1. 引言
气候变化已成为全球共同关注的热点问题之一,各国政府和研究人员对气候变化引起的环境和生态问题都给予了极大的关注[1] [2] 。气候变化有全球性的特点,但也有很强的地域性,不同地区的变化趋势差别很大[3] [4] 。
近年来,一些学者运用不同分析方法对我国不同地区的气候变化方面进行了研究,详细分析了这些区域气候变化的规律[5] [6] 。京津冀地区位于36˚N~43˚N,113˚E~120˚E之间,地处华北平原,包括河北省全部,内环首都北京市和天津市,东临渤海,北与东北地区、内蒙古地区相接,是我国受气候变化影响较大的地区之一[7] 。通过研究京津冀地区气温及降水的时空变化特征,对区域气候背景监测以及合理开发利用气候资源具有重要的现实意义。
2. 资料与方法
2.1. 资料
收集整理了京津冀地区83个站点1982~2010年共29年的气温和降水量数据,研究区所选站点分布均匀,且数据经过严格的质量控制。按春季(3~5月),夏季(6~8月),秋季(9~11月),冬季(12月至次年2月)的季节划分生成逐季序列,采用月平均气温、月降水量数据统计得到逐年的平均气温和年降水量。
2.2. 方法
运用一元线性方程xi = a + bti(x分别为年、季气温和降水,b为倾向值,i为时间序列),对年、季气温和降水的变化进行线性拟合,确定可信度和气候倾向率[8] [9] ;运用Mann-Kendall检测(以下简称M-K检验)方法,分析气候序列的突变特征,明确突变开始时间,并指出突变区域[10] ;采用经验正交函数分解(EOF)分析整个研究区域气候因子的空间异常分布特征[11] 。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 1982~2010年京津冀地区气温时空变化特征
3.1.1. 气温空间分布
京津冀地区气温空间分布差异较大,但整体上表现为南高北低,平原高于山区。京津冀地区年平均气温空间分布如图1所示,河北的坝上地区年平均气温在1.8℃~7.0℃之间,中南大部都在11.2℃~13.9℃之间,南北温差达13.1℃。整个京津冀地区高值位于河北省邢台市中南部和邯郸市中北部之间,其中邯郸的年平均气温为13.9℃,为研究区最高;低值区主要位于河北省张家口北部,其中张家口的康保年平均气温为1.8℃,为研究区最低。综合分析气温空间分布差异,在冀北高原受拔海高度和纬度的影响较大,而冀中南大部主要原因是由于地形对温度的影响。
3.1.2. 气温EOF分析
图2为京津冀地区近29年平均气温的EOF分析,由图可见,其收敛性很快,其中,气温EOF展开的第一特征向量场(图2a)的方差解释率已达到78.9%,因此,其第一特征向量场的分布情况即可较好的表示京津冀地区气温空间分布的基本特征。如图2a所示,总的空间分布表现为整个研究区一致为正,揭示了研究区气温空间的一致性变化,气温明显增加的区域位于中西部内陆地区;其时间系数(图2b)反映了京津冀地区近29年气温呈波动式的增加,年际变化较大,1983~1987年为下降趋势,1988年以后呈增加

Figure 1. The average annual temperature spatial distribution map Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in 1982-2010
图1. 1982~2010年京津冀地区年平均气温(℃)空间分布图
趋势,特别是1993年以后气温增加明显。这一变化与我国增暖始于1980年代后期,1990年代增暖迅速的情况较为一致[12] -[14] 。
3.1.3. 气温时间变化特征
图3为近29年京津冀地区年平均气温变化曲线,如图所示,京津冀地区气温常年值为11.3℃,年平均气温整体呈上升趋势,气候倾向率为0.44℃/10a,上升趋势异常显著,通过了α = 0.01的显著性检验。
从年代际变化上看,1982~1985年气温呈下降趋势,1986~1989年波动上升,90年代以后,年平均气温上升趋势明显,整体来看年际波动较大,其中90年代是年平均气温上升趋势最为明显的阶段,从这点讲,在全球气候变化背景下,京津冀地区气温变化与全国乃至整个北半球的变化趋势一致[15] 。但进入21世纪以来,气温变化趋于稳定并有下降之势。
京津冀地区四季平均气温变化如图4所示,京津冀地区各季平均气温整体均呈上升趋势。秋季平均气温为11.6℃,气温在10.1℃~13.2℃之间,气候倾向率为0.31℃/10a,在四季中是上升趋势最小的季节,但通过了α = 0.05的显著性检验,说明京津冀地区秋季气温上升趋势显著;其次为夏季,平均气温为24.5℃,气温在23.3℃~25.9℃之间,夏季气温整体呈增加趋势,气候倾向率为0.41℃/10a,通过了α = 0.05的显
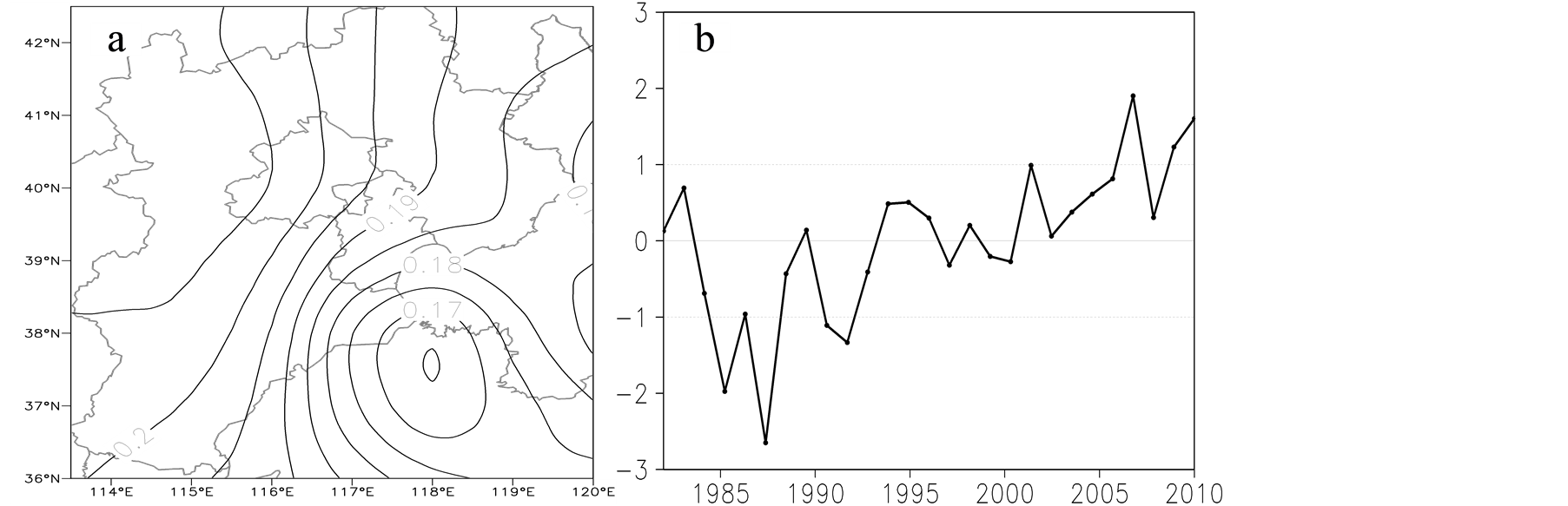
Figure 2. 1982-2010, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and the annual average temperature of EOF analysis of the first eigenvector field (a) and the time coefficient (b)
图2. 1982~2010年京津冀地区年平均气温EOF分析的第一特征向量场(a)及其时间系数(b)
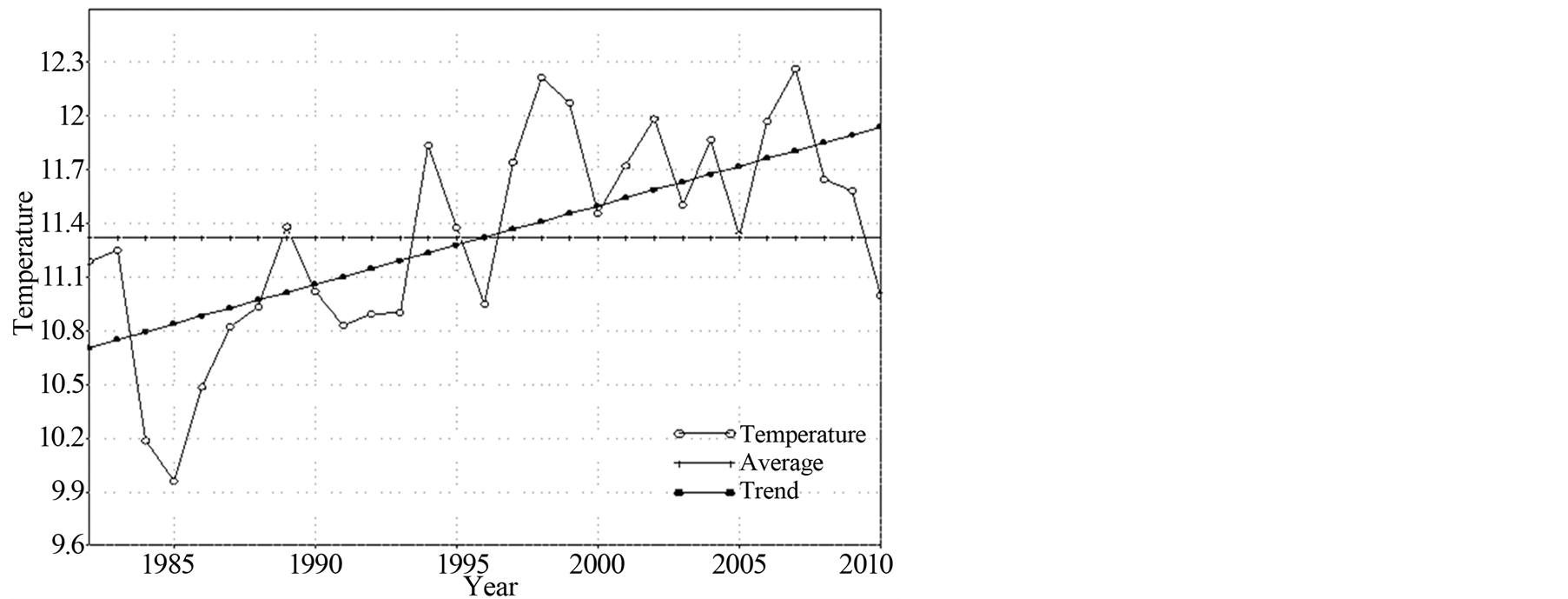
Figure 3. In 29 years (1982-2010) the curves of annual average temperature (˚C) of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
图3. 近29年(1982~2010年)京津冀地区年平均气温(℃)变化曲线
著性检验,增加趋势显著;春季气温与秋季气温大体相当,平均气温为12.6℃,气温在10.9℃~14.1℃之间,整体呈增加趋势,气候倾向率为0.47℃/10a,通过了α = 0.05的显著性检验,增加趋势显著;冬季为气温上升趋势最为明显的季节,平均气温为−3.5℃,气温在−5.6℃~−1.3℃之间,冬季气温气候倾向率为0.6℃/10a,通过了α = 0.05显著性检验,上升趋势显著。
3.1.4. 气温突变分析
采用Mann-Kendall法对京津冀地区1982~2010年的年平均气温序列进行突变性检验,如图5所示,近29年京津冀地区年平均气温正序列线(UF)和逆序列线(UB)在1993年前后出现交点,并在α = 0.05显著性水平置信曲线之间,由此可确定1993年为年平均气温的突变点。由图中的UF曲线分析可以看出,
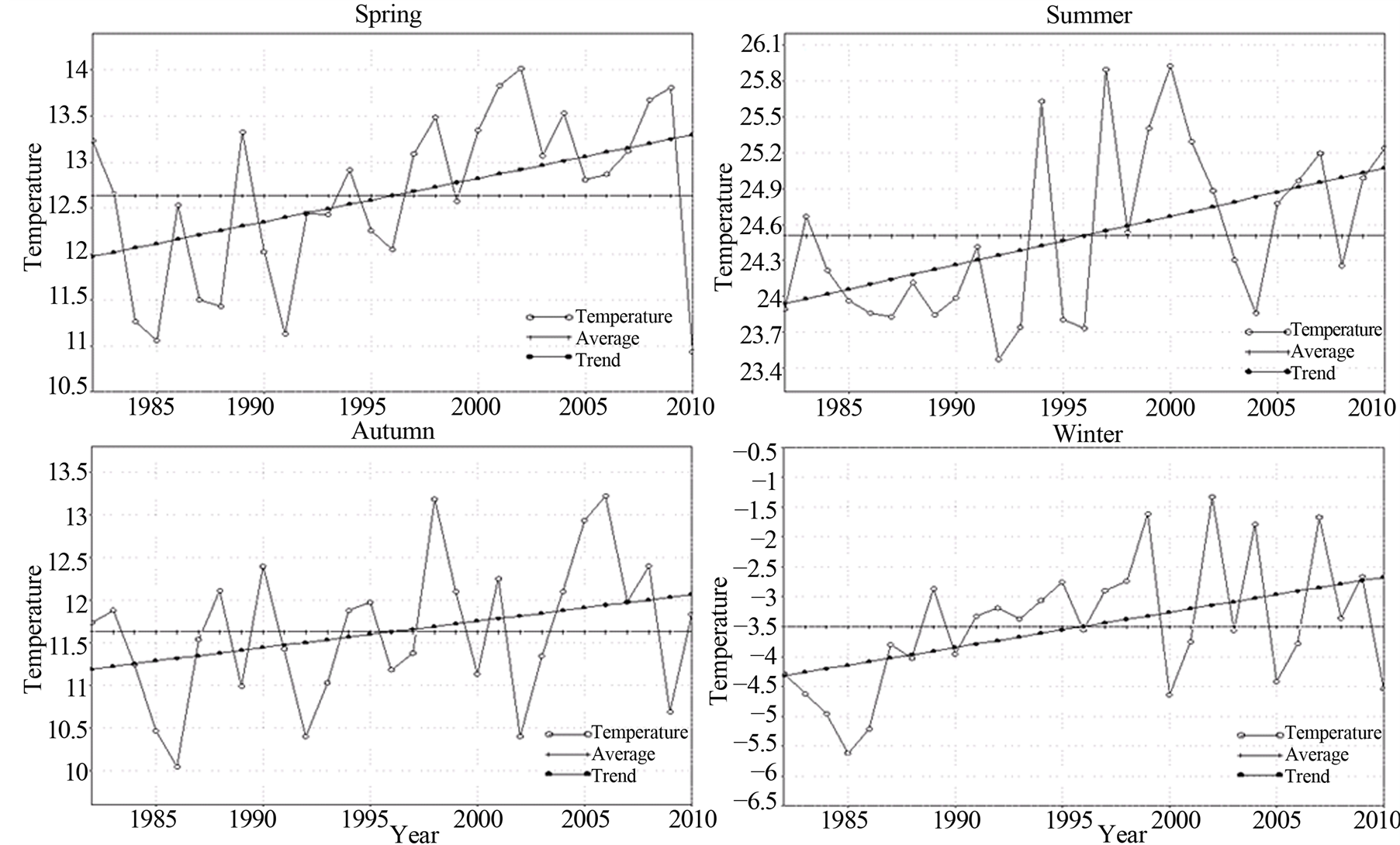
Figure 4. In 29 years (1982-2010) the curves of average temperature of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of each season
图4. 近29年(1982~2010年)京津冀地区各季平均气温(℃)变化曲线
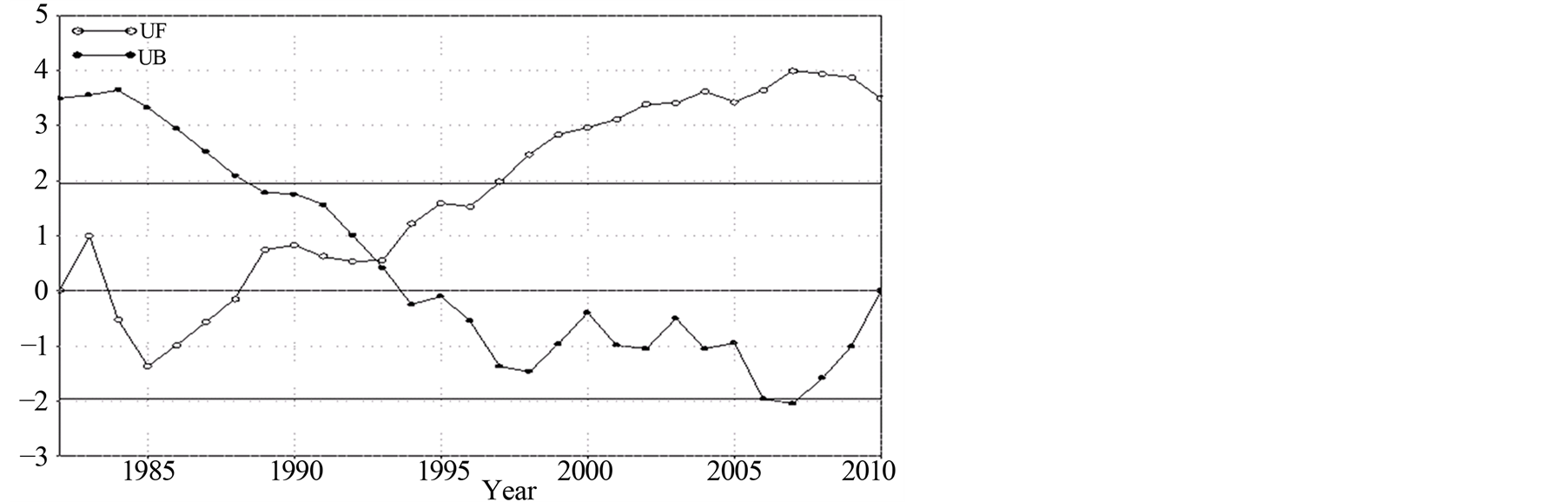
Figure 5. In 29 years (1982-2010) the curve of annual average temperature (˚C) of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of M-K
图5. 近29年(1982~2010年)京津冀地区年平均气温(℃)的M-K曲线
1990年代初期以前,UF < 0,表明该阶段是一个降温阶段。从1990年代开始,具体是在1989年以后,UF由负转正,平均气温有一个升温趋势,从1997年开始这种升温趋势异常显著,超过了α = 0.05的信度检验。同时使用滑动t检验的方法得到相似的结论(图略)。
3.2. 降水时空变化特征
3.2.1. 降水空间分布特征
京津冀地区年降水量空间分布如图6所示,由图可见,受大气环流形式、地理区域等因素的影响,京津冀地区年降水量空间分布不均,主要表现为在燕山和太行山迎风坡一侧降水量较大,平原地区的降水量普遍高于坝上地区,东部降水量明显大于西部。其高值区位于河北省唐山西部和承德南部之间;低值区主要位于张家口北部,其中张家口的康保年降水量为整个研究区最低。分析年降水量的空间分布差异,主要原因是由于山脉屏蔽作用,使得太行山和燕山山脉的东南迎风坡存在两个多雨中心,成为京津冀地区降水量较多的地区;在冀西北高原和冀中南平原存在两个少雨中心,成为京津冀地区降水量相对较少的地区。
3.2.2. 降水EOF分析
图7为1982~2010年京津冀地区年降水量的EOF分析,其中,前两个载荷向量累计方差达到55.9%,因此,前两个模态的分布情况可代表京津冀地区降水量空间分布的基本特征。降水EOF展开的第一特征向量场(图7a)的方差解释率为44.7%,且其空间分布表现为全区一致为正,揭示了研究区降水空间的一致性变化;其时间系数(图7b)表明研究区降水存在较大的年际变化,1997年以前以增加为主,1998~2002年为偏少期,2003年以后降水增加,这与前人研究的该地区降水变化特征基本一致[16] [17] 。第二特征向量场占总方差的11.2%,其空间分布表现为整个研究区呈反向变化的特点,北部偏少,南部相对偏多(图8a),该模态特征向量正值高值区在河北的邢台和邯郸东部,负值高值区位于承德中北部。第二特征向量的时间系数变化曲线(图8b),表明研究区降水这种南北反向分布的特征存在明显的年际变化,但无明显的年代际变化。

Figure 6. The annual precipitation (mm) spatial distribution map of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in recent 29 years (1982-2010)
图6. 京津冀地区近29年(1982~2010年)年降水量(mm)空间分布图
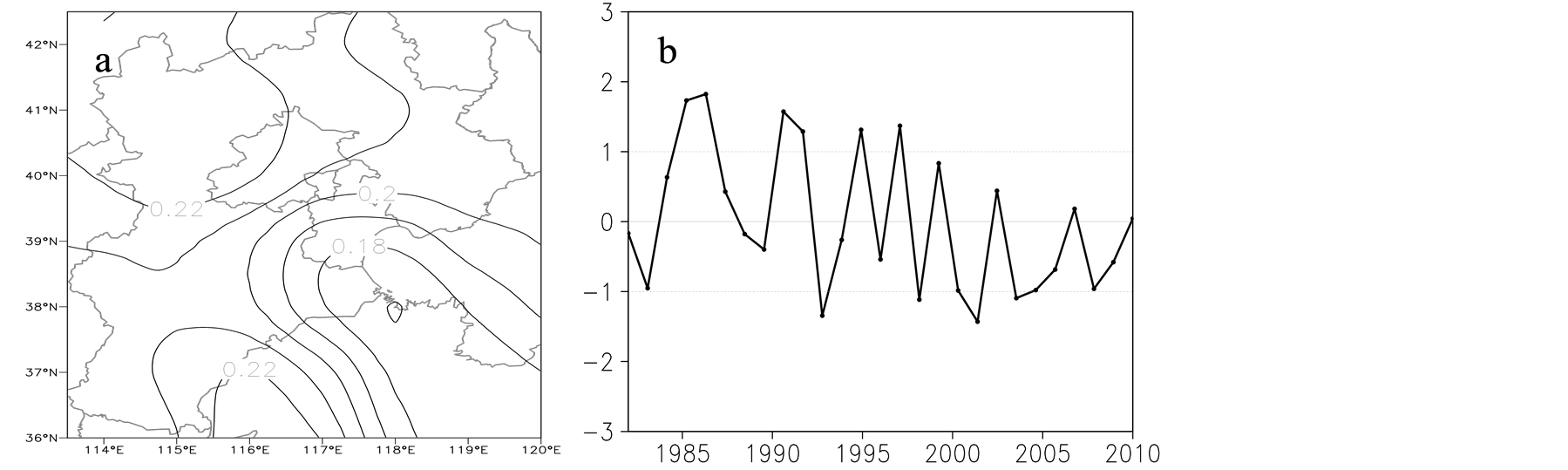
Figure 7. In 1982-2010, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and annual precipitation EOF analysis of the first eigenvector field (a) and the time coefficient series (b)
图7. 1982~2010年京津冀地区年降水量EOF分析的第一特征向量场(a)及其时间系数序列(b)
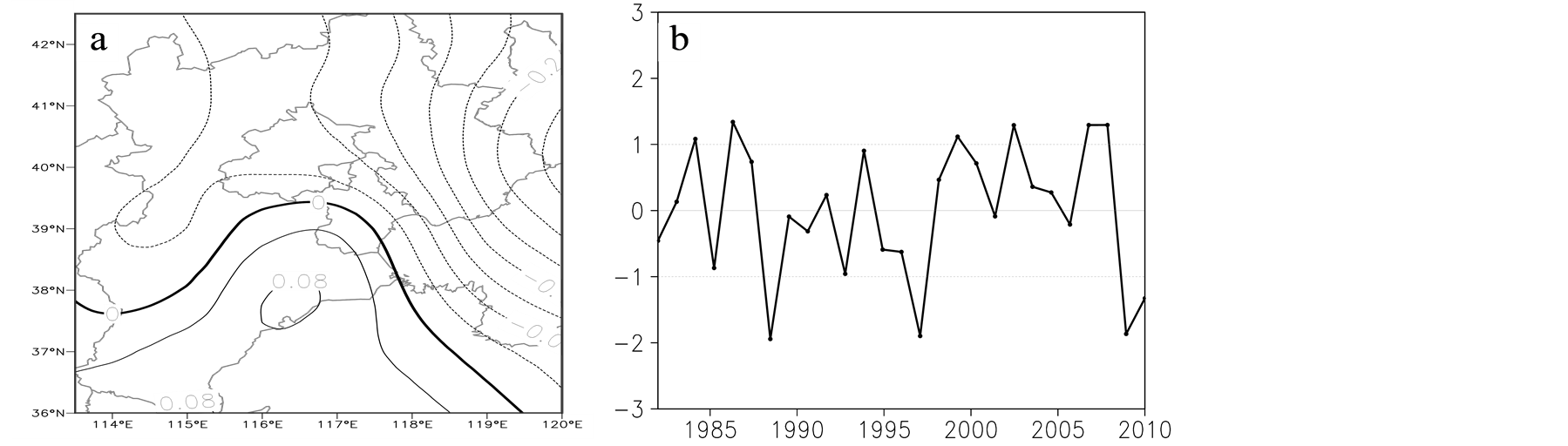
Figure 8. In 1982-2010, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region analysis of annual precipitation EOF second characteristic vector field (a) and the time coefficient series (b)
图8. 1982~2010年京津冀地区年降水量EOF分析的第二特征向量场(a)及其时间系数序列(b)
3.2.3. 降水时间变化特征
图9为近29年京津冀地区年降水量变化曲线,如图所示,京津冀地区多年平均降水量为504.9 mm,从变化趋势上看,年降水量整体呈下降趋势,其气候倾向率为−13.5 mm/10a,但下降趋势不显著,未通过α = 0.05的信度检验。从年代际变化上看,在1980年代年平均降水量略有减少,1990年代后年平均降水量呈增加趋势,并在1995年达到最大值,之后年平均降水量在波动中减少,最低值出现在2002年,进入21世纪后整体略有增加趋势,这与前人研究华北地区的降水特征较为相似[18] 。
图10为京津冀地区近29年(1982~2010年)四季降水量变化曲线,从图中可以看出,夏季是降水量最为集中的季节,平均降水量为336.5 mm,降水量在203.1~491.8 mm之间,占全年降水量的66.6%,从变化趋势上看,夏季降水量整体呈减少趋势,气候倾向率为−24.4 mm/10a,通过α = 0.05的显著性检验,说明京津冀地区夏季降水量减少趋势异常显著;其次为秋季,平均降水量为86.9 mm,降水量在39.6~189.1 mm之间,占全年降水量的17.2%,秋季降水量整体呈增加趋势,气候倾向率为8.4 mm/10a,但未通过α = 0.05的显著性检验,增加趋势不显著;春季和秋季降水量大体相当,平均降水量为72.2 mm,降水量在28.8~141.8 mm之间,占全年降水量近14.3%,春季降水量整体呈增加趋势,气候倾向率为1.7 mm/10a,未通过α = 0.05的显著性检验,增加趋势不显著;冬季为平均降水量最少的季节,仅有9.4 mm,降水量在1.1~28.2 mm之间,占全年降水量的1.9%,冬季降水量整体呈增加趋势,气候倾向率为0.9 mm/10a,未通过α = 0.05的显著性检验,增加趋势不显著。
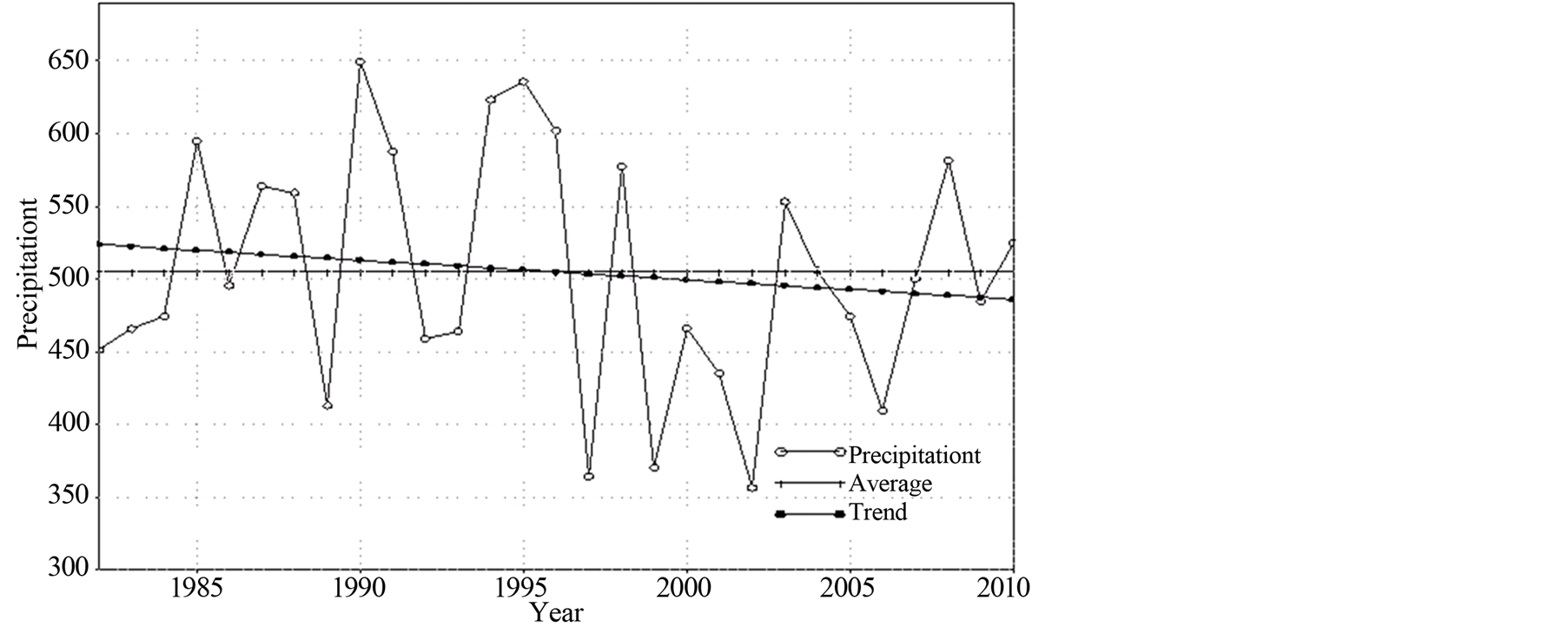
Figure 9. In 29 years (1982-2010) curves of precipitation (mm) in BeijingTianjin-Hebei region
图9. 近29年(1982~2010年)京津冀地区年降水量(mm)变化曲线
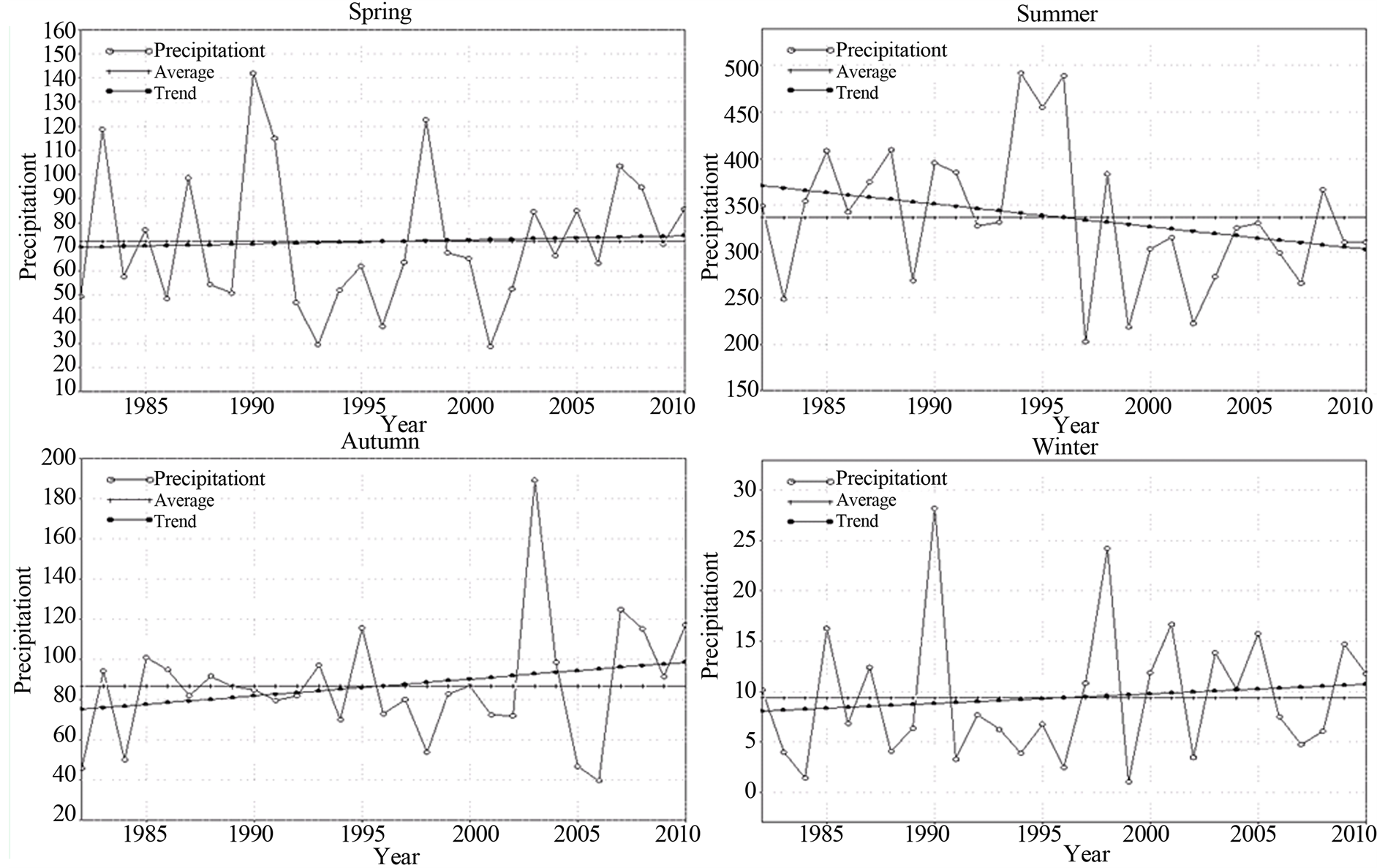
Figure 10. In 29 years (1982-2010) the curves of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of seasonal precipitation (mm)
图10. 近29年(1982-2010年)京津冀地区各季降水量(mm)变化曲线
3.2.4. 降水突变分析
图11给出了1982~2010年京津冀地区年降水量的M-K突变检验曲线,如图所示,近29年京津冀地区年降水量的UF和UB曲线变化都未超过α = 0.05显著性水平线,说明整体降水量的变化不明显;UF曲线在2001年之前大于0,说明在这段时间年降水量呈上升趋势,但在其他时间段年降水量都呈下降趋势,两线分别在1996年前后、1999年前后、2008年前后多处出现交点,表明在这段时期年平均降水量
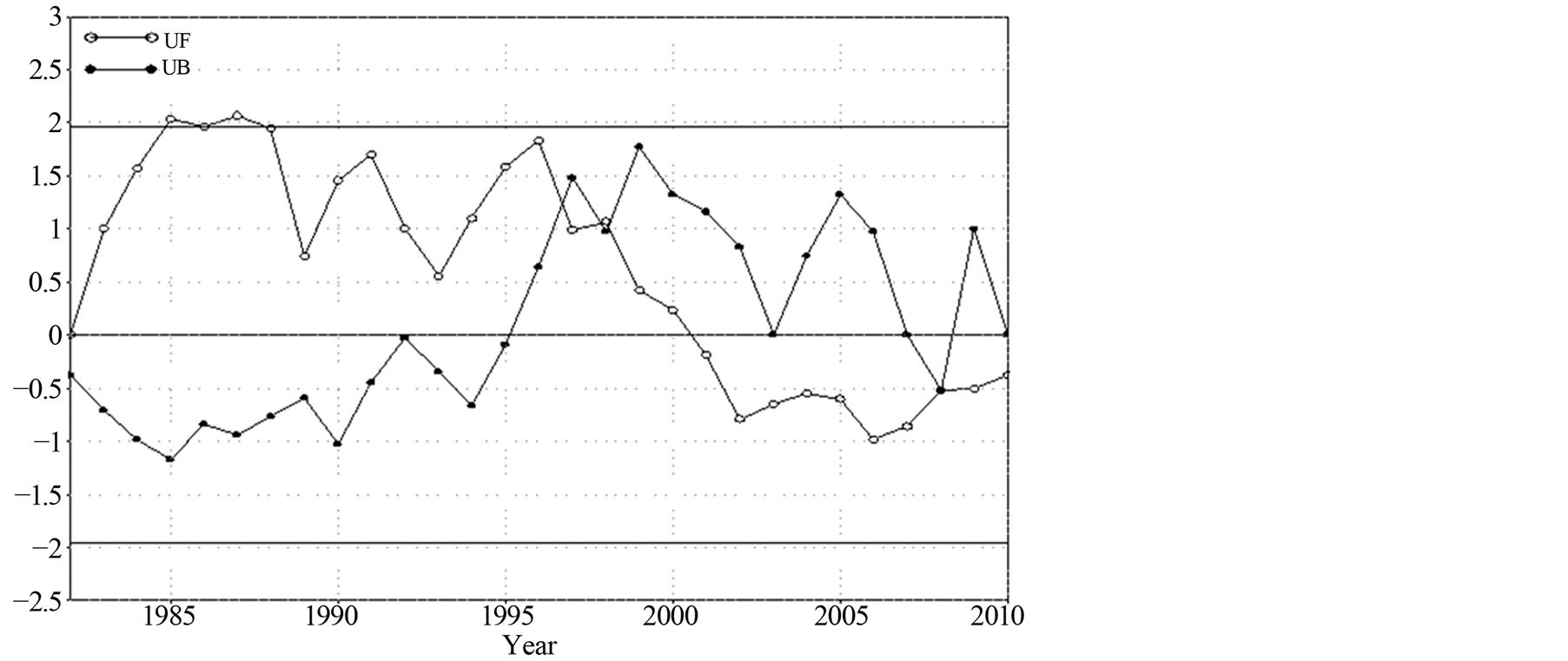
Figure 11. In 29 years (1982-2010) M-K curve of annual precipitation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
图11. 近29年(1982~2010年)京津冀地区年降水量的M-K曲线
发生了突变。对降水的突变分析同样采用了滑动t检验方法,结果与M-K方法分析结果基本一致(图略)。
4. 结论与讨论
利用京津冀地区83个站点1982~2010年近29年的气温和降水数据,分析了京津冀地区气候背景的时空分布及变化特征,得出以下结论:
1) 京津冀地区气温空间分布差异较大,整体上表现为南高北低,平原高于山区的特点,其高值区位于河北的中南部,其中邯郸的年平均气温为全最高,低值区位于河北张家口北部,张家口的康保年平均气温为全区最低;降水量空间分布不均,主要表现为在燕山和太行山迎风坡一侧降水量较大,平原地区的降水量普遍高于坝上地区,东部降水量明显大于西部,全区年降水量的空间分布既存在全区一致偏少的“一致型”,也存在北部偏少,南部相对偏多的“南北型”。
2) 从气温的时间变化上看,1982~2010年全区平均气温年际变化整体呈增加趋势,上升速率为0.44℃/10a,通过了α = 0.01的显著性检验,特别是1993年以后气温变化幅度较大,存在突变现象,各季气温均呈上升趋势,其中冬季上升趋势最为明显,其次是春季和夏季,秋季上升趋势最小。从降水量的时间变化上看,年降水量整体呈下降趋势,年际波动较大,气候倾向率为−13.5 mm/10a,但下降趋势不显著,未通过α = 0.05的信度检验。夏季降水量呈减少趋势,且减少趋势显著,其他季节均为弱的增加趋势,但不显著。
3) 通过对京津冀地区1982~2010年的年平均气温序列和年降水量序列进行突变检验分析,发现1993年为年平均气温的突变点,1990年代初期以前是一个降温阶段,1989年以后平均气温有一个升温趋势,从1997年开始升温趋势异常显著,超过了α = 0.05的信度检验线;近29年京津冀地区年降水量的UF和UB曲线变化都未超过α = 0.05显著性水平线,说明降水量变化不明显,2001年之前年降水量呈上升趋势,在其他时间段年降水量都呈下降趋势,1996年前后、1999年前后、2008年前后年降水量发生突变。
4) EOF分析表明,整个研究区气温呈一致性变化,气温明显增加的区域位于中西部内陆地区,时间系数表明年平均气温呈波动式增加,年际变化较大;降水自南向西北呈减少趋势,1997年以前以增加为主,1998~2002年为偏少期,2003年以后降水增加。
基金项目
公益性行业(气象)科研专项GYHY200806001。