1. 引言
中长期径流预报在防汛、抗旱、供水、发电、养殖、旅游、航运及改善生态环境等方面发挥显著作用[1] 。同时中长期径流预报系统的建立可为水利工程年和月水资源计划调度的制定提供年、月来水预报信息,能使人们在协调防洪、兴利、生态之间及各部门用水之间矛盾时,及早采取措施进行统筹安排,以获得最佳综合效益。传统的预报方法主要有成因分析和水文统计方法,成因分析法是基于分析大气环流与水文要素之间的联系,水文统计法是通过对水文资料的统计分析进行概率预测,它包括两大类,一类是分析水文要素自身随时间变化的统计规律,并以此预测,如历史演变法、时间序列分析法等;另一类是用多元线性回归法或逐步线性回归法,建立预报方案进行预报[2] 。20世纪70年代后期Box[3] 等人提出的自回归滑动平均(autoregressive moving-average, ARMA)模型在水文预报中得到广泛应用,90年代以来,人工神经网络(ANN)[4] 在水文预报中的应用逐渐增多。近年来,基于新的数学分支和计算机技术的发展,中长期水文预报拓展了新的研究途径,支持向量机由于其预测精度较高,鲁棒性强,泛化能力强等诸多优点,在处理小样本数据时具有其他模型无法比拟的优势,且具有良好的拟合和外推能力[5] ,越来越多地被应用到水文预报中。中长期径流预报的一个重要环节是预报因子的合理识别,为预报模型的构建奠定必要的基础,不同的识别方法会有不同的预报因子,进而导致不同的预报效果。本文以长江流域1980~2012共33年径流资料为依据,采用基于逐步回归–支持向量机方法对长江流域屏山、宜昌、大通、汉口4个站点未来的逐月和逐旬径流进行预报,并对各模型预报结果的优劣比较分析。
2. 支持向量机模型原理
支持向量机具有坚实的数学理论基础,是专门针对小样本学习问题提出的,通过统计学习中的 维理论和结构风险最小化原则实现[6] 。它将具体问题转化为一个二次型寻优问题,理论上可以得到全局最优解,并且对于小样本学习具有良好的泛化性能,能够进行高效、精确的预测,较好地解决了传统方法的经验依赖、局部极值等问题[7] 。
维理论和结构风险最小化原则实现[6] 。它将具体问题转化为一个二次型寻优问题,理论上可以得到全局最优解,并且对于小样本学习具有良好的泛化性能,能够进行高效、精确的预测,较好地解决了传统方法的经验依赖、局部极值等问题[7] 。
支持向量机通过实现选择好的某一个非线性变换,将输入向量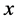 映射到高维特征空间
映射到高维特征空间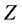 ;在这一特征空间中,构造一个最优分类超平面,使分类边界,即分类平面与最近点(支持向量)之间的距离最大,并且这种非线性变换是通过定义合适的核函数来实现,然后将
;在这一特征空间中,构造一个最优分类超平面,使分类边界,即分类平面与最近点(支持向量)之间的距离最大,并且这种非线性变换是通过定义合适的核函数来实现,然后将 问题转化为一个二次规划问题,从而求解。
问题转化为一个二次规划问题,从而求解。
给定训练集
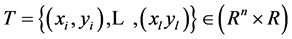 (1)
(1)
式中: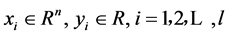 ,
,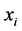 为输入变量,
为输入变量, 是
是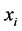 对应的输出值,
对应的输出值,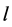 为样本个数。
为样本个数。
支持向量机回归的基本思想就是通过一个非线性映射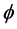 将数据
将数据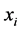 映射到高维特征空间
映射到高维特征空间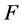 ,并在这个空间进行线性回归,即
,并在这个空间进行线性回归,即
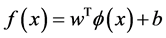 (2)
(2)
式中: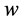 为超平面的权值向量,
为超平面的权值向量,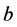 为偏置项。
为偏置项。
支持向量机实际上就是在约束条件(4)下求解下面的优化问题:
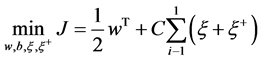 (3)
(3)
约束条件:
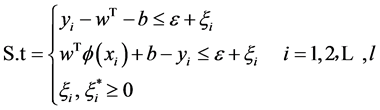 (4)
(4)
其中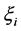 ,
,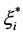 为松弛变量,分别表示在误差
为松弛变量,分别表示在误差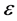 约束下
约束下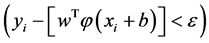 的训练误差的上限和下限;
的训练误差的上限和下限; 为
为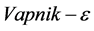 不敏感代价函数所定义的误差,当预测值在定义的误差
不敏感代价函数所定义的误差,当预测值在定义的误差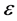 内,代价函数为0;当预测值在定义的误差
内,代价函数为0;当预测值在定义的误差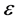 外时,代价函数为预测值与误差
外时,代价函数为预测值与误差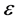 差的幅值。常数
差的幅值。常数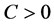 ,为惩罚函数,它控制对超出误差
,为惩罚函数,它控制对超出误差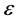 的样本的惩罚程度。
的样本的惩罚程度。
为求解这样一个优化问题,根据Kubn-Tucker条件,引入拉格朗日函数:
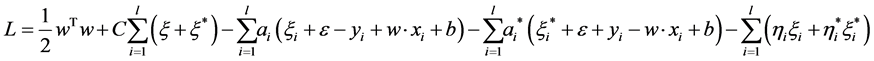 (5)
(5)
其中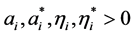 为拉格朗日乘子,根据
为拉格朗日乘子,根据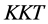 条件,如下等式和约束条件成立:
条件,如下等式和约束条件成立:
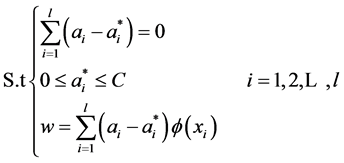 (6)
(6)
因此,非线性回归问题可以通过解式(3)的对偶问题求解:
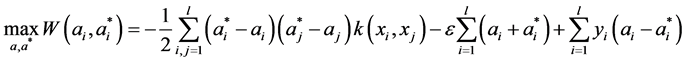 (7)
(7)
其中核函数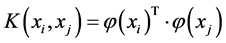 描述了高维特征空间的内积,可以在满足
描述了高维特征空间的内积,可以在满足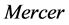 条件的情况下选取。常见的核函数有线性核函数、多项式核函数、径向基核函数、sigmoid核函数等,本文采用径向基核函数。
条件的情况下选取。常见的核函数有线性核函数、多项式核函数、径向基核函数、sigmoid核函数等,本文采用径向基核函数。
求解后得到 和
和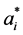 代入式(7),并由式(2)得到回归函数:
代入式(7),并由式(2)得到回归函数:
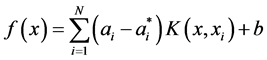 (8)
(8)
式(8)中 为支持向量个数。
为支持向量个数。
3. 试验流域与耦合模型的建立
3.1. 试验流域概况
长江流域面积辽阔,约占全国陆地面积的1/5,人口约占全国的1/3,经济总量占全国的41.1%。长江流域是我国经济最发达的地区之一,同时也是我国洪涝灾害最为严重的地区。长江流域相对丰沛的水资源条件为流域内农业、工业和社会发展提供了有力保障,在我国的社会发展过程中扮演者重要的作用。然而,受地理位置、气候及下垫面等因素的影响,长江流域降水、径流的地区分布不均,年内变化显著,是洪涝发生的重灾区。
3.2. 耦合模型的建立
通过分析长江流域屏山、宜昌、汉口、大通站断面的水文情势变化规律,识别影响该区域的大气环流因素,对该4个站点进行月、旬径流预报。影响月、旬径流的因素是在74项大气环流指数和前期径流共75项预报因子中进行选取,而现行的统计预报模式中,对预报因子的优化选择的方法有很多,本文通过相关系数法[8] 进行初选,然后利用逐步回归法[9] ,优选出与月、旬径流相关程度较高的6~8个预报因子。预报因子需要进行线性归一化处理,使得支持向量机的样本数据在(0,1)范围内。通过样本训练模型,然后对于训练好的模型预测,给定输入数据,就可以得到相应的预测输出。支持向量机进行模型率定时,采用交叉验证的方法优化函数参数。
根据资料情况,将研究过程分为两个阶段,即率定期为1981~2000年,检验期为2001~2012年。
4. 结果分析
选取平均相对误差(ART)、平均合格率(AP)作为中长期径流预报结果的评价指标,评价模型的模拟能力。其计算公式如下:
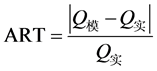 (9)
(9)
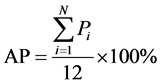 (10)
(10)
其中 为实测值,
为实测值,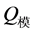 为模拟值,
为模拟值,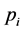 指第i个月的合格率,
指第i个月的合格率,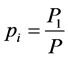 ,
,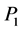 是合格的结果数,
是合格的结果数,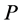 是实测序
是实测序
列的长度。而合格检验标准为: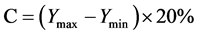 ,C为误差限,当
,C为误差限,当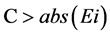 ,即误差绝对值小于误差限时,认为该结果合格。反之,认为不合格。
,即误差绝对值小于误差限时,认为该结果合格。反之,认为不合格。
由表1可以看出,四个站点率定期的月径流模拟平均相对误差为3.62%,检验期为23.77%,率定期的月径流模拟平均合格率达96.77%,检验期则只有49.29%,效果不理想。
由表2可以看出,四个站点旬径流模拟的相对误差在率定期和检验期与月径流模拟结果相差不大,但平均合格率在率定期和检验期都要优于月径流的模拟结果,特别是在检验期旬径流模拟的平均合格率相对于月径流模拟有了一定的提高,但预报效果仍然达不到实际应用的需求。
基于此,本文尝试先进行旬尺度的径流预报,然后将每个月3个旬的径流预报结果累加成月径流,结果如表3和图1~图4所示。
表3及表4分别是由支持向量机与人工神经网络旬尺度计算所得的月径流结果,即根据旬径流模拟计算月径流的过程。对比表1和表3可以看出,由旬尺度计算出所得的月径流结果均优于月尺度模拟结果,且有了较大的提高。其中平均相对误差降低了30%左右,平均合格率同样提高了35%左右,大通站更是提高了85.51%。比较表3和表4可以看出,支持向量机预测方法所得结果优于人工神经网络预测方法,其中检验期平均相对误差降低了约10%,检验期平均合格率提高了7%,尤其是汉口站和大通站均提高了20%左右,这是因为支持向量机模型以结构风险最小化原理为基础,对未来的径流样本有较好的泛化能力,其在解决小样本、非线性问题中表现出许多特有的优势。由图1~图4可以看出,在检验期的4

Table 1. The monthly runoff simulation results in each station
表1. 各站点月径流模拟结果

Table 2. The ten-day runoff simulation results in each station
表2. 各站点旬径流模拟结果

Table 3. The monthly runoff calculation result by ten-day scale
表3. 由旬尺度计算月径流结果
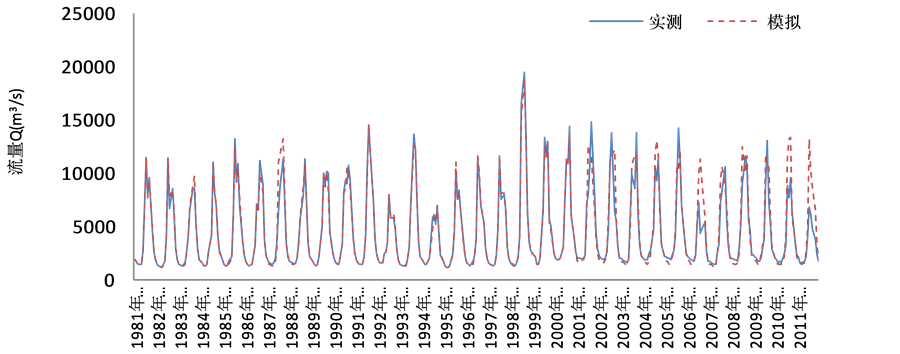
Figure 1. The monthly runoff simulation results calculated by ten-day scale in the Pingshan station
图1. 屏山站旬尺度计算月径流模拟结果
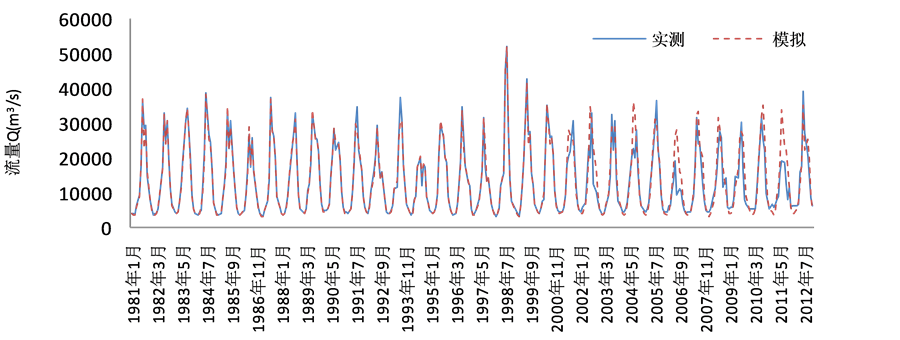
Figure 2. The monthly runoff simulation results calculated by ten-day scale in the Yichang station
图2. 宜昌站旬尺度计算月径流模拟结果
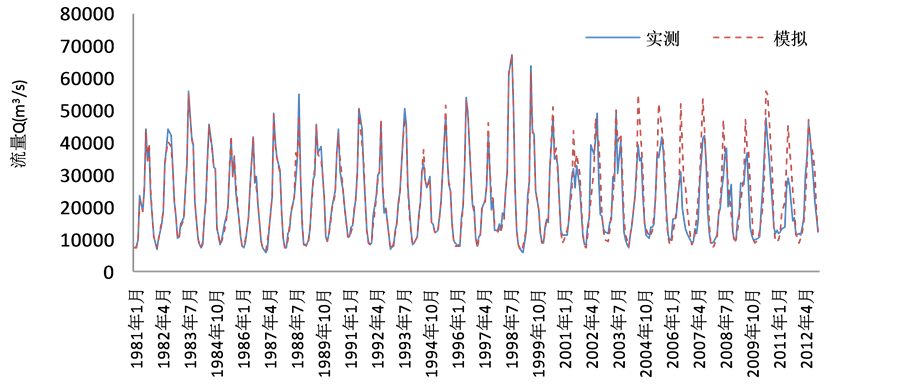
Figure 3. The monthly runoff simulation results calculated by ten-day scale in the Hankou station
图3. 汉口站旬尺度计算月径流模拟结果
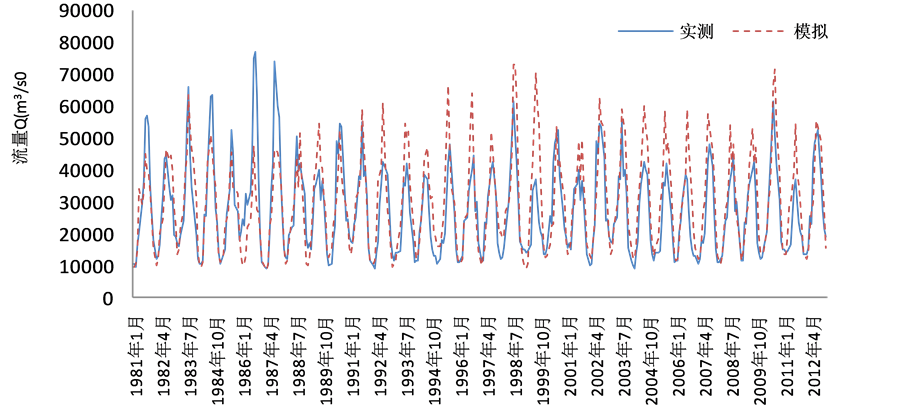
Figure 4. The monthly runoff simulation results calculated by ten-day scale in the Datong station
图4. 大通站旬尺度计算月径流模拟结果

Table 4. The monthly runoff simulation results of artificial neural network model calculated by ten-day scale [10]
表4. 人工神经网络模型旬尺度计算月径流模拟结果[10]
个站点的整个流量序列上,模型在中低流量区取得了较好的预测效果,在峰值预测上总体偏低,但总体取得了较好的预测效果。
总体而言,本文依据逐步回归方法支持向量机建立的耦合模型可以较好地用于长江流域中长期月、旬径流预报。同时,也为支持向量机这一机器学习方法用于其它流域的径流预测提供了一定的基础。
5. 结论
本文将支持向量机模型应用到长江流域中长期预报研究中,对长江流域屏山、宜昌、汉口、大通四个站点分别进行了月、旬径流预报,并且把月尺度模拟结果与旬尺度计算月径流结果进行比较,结果表明支持向量机模型模拟效果较好,率定期的平均相对误差较小,合格率较好,检验期的平均相对误差及合格率与率定期相比有一定的差距,旬尺度计算月径流有较好的预报精度。本次研究表明,支持向量机模型预测在径流预报中可以有较好的应用价值,为长江流域水文预报工作提供一定的参考。当然,本文中的支持向量机模型还有一定的优化空间,模型参数需要进一步的优化,以及模型精度的进一步提高,这些都有待研究。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(51339004、51279139);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(2042014kf1012、2042014kf0033)。

NOTES
作者简介:贾军伟(1991-),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为水文预报研究。