1. 引言
地下水与地表水的交互作用既是水资源研究的核心和热点,也是陆气相互作用中重要的物理过程。地表水与地下水的相互转化直接影响着地表水和地下水体的水质和水量。从水量方面来说,地表水体接收地下水补给又可能直接向地下水排泄。近年来,我国西北地区地下水位大幅下降,生态系统破坏严重,研究地表水与地下水间的关系也势在必行。
以前的模拟由于各种条件的限制,以单独研究地表水或者地下水为主,但是随着科技发展和社会进步,使地表水(SW)和地下水(GW)耦合模拟成为可能。在整个水文体系中它们并不是独立的组成部分,其相互联系非常紧密[1] 。国内外已出现一些集成地表水和地下水的模型,经过实践的检验和自身不断的发展,逐步形成了较为完善的模拟工具。Freeze和Harlan(1969)[2] 首次提出了流域尺度上水文响应耦合模型的概念和理论框架,Pikul和Street(1974)[3] 发现将一维的Richards方程与Boussinesq方程进行耦合,可以准确的模拟地下水水位,Li (2008)[4] 利用HydroGeoSphere模型对Toronto地区Duffins Creek流域的地下水与地表水系统进行耦合模拟分析,取得了较好的效果。熊立华和郭生练(2004)[5] 、贾仰文(2005)[6] 进行了分布式流域水文模型的研究,从水循环的物理机制入手,将产汇流、土壤水运动、地下水运动及蒸发过程等联系起来一起研究并考虑水文变量的空间变异性问题。胡立堂、王忠静(2007)[7] [8] 对国内外的地下水、地表水耦合模型进行了归纳分析,也取得了不错的效果。但是由于其模拟机理和适用范围不同,各模型间存在明显差别;同时由于结构复杂,并且需要大量参数和数据支撑,模型建立和率定非常耗时,导致在应用上受到一定限制。
因此根据研究区实际情况,研究简单、实用的地表水与地下水模型耦合计算的方法,准确、有效地模拟地表水与地下水系统之间的相互作用,对于水资源的科学评价、开发利用、有效管理以及生态环境的保护具有重要意义。
地下水对于维持生态系统健康、结构与功能稳定的重要性日益得到重视。近年来对依赖地下水的生态系统的研究正在形成一门新的交叉学科–生态水文地质学(Eco-hydrogeology),从水文地质学视角探索河流、湖泊与湿地等生态系统的演化过程与机制[9] [10] 。西安黑河流域位于陕西省西安市周至县境内,区内地表水地下水资源丰富,建有水源地,是向西安市提供饮用水的主要水源地。由于区内地质条件复杂这一特点,地表水渗漏作用强烈,对地下水存在很强的补给作用。本研究以西安黑河流域为靶区,基于探地雷达(Ground Penetrating Radar, GPR)技术,利用SWAT-MODFLOW耦合模型,模拟该地区的地下水资源及其地表水和地下水之间的相互作用,预测该地区未来地下水的动态变化。该研究对保障西安市800万市民供水至关重要,也是实现区域水资源有效保护和持续利用的关键。
2. 研究方法和数据
2.1. 研究区域概况
黑河流域位于秦岭以北,渭河以南的陕西省周至县境内。地理位置介于N33˚42ꞌ~N34˚13ꞌ、E107˚43ꞌ~E108˚24ꞌ。1999年在黑河建成黑河金盆水库水利枢纽,主要负责西安市供水。黑河全长125.8 km,集水面积2258 km2,径流深362 mm,多年平均径流量8.17 亿m3。流域内降水量丰沛,降水量年内分配极不均匀,汛期降水量大而集中,冬春两季干旱少雨。汛期6~10月降水占全年降水量的67.4%~78.2%。该区山高坡陡,同时又处于黄土高原地区,水土易于流失。地下水主要有孔隙水含水层和岩溶水含水层两种。孔隙含水层广泛分布在平原区,其组成以砂土、粉土、黏性土为主,厚度一般不足40 m。岩溶含水层以震旦系和寒武系的碳酸盐岩为主,岩性多变、厚度大、范围广,是水源地地下水的主要开采层区。黑河流域的地理位置如图1所示。
2.2. 研究方法
在地下水模型的模拟计算中,地下水的补给量和潜水蒸发量直接影响地下水动态模拟的结果,但是
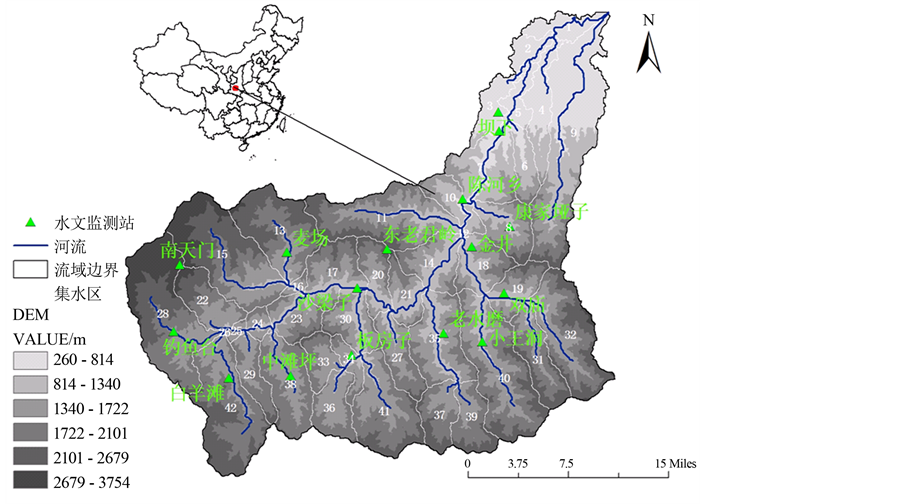
Figure 1. Location of Heihe river basin
图1. 黑河流域地理位置
通常很难对其进行准确估算和赋值。如果能在地区SWAT模型模拟和MODFLOW模型建立的基础上,根据SWAT分布式模型的特点,通过SWAT模型水文响应单元(HRU)与MODFLOW差分网格(CELL)的对应,构建SWAT-MODFLOW的交互界面,就能很好地解决这个问题。可应用ARCGIS软件,将SWAT模型地下水补给量与潜水蒸发量的模拟计算结果及空间分布引入MODFLOW相应的地下水补给子模块RCH和潜水蒸发子模块EVT中,对西安黑河流域地下水水位进行模拟,实现模型的耦合计算并与GPR的实测结果进行对比分析,实现对模拟结果的检验。
2.3. SWAT-MODFLOW耦合方法
SWAT模型是具有很强物理机制的半分布式流域水文模型,在SWAT模型中,流域被划分为多个子流域,在每个子流域内,根据不同的土地利用和土壤类型,再将每个子流域划分为1个或多个下垫面相对单一的水文响应单元(HRU),作为模型的基本计算单元。每个HRU的计算结果在子流域范围内进行累加,并演算到支流,最后通过河道汇流计算得到流域出口处的结果。Visual MODFLOW是由加拿大waterloo水文地质公司在MODFLOW软件的基础上,综合已有的MODFLOW、MODPATH、MT3D等地下水模型软件开发的,可进行三维水流模拟和溶质运移模拟。Visual MODFLOW以其简单实用的求解方法、广泛的适用范围及强大的可视化功能等特点,成为目前国际上应用最广泛的三维地下水流和溶质运移模拟评价的标准可视化专业软件系统。
在SWAT模型中,水文响应单元(HRU)是模型最基本的计算单元,反映了子流域内土地利用和土壤覆盖情况的综合影响,是分布式模拟计算的基础。代入研究区的基础数据,通过模拟,可以得到每个HRU内的地表径流、地下径流、壤中流、蒸发、渗漏量、地下水的补给量等计算结果,将HRU计算结果在子流域和整个流域进行累加,就得到计算模型要素在整个流域的空间分布。运行SWAT的hru analysis模块,即时获得full hrus矢量图层。根据SWAT中full hrus矢量图层和MODFL0W中有限差分网格(CELL)的特点,构建HRU-CELL的交互界面(图2)。图2中上半部分显示了SWAT模型1个子流域中HRU的空间分布,下半部分显示了MODFLOW中有限差分网格(CELL)的划分情况,网格中的数字分别对应SWAT
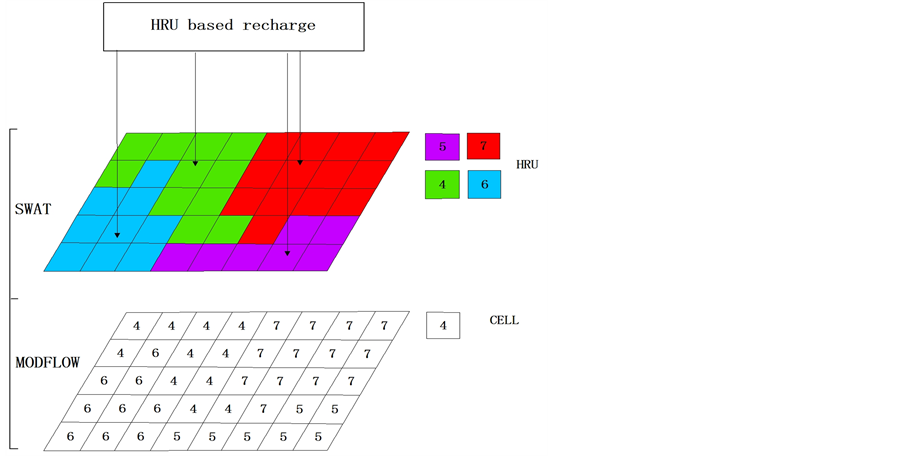
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of recharge computation in SWATMODFLOW
图2. SWAT模型与MODFLOW的HRU-CELL耦合示意图
模型中HRU的编号。通过这种对应,可以将SWAT模型计算的模型要素的空间分布赋值给MODFLOW,从而实现SWAT与MODFLOW的耦合计算。
2.4. SWAT-MODFLOW耦合计算在西安黑河流域的应用
2.4.1. SWAT模型率定及模拟计算
西安黑河流域属于干旱、半干旱气候,是一个面积较大的流域,流域内存在多种土壤类型和不同土地利用、植被覆被方式。概括起来,SWAT模型数据库可以分为空间数据库(又称图数据库)和属性数据库两大类,空间数据库主要包括流域DEM图、土地利用分类图和数字化土壤图。属性数据库主要包括3个存储有关土地利用、土壤属性以及气象站参数等的数据。根据研究区DEM、土壤和土地利用的分布,将西安黑河流域划分为42个子流域和107个水文响应单元(如图1)。子流域面积从541 km2到12.583 km2不等。在建模过程中,各站点日降水数据通过距离倒数法插值到每个子流域内,作为该子流域的面降水输入,而气温等其它气象数据则采用SWAT模型自带的方法进行插值。在模型控制文件(basins.cod)的配置中,产流模块采用SCS方程。潜水蒸散发的计算中,由于Priestley-Taylor公式已成功运用在黄河源区等高寒地区,因此本次研究也选该方法。
模型的率定和检验分为两个阶段:参数率定期为2005~2008年,其中2005年为模型的预热期;参数验证期为2009~2011年,其中2009年为预热期。水量平衡系数,相关系数和效率系数3个指标用于评价模型模拟结果。如果水量平衡系数大于0.20或小于0.20而且相关系数和效率系数均小于或者等于0.0,那么模型的模拟结果是“不可接受的”;如果水量平衡系数为0.0,而且相关系数和效率系数均为1.0,那么模型的模拟结果被认为是“优秀”;如果水量平衡系数被控制在±0.20以内,而且相关系数不小于0.80,效率系数不小于0.60,那么模型的模拟结果被认为是“可以接受的”[11] 。
输入研究区水文气象资料、土地利用、土壤类型资料、DEM以驱动SWAT运行,在率定模型最佳参数的基础上,模拟了基准期(2005~2008年)西安黑河流域的逐月径流。选取27个模型输入参数进行参数敏感性分析试验,设置参数采样间隔为10,每次参数变化值为0.05,利用SWAT-CUP敏感性分析工具进行了270次比较判断,确定对敏感性等级最高的6个参数:土壤表层有效含水量(SOL_AWC),浅层地下水再蒸发系数(GW_REVAP),基流回归系数(ALPHA_BF),产生基流的浅层地下水阈值(GWQMN),地下水滞后时间(GW_DELAY)等(如表2所示)进行模型的率定。利用2005-2008年陈河水文站逐月流量序列对月径流模拟进行率定,首先调整CN2、SOL_AWC、ESCO来拟合地表径流,再调整GW_REVAP、REVAPMN、GWQMN来调整基流。参数率定结果如表1所示。

Table 1. Main Parameters of Model Calibration
表1. 模型率定的主要参数
利用陈河站2009~2011年逐月流量数据进行模型验证,并采用Nash-Sutcliffe模拟效率系数、水量平衡系数和相关系数对模型的验证结果进行评价。验证期径流模拟效率及拟合情况见表2和图3。其值表明SWAT模型适合用于模拟西安黑河流域径流的变化。
2.4.2. SWAT与MODFLOW的耦合计算
根据西安黑河流域的水文地质条件,以陈河乡所在的集水区为研究区,建立区域的MODFLOW地下水模型。模型分为1层,为非承压的孔隙含水层。模型网格划分为每层32行 × 32列。对每个含水层,设置其渗透系数、地下水贮水率、给水度等参数和模型的边界条件。应用ARCGIS软件,将SWAT模型计算的地下水补给量和潜水蒸发量结果引入MODFLOW模型边界条件中的地下水补给子模块RCH和潜水蒸发子模块EVT中,进行地下水模拟计算。
3. 结果与分析
将SWAT模型与MODFLOW模型进行耦合,对西安黑河流域的地下水水位进行模拟。根据SWAT分布式模型的特点,将其水文响应单元(HRU)和MODFLOW的有限差分网格(CELL)进行空间对应,实现SWAT模型计算结果中具有空间分布特征的模型要素(地下水补给量和潜水蒸发量)引入MODFLOW的地下水补给模块(RCH)和蒸发模块(EVT)中,进行数据的传递,实现模型的耦合计算。
3.1. SWAT模拟结果分析
图3径流模拟结果表明,7年地表径流量与降水量、基流量的最大值出现的年份一致,均在黑河流域的丰水年2011年。7年地表径流量与降水量的最小值出现的年份一致,均在西安黑河流域的枯水年2008

Table 2. Simulated runoff results at the Chenhe station
表2. 陈河水文站点径流模拟结果
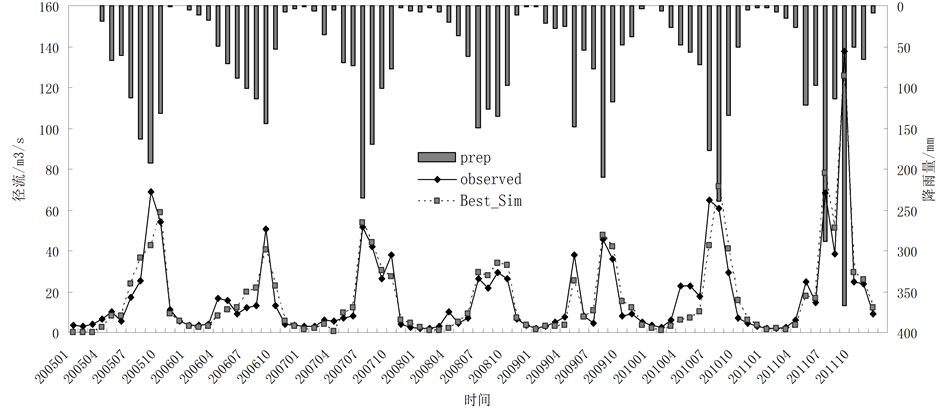
Figure 3. Comparison of simulated and observed runoff hydrograph during validation period
图3. 验证期模拟和实测径流过程对比图
年;而基流量最小值出现在2008年。
通过设置不同气候变化背景,未来40年西安黑河水源地径流量与现状相比有所增减,尤其是在非汛期,前20年处于减少趋势,这将持续加剧西安黑河中下游流域水资源短缺的现象;后20年处于增加趋势,其原因可能在于2040s~2050s期间,由于气候变化的原因,导致全球气温升高,极端天气气候事件频发,降雨量增加所致。这些气候变化影响了流域的水文状况,导致年径流变化很大[12] 。
3.2. MODFLOW模拟结果分析
图4中等值线为地下水模拟计算的结果,可以看出陈河乡所处的10号子流域地下水位以黑河为分界,黑河以西地下水位由西北向东南方逐步升高,黑河以东地下水位由南向北逐渐降低。利用GIS空间分析功能,利用DEM减去地下水位图即可得到地下水位埋深图,通过地下水位埋深图提取实测点的水位埋深,实现模拟值和实测值的对比分析。从埋深图可以得出,黑河两岸地下水位埋深较浅,向西北和东南方向逐渐升高,模拟结果和实际相符合。
3.3. 耦合计算结果的检验
区域内45个GPR实测地下水位的空间位置如图4所示,图5为2014年3月30日10号子流域的实测地下水位与模型计算地下水位的散点图,模拟结果的确定性系数为0.86,模拟结果与实测值的相关系数为0.89。计算得到的地下水水位随地下水补给量的变化趋势与实测地下水位的变化基本吻合。
西安黑河流域属干旱或半干旱地区,地下潜水位低,地表被第四系松散沉积层覆盖,包气带和饱和带介电常数有明显的差异,这一点正好适合探地雷达的应用条件。在分析研究区地质、水文资料的基础上,对西安黑河流域工作面进行了实地探测,通过对比分析处理雷达剖面图与该地区钻孔资料,验证了用探地雷达探测干旱半干旱地区地下潜水位的可行性,为该区域地下潜水位的动态监测以及保水提供技术支持。
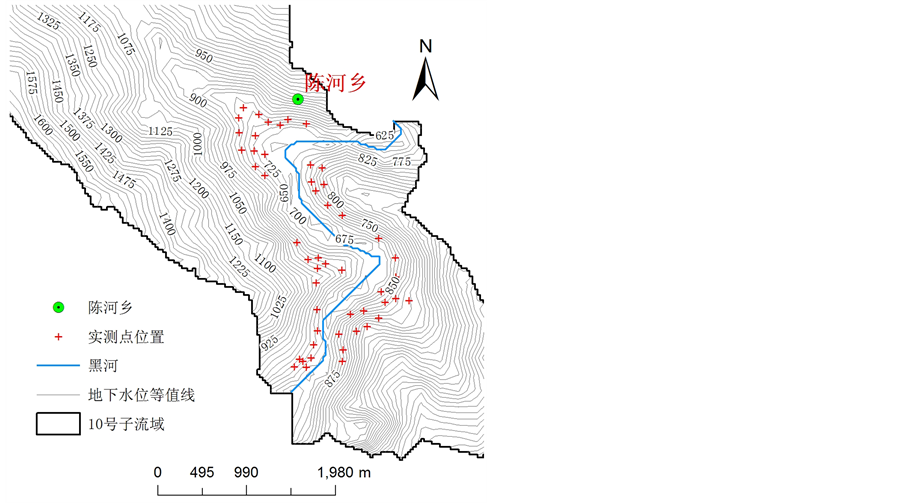
Figure 4. The spatial position of the measured groundwater sites
图4. 实测地下水位点的空间位置
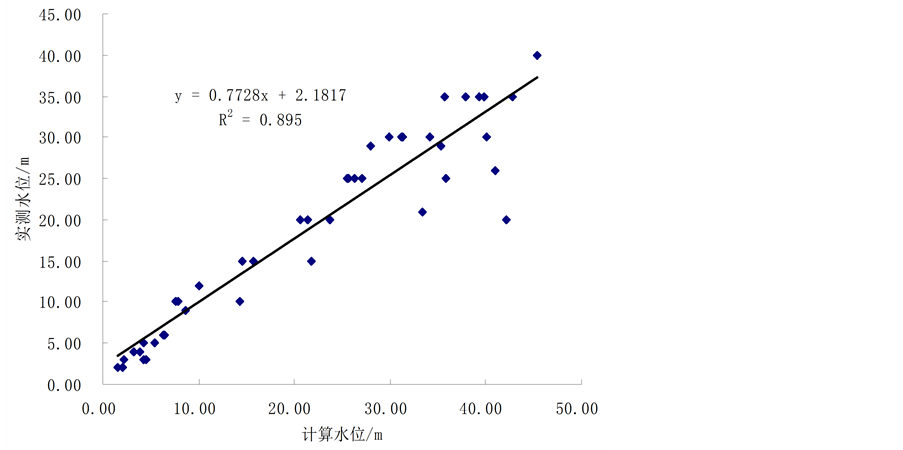
Figure 5. The scatter diagram fitting between simulated and measured water table at sub-basin 10
图5. 10号子流域实测地下水位与模拟水位埋深散点图
对10号子流域2014年地下水模拟计算结果表明,计算得到的区域地下水位与实测结果基本吻合。SWAT模型与MODFLOW的耦合计算对于更准确地模拟和预测地下水资源,进一步研究地表水与地下水之间的相互作用提供了科学方法,对于区域水资源的科学规划和管理,实现区域水资源的可持续利用具有实际意义。但是,在推广应用的过程中应注意以下问题:由于土壤的类型众多,应该针对各地不同的土壤取样实测相应的介电常数与含水率关系式,提高含水率测量的精确度;本文仅仅研究了陕西黑河流域,对其它类型的区域是否适用还需进一步研究;包气带作为联系地表水和饱和地下水的纽带,其厚度虽然在不同地理位置或厚或薄,但它具有储存和运输作用,其作用不容忽视,因此当集成模型考虑包气带的运动规律时,模型的物理机理将更趋完善,对包气带水文过程需要进行更加完善的处理。
4. 结论
应用GPR定量测量地下水位埋深,是无损检测理论和技术研究的热点问题和难点问题之一,它不仅涉及到电磁波在非均匀介质中的传播问题,而且还与现代信号处理技术密切相关,它将电子技术、电磁场理论和信息技术等融合在一起。
对西安黑河流域2014年地下水模拟计算结果表明:1) 计算得到的区域地下水位与实测结果基本吻合;2) 首次将GPR技术应用于SWAT模型与MODFLOW的耦合计算,并在分析研究区地质、水文资料的基础上,对西安黑河流域进行了实地探测,通过对比分析处理雷达剖面图与该地区钻孔资料,验证了用GPR探测干旱半干旱地区地下潜水位的可行性;3) 根据SWAT分布式模型的特点,将其水文响应单元(HRU)和MODFLOW的有限差分网格(CELL)相对应,将SWAT模型计算结果中的具有空间分布特征的模型要素(地下水补给量和潜水蒸发量)引入MODFLOW的地下水补给模块(RCH)和蒸发模块(EVT)中,实现了模型的耦合计算,该方法可以推广应用到其它类似的区域研究中去。地表水和地下水作用作为全球水循环的一部分,研究的范围已经涉及水文地质学、水文学、地球化学、生物学、气象学等,呈现出各学科的渗透交叉,综合集成全球水循环各组成部分的复杂系统模型,是地表水和地下水相互作用研究发展的必然趋势。
致 谢
感谢长安大学环境科学与工程学院周维博教授在数值模拟方法上的指导及王菊翠等老师在研究方案与验证数据方面的协助。
基金项目
中国地质调查项目(12120113004800);长安大学2013年国家级大学生创新创业训练计划项目(2013 10710060)。

NOTES
作者简介:席丹(1993-),女,陕西人,长安大学环境科学与工程学院,主要研究方向:水文学及水资源。
*通讯作者。