1. 引言
近年来,我国一些大中城市连续出现雾霾天气,环境质量引起人们的广泛深刻关注,成为社会公众热议的话题。而随着我国改革开放不断深化,国民经济持续快速发展,城市化、工业化进一步深入,我国城镇居民人均收入持续快速增长的同时,工业和生活“三废”(废水、废物和废气)的排放对我国环境质量造成了重大影响,这也是我国城镇居民医疗支出逐年攀升的重要因素之一。2007年,中国社会科学院发布了《社会保障绿皮书》。书中指出,从1990年至2004年的十五年间,中国城镇居民人均可支配收入增加了五倍多,与此同时,城镇居民的人均医疗保健费用却增加了将近二十倍,城镇居民医疗支出的增加速度远远超过其收入的增速。环境质量的下降对医疗支出的影响机制以及影响程度,这种影响是否因时期和地区的不同而存在差异都是我们研究的议题。本文将通过引入相关环境指标来刻画环境质量,建立统计模型来分析其中的数量经济关系,从而为我国未来经济、环境政策的制定提供良好建议和有力参考。
2. 研究现状与问题提出
2.1. 研究现状
在医疗支出及其影响因素的研究方面,国外学者[1] -[4] 研究的比较深入全面,无论在理论上还是在实证上。其中主要考虑的因素有:居民收入、生命周期、医疗保险、教育水平、医疗服务价格等影响因素。国内学者在国外已有研究的基础上,基于我国的实际国情做了针对性研究。徐润(2010)采用Grossman的健康资本需求模型,以面板数据为基础,对居民医疗支出的相关影响因素进行了实证分析。分析结果显示:城乡居民医疗支出的收入弹性确实存在差异,且农村高于城市;出生率和平均住院时间与农村居民医疗支出的关系不显著,与城市居民的医疗支出显著正相关;城市化率与城镇和农村的医疗支出均显示出正相关关系;老龄化和医生数与城镇居民医疗支出的相关关系不显著,但是与农村居民的医疗支出显示出正相关关系;教育水平、政府预算与城镇和农村居民医疗支出的关系均不显著。林相森和舒元(2007)[5] 在中国健康和营养调查2000年的调查数据的基础上,把医疗支出发生的过程分解为患病和治病两个阶段进行实证研究。研究结果指出对医疗支出影响最大的因素是地区的差异、是否居住在城镇、是否有医疗保险。何平平(2007)的研究指出医疗支出的增加是经济增长、人口老龄化、医疗保险的普及率、医疗技术进步和政府投入等因素相互作用的结果。以上研究揭示了对医疗支出产生影响的各个因素,但是都没有考虑环境质量的恶化对医疗支出的影响。而且,这类环境质量研究在一定程度上是对医疗支出与收入的计量经济学模型的扩展。
目前,对医疗支出的研究,引入环境因素进行考察的文章并不多。何明和王云敏(2011)[6] 以每平方米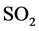 排放量作为环境污染的代理变量,将选定的29个地区分为两个部分分别建模,探讨了环境污染与医疗支出的数量关系。徐东林和陈永伟(2010)[7] 将工业二氧化硫排放量作为环境质量的代理变量,把全国各城市自治区按经济的发达程度将全国各省市自治区分为东部、中部和西部三个部分,实证结果证明,环境质量对城镇居民医疗支出的影响在我国东部、中部和西部各地区均为正值,环境质量的下降对我国城镇居民医疗支出有显著影响,说明环境恶化对我国城镇居民的健康状况有负面影响。
排放量作为环境污染的代理变量,将选定的29个地区分为两个部分分别建模,探讨了环境污染与医疗支出的数量关系。徐东林和陈永伟(2010)[7] 将工业二氧化硫排放量作为环境质量的代理变量,把全国各城市自治区按经济的发达程度将全国各省市自治区分为东部、中部和西部三个部分,实证结果证明,环境质量对城镇居民医疗支出的影响在我国东部、中部和西部各地区均为正值,环境质量的下降对我国城镇居民医疗支出有显著影响,说明环境恶化对我国城镇居民的健康状况有负面影响。
2.2. 问题提出
本模板本文在以上研究的基础上,做了进一步深入研究探讨。第一,在刻画环境质量时,不仅考虑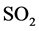 的排放量,也加入了其他众多环境指标作为其代理变量,比如:空气中的烟(粉)尘,工业和生活废水、废物等固体垃圾。尤其是近年来很多大中城市连续出现雾霾天气,雾霾的形成原因是由于大量极细微的尘粒、烟粒、盐粒等均匀地浮游在空中,使有效水平能见度小于10千米的空气混蚀的现象。人的呼吸道吸入霾后会对肌体产生伤害,严重会致死。大量有毒有害废水和废物排放后如不能及时处理,其中的各种物质会随雨水会随雨水沥滤进入土壤或者流入河流。沥滤进入土壤会污染人类赖以生存的地下水,流入河流会影响地表水中的动物,人类食用后会对人体造成极大危害。废水和废物通过发出恶臭、毒气、微粒扩散、自燃、焚烧方式等污染大气。在大量废水池和垃圾露天堆放的场区,臭气冲天,老鼠成灾,蚊蝇滋生,有大量的氨、硫化物等污染物向大气释放。在粉煤炭及尾矿堆放场,如遇四级以上大风,灰尘可飞扬20~50米,其表面可剥离1~1.5厘米,造成空气污染。因此,空气中的烟(粉)尘,工业和生活废水、废物等因素对医疗支出都有重要影响。用单一的二氧化硫对环境质量的刻画显然不够全面,因此加入更多的环境质量指标更具科学性。第二,在对全国各省市自治区分类时对各地区的环境状况的差异作进一步科学划分,不仅考虑各个地区经济发达程度,也考虑环境状况的实际差异,这种通过数据指标的地区划分来探讨研究环境质量对医疗支出的影响机制分析更合理。
的排放量,也加入了其他众多环境指标作为其代理变量,比如:空气中的烟(粉)尘,工业和生活废水、废物等固体垃圾。尤其是近年来很多大中城市连续出现雾霾天气,雾霾的形成原因是由于大量极细微的尘粒、烟粒、盐粒等均匀地浮游在空中,使有效水平能见度小于10千米的空气混蚀的现象。人的呼吸道吸入霾后会对肌体产生伤害,严重会致死。大量有毒有害废水和废物排放后如不能及时处理,其中的各种物质会随雨水会随雨水沥滤进入土壤或者流入河流。沥滤进入土壤会污染人类赖以生存的地下水,流入河流会影响地表水中的动物,人类食用后会对人体造成极大危害。废水和废物通过发出恶臭、毒气、微粒扩散、自燃、焚烧方式等污染大气。在大量废水池和垃圾露天堆放的场区,臭气冲天,老鼠成灾,蚊蝇滋生,有大量的氨、硫化物等污染物向大气释放。在粉煤炭及尾矿堆放场,如遇四级以上大风,灰尘可飞扬20~50米,其表面可剥离1~1.5厘米,造成空气污染。因此,空气中的烟(粉)尘,工业和生活废水、废物等因素对医疗支出都有重要影响。用单一的二氧化硫对环境质量的刻画显然不够全面,因此加入更多的环境质量指标更具科学性。第二,在对全国各省市自治区分类时对各地区的环境状况的差异作进一步科学划分,不仅考虑各个地区经济发达程度,也考虑环境状况的实际差异,这种通过数据指标的地区划分来探讨研究环境质量对医疗支出的影响机制分析更合理。
本文回顾了以往学者[8] [9] 提出了很多关于医疗支出的研究方法。通过引入环境质量的指标变量来构造医疗支出与环境质量、居民人均可支配收入之间的关系模型。在以往学者研究的基础上,进一步丰富了环境质量的刻画指标,选取了工业和生活废水排放总量、固体垃圾排放总量、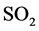 排放总量以及烟(粉)排放总量作为环境质量的代理变量,利用面板数据的系统聚类方法对2003~2011年全国31个省市自治区面板数据把全国各地区分类,然后再用面板模型分别对各类地区进行分析,并找出各类地区的影响医疗支出的主要因素和区别。
排放总量以及烟(粉)排放总量作为环境质量的代理变量,利用面板数据的系统聚类方法对2003~2011年全国31个省市自治区面板数据把全国各地区分类,然后再用面板模型分别对各类地区进行分析,并找出各类地区的影响医疗支出的主要因素和区别。
3. 实证模型说明及估计
3.1. 数据来源及变量说明
实证分析所使用的数据摘自2003~2011年国家统计局统计年鉴。包括各地区城镇居民人均医疗支出(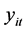 ),人均收入(
),人均收入(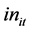 ),废水排放量,工业废物排放量,生活垃圾清运量,废气中二氧化硫排放量和废气中烟(粉)尘排放量,其中人均医疗支出为门诊病人人次均医疗费与出院病人人均医药费之和。经过相关分析发现废水排放量,工业废物排放量,生活垃圾清运量,废气中二氧化硫排放量和废气中烟(粉)尘排放量这些指标之间有较强的相关性,如果把这些指标都作为解释变量对被解释变量回归时就会产生多重共线性问题,从而会影响模型的估计效果,因此对环境指标进行了处理。根据相关分析的结果,把废气中二氧化硫和废气中烟粉尘合并为空气中的影响因素(
),废水排放量,工业废物排放量,生活垃圾清运量,废气中二氧化硫排放量和废气中烟(粉)尘排放量,其中人均医疗支出为门诊病人人次均医疗费与出院病人人均医药费之和。经过相关分析发现废水排放量,工业废物排放量,生活垃圾清运量,废气中二氧化硫排放量和废气中烟(粉)尘排放量这些指标之间有较强的相关性,如果把这些指标都作为解释变量对被解释变量回归时就会产生多重共线性问题,从而会影响模型的估计效果,因此对环境指标进行了处理。根据相关分析的结果,把废气中二氧化硫和废气中烟粉尘合并为空气中的影响因素(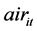 ),把废水,工业废物和生活垃圾合并为地面的影响因素(
),把废水,工业废物和生活垃圾合并为地面的影响因素(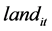 )。那么所使用面板即由2003~2011年31个省市自治区9年的人均医疗支出,人均收入,空气中的影响因素和地面中的影响因素4个指标构成,共1116个数据。
)。那么所使用面板即由2003~2011年31个省市自治区9年的人均医疗支出,人均收入,空气中的影响因素和地面中的影响因素4个指标构成,共1116个数据。
3.2. 模型设定
3.2.1. 面板数据单位根检验
对四个变量用ADF统计量检验可得:人均医疗支出(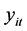 ),人均收入(
),人均收入(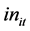 ),空气中的影响因素(
),空气中的影响因素(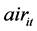 )和地面中的影响因素(
)和地面中的影响因素(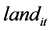 )4个指标都是一阶单整的。因此用人均医疗支出作为被解释变量,人均收入,空气中的影响因素和地面中的影响因素作为解释变量建立面板模型是可行的。
)4个指标都是一阶单整的。因此用人均医疗支出作为被解释变量,人均收入,空气中的影响因素和地面中的影响因素作为解释变量建立面板模型是可行的。
面板模型一般可以分为三类,混合模型,变截距模型和变系数模型[10] 。用协方差分析的方法对模型的设定进行检验。经过计算得到的两个F统计量分别为
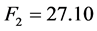
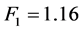
查F分布表,在给定5%的显著性水平下,得到相应的临界值为
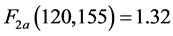
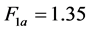
由于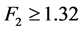 ,所以拒绝不变系数模型的假设,由于
,所以拒绝不变系数模型的假设,由于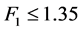 ,所以不拒绝变截距模型的假设。因此,模型采用变截距的形式。又经过Hausman检验拒绝原假设(随机效应模型),最终选择个体固定效应模型。
,所以不拒绝变截距模型的假设。因此,模型采用变截距的形式。又经过Hausman检验拒绝原假设(随机效应模型),最终选择个体固定效应模型。
3.2.2. 聚类分析方法
由于31个省市自治区的环境质量既有相似的一部分也有差异比较大的一部分。对这31个省市自治区用环境指标和人均收入结合起来对其进行分类,用面板数据的聚类分析方法把31个省市自治区分为成三类。
聚类分析就是将数据分组成为多个类。在同一个类内对象之间具有较高的相似度,不同类之间的对象具有较大的差别。聚类分析已经被广泛应用到各种领域中,其中,系统聚类法是最常用的聚类分析方法。系统聚类首先要确定点和点之间的距离,这可以用欧氏距离、平方欧氏距离、绝对值距离、夹角余弦、相关系数、Minkowski距离等。此外还要定义类间距离,采用的方法包括最短距离法、最长距离法、类平均法、重心法、离差平方和法等。这些选项不同,结果也可能不同。在确定了各种距离的选择之后,系统聚类一开始每一个观测值点都算为一类,这样,有多少观测值就有多少类。系统聚类首先把最近的两类划分为一类,这样总类数就减少了一个,然后把最近的两类划分到一起,这样类数就又少了一个,如此下去,当只剩下一类时,系统聚类就完成了[11] 。
传统的系统聚类分析对象一般是针对固定时期的不同个体的横截面数据,而面板数据同时具有时间序列特征和横截面数据特征,二维数据聚类分析往往不能满足人们分析问题的需要,而且基于单一的固定时期的聚类分析往往抹杀了指标的动态发展趋势及其发展状况,无法预测其未来发展轨迹和所属类别。
聚类分析需要解决两个核心问题[12] [13] 。一个是:如何衡量样本见的相似度,另一个是:采用何种聚类方法。下面将展示多指标面板数据将如何解决这两个问题。
相似性度量
从一组相当复杂的数据产生一个简单的分类结构,必要定义一个“相似性”测量度量指标,当对样本进行聚类分析时,样本间的“相似性”可以用距离来刻画。总体中第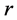 个样本和第
个样本和第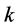 个样本之间的距离记为
个样本之间的距离记为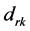 。
。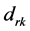 应该满足一下三个条件:
应该满足一下三个条件:
(1)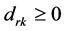 ,当且仅当
,当且仅当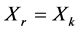 时,
时,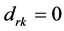 ;
;
(2)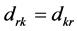 对一切
对一切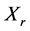 ,
,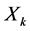 均成立;
均成立;
(3) ,对一切
,对一切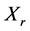 ,
,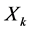 ,
,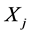 均成立。
均成立。
其中,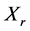 、
、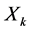 代表样本数据,本例中指代各种污染指标以及人均收入。
代表样本数据,本例中指代各种污染指标以及人均收入。
常见的刻画样本间“相似度”的距离有绝对值距离等上文提到的六种距离。本文经过试算后选择欧式距离来描述样本之间的“相似度”。当然,在加入时间维度后的多指标面板数据与横截面数据的欧氏距距离是有差异的,郑云兵(2008)[14] 称之为“欧式时空距离”,被重新定义为:
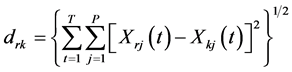 (1)
(1)
基于上面的公式,全体样本两两之间的距离就形成了一个距离矩阵,显然,该距离矩阵是一个对称矩阵,且对角线元素均为0,这里用一个下三角矩阵来表示距离矩阵:
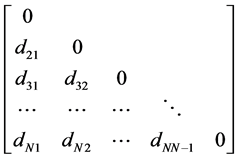

聚类方法
系统聚类分析的第二个问题是采用何种聚类方法,即采用哪种准则将不同类合并成一个新类,常用的系统聚类方法有最短距离法等上文提到的五种系统聚类方法。本文经过试算后采用离差平方和法(Ward Method)来对原始数据进行分类。同“相似度”一样,多指标面板数据的Ward法和横截面数据的Ward法也有所不同,记第 类样本间的离差平方和为,郑云兵(2008)[14] 构造的函数为:
类样本间的离差平方和为,郑云兵(2008)[14] 构造的函数为:
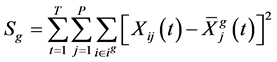 (2)
(2)
其中,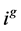 表示第
表示第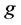 类中所有样本序号的集合;
类中所有样本序号的集合;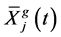 表示第
表示第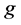 类所有样本第
类所有样本第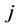 个指标在
个指标在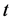 时间的平均值。
时间的平均值。
Ward法认为当两类合并时增加的离差平方和可以作为度量这两类之间的距离,并将有最小的离差平方和增量的两类优先合并。在合并时,当有离差平方和增量相等的情况出现时,应该分别同时合并。经郑云兵(2008)推导,在合并第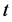 类和第
类和第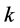 类时,他们之间的距离函数为:
类时,他们之间的距离函数为:
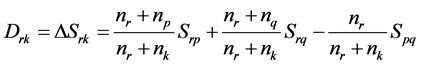 (3)
(3)
其中,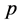 和
和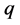 表示第
表示第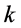 类的两个样本,
类的两个样本,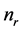 表示第
表示第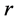 类的样本数量,
类的样本数量,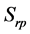 表示第
表示第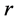 类与第
类与第 类合并成的新类的离差平方和,其它符号有类似的意义。
类合并成的新类的离差平方和,其它符号有类似的意义。
3.3. 聚类分析结果
基于上面介绍的多指标面板聚类分析方法,把全国31个省市自治区进行多指标面板聚类分析,其聚类谱系图如图1所示。
分类结果为
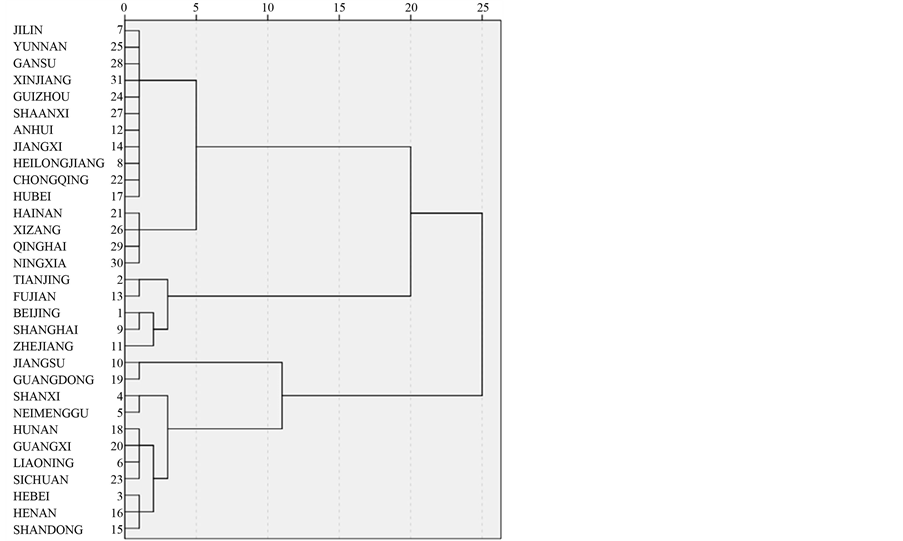
Figure 1. Hierarchical diagram
图1. 聚类谱系图
第一类:吉林,云南,甘肃,新疆,贵州,陕西,安徽,江西,黑龙江,重庆,湖北,海南,西藏,青海,宁夏;
第二类:天津,福建,北京,上海,浙江;
第三类:江苏,广东,山西,内蒙古,湖南,广西,辽宁,四川,河北,河南,山东。
3.4. 聚类分析结果
根据面板数据聚类分析的结果,建立变截距个体固定效应的面板模型,模型形式如下:
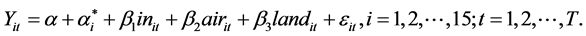 (4)
(4)
式中: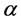 为15个省市的平均医疗支出,
为15个省市的平均医疗支出,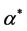 为
为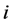 地区由于各个因素影响而对平均医疗支出的偏离,用来反映省市间的医疗支出的结构差异。本模型采用普通最小二乘LS方法对模型进行估计[15] 。
地区由于各个因素影响而对平均医疗支出的偏离,用来反映省市间的医疗支出的结构差异。本模型采用普通最小二乘LS方法对模型进行估计[15] 。
模型1是针对吉林,云南,甘肃,新疆,贵州,陕西,安徽,江西,黑龙江,重庆,湖北,海南,西藏,青海,宁夏等15个地区,建立变截距个体固定效应的面板模型,估计结果为:(表1)
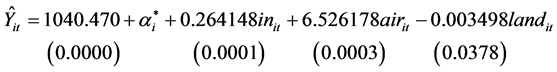 (5)
(5)
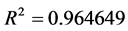
同理模型2:针对天津,福建,北京,上海,浙江5个地区建立变截距个体固定效应的面板模型。模型估计结果如下:(表2)
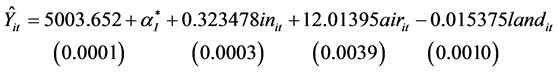 (6)
(6)
同理模型3:针对江苏,广东,山西,内蒙古,湖南,广西,辽宁,四川,河北,河南,山东等11个地区建立变截距个体固定效应的面板模型。模型估计结果如下:(表3)
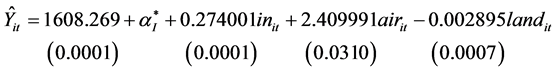 (7)
(7)
以上三个模型的各个参数系数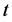 检验的
检验的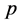 值在给定显著性水平下(
值在给定显著性水平下(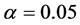 )是有效的。并且三个模型的可决系数
)是有效的。并且三个模型的可决系数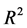 分别是0.96,0.98,0.96,均大于0.9,说明三个模型在不同分类的情况下,拟合优度很高。由DW值的结果看,自变量之间无自相关,所以模型效果良好。
分别是0.96,0.98,0.96,均大于0.9,说明三个模型在不同分类的情况下,拟合优度很高。由DW值的结果看,自变量之间无自相关,所以模型效果良好。

Table 1. The estimation of 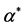 in the model 1
in the model 1
表1. 模型1中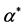 的估计结果
的估计结果

Table 2. The estimation of 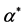 in the model 2
in the model 2
表2. 模型2中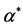 的估计结果
的估计结果

Table 3. The estimation of 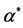 in the model 3
in the model 3
表3. 模型3中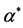 的估计结果
的估计结果
4. 实证模型分析
对吉林,云南,甘肃,新疆,贵州,陕西,安徽,江西,黑龙江,重庆,湖北,海南,西藏,青海和宁夏15个地区而言,从模型1的输出结果可以得出,2003~2011年,人均收入每增加一元,医疗支出则增加0.264元。由于空气中的影响因素和地面上的影响因素的系数显著不为零,说明这15个地区的空气中的影响因素和地面上的影响因素对医疗支出的影响具有统计上的显著性,空气中的二氧化硫和烟粉尘的总量增加(减少)一吨,则人均医疗支出增加(减少)6.526元。
对天津,福建,北京,上海,浙江5个地区而言,从模型2的估计结果可以得出,2003~2011年,人均收入每增加一元,医疗支出则增加0.323元,由于空气中的影响因素和地面上的影响因素的系数显著不为零,说明这5个地区的空气中的影响因素和地面上的影响因素对医疗支出的影响具有统计上的显著性,空气中的二氧化硫和烟粉尘的总量增加(减少)一吨,则人均医疗支出增加(减少)12.014元。
对江苏,广东,山西,内蒙古,湖南,广西,辽宁,四川,河北,河南,山东等11个地区而言,从模型3的估计结果可以得出,2003~2011年,人均收入每增加一元,医疗支出则增加0.274元,由于空气中的影响因素和地面上的影响因素的系数同样也是显著不为零,说明这11个地区的空气中的影响因素和地面上的影响因素对医疗支出的影响具有统计上的显著性,空气中的二氧化硫和烟粉尘的总量增加(减少)一吨,则人均医疗支出增加(减少)2.41元。
比较者以上三个模型可以得出,划分的三个类别中,人均收入对医疗支出的影响效果大体是相当的,具有较强的一致性,影响系数大约都为0.3,也就是说一元的收入中会有0.3元作为医疗方面的支出,符合现实情况。而空气中的影响因素对医疗支出的影响在这三类中的差异比较大,影响最大的是天津,福建,北京,上海,浙江5个地区,系数为12.01395,原因可能有:一、地区人口密度大,车辆数量多,产生的汽车尾气、工业废气也越多,对居民身体造成伤害的可能性更多;二、经济发达,随之而来的是资源高投入,产生的环境污染也较大,在治理上产生较高的成本,使得CPI上升,从而对医疗支出产生影响;三、对比其他地区,这5个地区的人均收入偏高,生活水平比较高,人们对医疗保健的重视程度也比较高,相应的消费投入也比较高。其次是吉林,云南,甘肃,新疆,贵州,陕西,安徽,江西,黑龙江,重庆,湖北,海南,西藏,青海和宁夏15个地区,系数为6.526,比较其他地区,不难发现这15个地区大多为西部地区,在能源资源方面占有绝对优势,尽管地区发达程度不如北京、上海等大城市,但是由于产业结构的差异,主要集中在重工业,还有粗放型的经济发展模式,都造成这一地区环境恶化,从而对居民健康产生危害,引起医疗支出增加。影响最小的是江苏,广东,山西,内蒙古,湖南,广西,辽宁,四川,河北,河南,山东等11个地区,系数为2.40,这类地区当中,江苏和广东为经济发达地区,其人口规模、汽车数量等也很大,但是以轻工业和电子业为主的产业结构对环境的负面效应也相应较小,因此系数偏小;内蒙古主要以畜牧业为主,人口密度偏小,空气中的废气排放量也偏小,环境成本造成的医疗支出也相应较小。此模型中的其他地区,主要人口密度小,山地居多的地方,空气污染对医疗支出的影响偏小。在地面的影响因素方面,第二类的最大。第一类和第三类对医疗支出的影响是大体相同的。第二类地区的地面影响因素的系数偏大,其原因主要为城市比较发达,人口密度大,相应的固体废弃物产生也较多,从而清理工业、生活垃圾显得尤为重要。
模型中三类地区的自发性医疗支出分别为:1040.470,5003.652,1608.269,此项主要反映了当地经济发展状况以及人们对医疗健康的重视程度,模型数据揭示了三类地区之间的差别,符合现实情况。
5. 结论与建议
本文基于面板数据由于各个地区的经济发展和环境各有其特点,从实证部分的模型结果可以得出人均收入的增加会刺激人们更多的增加医疗支出,对于发达地区,医疗支出明显偏高,我国三类地区城镇居民医疗保健支出和人均收入的关系全部显著为正,反映了我国城镇居民对增加医疗服务需求的愿望。而且,越是高收入的地区,自发式医疗支出和医疗支出偏好系数越高。这一结果说明,增加我国城镇居民的收入水平,建立长久的收入增长机制等一系列措施,可以改善我国城镇居民的健康状况。同时,医疗支出的增加因地区差异呈现比较明显的区别。环境恶化对地区人均医疗支出的影响很大,因此环境治理问题迫在眉睫,地区政府应当高度重视,把环境治理放在首位。环境质量不仅影响整个城市的健康度,也和居民的健康水平、生活水平息息相关。当前有些地方政府和企业以牺牲生态环境为代价来获取经济的暂时性增长。但是,却为经济增长付出了沉重的代价,为了改善城镇居民的健康水平必须做好环境保护工作。因此,各级政府和企业要摒弃“先污染,后治理”的观念,加强环保意识,做到以保护环境来优化经济增长,努力建立覆盖全社会的“减排”长效机制。