1. 引言
随着软硬件的快速发展,个人电脑、数码产品、各类网站等已经成为人们生活不可缺少的一部分,而这些设备中的软硬件系统日益复杂化,如何保证软硬件及通信系统的正确性和可靠性已经非常重要。在众多的方法中,模型检测是一种有效的形式化验证方法,其在设计阶段检测软硬件是否工作正确[1] 。
形式化方法是用数学和逻辑的方法来验证软硬件系统,其由系统或者程序的描述和性质的描述组成。模型检测主要的工作是建模和形式化推理,其主要思想是采用二元的思想和手段对系统的一致性、安全性等属性或系统的性质进行推理和证明。其中建模是对系统的行为规约进行描述,再用某种逻辑表示系统的静态性质,最后检查系统行为与要求是否一致。其主要方法是对状态空间进行穷尽搜索,在搜索终止时,对于不满足的性质能给出反例[2] 。随着模型检测技术的发展,产生了很多的模型检测工具,如SPIN、SMV、NuSMV等,其中SPIN是其中应用比较广泛的,适用于并行系统,并且在分布式系统、软件的形式化验证、协议的验证等方面取得了成功[3] 。
模型检测器SPIN支持设计和验证系统,它通过建模语言promela来直观、明白地描述设计,使用线性时序逻辑LTL来有力地、简明地描述系统需求,并通过有效的算法验证系统是否满足需求[4] 。SPIN支持随机、交互和指导性的自动机验证,通过模仿系统的执行产生C程序,探测系统的状态空间。SPIN验证主要关心的是进程之间的信息交互是否正确,而不是进程内部的具体计算,所以它的建模方式是:首先定义进程模板,每个进程模板作为一类进程的行为规范,实际系统可以看作是一个或若干进程模板实例的异步组合。
SPIN是一个基于计算机科学的形式化方法,其将先进的理论验证方法应用在大型负责软件系统的验证当中,现在SPIN被广泛的应用在工业和学术界。本文在研究模型检测工具SPIN的结构和原理的基础上,详细的阐述了其图形化界面iSpin的安装和使用。
2. SPIN原理和结构
2.1. SPIN的原理
SPIN是针对多线程软件的有效的检测工具,其主要检测进程之间的信息交互是否正确。SPIN从一个并发系统的高规格的描述开始,在分析没有语法错误之后,对系统进行交互模拟,直到确认系统拥有预期的设计行为,然后,SPIN产生一个on-the-fly验证程序,经检测器编译后被执行,在执行中如果发现了违背正确性说明的任何反例,将这些反馈给交互模拟机并通过重现细节来剔除引起错误的原因[5] 。
Promela建模语言描述的系统由一个或更多的进程模板组成,每个进程模板描述各个进程的行为,作为一类进程的行为规范,并能通过进程模板创建更多的进程。如通过关键词proctype开始说明进程。SPIN采用on-the-fly机制来构建自动机模型,将各个进程模板转换成一个有穷自动机,并发系统的全局行为通过计算自动机的异步交叉积得到的也少一个自动机。如果用A和S分别表示系统行为的集合所对应的自动机和待检测性质构造的自动机,L(A)和L(S)分别表示A和S所接收的语言,其中L(A)表示系统行为的集合,L(S)表示系统允许行为的集合。模型检测需要验证系统A是否满足规范S,即L(A) 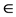 L(S)是否成立,被建模系统的行为集合是否都包含在性质所允许的行为集合中。那么系统性质所不允许的行为集合为语言L(S)的补,记作
L(S)是否成立,被建模系统的行为集合是否都包含在性质所允许的行为集合中。那么系统性质所不允许的行为集合为语言L(S)的补,记作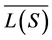 ,那么系统验证就是要检测性质规范S不允许的行为系统A是不会做的,即
,那么系统验证就是要检测性质规范S不允许的行为系统A是不会做的,即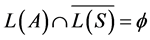 ,如果交集不为空,那么其中任何一个行为都可以作为反例。
,如果交集不为空,那么其中任何一个行为都可以作为反例。
一般情况下,求一个自动机的补自动机是比较困难的,这里利用LTL可以避免求自动机的补。首先将LTL公式转换成它的NNF形式,若LTL公式是f,公式f的补为~f即为不满足系统要求的性质,构造一个对应的Büchi自动机S~f来识别~f,这样检测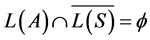 是否成立就可以转换为检测
是否成立就可以转换为检测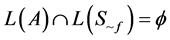 是否成立。具体的做法是检查是否存在一个从初始状态可达的环路包含一个至少一个接受状态来检查自动机是否为空,如果不满足,生成的自动机组合中必然存在一个可接受回路,这个回路以动作路径的方式给出反例。
是否成立。具体的做法是检查是否存在一个从初始状态可达的环路包含一个至少一个接受状态来检查自动机是否为空,如果不满足,生成的自动机组合中必然存在一个可接受回路,这个回路以动作路径的方式给出反例。
在检测自动机的交是否为空时,SPIN采用算法深度优先算法遍历自动机,并采用偏序简化技术来消除冗余。
2.2. SPIN基本结构
SPIN首先接受Promela语言描述的系统,经分析没有语法错误后,对系统进行交互模拟来验证系统的行为是否符合预期。然后,SPIN从系统的高级规约中生成一个优化的on-the-fly验证程序,经检验器编译后被执行,执行中如果发现了任何反例,就回到交互模拟执行再继续探测,确定产生反例的原因。SPIN的基本机构如图1所示,其描述了整个的检测过程[6] 。
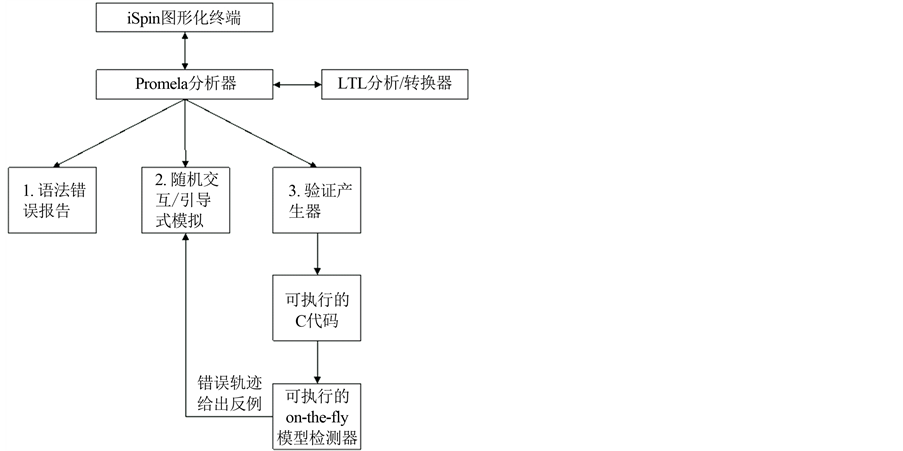
Figure 1. The basic structure of SPIN
图1. SPIN的基本结构图
3. 建模语言Promela
Promela(Protocol/Process Meta Language)是一种用来对有限的状态系统建模的形式描述语言,其类似C程序语言,允许动态创建并行进程,在进程之间使用消息通道进行同步或异步的通信。因此,一个模型由进程、消息通道、全局对象、变量组成[7] 。
Promela语言强调模型进程间的通信,并且在一个时刻只能有一个状态发生变化。Promela语言有丰富的进程交互原语,非确定性控制机构等主流语言没有的特点,能够构建高水平的分布式系统模型[8] 。
4. 线性时序逻辑LTL及其到自动机的转换
线性时序逻辑LTL是一种形式化符号,能描述系统在执行路径上的性质,还可以表示系统的安全性、活性等。一个LTL公式由原子命题p和一元、二元、布尔、时序运算符的组合而成[9] 。其语法如下:
f ::= p
|true
|false
|(f)
|f binop f
| unop f unop ::= [] (总是)
| <> (有时)
| ! (逻辑非)
binop ::= U (直到)
| && (逻辑与)
| || (逻辑或)
| -> (实现)
| <-> (等价)
如上所说,SPIN将LTL公式转换为自动机,例如,LTL公式[](p U q)表示在q是真的之前,p一直保持为真。该公式用PROMELA语言表示如图2所示。
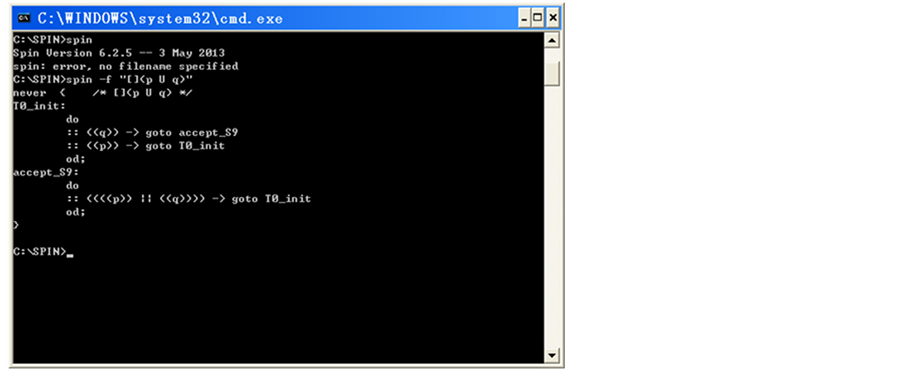
Figure 2. LTL formula syntax Promela representation
图2. LTL公式的Promela语法表示
可以看出自动机包含一个初始状态T0_init和一个接受状态accept_S9,那么该LTL公式对应的状态机如图3所示。
5. 模型检测器SPIN的安装和iSpin的使用
SPIN支持很多平台,如Unix\Linux系统、Windows、Macs等,本文在windows环境安装Spin和iSpin有以下步骤[9] -[11] :
1) 安装C编译器MinGW,如D:\MinGW;
2) 下载pc_spin*.zip的最新windows版并解压到如C:\ispin;
3) 下载安装Tcl/Tk;
4) 安装Graphviz;
5) 配置系统环境变量,如:“D:\MinGW\bin\;C:\spin;
6) C:\Tcl\bin;C:\ProgramFiles\Graphviz2.34\bin”;
7) 安装成功,双击C:\ispin中的ispin.tcl来运行Spin和ispin。
6. SPIN应用研究
SPIN的应用非常广泛,可以检测协议、验证算法的正确性等。下面详细的描述了使用iSpin验证了Dolev,Klawe和Rodeh提出的无向环上的选举算法[12] 。根据算法的描述,其模型描述为:
#define N 5 /* number of processes in the ring */
#define L 10 /* 2xN */
byte I;
mtype = { one, two, winner };
chan q[N] = [L] of { mtype, byte};
proctype nnode (chan inp, out; byte mynumber)
{bit Active = 1, know_winner = 0;
byte nr, maximum = mynumber, neighbourR;
xr inp;
xs out;
......
}
init {
byte proc;
byte Ini[6] ; /* N<=6 randomize the process numbers */
atomic {
I = 1; /* pick a number to be assigned 1..N */

Figure 3. LTL formula [] (p U q) state machine
图3. LTL公式[] (p U q)的状态机
do
......
od
}
}
首先,在iSpin中打开leader.pml,其使用promela语言描述了Dolev,Klawe和Rodeh提出的无向环上的选举算法。同时,我们列出了使用ltl语言描述的一些即将被验证的属性。如:p0,p1,p2,p3,p4.下面我们将通过具体的演示iSpin的使用。
iSpin提供了很多标签,如Edit/View,Simulate/Replay,Verification等等。每个标签下面又提供了很多选择。如图4显示了标签Edit/View下面的功能有Syntax Check,Redundancy Check等。
通过在Edit/view标签中的Syntax Check,Redundancy Check之后,通过Simulate/Replay标签有(Re)Run,Stop和Rewind等进行一个随机模拟的运行。通过查看消息序列图MSC能查看各个进程之间通过通道进行的消息交互(图5)。
下面通过分析leader选举算法,来熟悉iSpin的使用过程,打开Verification标签,验证p3属性的选择如图6所示。
验证p4属性的如图7所示。
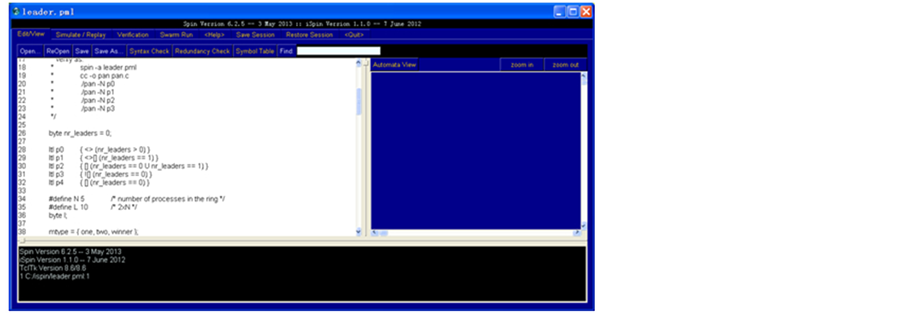
Figure 4. Edit/View label
图4. Edit/View标签
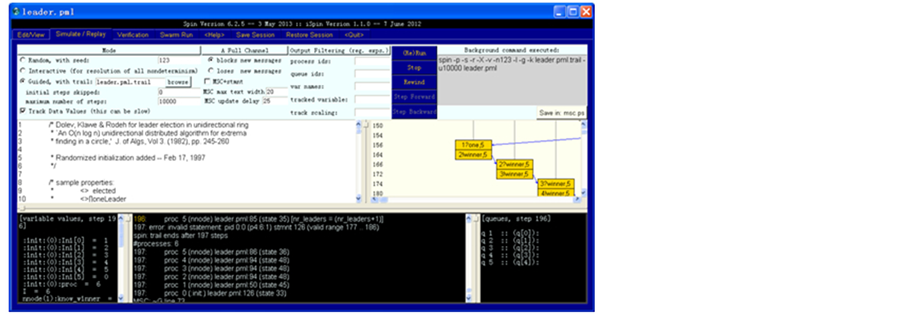
Figure 5. Simulate/Replay label
图5. Simulate/Replay标签
P4属性在被验证出错之后,通过点击Simulate/Replay标签中的Run运行,能得到一条错误的路径,如图8所示。
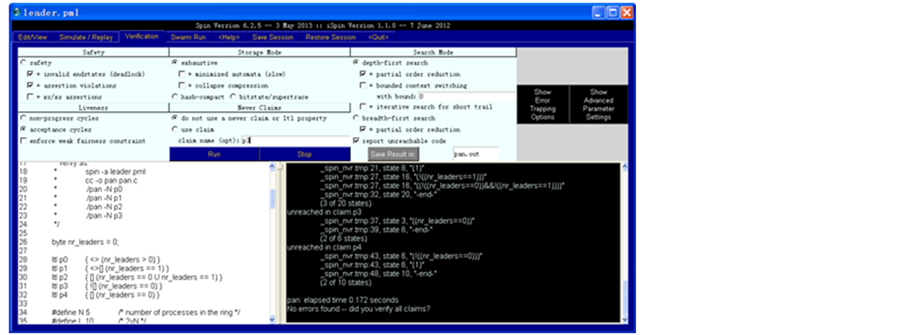
Figure 6. Verify a correct LTL property
图6. 验证一个正确的LTL属性
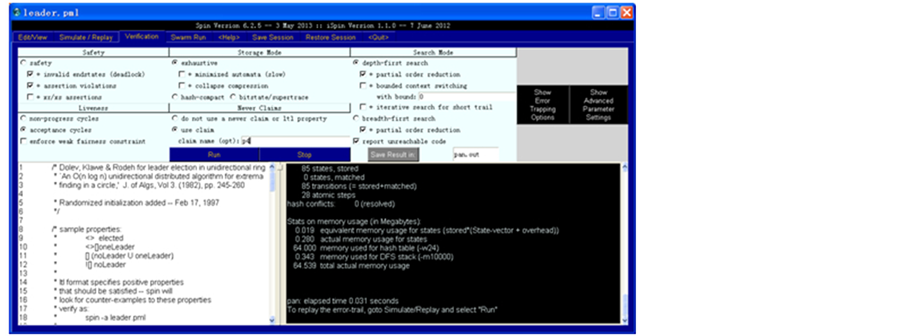
Figure 7. Verify an error LTL property
图7. 验证一个错误的LTL属性
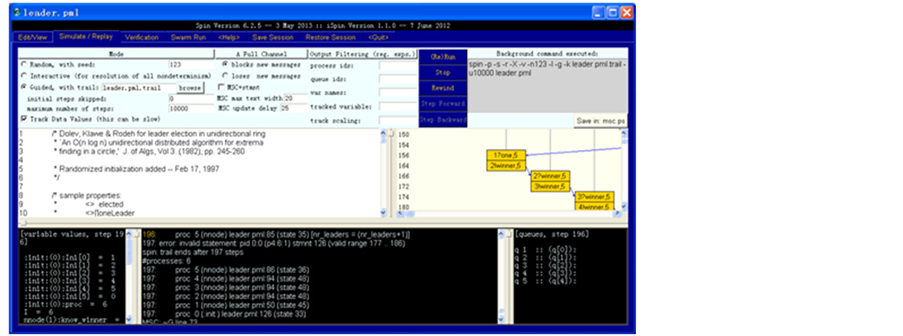
Figure 8. View a counterexample error
图8. 查看出错的一个反例
我们选用了环选举算法,并验证了性质p3:ltl p3{![] (nr_leaders == 0) }和性质p4:ltl p4{ [] (nr_leaders == 0)},并得出p3:No errors found -- did you verify all claims?的结论,而p4:To replay the error-trail, goto Simulate/Replay and select "Run",在Simulate/Replay中我们找到了一条错误的路径。
7. 结语
SPIN一个成功并被广泛接受的分析验证并发系统逻辑一致性的检测工具,其将先进的形式化验证方法应用在大型的软件系统中,对软件的有效性、可靠性进行分析。本文研究了SPIN的原理和结构,包括建模语言Promela和线性时序逻辑LTL到自动机的转换等。在此基础上,详细介绍了SPIN图形化界面工具iSpin的安装和使用,并通过具体实例进行了分析。模型检测可以有效的验证并发系统的正确性和其他性质,具有广阔的应用前景。