的原生质体。
2.3. 细胞壁合成时间进程
原生质体培养过程中,培养2 h前每隔30 min取样,2 h后每隔1 h取样,用Calcofluor White染色,倒置显微镜下紫外激发下观察并取图。
2.4. 离心力的加载
将包埋好原生质体的琼脂条置于离心管中,在水平转的离心机上按不同的条件处理:1) 离心力为25 g条件下离心15 min、1 h、6 h、9 h、12 h;2) 在离心力为1 g、10 g、25 g、50 g、80 g条件下离心6 h。离心完成后,取出琼脂条,置于6 cm培养皿中,在培养皿中添加3 mL MS培养基(添加2,4-D 1 mg/L,6-BA 1 mg/L,蔗糖2%),黑暗条件下培养3~4 d,用倒置显微镜观察并取图。实验重复4次。
2.5. 图象的获取与分析
显微观察和摄影采用Olymus CK40倒置显微镜,通过万能图象捕获软件获得。代表性的图像用Image-Pro PLUS软件(Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD)进行形态和统计分析。每个处理至少测量100个细胞。
2.6. 统计与分析
采用SPSS软件对实验结果进行统计学分析。P值小于0.05时认为差异显著。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 细胞神长方向与离心力大方向存在相关性
对琼脂糖包埋后的烟草原生质体,施加25 g的离心力9 h,加载完成后对样品进行显微摄像,发现原生质体未出现明显的形变,仍保持初始时圆球状(图1B),表明离心力没有引起细胞本身的弹性形变。25℃黑暗条件下培养4 d后,烟草原生质体定向伸长方向倾向与离心力的方向垂直(图1C)。20%的细胞伸长的方向与施力的夹角在45˚~60˚,67%的细胞伸长的方向与施力的夹角在65˚~90˚,表明细胞伸长方向与应力的主方向具有显著的相关性(P = 0.001,图2B)。相对未加载力的组群中,细胞伸长的的方向没有任何偏向性(图1D),是随机的(P = 0.73,图2A)。
3.2. 离心力的大小与细胞伸长存在剂量效应
为了测试应力大小是否与细胞伸长存在剂量关系,在保持施加离心力时间不变的条件下,分别预设施力大小为1 g、11 g、25 g、50 g和80 g。图3结果表明,施力大小与细胞的定向伸长存在明显相关性(P < 0.01)。当施加力的强度低于10 g时,应力大小与细胞的定向伸长不具相关性。随着应力的增加,细胞沿同一轴向定向伸长的趋势增强。但是,当应力强度大于50 g时,细胞的活力明显降低,60%的细胞不发生任何膨胀,最后褐化死亡。
3.3. 施力时间与细胞伸长的关系
应力大小与细胞伸长存在一定的剂量关系,是否在相同力的条件下,施力时间也与细胞伸长存在相关性。为了证实这个假设,在施力大小为25 g恒定条件下,选定施力时间分别为15 min、30 min、3 h、6 h、9 h、12 h、24 h。图4结果表明,离心7~9 h后培养,细胞的伸长与应力的方向具有明显的相关性,低于这个时间。细胞伸长的相关性不明显。时间超过9 h后,细胞伸长的数量降低,细胞活力测定表明,
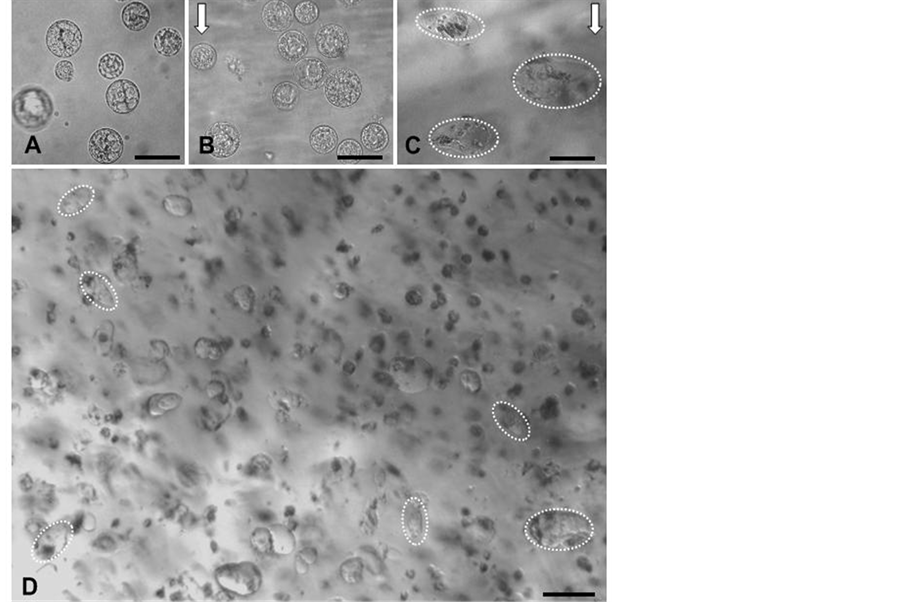
Figure 1. Microscopic observation of tobacco protoplasts embedded in agarose gel. (A) The protoplasts unloaded centrifugal force; (B) The protoplasts did not exhibit obvious plastic deformation immediately after loading 9 h. White arrow shows the orientation of centrifugal force; (C) After incubation for 4 d, the protoplasts tended to elongation with an axis perpendicular to the externally applied centrifugal force. The white dotted ellipses show the cell’s outline. White arrow shows the orientation of centrifugal force; (D) The orientation of the protoplasts elongation is random under the culture for 4 d without loading centrifugal force. The white dotted ellipses show the cell’s outline. Bar = 20 μm in (A), (B), (C) and Bar = 30 μm in (D)
图1. 烟草原生质体包埋琼脂块中施力前后显微图像。A图为离心前的状态;B图为离心9 h后培养前的状态,原生质体没有明显的形变,白色箭头示力的方向;C图为离心后培养4 d的细胞,细胞伸长的方向倾向与应力方向垂直,白色椭圆虚线示细胞轮廓,白色箭头示应力方向;D图为没有施加应力培养4 d的细胞,白色椭圆虚线示部分细胞的轮廓。图A、B、C中Bar = 20 μm,图D中的Bar = 30 μm
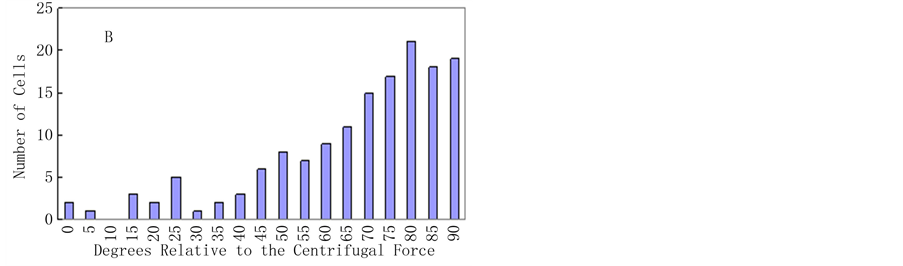
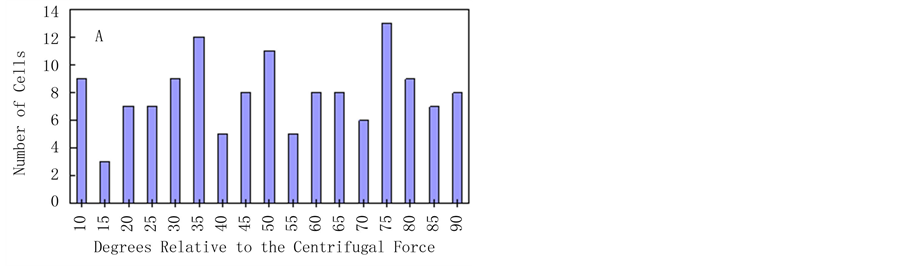
Figure 2. Distributions of the axis of elongation of regenerated protoplasts cultured for 4 d. The axis of elongation, relative to the direction of the centrifugal force, was measured for >150 cells per experiment. Values represent the sum of four separate experiments. (A) Cells that were not centrifuged. P = 0.73; (B) Cells that were centrifuged for 9 h. P = 0.001. The P values indicate the probability that the distributions are random
图2. 烟草原生质体培养4 d后细胞伸长轴与应力方向夹角分布图。图A为未施力情况。P = 0.73;图B为施力后的情况,P = 0.001。实验数据统计150个细胞。夹角指椭圆长轴与应力面所形成的角度
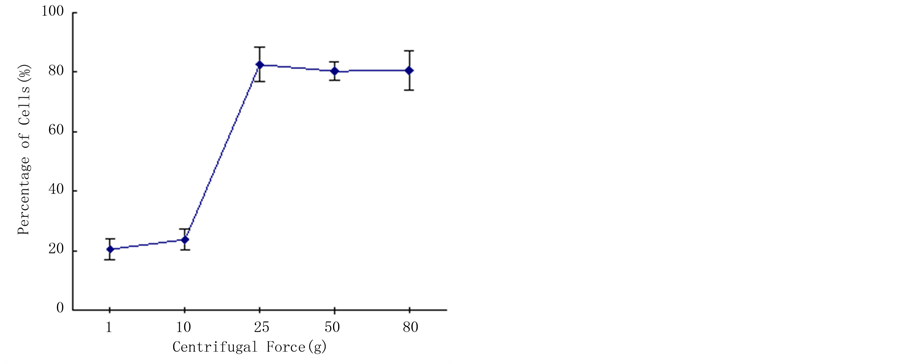
Figure 3. Effect of the intensity of loading force on the preferential orientation of embedded protoplasts
图3. 离心力强度对烟草原生质体伸长的影响
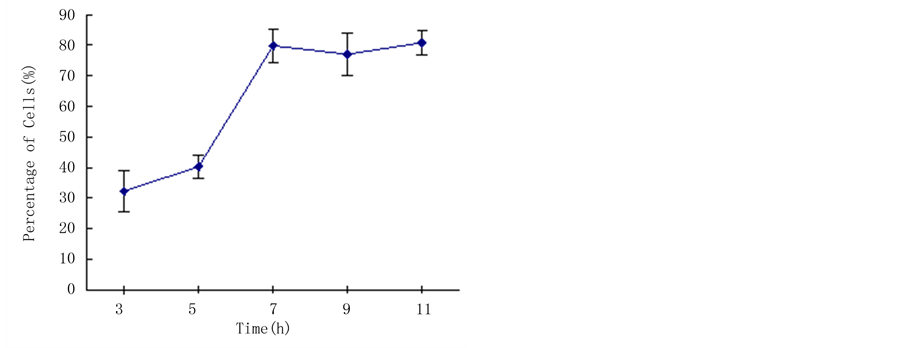
Figure 4. Effect of loading force time on the preferential orientation of embedded protoplasts
图4. 施力时间对烟草原生质体伸长的影响
细胞的活力下降,培养过程中部分细胞逐渐死亡。
3.4. 原生质培养过程中细胞壁合成的时间进程
实验表明,在恒定应力条件下,细胞定向伸长与施力的时间存在相关性。为了证实细胞定向伸长是否要求细胞具有完整的细胞壁来固定细胞发育轴向并通过细胞壁-质膜-骨架这个整体来参与应力响应过程。实验采用荧光染料Calcofluor White(荧光增白剂)确定烟草原生质体培养过程中新细胞壁合成进程。结果表明,烟草原生质体从2 h开始合成新的细胞壁(图5A),随着细胞的进一步培养,新合成的细胞壁以patch的形式沉积在细胞表面(图5B~E)。直到7~8 h后,整个原生质体表面出现均匀的荧光(图5F~H),说明细胞表面新的细胞壁合成完全。
3.5. 微管骨架与离心力之间的关系
前人研究表明,细胞定向伸长与细胞骨架系统存在一定联系。为了证实细胞骨架对应力的响应导致微管重排,从而引起细胞定向伸长的行为。实验以微管结合蛋白与GFP构成融合蛋白的转基因烟草为材料。实验表明,微管骨架在施力前,细胞核处于细胞的中央,微管从细胞核表面向细胞周质呈网状放射性排列(图5I~J)。施力后,细胞核逐渐位移偏向细胞的一端,且微管呈成束状排列趋向平行于应力的方向
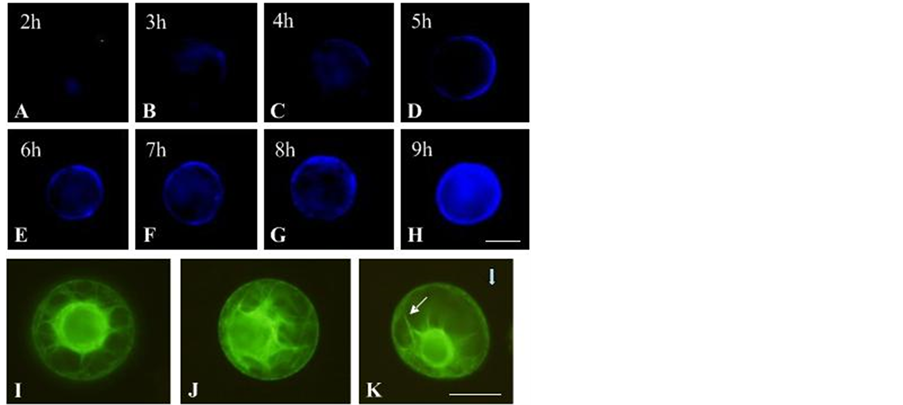
Figure 5. Change of cell wall synthesis during the course of tobacco protoplast culture and cortical microtubules reorientation protoplasts subjected to a centrifugal force. (A)-(H) Showed the change of cell wall synthesis that was stained with Calcofluor White every 1 h during the course of protoplasts culture; (I)-(K) Showed the change of cortical microtubule; (I)-(J) Indicated uncentrifuged protoplasts have cortical microtubules that arranged in a random configuration; (K) showed that cortical microtubules are arranged in a relatively parallel configuration relative to the centrifugal force. The white thick arrow shows the orientation of centrifugal force, and the thin arrow shows that the microtubule bundles. Bar = 20 μm
图5. 烟草原生质体培养过程细胞壁合成的时间进程与微管变化图。图A~H为细胞壁合成时间进程,原生质体培养过程中每隔1 h取样,荧光染料Calcofluor White显示新合成的细胞壁。图I~K为原生质体受力前后微管骨架的变化,图I~J为受力前微管的分布,微管从细胞核表面向细胞表面呈网状排列,图K显示原生质体受力后的微管骨架分布,主要微管成束状与应力方向平行,白色粗箭头示应力方向,细箭头示。Bar = 20 μm
(图5K)。这一结果与前人报道结果相同[11] 。
4. 讨论
目前,已有很多工作在植物组织、器官和细胞水平上采用不同的实验方法探讨了植物细胞对外界应力响应的生物学反应,结果表明外界应力与植物细胞的生长发育存在明显的关联性[12] 。本文以离心力作为外在的机械应力,测试了不同强度的应力以及在恒定应力条件施力时间对植物细胞的活力和细胞定向伸长的影响,结果表明外界应力与细胞的伸长反应存在剂量依赖的关系。随着应力的增强,细胞的活力降低,推测可能是由于植物细胞难以通过生理补偿应对极性生理损伤而产生一种自主凋亡[7] [13] ,这需要实验进一步证实。植物在整个生长环境中随时都受到来自外界或细胞间的应力作用,而这些力通常是长期起作用的。为了验证外界应力是在瞬时或者短时能否引起细胞产生形变响应,实验检测施力不同时间下细胞形变状况,施力后细胞培养起始时期,细胞的形态未发生明显塑性形变,与未施力下的形态一样保持原生质体的圆形状。这表明,细胞的定向伸长不是由于外界应力导致细胞本身形变而引起的,而是细胞感受外界应力信号后为将来的细胞伸长提供指导性信息。实验结果还表明,细胞对外界应力信号的感应不是瞬时过程,而是有一定的累积效应。有研究表明,对烟草细胞施加15 min的离心力后,细胞就能以倾向性的定向伸长响应力学信号[11] 。然而,本实验多次结果表明,对细胞的施力时间至少在6小时左右才能更好地表现出细胞倾向性定向伸长与应力的相关性。植物细胞形状的控制需要细胞壁的伸展性和刚性等综合因素作用,细胞壁能为完整细胞的形状提供物理限制[14] 。实验对原生质体细胞壁合成的时间进行研究表明,新细胞壁的完全再生,与应力条件下原生质体的倾向性伸长是一致的,这就暗示细胞对应力的响应要求细胞结构的完整性从而影响细胞的进一步发育。
对动物细胞研究表明,动物细胞外部应力与细胞骨架张力作用的位点位于细胞表面的黏附点,包括细胞间的黏附和细胞与胞外基质的黏附[15] 。这暗示细胞质和胞外基质的联系与细胞的发育有关。细胞壁–质膜–微管骨架是植物细胞生长发育的完整统一体。许多研究已证实机械应力对植物细胞周质微管产生较大影响[16] -[18] 。本实验结果也证实了外界应力引起细胞微管骨架系统的重排。尽管没有明显证据表明周质微管的重排与外界应力施加时间之间的对应关系,但是毋庸置疑的是细胞骨架与细胞壁明显构成植物细胞完整的功能整体。在应力响应事件中,微管作为细胞内物质运输的轨道,它感受外界应力后引起的重排,可以指导新合成细胞壁的沉积位点。
项目基金
湖北省教育厅杰出中青年基金(Q20081013)和国家自然科学基金(30970279)资助。

NOTES
*通讯作者。