1. 引言
交通拥堵已经成为当今城市交通的通病,也是令交通管理部门最为头疼的问题。
造成我国城市交通拥堵现状的原因是多方面的;表面上看来,主要是由于大中城市交通需求增长过快而导致的交通供需失衡,同时,部分城市的路网结构不合理、不同交通方式增长缺乏有效协调也加剧了城市交通拥堵,在造成巨大经济损失的同时也给出行者带来了很多苦恼。然而,交通领域的专家则指出,对大中城市交通复杂系统特征及交通流演化机理认识不清、交通规划、管理与控制缺乏科学的理论指导才是造成这一现象的深层次原因。
城市交通系统是一切城市活动的载体,是整个城市系统赖以存在和发挥效能和物质基础。城市交通流系统是由人、车、路三要素构成的动态、开放的复杂巨系统,同时还受到交通控制子系统、交通诱导信息以及所处环境等诸多因素的影响,表现出了极其复杂的演化规律。近年来的研究表明,交通流系统具有动态性、随机性、非线性、时空相关性等突出特征,同时也存在混沌、自组织、涌现等复杂行为。实际的交通流系统中,时常呈现出来众多的复杂交通现象,如幽灵塞车、时停时走、宽运动阻塞、同步流等。交通流理论是研究交通流状态随时间和空间变化规律的模型和方法体系,可以揭示交通现象形成及演化的机理。针对这样的复杂巨系统,近年来兴起的复杂性科学是系统科学和非线性科学的进一步发展、充实和深化,是系统科学研究的最新、最前沿的领域。而其中的复杂网络方法为我们研究系统复杂性提供了一个新视角、新方法。
城市交通系统一般由道路子系统、流量子系统以及管理子系统组成;相应地复杂性研究工作涉及到整个构成系统的方方面面。当前的研究工作多集中于道路子系统的复杂性研究,例如城市道路网络的复杂性特征及演化过程等。针对流量子系统(交通流系统)的复杂性研究成果尚不多见[1] -[6] 。
本文旨在分析我国城市交通流现状的基础上,从复杂性科学的视角及研究方法入手,探究城市交通流系统时空和行为复杂特性的成因,并进一步指出城市交通流系统复杂性的研究思路。
2. 城市交通流分析
2.1. 城市交通现状
城市交通的突出问题就是普遍存在于世界各国城市当中的交通拥堵。可以说,城市交通拥堵,到处都有,只是程度不同。交通拥堵致使城市环境日益恶化,行车速度降低,行车时间及耗油量明显增加;同时也增加了汽车尾气排放量,加剧了城市当中的环境恶化。尾气和噪声这两个交通污染源已成为世界各大中城市主要的污染源,严重的交通拥堵所造成的经济、安全和环境等方面的重大损失已引起社会的广泛关注,也是世界各国需要共同面对的难题。
美国得克萨斯州运输研究所曾对美国39个主要城市进行研究,估算美国每年因交通拥堵而造成的经济损失大约为410亿美元,12个最大城市每年的损失均超过10亿美元。2005年,美国因交通拥堵而造成的延误预计将超过110亿小时,预计到2020年,因交通问题而造成的损失每年将超过1500亿美元。俄罗斯首都莫斯科常住人口约1056万,市区面积约1081平方公里,各种汽车的保有量约400万辆。莫斯科的道路拥堵问题也相当严重,行车难问题已成为影响民众生活质量和社会经济发展的一大障碍。巴西圣保罗市曾被《时代》周刊杂志评价为全球交通最糟糕的城市。近年来,圣保罗商用车销售数量飞涨,每天都有大约1000辆新车上路。高峰时间,整条堵车长龙可以排到120英里以外。墨西哥城是世界堵车最为严重的城市之一,每天有700至800万辆机动车在路上行驶,每年新增机动车数量达到25万辆。
我国当前正迈入汽车大众消费阶段,汽车总量特别是私人小汽车的数量急剧增加;而另外一方面,我国现有城市路网一般都是密度低、干道间距过大、支路短缺、功能混乱,属于低速的交通系统,难以适应现代汽车交通的需要,阻碍着汽车化在城市中的实现。可以看到,中国各大城市交通拥堵日趋严重,并且开始由城市中心区向郊区蔓延;中小城市也普遍出现了交通拥挤现象。2010年,中国科学院可持续发展战略研究组首席组长、科学家牛文元的研究成果表明,因为交通拥堵和管理问题,中国15座城市每天损失近10亿元财富。
我国各主要城市的道路都在超负荷运转,其中部分城市的道路饱和度如表1所示。道路饱和度越大说明交通拥堵越严重,交通流密度越大,行车速度越慢。
而与此同时,我国的交通需求还将进一步快速增长。表2说明了我国部分城市机动车保有量状况(截止2012年)。
此外,我们以收集到的1991年至2012年的我国机动车保有量数据为基准(数据来源为历年中国统计年鉴等),采用多项式拟合(三次)的方式对未来五年机动车保有量趋势进行预测。所有的操作都在Excel 2007中完成,结果如图1所示。
从图中可以看出,较之当前,未来的机动车保有量将会迅速增长。而这些机动车都将对道路形成需求,而我国城市的国土资源是有限的,道路的供给是有限的,再加之城市道路共有资源的特性,道路的过度使用和随之而来交通拥堵问题必将在现有的政策框架下产生。也就是说,未来的交通需求与交通供给之间的矛盾将会进一步突显,城市交通拥堵的治理压力巨大。

Table 1. Road saturation of some cities
表1. 部分城市道路饱和度

Table 2. Car ownership of some cities (millions)
表2. 部分城市机动车保有量(万辆)

Figure 1. Forecasting amount of car ownership from 2013 to 2017
图1. 2013~2017年汽车保有量预测
针对城市交通拥堵,世界各国也都采取了一些积极主动的治理措施,但是治理效果都不够理想,其中的原因之一就是对城市交通流系统的动态性和时空复杂特性等本质认识不足,从而无法从交通科学的角度根治城市交通拥堵这一顽疾。日益严重的城市交通拥堵和收效甚微的拥堵治理策略,迫使我们认真研究城市交通流系统复杂性的根源所在,从而制定更为科学有效的拥堵治理策略。同时,这也是交通科学研究工作当中的关键性基础理论问题之一。
2.2. 城市交通流特性分析
在道路上行驶的车辆群称为交通流,不同的交通流表示不同的车辆群体运行状态。通常情况下,可以选用速度、流量和密度三个参量来描述交通流状态。一般说来,城市交通流具有如下一些特性:
1) 时空分布易变。城市交通流系统状态会随着时间与空间的变化而不断变化。除此之外,交通流状态也会受到一些人为因素及环境因素的影响,如一辆车驾驶失误,可以引起后随车辆车速和车间距离出现很大改变。
2) 变化呈现出随机性。描述交通流状态的相关参量表现出一定的随机特性,给相应的预测工作带来挑战。交通流状态参量符合一般条件下的统计规律,可以用统计方法研究其分布特性,进而揭示交通流的时空分布特征。
3) 拥堵表现出一定的可预见性。拥堵按照其产生的原因,可以分为“常发性”和“偶发性”两种。常发性拥堵是由于道路通行能力小于交通需求,拥堵产生的地点和时间都有规律性,一般在交通高峰和道路瓶颈处最易出现。偶发性拥堵由随机交通事件诱发,发生地点、时间都具有不确定性,还经常由此而产生交通事故,造成交通堵塞、车辆损坏、人员伤亡,是监控的重点。
特别地,我国城市交通流还普遍呈现出交通流量大,行车速度慢,交通密度大,道路饱和度高,机非人混行严重等特殊情况,这些情况与国外城市差别较大。这就要求我们要针对国内城市交通流复杂系统的实际情况展开研究,探求我国交通流系统复杂性的深层次成因。
3. 城市交通流系统复杂性成因
一般认为,复杂系统的整体现象源自于系统的规模与结构两部分。大城市交通流系统规模巨大,由出行者、道路、信号灯、环境等众多元素构成。同时,城市路网结构错综复杂,出行者数以万计且行为各异,环境复杂多变且难以预测,这些因素相互影响、共同作用,使得城市交通流系统呈现出众多复杂特性[7] 。总体来讲,城市交通流系统复杂性成因主要归结为四个方面,即个体出行者、城市路网、外部环境和多种要素间作用机理。复杂性成因的关系如图2所示。
3.1. 个体出行者影响因素
个体出行者是城市交通流系统构成的主体要素,出行者的出行动机、出行决策、在途行为等对交通流的演化过程影响较大。受限于复杂的决策背景、众多且难以量化的影响因素以及个体之间决策的差异性等原因,出行者的决策过程是一个复杂多变的过程,难以用一个统一的数学范式表示。准确理解人们的决策行为是解开城市交通流系统复杂性的理论基础。
决策科学的发展经历了三个阶段:即经验决策阶段、科学决策阶段和行为决策阶段。当前,现实当中的出行者决策主要依赖于经验决策;研究领域当中的主要理论基础是科学决策理论;有部分学者提出将行为决策理论引入出行者决策过程,开展出行决策研究[8] [9] 。
行为决策分析与建模考虑有限理性的决策框架,其典型代表理论为“前景理论”及“累积前景理论”。“前景理论”将风险型决策的效用评价体系从一般效用评价体系中区分出来,分为获得和损失两种情况对出行者的风险态度进行描述,其中有三条基本特征:1) 人们在评价某一结果的效用时,相对结果本身而言,通常对其相对于一个参考水平的偏离程度更敏感;2) 人们对损失的规避程度往往大于对相同收益的偏好程度;3) 由于“不完全理性”,人们无法准确评估事件的不确定性,从而过于重视极端的小概率事件,而忽视较常见的大概率事件。较之于科学决策的效用理论,行为决策的参考点依赖理论可以更为准确的描述现实中的出行选择行为。考虑有限理性人的出行决策规则,可以为研究者提供一种新的交通
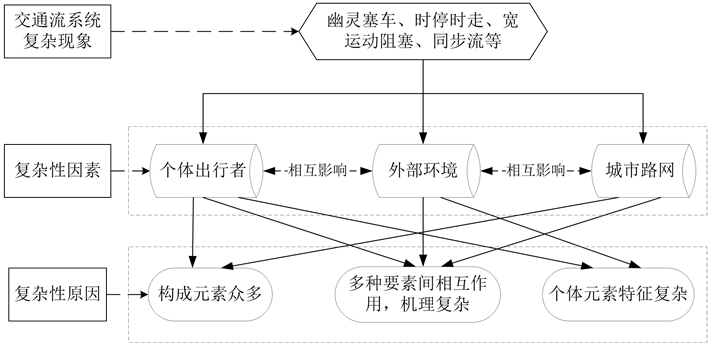
Figure 2. Relation schema of causes on complexity of urban traffic flow systems
图2. 交通流系统复杂性原因关系图
流复杂性分析范式。但是,有限理性人假设也并非完美无暇,尚存有很大的改进空间。
经济学理论认为当一项资源无需付费就能使用时,该资源将会被过度使用,具有这种性质的资源被称为共有资源,例如我国的城市道路。目前,消费者只要购买了汽车,无需付额外的道路使用成本便可以自由使用城市道路。消费者基于个人效用最大化,在出行时一定选择个人认为最优化的交通方式。于是,购买和使用小汽车成为越来越多人的选择。但是,基于个人效用最大化(个体理性)的选择的结果并非是集体效用的最大化(集体理性),而是相反,导致集体的非理性,其结果道路上的机动车越来越多,造成越来越严重的交通拥堵。
鉴于此,个体出行者决策过程的复杂多变以及绝对数量的不断增长,是造成城市交通流系统复杂性的原因之一。
3.2. 城市交通路网影响因素
城市道路网络构成了城市的骨架,是一个典型的点边构成的网络。构成城市路网的道路以及交叉口众多,而且道路及交叉口通行能力各异,所承担的载运功能也有所不同。
可以将道路抽象为网络当中的线,而将道路交叉口抽象为网络当中的节点;当然,有时为了研究的方便,也可以采用对偶抽象的方式。已有的研究结果表明,不同国家不同城市的道路网络在进行拓扑分析后,都可以将其抽象为无标度网络,并且表现出了小世界特性[6] 。城市交通网络具有绝大多数复杂加权网络的特征。从复杂网络的研究角度来看,城市交通网络具有网络连接的稀疏性、连接结构的复杂性、时间空间的复杂性(如混沌与分形)、网络节点(边)之间的同步运动等复杂特征。特别地,道路网络结构的不同,会很大程度的影响交通流运行特征及交通拥堵特性[10] [11] 。
城市道路网络是交通流的载体,交通流系统是运行在城市道路网络上的特殊复杂系统。交通流系统的动力学机制和演化机理与城市道路网络结构及特征密不可分。可以说,城市道路网络的复杂特性是城市交通流系统复杂特性的重要基础,而城市交通流系统复杂特性是城市道路网络复杂特性的集中体现。
3.3. 多种要素之间作用机理影响因素
如前所述,城市交通系统是由多种性质不同的要素组成,相应地,每一种要素的组成元素也有可能数以万计。更为重要的是,这些要素之间并不是孤立的;相反,它们之间相互影响、相互制约、共同作用,使整个交通流系统表现出极为复杂的非线性动力学特征。
更为重要的是,各种要素之间的作用机理目前尚处于研究之中。当我们将大量相互作用的微观元素构成的整体看作是一个完整的系统时,就会有一些全新的属性或者规律或者模式产生,这就是所谓的“涌现”思想[12] 。比如,出行者之间在出行方式选择、出行时间选择、路径选择等方面,依据出行情境的不同,分别构成了合作或者非合作博弈关系;又如,动态运行的交通流系统会明显受到城市道路网络的制约和出行者及一些外部环境的影响,但是定量的影响关系目前尚不知道;在先进出行者信息系统环境下,信息会对出行者的出行产生重要的影响,反之,出行者的出行行为也会改变交通信息本身所提供的内容,关于信息与出行者之间的相互作用机理也是当前研究的一个重要课题。诸多元素间的作用机理是城市交通流系统复杂性研究当中的难点。
针对多要素之间的相互作用机理,研究者们引入了元胞自动机、多Agent、复杂网络传播机制等多种研究方法,并在相应的研究领域内取得了显著成果,在一定程度上揭示了这些影响因素相互之间的作用机制及拥堵形成及传播机制。但是,科学准确的交通流多体系统之间的影响机理目前尚不明晰,“涌现”的过程及结果也有待于更深一步的研究。
3.4. 外部环境影响因素
城市交通流系统是一个处于自然环境与人类社会共同作用当中的开放式系统,其运行状态不可避免的受到外界环境因素的影响。来自于外部环境的影响因素众多,这些因素往往影响力较大且不可控制,诸如极端天气、自然灾害、交通事故、恐怖袭击、大型活动等多种情况。
外部环境的变化会直接影响到路网结构与功能的改变(如造成道路中断、信号灯暂停工作等),同时也影响到出行者的出行决策行为以及出行需求等。
当前的研究表明,人类在一些突发事件(包括常规及非常规突发事件)情境下,情绪、思维及理智程度都与正常情况下表现的大不相同。相应地,交通流运行状态及特征也与常态下的交通流特征存在显著差异。总体说来,城市交通流系统受外部环境因素的影响很大,时常表现出的大拥堵、大瘫痪往往都是由一些外部环境因素引起[13] -[15] 。针对涉及到城市交通流系统的外部环境因素,有必要专门进行研究,这是造成城市交通流系统复杂性的一大主要诱因。
4. 结束语
城市交通流系统复杂性研究涉及到复杂性科学、交通科学、交通工程、人类行为学、决策科学等诸多前沿学科,是一项富于现实意义且具有挑战性的研究课题。
本文分别从个体出行者、城市路网、多种要素间作用机理和外部环境四个方面探究了造成城市交通流系统复杂性的主要成因,指出了交通流系统复杂性研究工作的难点及重点。揭示交通流系统复杂性是交通科学的基础,也是交通问题研究分析的前提,直接决定着交通规划决策、运营管理控制及交通评价改进的执行效果。
基金项目
教育部人文社会科学研究青年基金项目(12YJC630200);甘肃省社科规划项目(13YD066);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(1308RJYA042)。