1. 引言
“牛鞭效应”是指供应链中需求信息自下而上逐级放大的现象,由于信息的不对称性,导致供应链上游企业不得不维持较高的库存,极大削减了供应链的整体利益。“牛鞭效应”是供应链中最为重要的性能指标,也是供应链中最为重要的绩效指标[1] 。
纵观现有的文献,国内很多专家、学者就如何削减牛鞭效应进行了研究,主要提出了三类削减牛鞭效应的方法:1) 从供应链管理战略角度提出了精益管理、精柔协同管理、快速反应战略三种方法;2) 从库存管理角度提出了优化策略;3) 从工具方法角度提出了信息化、物流网络化、运用博弈理论优化等方法。如:任江从精益供应链管理方面提出供应链牛鞭效应的解决之道[2] ;郑磊等提出了TPL与精柔协同供应链集成运作弱化牛鞭效应[3] ;李翀针对牛鞭效应问题,在库存策略的参数优化设计方面提出了牛鞭效应的控制策略[4] ;郑端总结出以供应商管理库存和提高信息共享来弱化牛鞭效应的方法[5] ;熊伟指出实施快速反应战略是弱化牛鞭效应的最有效途径[6] ;邢镇等提出了用物流网络化方法来弱化牛鞭效应的信息变异幅度,从而减小其对整个供应链正常高效运作的不利影响[7] ;单宝伟论述了博弈理论在供应链牛鞭效应中的应用[8] ,但未以某一供应链为例进行博弈分析。
博弈论可以帮助人们深刻理解各种社会问题与经济行为,目前在管理学、经济学、计算机科学、生物学、国际关系、政治学、军事战略等学科都有广泛的应用[9] 。本文建立博弈模型对牛鞭效应进行分析,考虑到了供应链上游成员有意削减牛鞭效应的行为,对供应链成员相关行为的经济原因进行研究,并为削减牛鞭效应提出相关建议。
2. 完全信息静态博弈理论
博弈论又名对策论,是从上世纪50年代发展起来的,按照博弈方所掌握信息的完备程度,分为完全信息博弈与不完全信息博弈,按照博弈者的先后顺序、博弈持续的时间和重复的次数进行分类,可分为静态博弈与动态博弈[9] 。
静态博弈是指博弈中参与者同时采取行动,或者尽管参与者行动的采取有先后顺序,但后行动的人不知道先采取行动的人采取的是什么行动,静态博弈分为完全信息静态博弈(纳什均衡)和不完全信息静态博弈[9] 。
本文设定了一个IT企业供应链,在一个多级供应链中,存在供应商、生产者、批发商、分销者、零售者、客户等[10] 。为了方便计算,假设本供应链存在供应商、生产者、分销者、零售商、客户五个部分,如图1所示。
在本文建立的模型中,后行动者不知道先行动者采取的选择,但了解其他供应链成员的真实类型,因此本博弈属于完全信息静态博弈。根据纳时均衡的存在性定理,即在任何一个有n个博弈方存在的有限博弈中,都至少存在一个纳时均衡,知此博弈存在纳时均衡[11] 。
3. 模型建立
供应商E为生产者D提供手机芯片,单位成本H元。生产者D将从供应商E采购来的手机芯片装配到手机中,手机单位成本H(1 + α1)元。分销者C从生产者D购得手机的单位成本为H(1 + α1)(1 + α2)元。零售者B从分销者C购得手机单位成本为:H(1 + α1)(1 + α2)(1 + α3)元。
假定零售者B通过市场调查可以准确地预测出一个周期内客户A的市场需求F。
零售者B有两个选择:1)向上游分销者C准确报告需求(β1);2)向上游分销者C报告扩大了L1(百分数)之后的需求(1-β1)。
分销者C接到供应链下游报告的需求后可能认为下游的报告是正确的(β2);也可能认为下游的报告是虚假的(1-β2),在这种情况下,分销者会推测下一个周期的需求比零售者报告的需求少S2(百分数)。分销者C然后向生产者报告需求,有两个决策:1) 准确报告其预测的需求(β3);2) 报告扩大了L2(百分数)之后的需求(1-β3)。
生产者D接到供应链下游报告的需求后可能认为下游的报告是正确的(β4);也可能认为下游的报告是虚假的(1-β4),在这种情况下,生产者会推测下一个周期的需求比分销者报告的需求少S3(百分数)。生产者D然后向供应商E报告需求,有两个决策:1) 准确报告其预测的需求(β5);2) 报告扩大了L3(百分数)之后的需求(1-β5)。
供应商E接到供应链下游的需求报告后可能认为下游未夸大需求,则其会按接到的需求准备芯片(β6);也可能会认为下游夸大了需求,则会按接到需求的(1-S4)准备芯片(1-β6)。
对于供应链上的每个成员,如果其供大于求,则其将承担多生产产品的损失;如果其需大于供,那么其将承担缺货损失,对于供应链成员B、C、D,其缺货损失率分别为QB、QC、QD;其上游企业将承担利润损失。
在博弈过程中,我们讨论在不同策略组合下供应链成员的损失W。
4. 博弈分析
4.1. 零售者B与分销者C的博弈分析
零售者B与分销者C的博弈分析如表1所示:
当(1 + L1)(1 - S2) > 1时:
零售者B的期望损失为:

分销者C的期望损失为:
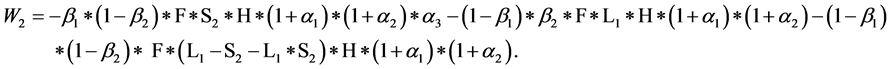
令: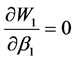 ,解得混合策略纳时均衡
,解得混合策略纳时均衡
令: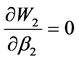 解得混合策略纳时均衡
解得混合策略纳时均衡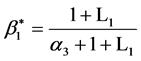

Figure 1. The supply chain of this paper
图1. 本文设定的供应链

Table 1. The game theory table of the retailer B and the distributor C
表1. 零售者B与分销者C的博弈
将上述参数带入损失函数,得到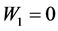
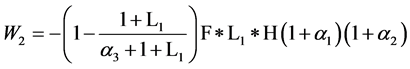
当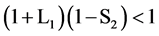 时:
时:
零售者B的期望损失为:
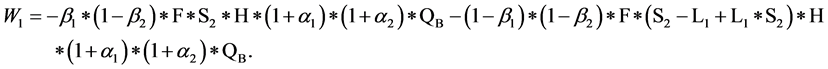
分销者C的期望损失为:

令: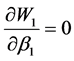 ,解得混合策略纳时均衡
,解得混合策略纳时均衡
令: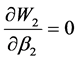 ,解得混合策略纳时均衡
,解得混合策略纳时均衡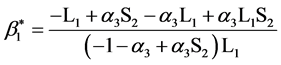
将上述参数代入损失函数,得到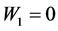

结果分析:
1) 分销者C的最优策略为 ,即按照零售者B的报告需求进行生产;
,即按照零售者B的报告需求进行生产;
2) 零售者B的最优策略介于0到1之间,并与价格成负相关,即价格越大,零售者越倾向于夸大需求,以防止缺货损失。
在下面的博弈分析中,我们着重分析供应链上游成员的最优策略。
4.2. 分销者C与生产者D的博弈分析
同理,可以列出分销者C与生产者D的博弈分析表,如表2所示:

Table 2. The game theory table of the distributor C and the manufacturer D
表2. 分销者C与生产者D的博弈
注:“准”代表供应链成员在其参与环节未夸大需求或者缩小产量,“假”则反之,下同。
当: 时,
时,
分销者C的期望损失为:

生产者D的期望损失为:
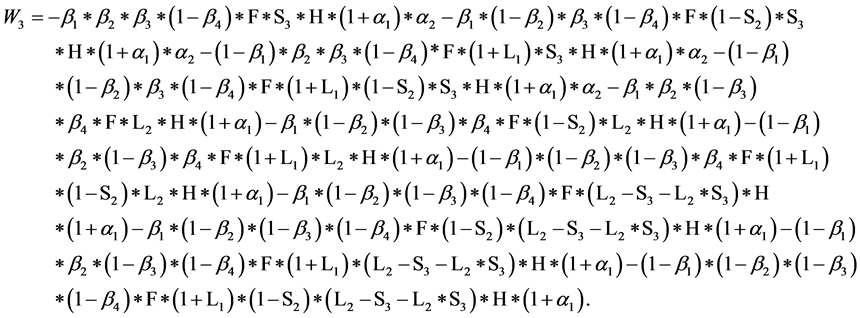
当: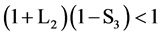 时,
时,
分销者C的期望损失为:

生产者D的期望损失为:
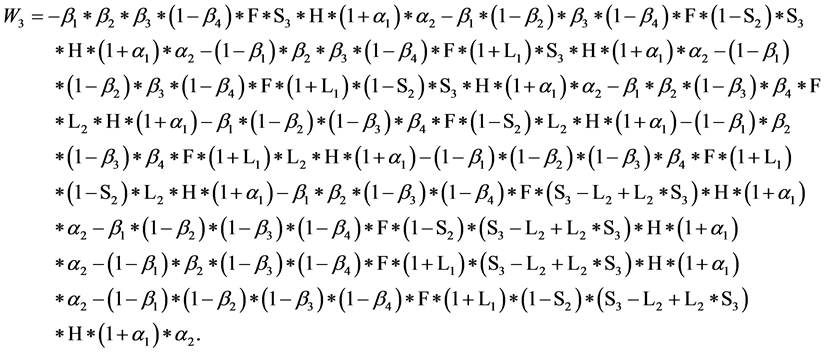
令 运用Maple软件解得混合策略纳时均衡:
运用Maple软件解得混合策略纳时均衡: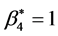 ,即分销者C的期望损失为0。从而验证
,即分销者C的期望损失为0。从而验证
了4.1的结论:在供应链中下游企业因把握着渠道而具有很大的话语权,上游企业不得不按照下游企业的要求进行生产。
4.3. 博弈结论
按照同样的原理,列出生产者D与供应商E的博弈分析表(见附录),令 运用Maple软件解得混合策略纳时均衡:
运用Maple软件解得混合策略纳时均衡: ,即达到均衡时,供应商E按照生产者D的要求进行生产,生产者D的期望损失为0。这说明供应商E不得不按照生产者D的要求进行生产,进一步验证了4.2的结论。
,即达到均衡时,供应商E按照生产者D的要求进行生产,生产者D的期望损失为0。这说明供应商E不得不按照生产者D的要求进行生产,进一步验证了4.2的结论。
本博弈结果分析:
1) 在供应链中,由于渠道的重要性,下游企业具有很大的话语权,上游企业不得不按照下游企业的要求进行生产;
2) 由于企业追求利润最大化,供应链下游企业存在故意夸大需求的败德行为,即可能故意夸大需求以防止缺货,而且物资价格越大,则缺货成本越大,下游企业更倾向于夸大需求。但由于下游企业具有很大的话语权,因此下游企业盲目扩大需求不仅不会给自己带来利益,反而会导致供应链库存过剩,对供应链的整体利益造成损失;
3) 造成供应链需求放大的根源主要在于下游企业,因此,削减牛鞭效应重点在于对供应链下游企业进行有效管理与控制。
5. 从博弈中得到的启示与建议
牛鞭效应是供应链存在的重要问题之一,影响着供应链整体利益,究其原因,有需求的不确定性、供应链各参与方(主要是下游企业)为了达到自身利润最大化而采取的败德行为等,而可能导致生产过剩,使供应链整体利益受到损失。
据博弈分析可得:当下游企业规范自身行为不盲目扩大需求时,供应链整体利益达到最优;由于渠道决定一切,供应链上游企业不得不按照下游企业的要求进行生产,因此,下游企业无需盲目扩大需求。
根据博弈分析,作者提出以下两点建议:
1) 虽然我国成立了供应链战略联盟与供应链联盟,但由于供应链联盟内部的信息共享既是各成员的义务也是其权力,供应链联盟各成员担忧由于联盟将企业机密暴露给竞争对手而在未来市场竞争中失去优势,而为了保护各自的企业机密,会采取一些防范和保护措施,同时希望供应链其他成员能毫无保留地进行合作,以使自己在联盟中获得最大的利益,这就造成供应链各成员以自身利益为出发点,有保留地进行合作,使盟友间的信任度降低,使供应链的整体利益受到很大的影响[12] 。1985年,Pasternack首先提出了供应链契约的概念[13] 。纵观现有的论文,关于供应链契约的研究主要涉及决策权威、定价策略、最小订购量、灵活订货、退货/回购策略、分配原则、提前期、质量等[14] ,因此,需要加强关于诚信方面供应链内部契约机制的研究,根据博弈分析的结论,契约应侧重加强对供应链下游企业的管理与控制,及时制定供应链联盟契约政策,对于不诚信的供应链成员给予必要的惩罚,以加强供应链成员的互信与诚信,减少败德行为的发生,并及时淘汰不诚信的供应链内部成员;
2) 我国的物流信息技术还比较落后,虽然我国的一些世界500强民族企业(如:联想集团)建立了供应链信息系统,但是其系统还只是企业内部的闭环供应链信息系统。因此,很有必要开发跨企业的供应链信息共享系统,以便供应链各个成员能够及时发布供需信息,以信息换取价值。

附 录