1. 引言
多用户多输入多输出(MU-MIMO)无线通信系统在当今通信领域已得到广泛应用[1] ,它能提供改善频谱效率和无线链路传输性能的巨大潜力。一般来说,每个用户与基站(BS)之间的信道需要正交,这就使得它们之间的通信需处在不同时频资源上,从信息论的观点上看显然不是最佳的。如果不同用户与基站之间的通信能在同一时频资源上进行,就可以得到更高的频谱使用率[1] ,但这需要复杂的解码技术来消除用户间干扰,如上行系统中的最大似然(ML)解码[2] ,下行系统中的脏纸编码(DPC) [3] 。
大规模天线(Massive MIMO)系统[4] -[8] 不同于一般的MIMO系统,基站拥有大量天线,同时在同一频段上服务于多个用户终端。根据大数定理,不同用户与基站之间的信道趋于正交[9] [10] ,这样小区内用户间的干扰就可以用简单的线性解码来消除,因此提高了频谱效率[11] 。此外,大规模天线还可以减少系统的发射功率。上行系统减少发射功率可以使终端电池消耗减慢;下行系统基站的电功率消耗来自于功率放大器、相关电路和冷却系统[12] ,故减少发射功率可以削减基站的电力消耗。
大规模天线系统中,由于巨大的天线数目及多个用户同时同频通信,选择一个低解码复杂度的解码器显得尤为重要。线性解码器如最小均方误差(MMSE)和迫零(ZF)解码器,其解码复杂度相对于ML解码已大大降低,但是它们都需要求信道矩阵的逆矩阵,当天线数很大时计算复杂度仍然比较高[10] [13] [14] 。另一方面,最大比合并(MRC)解码器是一种简单的线性解码器,它不需要对信道矩阵求逆,计算复杂度明显降低。文献[9] 应用随机矩阵理论,得到了大规模天线系统中MMSE、ZF和MRC解码可达到的理论速率。文献[15] 给出了MMSE和ZF解码关于成对错误概率(PEP)的近似表达式。
本文对大规模天线系统中的MRC解码及其性能作出详细的分析,主要工作包括以下几个方面:1)给出了MRC解码方法PEP的解析公式。2) 理论证明了①当天线数M固定时,随着信噪比 逐渐增加并趋于无穷大,用MRC解码方法得到的PEP会有一个下界;②当
逐渐增加并趋于无穷大,用MRC解码方法得到的PEP会有一个下界;②当 固定时,随着M逐渐增加并趋于无穷大,用同样解码方法得到的PEP降为零。3) 给出并证明了MRC解码方法的能量尺度律(power scale law)。即当
固定时,随着M逐渐增加并趋于无穷大,用同样解码方法得到的PEP降为零。3) 给出并证明了MRC解码方法的能量尺度律(power scale law)。即当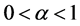 时,随着天线数的增加,每根天线的能量可以按
时,随着天线数的增加,每根天线的能量可以按 而减少并能保持PEP趋于零。而当
而减少并能保持PEP趋于零。而当 时,上述结论不成立。这个结论纠正了文献[7] 中给出的相应结论。最后,仿真证实了上述结论。
时,上述结论不成立。这个结论纠正了文献[7] 中给出的相应结论。最后,仿真证实了上述结论。
符号说明:斜黑体字母代表矩阵或矢量。 和
和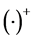 分别表示矩阵的转置和共轭转置;
分别表示矩阵的转置和共轭转置; 表示矩阵的迹运算,
表示矩阵的迹运算, 表示Frobenius范数,
表示Frobenius范数, 表示矩阵的第j行,
表示矩阵的第j行, 表示矩阵的第i行第j列分量;运算符
表示矩阵的第i行第j列分量;运算符 表示数学期望,
表示数学期望, 表示方差。
表示方差。
2. 系统模型
假设有这样一个大规模天线蜂窝系统,本文考虑单个小区内用户与基站之间的收发状态。假设小区内有1个基站和K个用户,每个用户仅有1根发射天线,基站有M根天线(M可能是几十或几百),其基本的输入输出方程可以表示为
 (1)
(1)
其中 是一个M维列向量,它表示基站接收到的信号;
是一个M维列向量,它表示基站接收到的信号;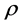 是接收到的信噪比(SNR);
是接收到的信噪比(SNR); 表示信道矩阵,其维数是
表示信道矩阵,其维数是 ,其中每个分量分别表示每个用户与基站天线之间的信道增益,即
,其中每个分量分别表示每个用户与基站天线之间的信道增益,即 表示用户j与基站天线i之间的信道增益。本文假定
表示用户j与基站天线i之间的信道增益。本文假定 是一个独立同分布,均值为0、方差为1的复高斯随机变量;
是一个独立同分布,均值为0、方差为1的复高斯随机变量; 是用户发送的信号,其中
是用户发送的信号,其中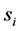 表示第i个用户所发送的信号,并且假定每个信号的平均能量为1。同时
表示第i个用户所发送的信号,并且假定每个信号的平均能量为1。同时 ,即
,即 是第i个用户的星座图;
是第i个用户的星座图;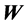 表示噪声,它也是一个M维列向量。
表示噪声,它也是一个M维列向量。 的每个分量也是均值为0、方差为1的复高斯随机变量。在本文中,我们假设信道是慢平坦衰落的,并且基站知道信道状态信息
的每个分量也是均值为0、方差为1的复高斯随机变量。在本文中,我们假设信道是慢平坦衰落的,并且基站知道信道状态信息 。
。
3. MRC的解码方法和性能分析
3.1. MRC的解码方法
常用的线性解码方法ZF/MMSE解码具有良好的性能,但是它们需要对信道矩阵求逆,因而当M很大时解码复杂度仍然比较高。MRC解码不需要求逆矩阵,计算复杂度明显降低,本节的目的就在于做出它的性能分析。
MRC均衡器可表示为
 (2)
(2)
将此均衡器乘到方程(1)两边得到
 (3)
(3)
设K维向量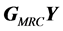 和
和 分别为
分别为 和
和 ,它们第j个元素分别记为
,它们第j个元素分别记为 和
和 。这样,上式可表示为如下K个等式
。这样,上式可表示为如下K个等式
 (4)
(4)
对于一个给定的j ,MRC解码法就是从上述第j个方程中解出第j个用户的信息
,MRC解码法就是从上述第j个方程中解出第j个用户的信息 。但是从等式中可以发现,传输信号
。但是从等式中可以发现,传输信号 都涉及在里面。因此,
都涉及在里面。因此, 就会产生干扰,通常的情况是将这些干扰当作噪声来处理。
就会产生干扰,通常的情况是将这些干扰当作噪声来处理。
基于上述分析,MRC解码器的解码方法可以表述为
 (5)
(5)
3.2. 成对错误概率公式
本小节对上述MRC解码方法的性能从以下几个方面做出分析:1) 给出系统PEP表达式;2) 当基站天线数M固定,信噪比 趋于无穷大时,分析PEP的渐近性能;3) 当信噪比
趋于无穷大时,分析PEP的渐近性能;3) 当信噪比 固定,基站天线数M趋于无穷大时,分析PEP的渐近性能。
固定,基站天线数M趋于无穷大时,分析PEP的渐近性能。
在方程(1)中,我们对各个符号作如下表示: ,
, ,
, ,
,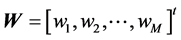 。这样方程(3)可以表示为
。这样方程(3)可以表示为
 (6)
(6)
假设系统有两个不同的码本 和
和 ,当发射信号
,当发射信号 ,接收端判决为
,接收端判决为 时产生误码。记
时产生误码。记 ,
, ,则上述方程组中第j个方程可表示为
,则上述方程组中第j个方程可表示为
 (7)
(7)
为了做出性能分析,假设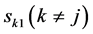 为0均值、单位方差的复高斯随机变量。因此,根据本文的假设及高斯分布的性质得到:
为0均值、单位方差的复高斯随机变量。因此,根据本文的假设及高斯分布的性质得到:
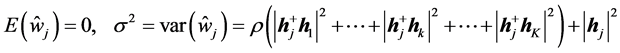
从而可以得到下面条件概率密度函数
 (8)
(8)
因此
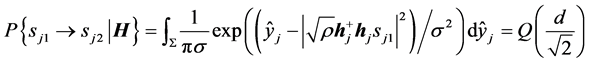 (9)
(9)
其中积分区域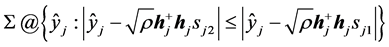 ,Q为Q函数,
,Q为Q函数, ,
, 。
。
由于信道矩阵 的概率密度函数
的概率密度函数
 (10)
(10)
对(9)式中 作平均得到PEP如下:
作平均得到PEP如下:
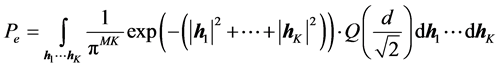 (11)
(11)
公式(11)涉及到Q函数,很难得到一个显式表达式,但是我们可以做出渐近分析,其主要结果如下。
定理1 针对上述给定的系统模型,MRC解码的PEP具有以下性质:
1) 当天线数M固定,信噪比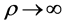 时,有
时,有
 (12)
(12)
这里 是一个正常数。
是一个正常数。
2) 当信噪比 固定,天线数
固定,天线数 时,有
时,有
 (13)
(13)
证明过程见附录。
从上面的定理可以看出:当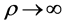 时,用MRC解码所得到的PEP不趋于零,最终会有一个下界,一般称之为错误平台;而当
时,用MRC解码所得到的PEP不趋于零,最终会有一个下界,一般称之为错误平台;而当 时,最终得到的PEP趋于零,说明增加基站天线数可以改善MRC解码方法的性能。
时,最终得到的PEP趋于零,说明增加基站天线数可以改善MRC解码方法的性能。
3.3. 能量尺度律(Power Scale Law)
在本小节中,假设基站的总能量为E,而每根天线的接收信噪比 ,其中
,其中 。则可以得到下面的结论。
。则可以得到下面的结论。
定理2 在上述的系统模型下,假设每根天线的能量为 ,E是给定的总能量。选用MRC解码得到的PEP满足:
,E是给定的总能量。选用MRC解码得到的PEP满足:
1) 当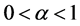 时,则有
时,则有
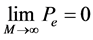 (14)
(14)
2) 当 时,则有
时,则有
 (15)
(15)
其中 是一个正常数。
是一个正常数。
证明过程见附录。
可以发现,当 时,PEP并不会随着M的增加而趋于零,后面的仿真可以清楚地证明这一点。
时,PEP并不会随着M的增加而趋于零,后面的仿真可以清楚地证明这一点。
4. 仿真分析
本小节通过仿真来验证所推导的表达式,假设信道是慢平坦衰落的,并且基站已知信道状态信息。整个仿真分为三个部分:第一、二部分是基于方程式(1)给出的分析,在其它参量不变的情况下,分别给出了信噪比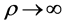 和天线数
和天线数 时PEP的渐近趋势,并各自做出了比较;第三部分探讨的是power scale law问题,如3.3节所给定的假设,讨论了
时PEP的渐近趋势,并各自做出了比较;第三部分探讨的是power scale law问题,如3.3节所给定的假设,讨论了 和
和 时PEP的趋近情况。
时PEP的趋近情况。
图1是在给定假设用户码本为BPSK,小区内用户数 ,基站天线数目M分别取20、30、40,信噪比的取值范围为[−8:2:22] dB。从图中可以看出,随着信噪比的增加,曲线都呈下降趋势,最终出现错误平台;但如果固定信噪比,则可以看出随着M的增加,PEP越来越小,并且下降的幅度变大。故在
,基站天线数目M分别取20、30、40,信噪比的取值范围为[−8:2:22] dB。从图中可以看出,随着信噪比的增加,曲线都呈下降趋势,最终出现错误平台;但如果固定信噪比,则可以看出随着M的增加,PEP越来越小,并且下降的幅度变大。故在

Figure 1. PEP of MRC decoding when M equals to 20, 30, 40 respectively
图1. M = 20, 30, 40 MRC解码方法PEP
大规模天线系统中,增加基站天线数目可以明显改善MRC解码法的性能,这也证实了前面所推导表达式的正确性。
图2所选用码本为4-QAM,用户数目仍然为8,信噪比分别取3 dB和6 dB,天线数目变化范围为[20:20:120]。从图中可以看出,随着M的逐渐增加,PEP呈现线性下降趋势,最终趋于零。
图3是在power scale law条件下所讨论的关于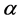 值的变化对PEP所产生的影响,给出了
值的变化对PEP所产生的影响,给出了 和
和 时的对比仿真曲线。这里用户选用的码本仍然是4-QAM,用户数为8,信噪比为6 dB,天线数目为[30:30:180]。从图中可以看出,当
时的对比仿真曲线。这里用户选用的码本仍然是4-QAM,用户数为8,信噪比为6 dB,天线数目为[30:30:180]。从图中可以看出,当 时,随着天线数目的增加PEP趋于零;当
时,随着天线数目的增加PEP趋于零;当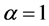 时,随着天线数目的增加,PEP下降得越来越平缓,最终也到达不了零。
时,随着天线数目的增加,PEP下降得越来越平缓,最终也到达不了零。

Figure 2. PEP of MRC decoding when SNR equals to 3, 6 dB respectively
图2. SNR = 3, 6 dB MRC解码方法PEP

Figure 3. PEP of MRC decoding when α equals to 0.5, 1 respectively
图3. α = 0.5,1 MRC解码方法PEP
5. 结束语
基于大规模天线蜂窝系统,本文研究了对接收端采用MRC解码法的PEP性能并且分析了不同条件下PEP的渐近趋势,结论显示出信噪比和基站天线数目的增加都有利于降低PEP。MRC解码方法的计算复杂度比MMSE和ZF都要低,并且随着天线数目的增加,其优势的体现更加明显。而大规模天线是未来移动通信发展的必然趋势,因而MRC解码法将会得到更加广泛的应用。
致 谢
感谢国家自然科学基金资助项目(61372093)。
附 录
定理1的证明:
应用Q函数的下界和其Chernoff上界公式[16] 得到
 (16)
(16)
故有
 (17)
(17)
从而PEP下界可以表示为
 (18)
(18)
所以
 (19)
(19)
这里大于0是因为被积函数是个正数,在 上积分必然大于0。这样就得到了定理1中当信噪比趋于无穷大时PEP的渐近性能,下面继续证明第二种情况。
上积分必然大于0。这样就得到了定理1中当信噪比趋于无穷大时PEP的渐近性能,下面继续证明第二种情况。
由Q函数的Chernoff上界公式(16)得到
 (20)
(20)
然后对 求平均,记为下式
求平均,记为下式
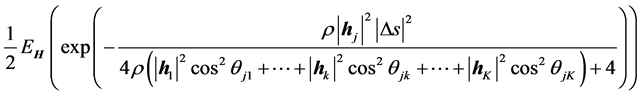 (21)
(21)
因为 ,且
,且
 ,
,
所以得到
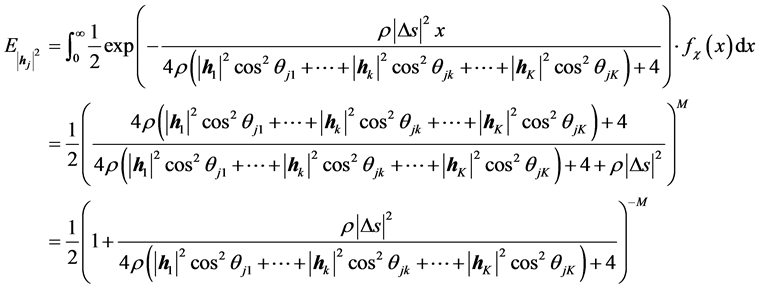 (22)
(22)
令 ,将
,将 划分为两个区域:
划分为两个区域: 和
和 ,对
,对 。从而
。从而
 (23)
(23)
其中不等式是依据 ,
, 。由Markov-Chernoff不等式得
。由Markov-Chernoff不等式得 ,而
,而 ,由此我们就得出了定理1第二部分的结论。
,由此我们就得出了定理1第二部分的结论。
定理2的证明:
依据3.3节给出的假设,用类似于定理1第二部分的证明过程得到
 (24)
(24)
这里
 ,
,
区域 和
和 。
。
当M趋于无穷大时,上式被积函数应用洛必达法则得到
 (25)
(25)
其中 ,
,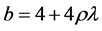 。从最后的等式可以看出,当
。从最后的等式可以看出,当 时为结果0,即此时
时为结果0,即此时 ;当
;当 并不等于0。为了证明
并不等于0。为了证明 ,需利用Q函数的下界公式(16),下面继续给出证明。
,需利用Q函数的下界公式(16),下面继续给出证明。
当 时,由公式(16)并对
时,由公式(16)并对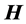 求平均得到
求平均得到
 (26)
(26)
类似地,可以得到
 (27)
(27)
这里得到第二个等式是利用洛必达法则,由此我们得到了想要的结论。