1. 引言
区域交通可达性已经成为旅游发展的影响因子[1] ,探究旅游目的地交通可达性改变下旅游发展效应成为当前研究的焦点。
国外学者的研究主要集中在铁路网络可达性的演变以及交通可达性对区域经济的影响等方面,Javier [2] 、Gutierrez [3] 和Gonzalez [4] 等对欧洲高速铁路网、公路网的改变引起的欧洲各城市可达性变化进行了研究;Keeble、Linneker通过对交通路网格局改变下可达性分析,通过对比建设前后可达性的时空演化,得出区域边缘区可达性提高对经济效益最大[5] [6] 。国内学者对交通网络可达性相关研究主要集中于从不同尺度下探究交通可达性空间结构、时空演化特征及其效应分析,王振波等探讨了中国县域可达性及其区域划分,并分析了其与人口分布的关系[7] ;胡浩等以国家历史文化名城为研究对象,分析了交通可达性的集聚效应[8] ;吴威等以长三角地区为例探究了20世纪80年代以来的综合交通可达性及其时空演化[9] ;徐旳、陆玉麒以江苏省为例分析经济发达省份高等级公路网络的演化及由此引起的省内通达性空间格局的变化[10] ;陈松林、朱兵等从省域尺度下探究了交通可达性空间格局[11] [12] ;陈刚等分析了区域可达性及其与旅游经济相互关系[13] [14] ;徐维祥等以浙江省11个地级市为研究对象,探讨了城市可达性与城市对外经济联系的时空演变[15] ,蒋海兵以京沪高铁为例分析了高铁影响下的区域可达性空间分异特征[16] ;吴旗韬从交通可达性的视角探究了港珠澳大桥时空压缩效应[17] 。归纳已有研究成果,在区域交通可达性空间特征、时空格局演化、交通改变下区域可达性空间特征与效应分析等方面取得丰硕的成果,但是对特殊的西南边疆山区交通可达性时空演化特征及其旅游效应缺乏系统分析。
借鉴前人研究成果的基础上,利用加权平均旅行时间指标建立路网交通可达性模型,运用ArcGIS网络分析工具测算了云南省16个州市中心城市1996年、2001年、2006年和2011年交通可达性值,分析了云南省交通网络的时空间格局特征,并运用广义可加模型探究了云南省交通可达性的旅游效应。
2. 研究区域、方法与数据选取
2.1. 研究区域概况
云南地处云贵高原西部,地形复杂,历史上交通运输十分落后[18] ,20世纪90年代以来,云南省抓住国家实施西部大开发战略、中国–东盟自由贸易区的建立和泛珠三角区域合作等重大机遇,高速公路不断完善,铁路路网不断拓展,交通网络发展进入快速发展的新时期。1996年,云南省交通网络由干线公路、普通公路组成,通车里程约7.029万千米。到2001年云南省基本上形成了以国道、省道、县道为主体的公路网络,通车里程约为16.3953万千米。2001~2006年期间,国道、省道继续建设并提升,高速公路大规模建设同时进行,公路网络格局发生了很大变化。到2011年,初步形成了以国道、高速公路为主干的云南省公路交通网络,通车里程约21.4524万千米。由于云南省特殊的地理区位和地形特征,铁路发展缓慢,铁路运输网并未形成,总体水平较低。
2.2. 研究方法
2.2.1. 可达性评价方法
采用加权平均旅行时间计算节点城镇的可达性,其公式为:
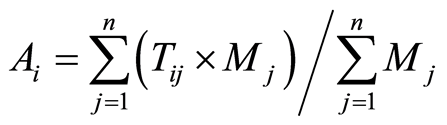 (1)
(1)
式中:Ai表示区域内节点i的可达性,Tij表示节点i到节点j所花费的最短时间,Mj为节点j的权值,权值取各节点相应年份的GDP总值。为了更好地反映各节点可达性水平的相对高低,采用可达性系数表达,公式为:
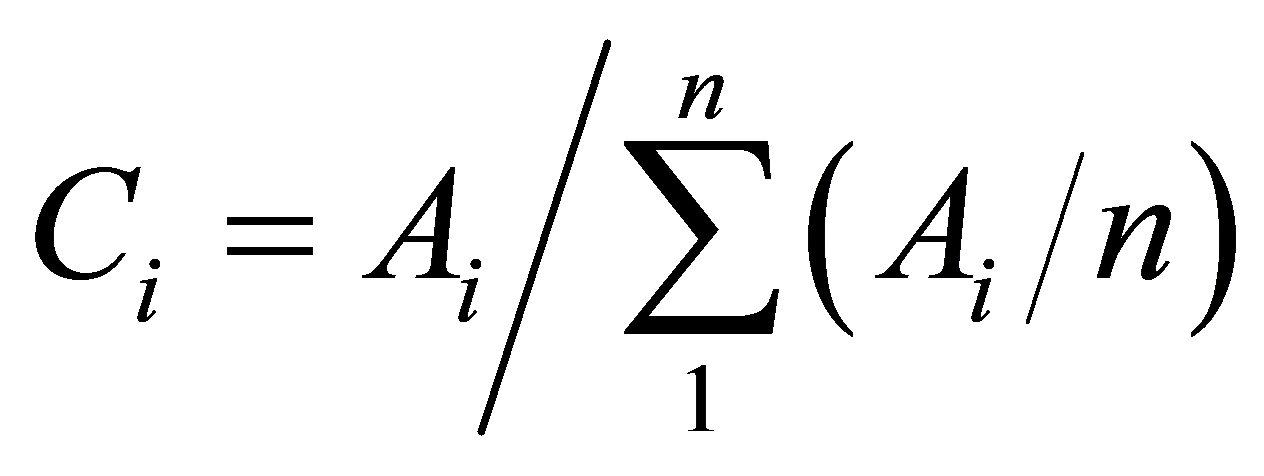 (2)
(2)
式中,Ci为i的可达性系数,n为节点个数。
2.2.2. 旅游效应评价方法
GAM模型是基于数据驱动,而不是模型本身,数据决定着响应变量和预测因子之间的关系,而不是假设响应变量与预测因子间的某种参数,具有相对客观性[19] 。采用广义可加模型(GAM)的方法,分析交通网络与旅游变化的关系,其表达式为:
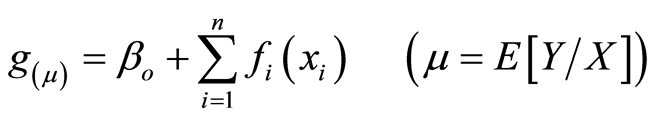 (3)
(3)
中:函数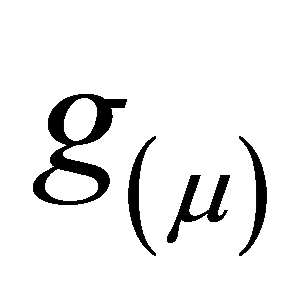 为联系函数,
为联系函数,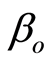 为常数截距项,
为常数截距项,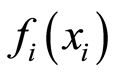 为用来描述
为用来描述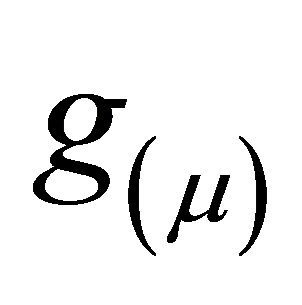 与第i个解释变量关系的非参数函数,可通过局部加权回归平滑或样条平滑得到,本文采用样条平滑法。GAM预测模型拟合结果的评价指标为模型的偏差(D2),其计算公式如下:
与第i个解释变量关系的非参数函数,可通过局部加权回归平滑或样条平滑得到,本文采用样条平滑法。GAM预测模型拟合结果的评价指标为模型的偏差(D2),其计算公式如下:
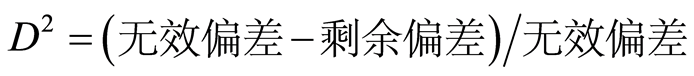 (4)
(4)
式中,D2表示线性回归模型中的回归系数。
2.3. 数据来源与处理方法
以2011年行政区划为基准,选取16个州市作为研究单元,根据云南省交通发展建设历史阶段性特征,选取了1996年、2001年、2006年和2011年四个等时间截面。通过ArcGIS10.0网络分析模块测算出不同时间断面16州市的中心节点城市与其他节点城市之间的最短路径(最短旅行时间),随后根据公式(1)计算出各节点城市与其他节点城市的加权平均旅行时间。
根据中华人民共和国行业标准规定的公路设计速度,结合边疆山地的区域特点,拟对其交通时速进行重新设定(见表1);主要从两方面考虑:一是边疆山地交通普遍很差,基于空间阻隔模型,构造距离矩阵测算的通达性结果往往与游客的感觉不一样;二是边疆山地的交通线往往在狭长的高山峡谷地带穿行,容易受自然灾害的破坏而中断。铁路运行时间根据各个时间段的铁路运行时刻表来确定。云南省的道路网发展数据(包括铁路、高速公路、国道、省道和一般道路)主要来源于《中国交通地图册》(中国地图出版社,1996年,2001年,2006年,2011年)。云南省旅游面板数据(包括入境旅游人次、旅游外汇收入、国内旅游人次、国内旅游收入、旅游总收入)来自《云南旅游统计年鉴》以及云南各州市旅游局官方网站。
3. 云南省路网交通可达性时空演化
3.1. 陆路网络可达性空间格局
利用公式(1)计算出云南省16个城镇节点不同时间断面的加权平均旅行时间,采用ArcGIS空间分析可视化功能,得出其空间格局(见图1)。
1) 云南省可达性空间格局总体呈现以昆明为中心向外围区域递减的“核心–外围”模式,可达性等值线大致呈不规则环状分布。4个时间断面的可达性低值区均位于昆明及其周边地区;由于昆明位于云南省区域发展的中心,可达性最优;香格里拉、泸水、昭通部分等地区位于云南省地形复杂的边缘区域,与其他城市相距较远,可达性始终最差。
2) 根据可达性值的大小,将区域内主要城市可达性水平划分为4个层次:可达性好的城市包括昆明、曲靖、玉溪和楚雄,可达性较好的城市包括大理、蒙自、普洱和临沧,可达性一般的城市包括丽江、保山、文山、芒市和景洪,可达性差的城市包括香格里拉、泸水以及昭通。昆明位于区域发展的中心,交通发达,不同时间断面均有多条干线公路构成辐射型公路网络,故可达性始终是最优的;楚雄、曲靖和玉溪三市分别位于昆明市的周边,主要承担区内外的联系,受此影响三市的可达性水平好;其中大理和普洱是云南省旅游资源禀赋较高的旅游城市,资源和区位优势明显,可达性处于较好的层次。由于本文可达性指标采用节点中心城市GDP的几何平方根的加权平均旅行时间,中心城市可达性水平不仅受区位因素、交通基础设施状况影响,还受到城市本身经济总量的影响,因而使得边境旅游城市可达性水平也有一定的提升空间。
3.2. 路网可达性动态演化格局
1) 1996~2011年15年间,各中心城市节点的可达性水平均有大幅度的提升。云南省16个节点城镇最短加权旅行总时间由143.59 h缩减至58.72 h,节省了84.87 h;中心城市平均加权旅行时间由8.97 h减少到3.67 h,年均减少5.3 h,平均可达性变化率为40.9%;但不同时间段交通可达性改善幅度有较大差别:第一阶段(1996~2001年)各中心城市平均加权旅行时间减少2.65 h (29.51%),年均减少0.53 h (5.9%);第二阶段(2001~2006年)减少1.49 h (23.54%),年均减少0.298 h (4.7%);第三阶段(2006~2011)减少1.17 h (24.13%),平均减少0.234 (4.82%)。对比不同时间段年均可达性变化值可以看出,第一阶段可达性优化

Table 1. The design speed of each level highway
表1. 各等级公路设计速度
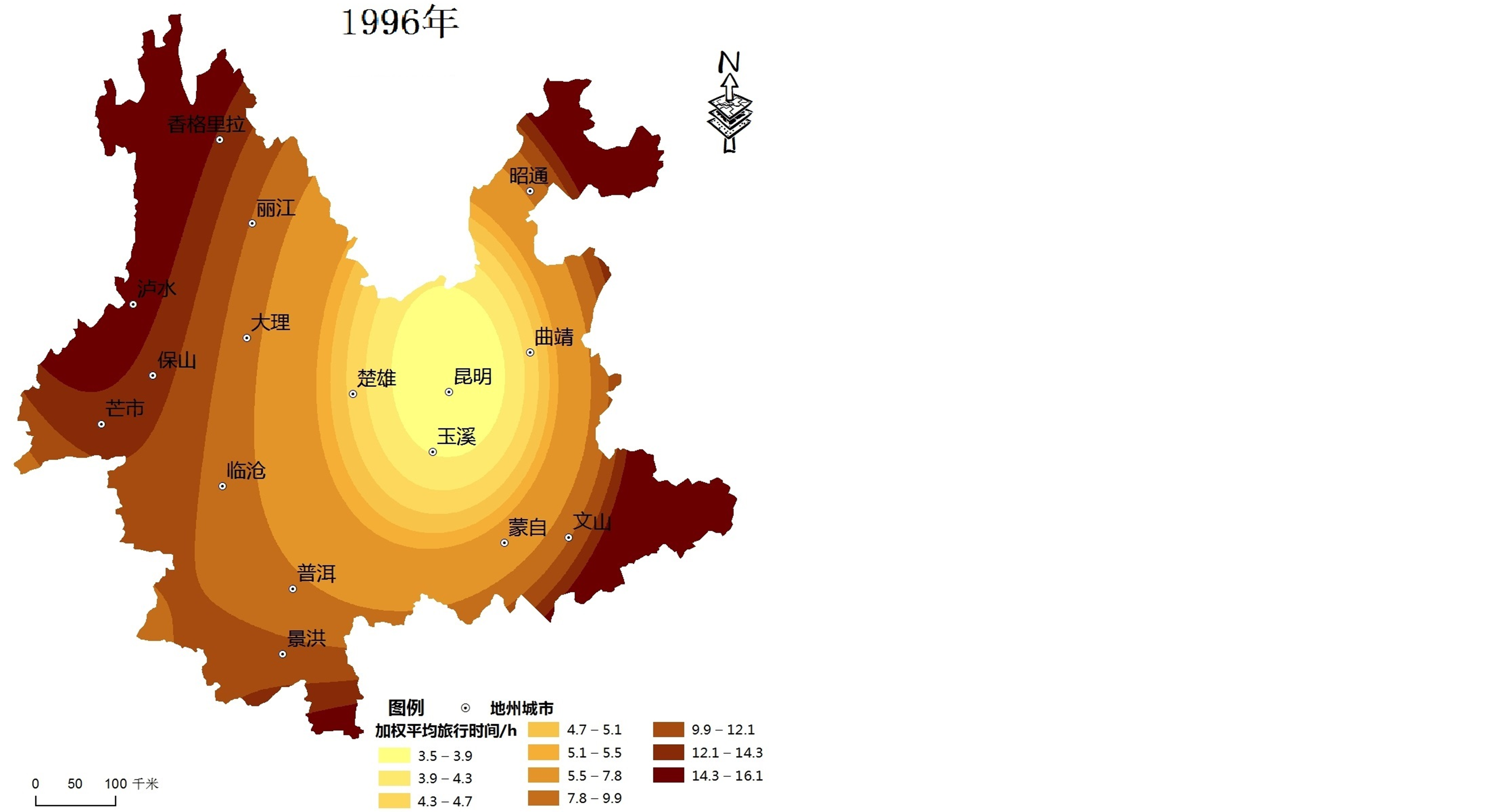
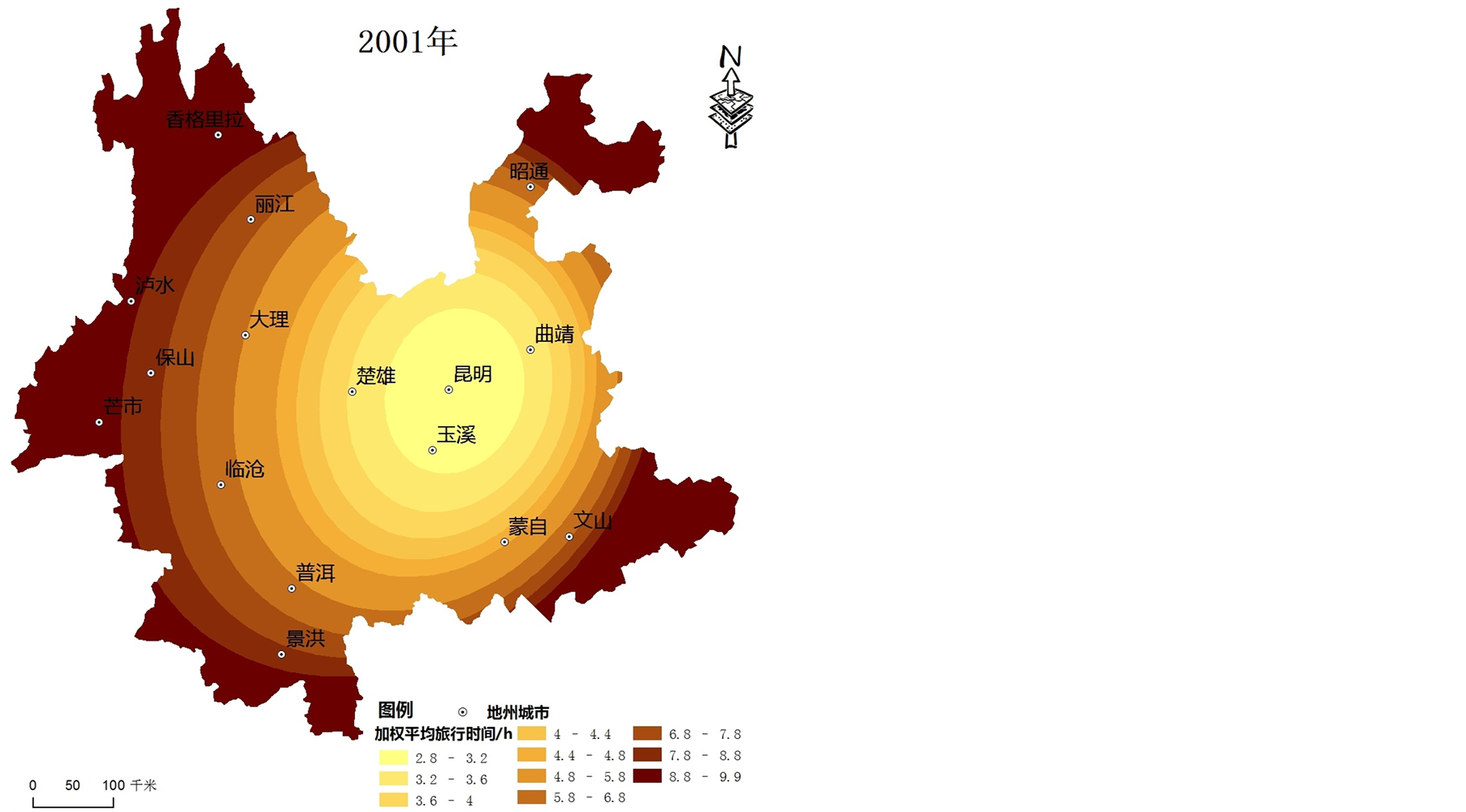
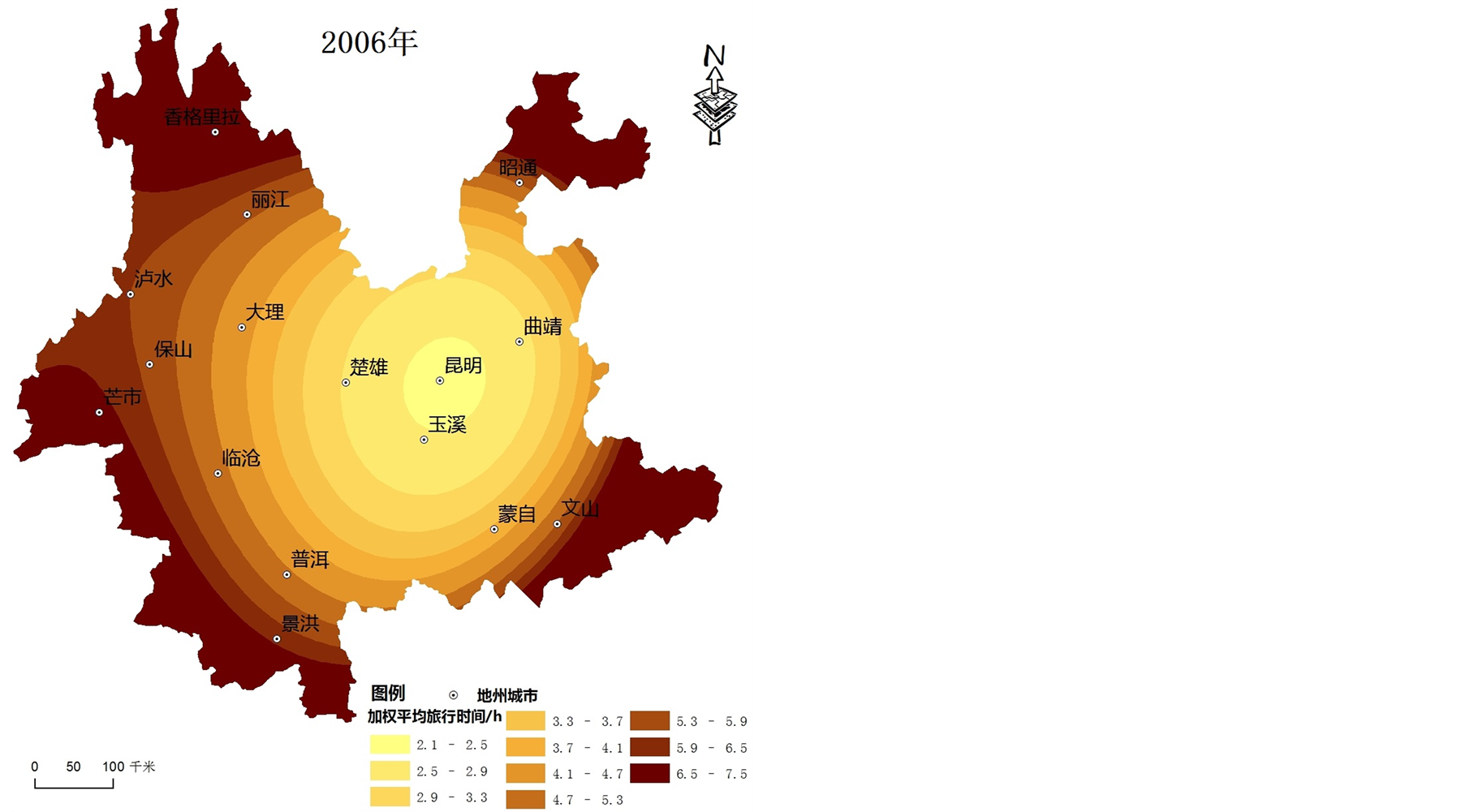
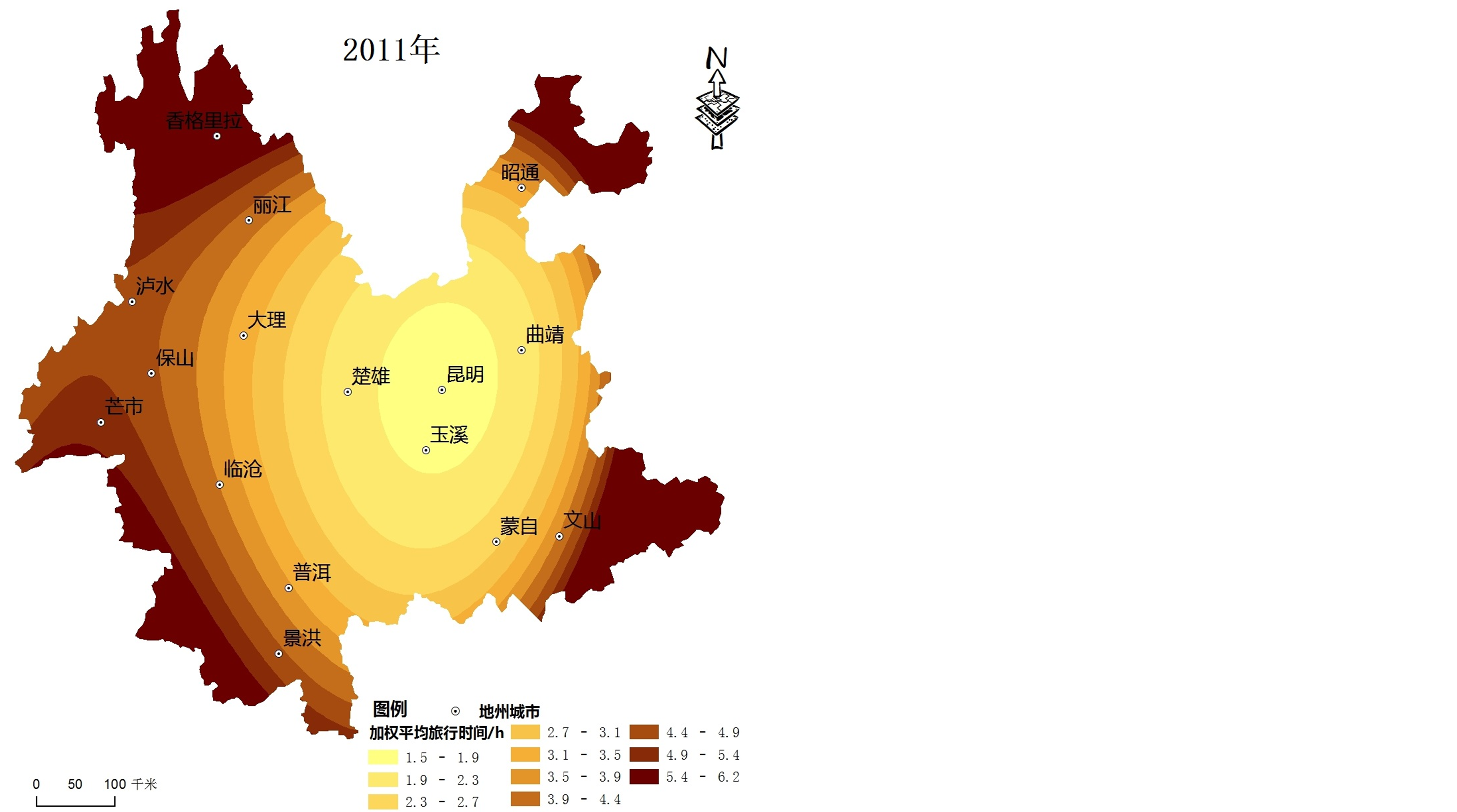
Figure 1. The spatial-evolution of road accessibility in Yunnan during 1996-2011
图1. 1996~2011年云南省交通可达性空间格局演化
程度更为显著,是由于该阶段国道等级提升、高速公路大规模扩建和铁路网络的建设促使云南路网结构发生了较大变化,使得第一阶段可达性的提升较为显著。第二阶段公路网络的发展仍以高速公路大规模建设为主,城镇节点可达性进一步提升,但相比第一阶段可达性的改善程度仍存在一定差距;第三阶段在云南桥头堡战略的影响下,以高速公路和铁路的建设为主,进一步改善和加强了昆明与各地州市间的交通,高等级公路网络已初步形成,交通可达性差距进一步缩小。
2) 由于云南省地形与交通建设的特殊性,不同时间段交通可达性变化空间格局差异较大,边缘地区可达性值提高幅度始终大于中心地区(见图2)。
第一阶段(1996~2001年),可达性值变化幅度空间分布呈现出以昆明为核心向四周逐渐增强且略向南北突出的趋势,滇中地区可达性值变化幅度更加明显。深入分析可知,昆明、玉溪、楚雄高速公路相继建成通车,提升了滇中地区可达性。
第二阶段(2001~2006年),可达性值变化幅度分布由“杭瑞高速–昆磨高速”沿线地区向滇西、滇东南地区逐渐扩大,且略向南突出,其中,丽江、保山市可达性变化值有较大幅度提升,丽江市可达性变化值最大。深入分析可知,杭瑞高速对保山和丽江市的可达性提升有着较大的推动作用,高速公路的优化和完善大幅度提高了区域边缘地区的可达性,丽江市受益最为显著。
第三阶段(2006~2011),可达性值变化幅度空间分布呈现出略向西突出的趋势,滇西地区可达性值变化幅度明显。深入分析可知,在公路建设方面,改造和新建了保山、临沧等地的对外公路6条(新建一条),道路等级提升和铁路公路的兴建也进一步提升了滇西北、滇西地区可达性。
3.3. 中心旅游城市相对可达性演化
由于可达性系数已经消除了不同年份可达性水平的影响,因此依据可达性系数计算的标准方差(见表2)就可以反映出不同时间断面可达性分布的均衡性。
据计算结果可知,2001年与1996年比较,可达性系数标准方差略有下降,2006年与2001年相比,其值有所下降,而2011年与2006年相比略有上升。深入分析认为:第一阶段(1996~2001年)云南省内高速公路网络的建设仍处于初始阶段,只有部分城市受益于高速公路的建设,从而导致了中心城市可达性分布的不均衡性;第二阶段(2001~2006年)公路网等级的提高和高速公路建设的快速发展阶段,多条高速公路纵横交错形成了较为完善的高速路网,中心城市节点可达性都显著提高,使得可达性趋向于相对均衡;第三阶段(2006~2011年)随着公路交通网络的成熟,新建设交通通道减少,中心城市可达性出现“优者更优,劣者更劣”现象,可达性不均衡的趋势加强。
4. 旅游效应分析
运用R软件中对交通可达性和旅游变化进行GAM建模,分别将入境旅游流变化、旅游外汇收入变化、国内旅游流变化、国内旅游收入变化和旅游总收入变化单独与交通可达性进行分析,GAM模拟结果如图3所示。
运用公式(4)对GAM模拟结果进行解释偏差统计分析(如表3)。结果表明,云南交通网络可达性与旅游变化拟合较好,二者呈正相关关系,尤其是可达性与入境旅游流变化和旅游总收入变化呈现出明显的正相关关系。云南省日益完善的交通网络增强了云南的旅游吸引力,弱化了旅游出入壁垒。即交通可达性的变化,对旅游发展产生了正溢出效应。
1) 1996~2011年路网交通对入境旅游流变化的解释贡献率为73.7%,对外汇旅游收入变化的解释贡献率最高,达到90.1%。这表明:路网交通通达性对入境旅游变化具有显著作用,即入境旅游趋于向路网可达性高的地方集聚。
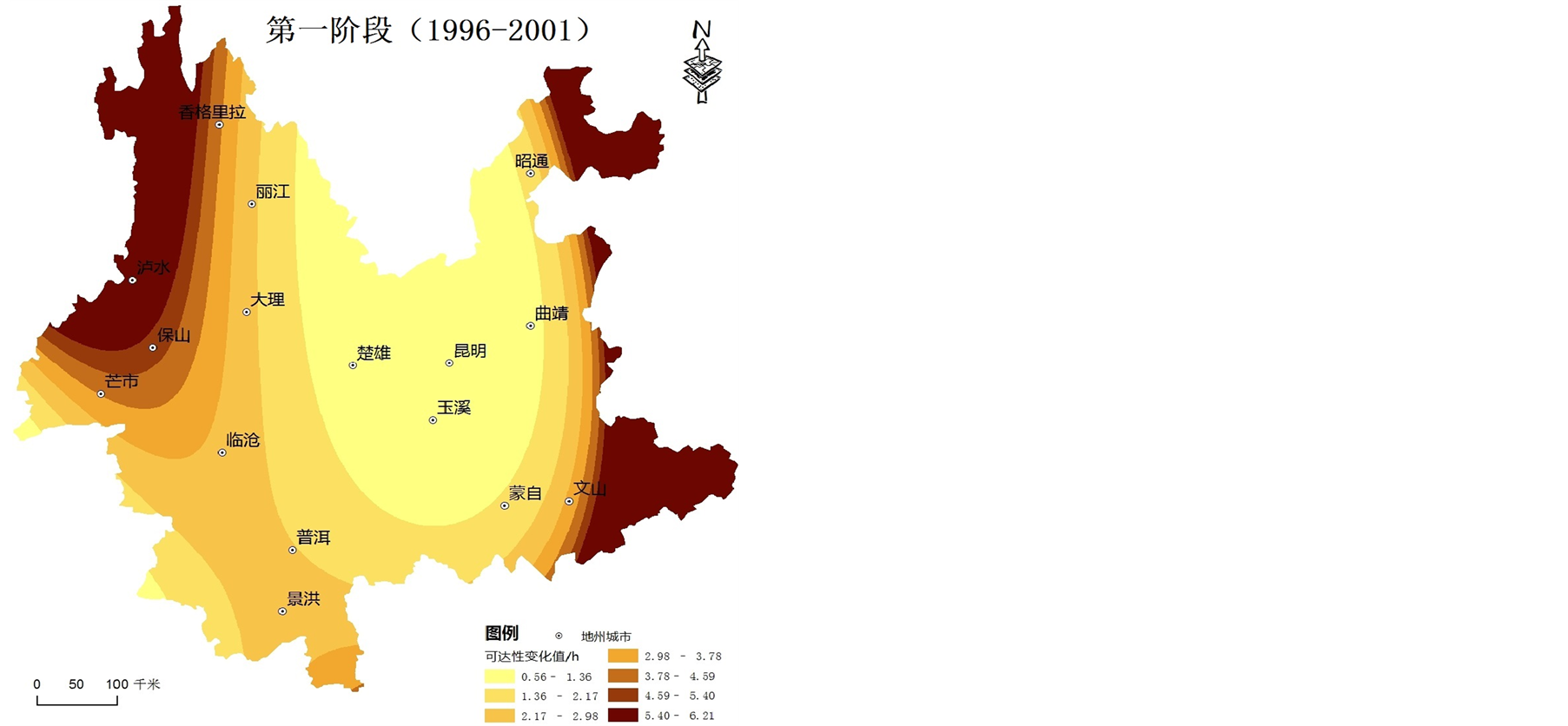
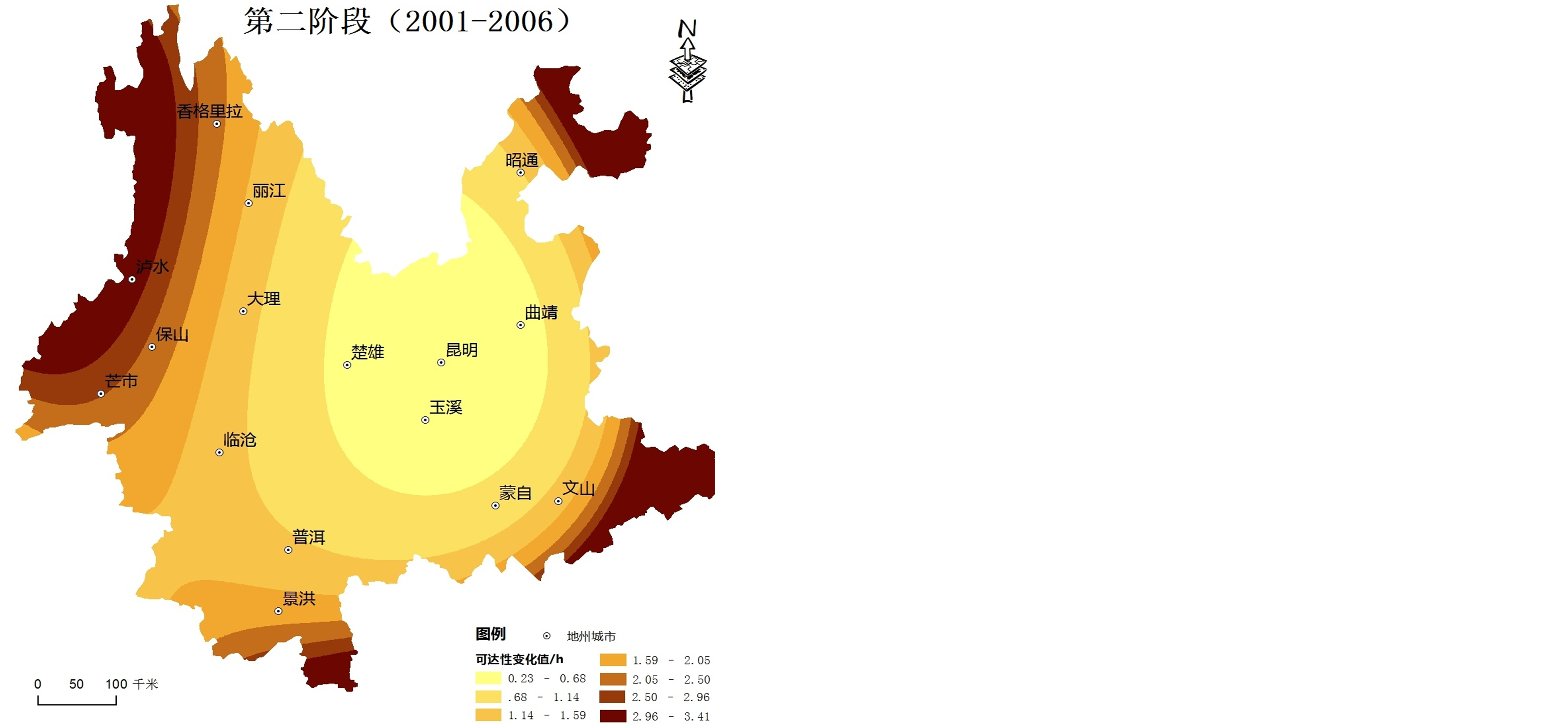
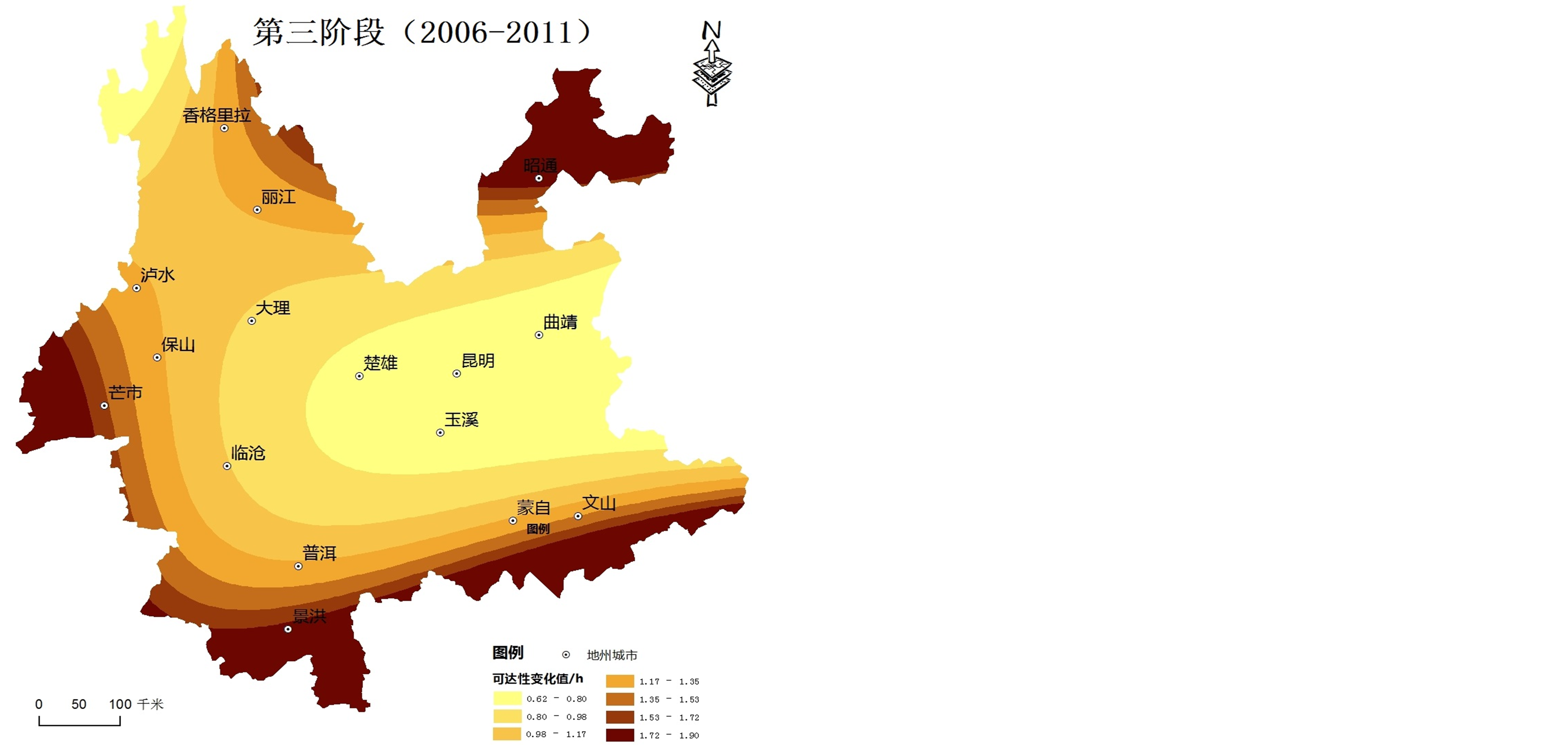
Figure 2. The change of road accessibility values in Yunnan during 1996-2011
图2. 1996~2011云南省陆路网络阶段可达性变化格局

Table 2. The major cities’ accessibility coefficient in Yunnan, 1996-2011
表2. 1996~2011年云南省中心城市公路可达性系数
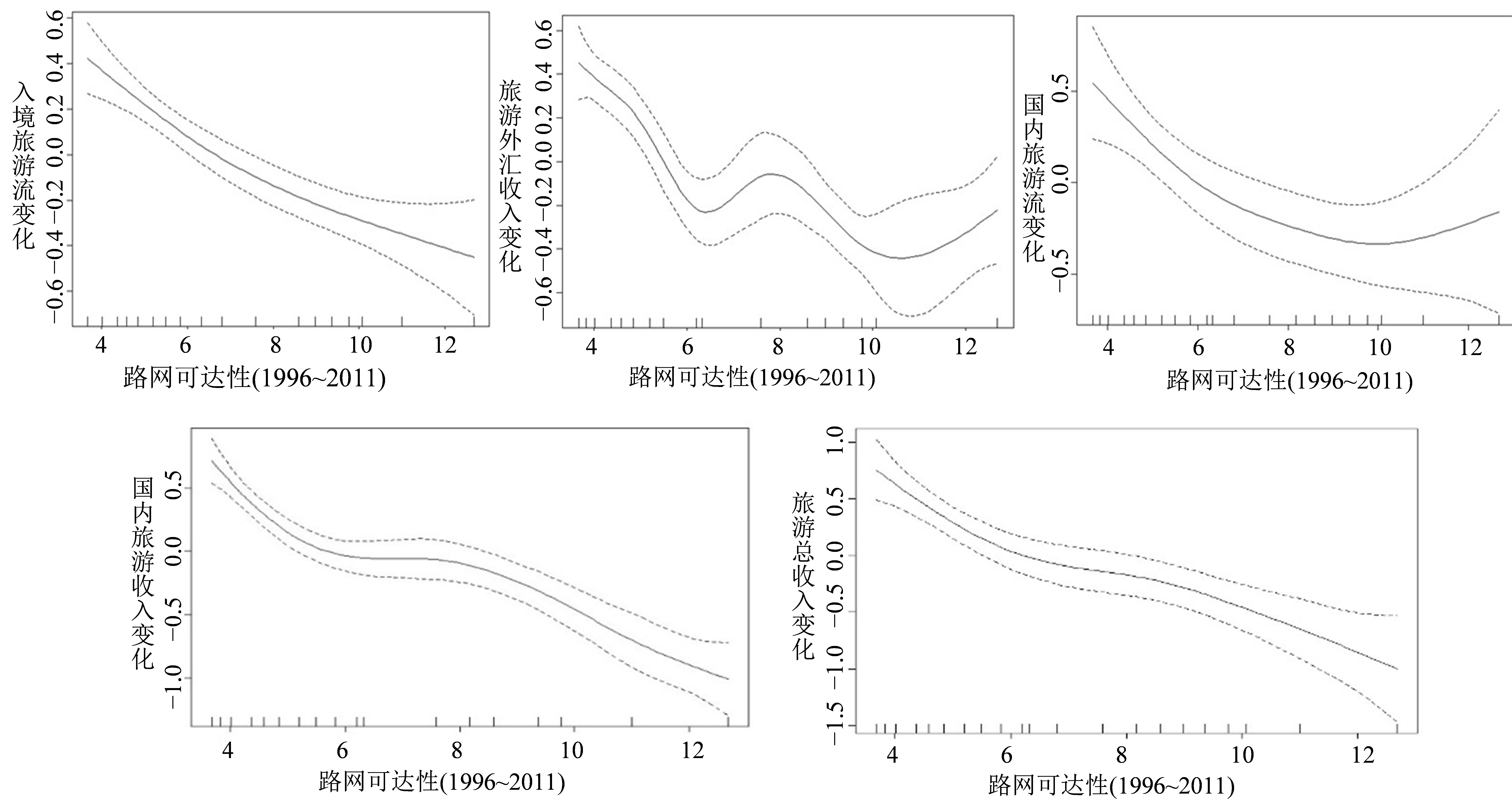
Figure 3. GAM model analysis of transport accessibility and travel changes
图3. 交通可达性和旅游变化GAM模型分析

Table 3. The statistical analysis results of GAM
表3. GAM分析结果统计
注:***、**分别代表1%、5%显著性水平。
2) 路网交通对国内旅游流变化和国内旅游收入变化的解释作用具有较大差异。从路网与国内旅游流变化拟合曲线可以看出,在1996~2011年期间,二者之间关系较为复杂。这一时期,路网对国内旅游流变化的解释贡献率仅为49%,而路网交通对国内旅游收入解释贡献率为91.6%,表现出了较为显著的溢出效应。这主要因为铁路在云南旅游发展的作用中主要为对外联通,由于地形的限制对国内旅游影响较小,但是交通收入作为旅游业主要收入之一,所以路网对国内旅游收入的溢出效应非常显著。
3) 路网交通对云南旅游总收入增长变化的解释贡献率为77.5%,即路网交通与旅游之间存在正相关关系,且显著性很高,交通网络和可达性的改善增加了云南旅游总收入。因此,陆路网交通对云南旅游发展具有积极的推动作用。
5. 结语
1) 1996~2011年期间,云南省交通条件有较大的提升,由于受到云南省特殊地理位置和地形地貌条件影响,可达性空间格局变化不大,总体呈现以昆明为中心向外围区域递减的“核心–外围”模式;各中心城市节点的可达性值变化有所差异,在4个时间截面中昆明、曲靖、玉溪和楚雄一直是可达性好区域,香格里拉、泸水以及昭通可达性始终较差;
2) 15年来,云南省整体可达性明显优化,各中心城市节点的可达性水平均有大幅度的提升,但在不同阶段可达性优化特征不同,第一阶段(1996~2001)可达性的提升明显高于第二阶段(2001~2006)和第三阶段(2006~2011);由于云南省地形与交通建设的特殊性,不同时间段交通可达性变化空间格局差异较大,边缘地区可达性值提高幅度始终大于中心地区;
3) 云南交通可达性对入境旅游变化和国内旅游变化具有显著作用,主要表现为入境旅游趋于向路网可达性高的地方集聚;
4) 云南交通网络可达性与旅游变化拟合较好,二者呈正相关关系,尤其是可达性与入境旅游流变化和旅游总收入变化呈现出明显的正相关关系,交通可达性的优化对旅游发展产生了正溢出效应。
致 谢
感谢国家自然科学基金项目“边疆山区交通与旅游空间结构耦合及关联机制研究”(41361037);国家科技支撑计划课题(2013BAJ07B02);云南省教育厅科学研究基金项目(2013J094);2014年云南师范大学研究生科研创新基金资助。

NOTES
*通讯作者。