1. 引言
景观格局是生态过程的载体,景观格局的变化影响着地表径流、生物地球化学循环等一系列生态和水文过程,进而对水质产生重要影响[1] 。20世纪70年代以来,国内外学者对区域景观格局与地表水水质之间的关系开展了大量研究,主要集中在景观类型的面积与水质的关系方面[2] [3] 而随着研究的进一步深入,以及3S技术发展,景观格局对水质的影响已逐渐受到关注,景观格局与地表水水质之间的关系已成为国内外研究的热点[4] 。
本研究以广州市南沙区新垦镇南沙湿地公园的人工滨海湿地为研究对象,以2010年的该湿地水质监测数据、植被群落调查资料为基本信息,采用相关性分析方法,从景观水平来分析南沙湿地公园的人工湿地景观格局对湿地水质的影响,以期为城市滨海湿地的环境保护提供借鉴。
2. 研究地点概况
研究地点位于广州市南沙区新垦镇的南沙湿地公园。该公园处于广州市南端,珠江入海口西岸(东经113˚33′07″~113˚39′58″、北纬22˚26′55″~22˚35′40″),是广州市最后一片大面积湿地。
南沙湿地公园内植被以红树科、禾本科和菊科植物为主,有高等植物318种,其中真红树10种、半红树6种。该地区属南亚热带海洋性季风气候,气温温和,夏季长,冬极短,年平均气温为21.8℃,降水量充沛,年平均降水量为1650 mm,年均日照时数为2000 hr。湿地公园是在滩涂上围筑而成的围垦地,土壤为潮滩盐土。
南沙湿地是候鸟迁徙必经地之一,鸟类种类丰富,以冬候鸟居多,数量占总数约72%,每年冬季有多达10万只的候鸟从遥远的北方飞来这里过冬,园内主要优势种为一些体型较大的涉禽和游禽[5] 。其中有国家Ⅰ级保护鸟类东方白鹳(Ciconia boyciana)和国家Ⅱ级保护鸟类黑脸琵鹭(Platalea minor)和白琵鹭(Platalea leucorodia)等濒危鸟类。
由于研究地点的人工湿地为无瓣海桑和芦苇混合种植,因此研究对象包括了无瓣海桑人工湿地和芦苇人工湿地。
3. 试验方法
3.1. 湿地水体的水质测定
在南沙湿地公园的无瓣海桑样地、芦苇样地和入水口(未种植湿地植物的对照水体),每月上旬定期一次采集水样,每个采样点取水面下0.5 m处的水样混合,采集量500 mL,用聚乙烯瓶密封保存,当天送分析室。
对水样进行总氮、总磷、锌、铜、铅、镉、COD、DO、BOD、pH值、氧化还原电位、电导率、盐度13个指标测定,其中对盐度、氧化还原电位、电导率和pH值等易变指标进行现场测定,其余指标为实验室测定。总氮和总磷用过硫酸钾氧化法测定[6] 。DO用碘量法测定,COD用碱性高锰酸钾法测定,BOD用五日培养法测定[7] 。
3.2. 植被群落的调查方法
如图1所示,设置20 m × 20 m无瓣海桑样地3个、10 m × 10 m芦苇样地3个。每个无瓣海桑样地布设10 m × 10 m的样方3个,每个芦苇样地布设5 m × 5 m的样方3个。以样地为基本单位,分别记录种名、盖度、胸径、树高、株数等数据。
3.3. 景观格局指标的选取
根据研究地点的分布图(图1),选取适宜的景观格局指数,如斑块密度、斑块面积、斑块周长面积比等等,与净化功能进行相关性分析。
4. 结果与分析
4.1. 南沙人工湿地的水质
南沙湿地公园中,入水口没有种植任何植物,其上游为珠江,上游地区水体受到工业污染和居民生活污水的影响较大。无瓣海桑和芦苇对由外界进入湿地公园内的水体质量影响结果如下。
4.1.1. 湿地水体N含量
各样地平均TN值12月最高,7、8月份最低(图2),即秋冬季的污染高于夏季,与李睿华等[8] 研究
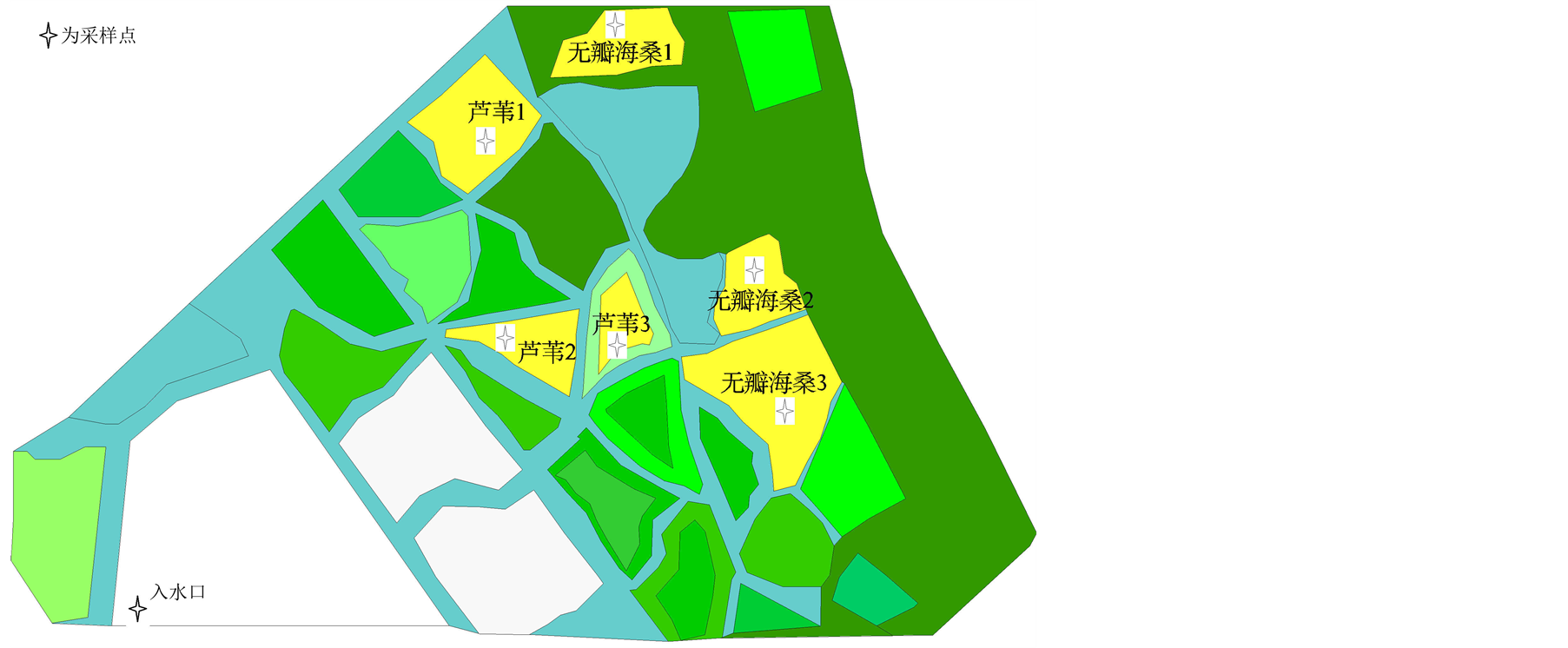
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of sample plots
图1. 样地设置示意图
结果一致。夏季时雨水量大,水量增多,水体N含量相对减少;另一原因可能是该段时期是植物生长旺盛时期,植物体自身生长也需要大量N。由图2可见,各样地对TN的净化效果较明显。其中,7月份和12月份芦苇湿地对N去除率分别为63.8%和77.8%;无瓣海桑湿地对N去除率为41.4%和36.9%。9月和11月,无瓣海桑湿地附近水域中N含量比入水口的高,由于南沙湿地为人工湿地,进入系统的水体并不是由潮汐决定水流,初步认为是由于这两个月无瓣海桑湿地对N的去除率较上月降低,之前积累的N仍未被完全去除,这一现象有待进一步研究。可见,无瓣海桑对N的去除效果不及芦苇。
4.1.2. 湿地水体P含量
各样地TP的变化总体是随着季节的推移逐渐减少(图3)。P是植物体中诸多化合物的成分之一,并以多种方式参与新陈代谢,同时增强植物体对外界环境的适应能力。11月和12月磷含量骤降,其可能原因是气温下降,水体在进入湿地系统前,水体的P被流域中或附近的其他植物吸收较多。7月份进入系统的P含量最多,无瓣海桑湿地和芦苇湿地对P的去除率分别为75.4%和26.1%;12月份时,无瓣海桑湿地和芦苇湿地对P的去除率分别为20.1%和23.5%。可见,无瓣海桑对P的净化效果较好。
4.1.3. 湿地水体COD值
化学需氧量(COD)是衡量水体中有机物含量的指标,其数值越大则有机物污染越严重。7月和8月时,无瓣海桑湿地对COD有明显抑制作用,去除率最高达22.1%。芦苇湿地则在12月份达到最大去除率18%,对COD去除效果不及无瓣海桑湿地。在9月、10月和11月由于枯枝落叶增多,且分解速率加快,致使水体中有机物含量增加,出现两种样地周围水体COD的含量增加(图4)。
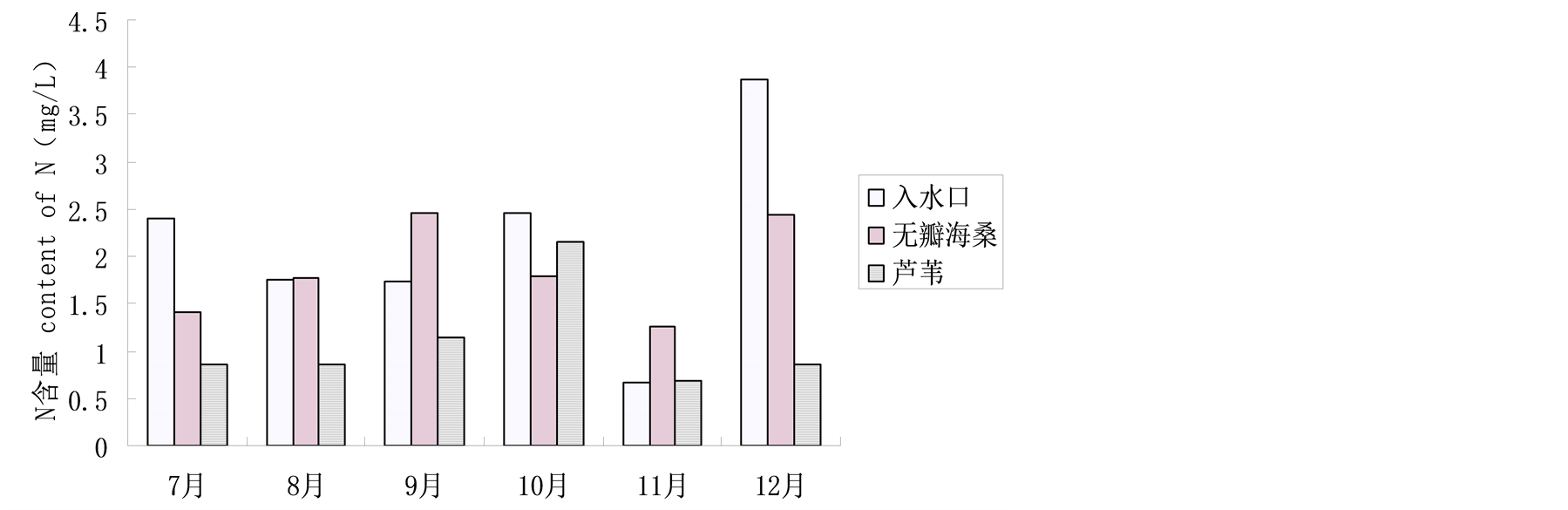
Figure 2. TN contents of different plots in different months
图2. 不同月份各样地水体N值
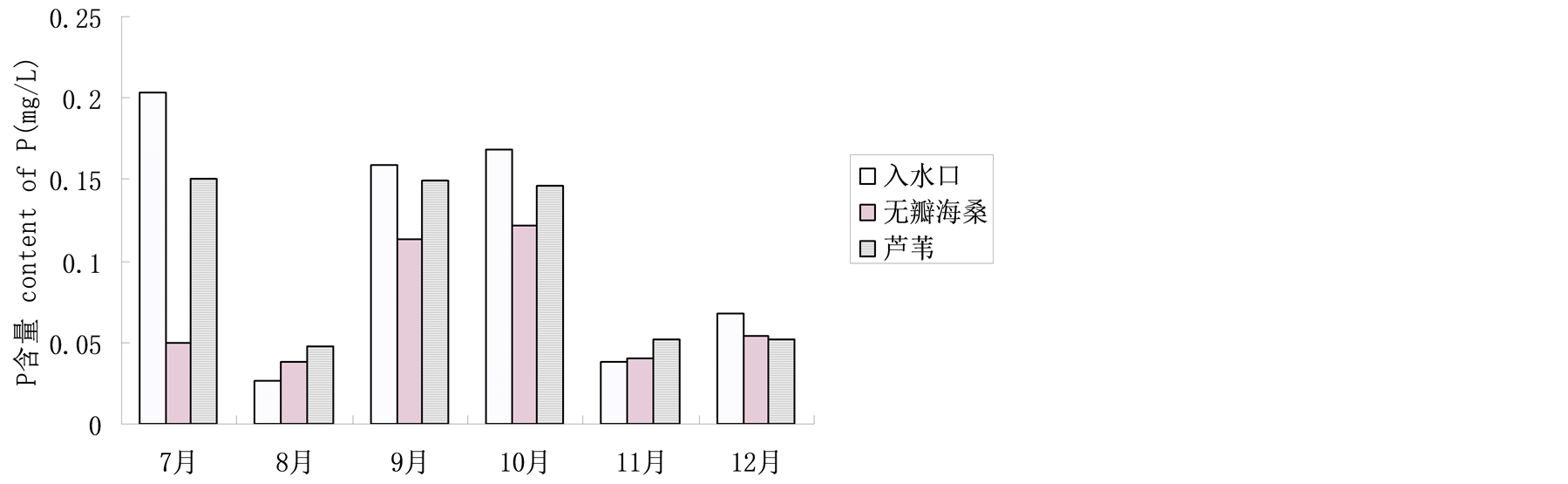
Figure 3. TP contents of different plots in different months
图3. 不同月份各样地水体P值
4.1.4. 湿地水体pH值
如图5所示,几个月中pH值的变化在6.25~8.16之间,其中绝大数月份无瓣海桑湿地的pH值均低于入水口和芦苇,原因是无瓣海桑植物体中含有单宁,单宁具弱酸性可引起pH值的下降[9] 。
4.1.5. 湿地水体BOD值
BOD是表示水中有机物等需氧污染物质含量的一个综合指标,主要用于监测水体中有机物的污染状况。由图6可知,在经过无瓣海桑湿地和芦苇湿地后,水体BOD均有不同程度的降低,其中无瓣海桑湿地的BOD去除率(最大值达43.9%)高于芦苇湿地(去除率最大值26.8%)。11、12月份对BOD去除效果高
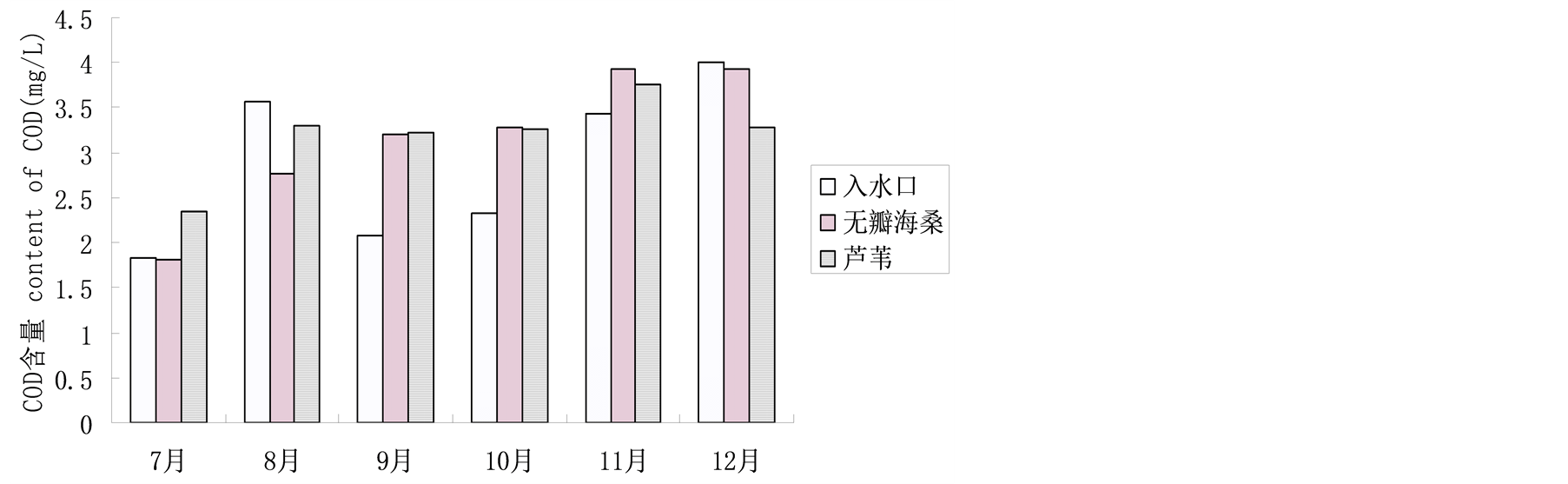
Figure 4. COD of different plots in different months
图4. 不同月份各样地水体COD值
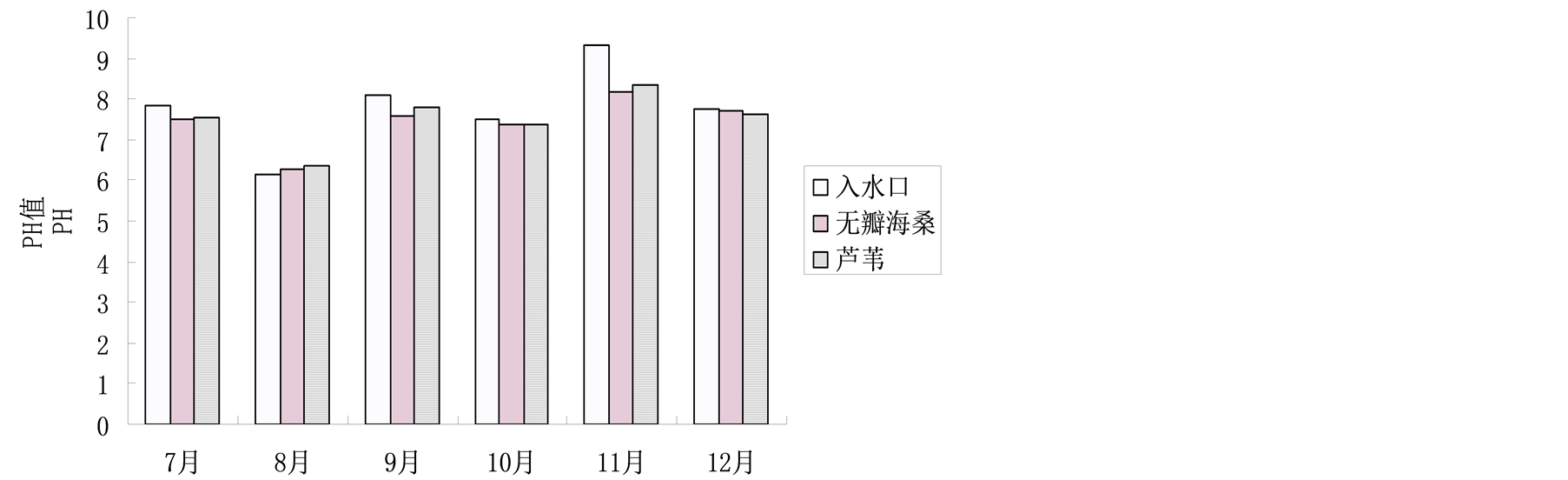
Figure 5. PH values of different plots in different months
图5. 不同月份各样地水体pH值
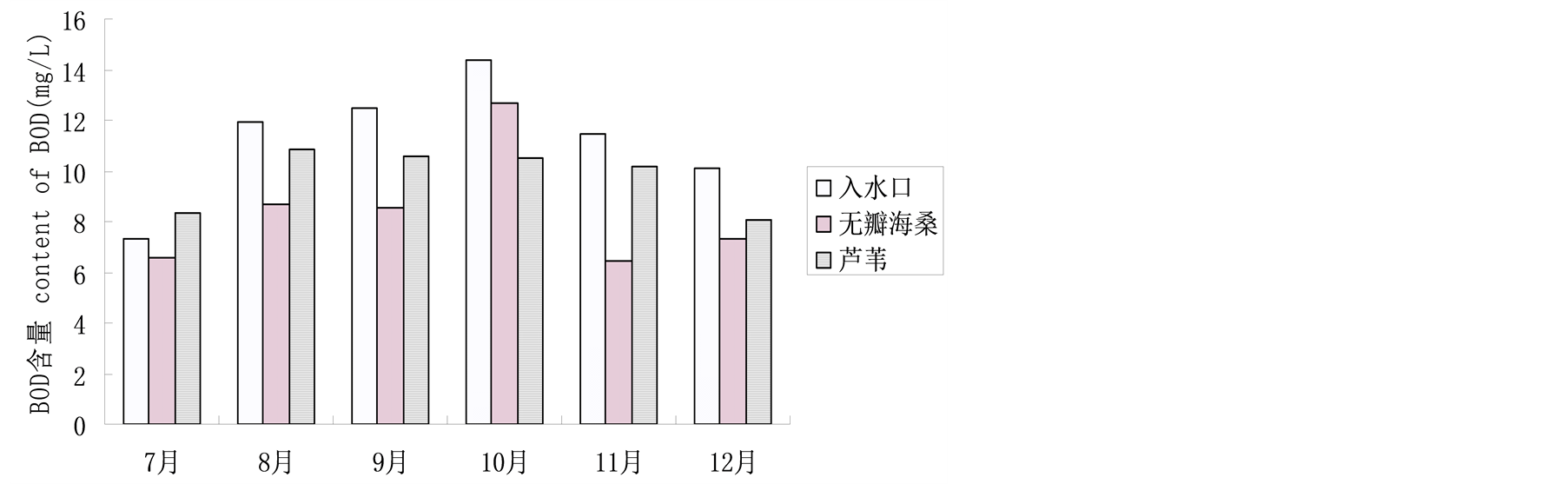
Figure 6. BOD of different plots in different months
图6. 不同月份样地各水体BOD值
于7、8月份。
4.1.6. 湿地植物对水体Zn值的影响
水体Zn含量在经过湿地植物后呈递减趋势(图7),7月和10月无瓣海桑湿地和芦苇湿地附近水域中Zn含量增加,这是由于植物对Zn的吸收量大,同时归还量也较大[9] 。芦苇湿地对Zn的吸附率在10月达81.9%,其余月份在21.3%~42.3%之间,无瓣海桑湿地对Zn吸附率在13.5%~31.9%之间。参照《海水水质标准》,湿地中大部分水体属于第二类水体(Zn含量 ≤ 0.050 mg/L)。9月份和10月份经过芦苇净化过的水体已经达到Zn含量 ≤ 0.020 mg/L,属第一类水体。
4.1.7. 湿地水体Cu含量
Cu是植物正常生命活动所必需的微量矿质元素,广泛参与植物生长发育过程中的多种代谢反应,Cu也是对植物生长有毒害的重金属元素之一,植物器官中的Cu含量只要轻微超过它的最佳含量就会产生毒害[10] 。南沙湿地各样地水体Cu含量见图8。在7~10月,入水口的Cu含量较低,在0.008 mg/L~0.014 mg/L之间,大部分时间该水体符合《海水水质标准》中的第二类水体(Cu含量 ≤ 0.010 mg/L)。芦苇湿地对Cu的净化效果十分明显,7月份芦苇湿地对Cu的吸附率达76.9%,10月份为49.1%。无瓣海桑湿地对Cu的吸附率在7月份为76.6%,然而在之后的月份并未显示明显的净化效果。在8、9月份时,无瓣海桑湿地和芦苇湿地附近水体中铜含量,相比从入水口进入湿地的铜含量反而增加,原因待进一步研究。
4.1.8. 湿地水体Cd含量
Cd对植物体具有明显危害作用,高浓度Cd会阻碍植物生长发育,并造成植物体内残留Cd [11] 。如
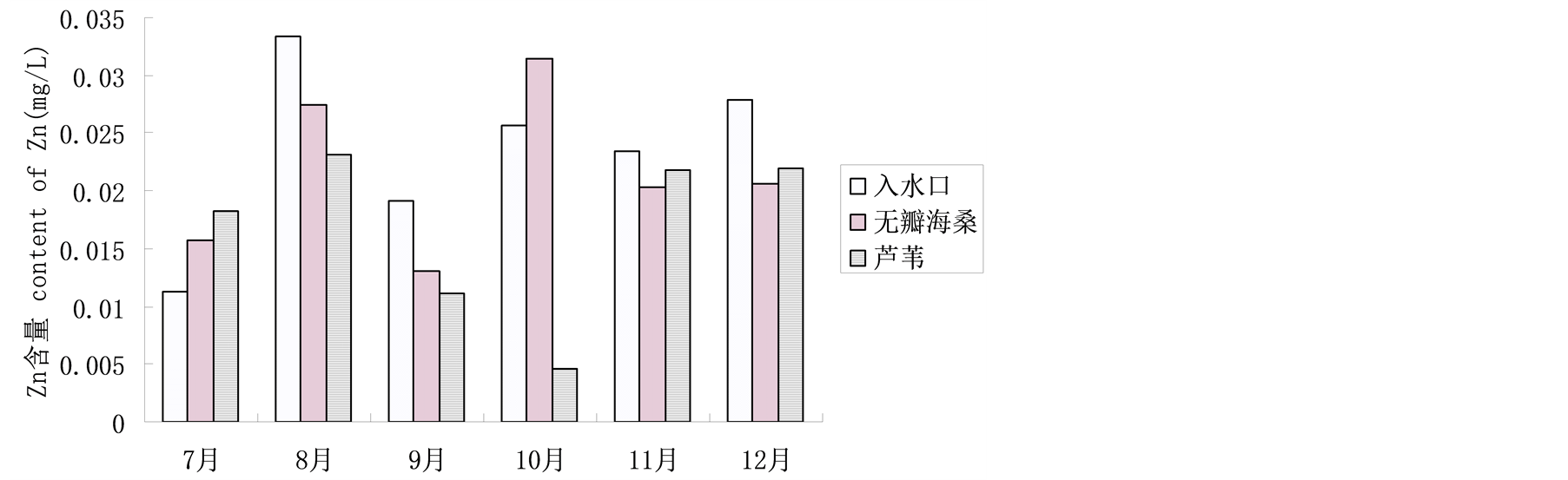
Figure 7. Zn values of different plots in different months
图7. 不同月份各样地水体Zn值
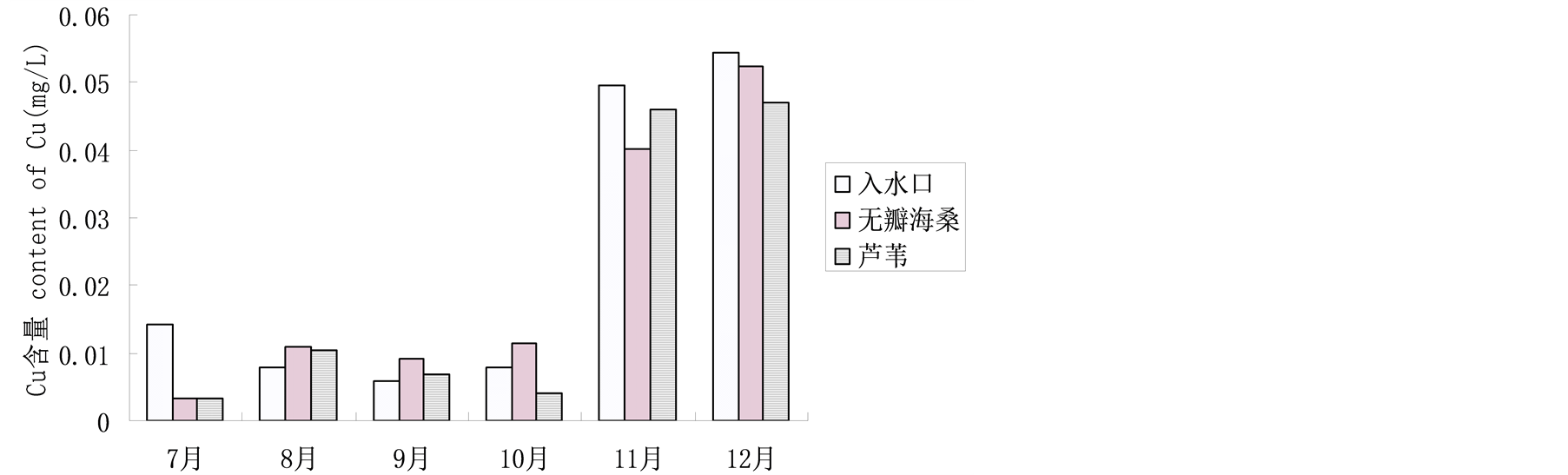
Figure 8. Cu values of different plots in different months
图8. 不同月份各样地水体Cu值
图9所示,南沙湿地水体中Cd的含量范围在0.0142 μg /L~0.1318 μg /L,参照《海水水质标准》可知,南沙湿地中水体并未受到Cd污染。芦苇湿地对Cd的净化效果明显,吸附率为12.38%~64.57%,无瓣海桑湿地对Cd的吸附率为5.61%~44.61%。
4.2. 南沙人工湿地景观格局指标与水质各指标的关系
南沙人工湿地的水样采自芦苇和无瓣海桑固定样地。由于研究区域为人工湿地,空间分布均匀,因此只选择了斑块面积进行分析。斑块面积直接影响到生物物种的分布和生产力水平,以及景观的功能。一般较大的斑块可以更好的保护某种基因和物种多样性,其数量的增多则有利于物种多样性和景观的异质性。
南沙湿地公园中共有大小斑块35个,斑块面积在0.06 hm2~0.274 hm2之间。其中大型斑块中植物种类较单一,本研究所选取的是斑块主要由芦苇和无瓣海桑为建群种。斑块面积与水质各指标的关系结果见表1。斑块面积与无瓣海桑斑块附近水体中的绝大多数指标并无显著性差异,即斑块的大小变化对斑块附近水域中水质无明显影响。水体BOD和pH值与斑块面积呈负相关,即斑块面积越大,水体BOD、pH值越低。其中斑块面积与水体Zn含量显著相关,且为正相关(P < 0.05,表1),表明斑块面积越大,水体Zn的含量越高,与章金鸿等(2000)的研究结果相符,即进入红树林湿地中Zn元素主要被林下土壤吸收[12] ,经过长期富集作用,面积越大的斑块累积的Zn量越高。
由表2可知,斑块面积与芦苇斑块附近水体中的各项指标并无显著性差异,水体中的BOD、TN、TP、Cd含量与斑块面积呈负相关。即斑块面积越大,水体中的BOD、TN、TP、Cd含量越低。
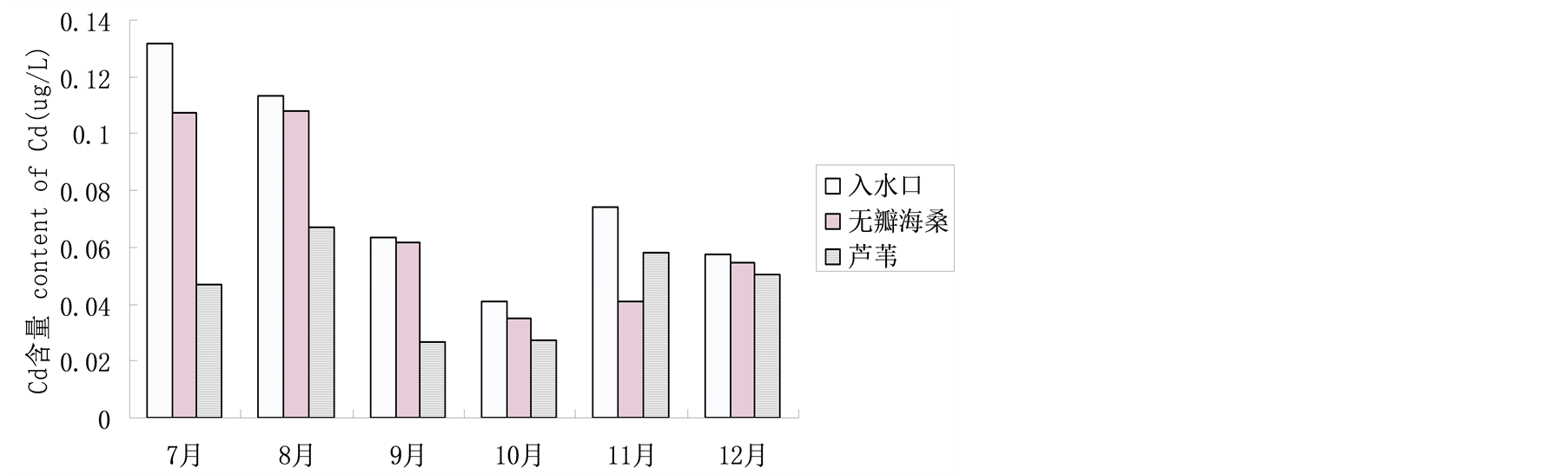
Figure 9. Cd values of different plots in different months
图9. 不同月份各样地水体Cd值

Table 1. Correlation analysis of water index and plaque area of Sonneratia apetala wetland
表1. 无瓣海桑斑块面积与水质指标相关分析

Table 2. Correlation analysis of water index and plaque area of Phragmites communis wetland
表2. 芦苇斑块面积与水质指标相关分析
5. 结论
地处珠江入海口西岸的广州市南沙湿地属于人工湿地,湿地内的斑块面积、分布以及斑块内植物的种类等均为人为控制。通过研究斑块面积指数和水体中各个指标的关系,发现经过南沙湿地的水体中部分指标均有所下降,具体表现为:1) 无瓣海桑湿地附近水体中的BOD和pH值与斑块面积呈负相关,即斑块面积越大,水体中的BOD、pH值越低;2) 斑块面积越大,水体中Zn的含量越高;3) 芦苇湿地附近水体中的TN、TP、Cd、BOD与斑块面积呈负相关,即斑块面积越大,TN、TP、Cd、BOD的值越小。可见人工湿地在防治水体富营养化上有一定的作用,但在构建人工湿地时应该注意斑块面积的合理分布。
基金项目
国家科技支撑计划专题(2009BADB2B0104)。