1. 引言
景观类型斑块特征是研究景观要素特征的一个重要参数[1] [2] ,斑块形状、大小及数量是描述斑块特征的重要指标[3] [4] 。其中斑块的几何形状是景观空间结构的主要特征之一[4] 。目前研究景观要素班块形状的量化指标主要有形状指数和分维数。通常,形状指数可用来分析景观中斑块的形状特征,但不能直接度量斑块复杂性,而分维数却是用来刻画斑块边界复杂形状的主要工具[5] 。应用分形分维数量化森林景观斑块特征,可以在多尺度上观察景观要素变化,从而在面对模糊性的情况下实现可预测性[6] ,进而有利于研究景观的结构组成特征和空间配置关系,揭示景观结构与功能之间的关系[7] [8] 。扎尕那林区自然条件优越,森林景观资源丰富,是长江、黄河上游支流白龙江、洮河、大夏河的重要水源涵养林区[9] 。针对该林区森林植被景观特征及相关性研究相对较少。本文结合RS和GIS技术,从景观斑块特征方面对迭部扎尕那林场乔木林进行分形分析,以期从景观尺度上为该区森林生态系统的可持续健康发展提供科学依据。
2. 研究区概况
扎尕那林场所在的迭部县位于甘肃省甘南藏族自治州,地理位置为102˚57'03"E~103˚15'07"E,34˚11'37"N~34˚18'06"N [10] 。扎尕那林场位于迭部县益哇乡东北部,北与卓尼县交壤、西南与四川若尔盖县相邻,平均海拔3500米,是一座完整的天然“石城”。该地区属高原亚温带湿润大陆性气候,年平均气温4.6℃,年平均降水量为698.6毫米。境内气候温和,森林发育茂盛,地形复杂,坡陡沟深,保存有丰富的生物资源,是我国种子植物物种多样性最为丰富的温带森林植物区系之一,也是甘肃省针叶树种分布最集中的地区。扎尕那林区森林植物区系成分复杂多样,受地形地貌的影响,植被在分布上具有明显的垂直变化及阴阳坡差异,植被垂直分带的分布自上而下为海拔3800~4200 m为高山灌丛及高山草甸带;2500~3800 m为亚高山针叶林带;2500 m以下为针阔叶混交林带。主要树种有秦岭云杉(Picea aspcraia Mast)、岷江冷杉(Abies recurvata Mast)、紫果云杉(Picea purpurea Mast)、垂枝云杉(Sabina pingii)、糟皮云杉,此外还有华山松(Pinus armandii Franch)、油松(Pinus tabuliformis Carrière)、铁杉(Pinaceae)、落叶松(Larix gmelinii (Rupr.) Kuzen)等分布。阔叶树种有红桦(Betula albosinnensis)、白桦(B. platyphylla)、山杨(Populus davidiana)、槭树、高山柳(Salix cupularis)、辽东栎(Quercus liaotungensis)、椴(Tilia tuan Szyszyl)等[9] 。
3. 研究方法
3.1. 数据来源与处理
以迭部县扎尕那林场1:5万林相图为基本图件,在ArcGIS10环境下完成林相图乔木林斑块的数字化,形成各林种分不同龄组的斑块分布图。根据研究地区森林分布现状以及林相图精度,将该林区乔木林划分为冷杉、云杉、针叶混交、针阔混交、油松、红桦和白桦等7种类型,类型合并数字化林相图有关斑块,再转化为格网分辨率为10 m的Grid格式,形成乔木林按林种分布的斑块分布图。
3.2. 分维值计算
分形维数是分析各景观类型形态结构的主要工具,其计算方法有很多,其中周长–面积关系的算法适用于测量景观要素斑块的边界分维数[11] 。
单个斑块的分维数的计算方法如下[12] :
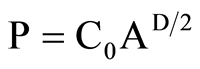 (1)
(1)
式中,P是斑块的周长,A是斑块的面积,D是分维数,C0是常数。
通常,将(1)式两边取对数,得到
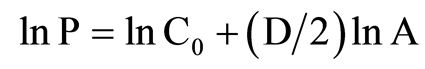 (2)
(2)
令C =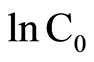 ,b = D/2,则(2)式可以写成
,b = D/2,则(2)式可以写成
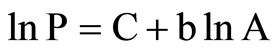 (3)
(3)
即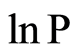 为
为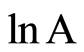 的线性函数,C为该直线在
的线性函数,C为该直线在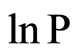 轴上的截距,b为该直线的斜率,分维D = 2b,即分维就是该直线斜率的2倍。
轴上的截距,b为该直线的斜率,分维D = 2b,即分维就是该直线斜率的2倍。
对于栅格景观而言,C0 = 4。D的理论范围值在1.0~2.0之间,D = 1,则斑块形状为欧几里得正方形;D = 2,则表示该斑块的形状最为复杂[13] 。另外,分维值的大小也可反映景观的稳定程度[14] 。
4. 结果与分析
4.1. 乔木林景观结构特征分析
在GIS10软件环境下,对各乔木林斑块进行空间分析,生成各乔木林斑块面积、周长等基本参数(表1)。
从基本的斑块参数可以看出,研究区森林景观组成中冷杉林占绝对优势,其面积占到所有乔木林总面积的50.1%,周长占乔木林总周长的44.1%。其次是云杉林、针阔混交林和针叶混交林,三者的面积和周长分别占到乔木林总体的40%和44%。而红桦、白桦和油松这三种阔叶林面积和周长只占乔木林总体的9.9%和12%。可见该区的森林类型的主体是以云杉和冷杉为主的针叶林,尤其是冷杉,可视为该林区的优势树种。平均斑块面积为某景观组分斑块总面积与斑块数的比值,可用来对比不同景观的聚集及破碎程度[15] 。冷杉林的平均斑块面积远高于其它类型,说明冷杉林在分布上也是以大斑块的形式集中成片分布。相比之下,云杉林面积在各林种中占第二位,但平均斑块面积仅高于油松林和白桦林,远低于其它类型,可见云杉林的分布较为分散,破碎化程度较高。红桦林和油松林是两种主要的阔叶林种,红桦林面积略高于油松林,但油松的斑块数明显多于白桦林,而平均斑块面积远小于红桦林,说明红桦林虽然面积较小,但在分布上较为集中,而油松林则较为零散。再将红桦林与云杉林相比,云杉林面积占乔木林总面积的16.9%,红桦林只占4.7%,而红桦林的平均斑块面积却高于云杉林,更说明了红桦林在分布上较为集中的特点。白桦林分布面积最小,只占乔木林总面积的1%,是该区非常稀有的类型,平均斑块面积也最小,说明分布也很零散。
4.2. 不同林种斑块分形特征分析
根据各乔木林景观斑块的面积和周长,拟合回归模型,得出不同林种的景观分维数(表2)。不同林种分维值大小的排列顺序为红桦 < 白桦 < 油松 < 针阔混交 < 针叶混交 < 云杉 < 冷杉,各林种的分维值都比较接近,介于1.1~1.3之间,说明7种类型的斑块边缘界限复杂程度相当。相比处于青藏高原东北边缘地带的祁连山南坡扎麻什林场,该区乔木林分维值在整体上略高一些[16] 。该区乔木林各林种分维值分布的基本趋势是针叶林大于混交林,混交林大于阔叶林。针叶林的分维值在1.25~1.27之间,混交林在1.23~1.25之间,阔叶林在1.10~1.15之间,基本上呈现出面积分布越广、分布海拔范围越高的森林类型斑块分维数也大的趋势。植被斑块分形特征数与植被受人类活动的影响有关,而且不同方式的人类活动影响的结果也不一样。如果是放牧、砍伐等活动,可能会造成植被斑块破碎化严重,使得一定区域斑块总面积减少而周长增加,且斑块形状的不规则程度加大,其结果可能会引起分维值增加。而如果是开垦农田或建筑人工建筑物,尤其是农田,若和原来的自然植被相间分布,则会造成大量的自然植被斑块边界规则化,最终造成植被斑块分维值大幅度减小。针叶林分布面积广,而且分布的海拔范围较高[9] ,更多地呈自然状态分布,而且高海拔区域人类活动以放牧为主,受其破坏形成的边界也多呈不规则状。而阔叶林分布面积较小,零星镶嵌于自然及人工景观之中,而且分布的海拔范围较低[9] 。低海拔区农田及居民区分布较多,使得阔叶林地多与农田或居民地相连,其边界形状也较为规则。阔叶林中分布面积最多的红桦林分维数最低,可能红桦林斑块多与农田相邻。
4.3. 按年龄结构的乔木林景观斑块分维特征分析
4.3.1. 乔木林年龄结构分析
根据分龄组的斑块分布图进行空间分析,得到各林种不同龄组斑块面积、周长等基本参数(表3)。可以看出,扎尕那林区云冷杉林及针叶、针阔混交林基本上是近成过熟林,几乎没有幼龄林分布。近成过

Table 1. Essential features of the arbor landscape of Zha Gana Forest in Diebu
表1. 迭部扎尕那林区乔木林景观斑块基本特征

Table 2. Patches fractal features of different forest
表2. 不同林种斑块分维特征

Table 3. Patches fractal dimension for different forest of various age
表3. 各林种不同龄组斑块分维值
熟林冷杉林面积达到冷杉林总面积的99%,云杉林为78%,针叶、针阔混交林分别为96.8%和90.4%。整个林区乔木林中90%的区域为云冷杉林及混交林,可见从年龄结构上看该区森林年龄结构老化且单一,很容易引起森林生态系统结构及功能的不稳定。阔叶林中油松林以中龄林为主,面积占86.6%。红桦林和白桦林各龄组面积分布较为均匀,其中红桦林近成过熟林、中龄林、幼龄林分布面积分别占红桦林总面积的37.9%,46.9%,15.2%,白桦林分别占48.2%、21.1%和30.7%。
4.3.2. 按年龄结构的斑块分维特征分析
由各斑块的面积和周长,拟合回归模型,得出各林种不同龄组的景观分维数(表3)。
由于斑块数较少(1~2个)而无法计算分维数,冷杉林、针叶混交林和白桦林只计算了近成过熟林的分维数,油松林只计算了中龄林的分维值(表3)。按年龄结构计算的斑块分维数各龄组之间的差别较大。其中近成过熟白桦林的分维数最大为1.6486,其次是中龄针阔混交为1.4218,这两种类型都是面积较小的林种,其中近成过熟白桦林面积只占乔木林总面积的0.5%,中龄针阔混交林面积也只占乔木林总面积的1.2%。这两种类型的斑块数也较少,它们可能是以不规则的方式零散地镶嵌于其它类型中间。另外,这两种类型分维值接近1.5。有研究表明:当D = 1.5时,表示该景观要素处于一种类似于布朗运动的随机状态,即最不稳定状态;D值越接近1.5,就表示该景观要素越不稳定[14] 。可见,与其它类型相比,这两种类型当前处于较为不稳定的状态。中龄红桦林分维值最低,且接近1,说明其分布形状在各类型中最为规则,可以推测中龄红桦林与与农田呈相间分布的斑块最多。其余各类型分维值相差不大,在1.2~1.3左右。
5. 结论与讨论
通过对迭部县扎尕那林区乔木林景观斑块的分形分析,得到如下结论:
1) 研究区乔木林景观组成以针叶林为主,其中冷杉林面积占到乔木林总面积的50.1%,且平均斑块面积较大,分布较为集中完整,是该林区的优势林种。云杉林、针阔混交、针叶混交林面积差别不大,三者的总面积占乔木林总面积的40%。云杉林平均斑块面积水平相对较低,分布较为分散,破碎化程度较高。阔叶林分布很少,面积只占乔木林总面积的9.9%。红桦林是阔叶林中分布面积最多,平均斑块面积较最大,分布较复杂为集中的类型,而油松林和白桦林在分布上很零散。
2) 乔木林各林种斑块分维值整体较低,介于1.1~1.3之间,7种乔木林类型的斑块边界形状复杂程度相当。不同林种景观斑块分维值大小排列顺序为红桦 < 白桦 < 油松 < 针阔混交 < 针叶混交 < 云杉 < 冷杉。各林种分维值分布的基本趋势是针叶林大于混交林,混交林大于阔叶林,基本呈现出面积分布越广、海拔分布范围越高的类型分维数也越高的趋势。阔叶林中分布面积最大的红桦林分维数最低,可能红桦林斑块多与农田或居民地相邻。
3) 扎尕那林区森林年龄结构老化且单一,占整个林区乔木林总面积90%的云冷杉林及混交林种基本上是近成过熟林。按年龄结构计算的分维数值各龄组之间差别较大。面积只占乔木林总面积的0.5%和1.2%的近成过熟白桦林和中龄针阔混交林的分维数较大(分别为1.6486和1.4218),接近1.5,当前处于较为不稳定的状态。中龄红桦林分维值最低,且接近1,说明其分布形状在各类型中最为规则,可以推测中龄红桦林与农田呈相间分布的斑块最多。
景观斑块的分维数是描述景观斑块形状特征的一个重要参数,它不随尺度的改变而变化,能科学地反映出景观镶嵌结构中要素斑块的特征[17] 。但是,景观中斑块的分维是指斑块边界的分维,分维值的区间介于1~2。论文对主要乔木林林种的景观斑块形状进行分形分析可得到不同的分维值,但在不同龄组乔木林景观斑块分形分析中,由于各小斑块数量较少,计算的分维值落在区间之外,这从理论上讲没有意义[18] ,应值得注意。景观斑块特征的量化不仅可以利用分维数这个工具,还有很多指标,如多样性指数、均匀度、破碎度、形状指数等参数,因此,运用分形维数结合以上指标可较全面的反映斑块特征及变化的内在机制,以更好地揭示景观特征、分析区域景观格局变化。
基金项目
冻土工程国家重点实验室开放基金项目(SKLFSE201002);甘肃省教育厅研究生导师计划项目(1104-07)。

NOTES
*通讯作者。