1. 引言
社会经济的发展使人们对信息的需求急剧增加,信息量呈指数增长。光纤近30 THz的巨大潜在带宽容量,使光纤通信成为支撑通信业务量增长最重要的技术。于是提高光纤端面的相关指标——如插入损耗、回波损耗等至关重要,拉锥光纤技术应运而生。
通过研究耦合器的拉锥过程,人们研究了各种形状的拉锥。1985年W. Burns [1] 证明了在加热火焰不偏移情况下,拉锥光纤模型绝大多数符合抛物线型。为得到更丰富的拉锥光纤结构,人们设想在光纤拉锥过程中,可以通过移动火焰来实现不同形状的拉锥模型,如正弦模型,多项式型,同时为满足器件小型化和低损耗的要求,要求锥区短且引入的损耗低。由此J. Love等[2] 人通过研究不同拉锥模型对损耗的影响及其与拉锥长度的关系,提出了在最小长度内实现低损耗的锥区形状模型,并得出渐变条件。
研究表明,通过控制拉锥参数可以得到任意锥度的拉锥光纤。1991年R. Kenny和T. Birks [3] 首次提出利用火焰复扫的方法实现任意形状的拉锥光纤,建立了拉锥速度和火焰复扫速度对拉锥光纤形状影响的理论模型。第二年,T. Birks [4] 完善了这一模型,并以此为基础研制出相应的拉锥机,利用理论指导预测拉锥光纤的形状。2010年,S. Pricking和H. Giessen [5] 对复杂形状的拉锥进行了更加精确和详细的研究,在文章中他们考虑了加热火焰的移动以及火焰温度的分布对拉锥直径的影响,并通过实验,验证了模型的正确性,精确地得到了形状十分复杂的拉锥光纤。
近年来,人们开始研究不同材料光纤的拉锥以及探索拉锥光纤在传感方面的新用途。2010年N. Healy等[6] 人利用熔接机对硅材料光纤进行拉锥,利用硅对光的强束缚能力,形成了纳米量级的硅光波导,这种光学元件为实现光的单向传输、光隔离器件等提供了一条新路径,为硅光电器件的应用提供了基础。Eric Lepine [7] 等人对硫化物光纤进行了拉锥实验,提高了硫化物光纤表面的倏逝场,增强了传感的灵敏度。同时,利用拉锥光纤的表面倏逝场可以制成多种传感器,如压力传感器[8] ,湿度传感[9] ,化学传感器[10] [11] ,液体折射率传感器[12] ,它们的基础均为桥型拉锥光纤。拉锥光纤在传感领域的应用由此可见一斑。
桥型光纤(即拉锥后两锥端未拉断)示意图如图1。
桥型拉锥光纤结构主要分为三个部分:原始光纤、锥形过渡区域及锥腰区域。从标准光纤到锥腰的过渡过程中包层和纤芯的比例基本都保持不变。原则上只要拉锥时使锥区角度足够小,就可以将损耗控制在任意小。但锥区角度越小,拉锥光纤的过渡区域也越长,对于拉锥光纤构成的器件来说太长的过渡区对器件的封装、小型化和稳定性都极为不利,因此我们需要找到一个实现低损耗拉锥的基本条件,即能实现低损耗要求的最小长度的锥区形状[13] 。J. Love和W. Henry等人[4] 通过研究拉锥光纤锥区的模式的变化,提出了光纤拉锥低损耗的条件:渐变准则,低损耗拉锥的锥角可以通过该准则来确定。
在此基础上,人们又提出了异种光纤的熔融拉锥[14] (从大数值孔径光纤传输到小数值孔径光纤)理论,并获得低损连接效果,这为不同种光纤之间的耦合提供了一种简单实用的方法(图2)。
本文的主要工作是对具有锥形端的单根光纤与平端面之间耦合效率进行分析研究,同时较为精准的得到最大耦合效率时拉锥机的主要放电参数(图3) [15] 。
所使用的熔融设备是南京吉隆光电生产的光纤熔接机,并在其原有熔接功能的基础上加以改造。当处理好的两根平端面光纤按照熔接的步骤开始放电熔接时,固定该两根光纤的夹具先是沿着光纤轴向靠拢,使得两光纤端面熔接,然后再沿着光纤轴向分离,光纤获得轴向拉力,从而改变端面附近的光纤轴
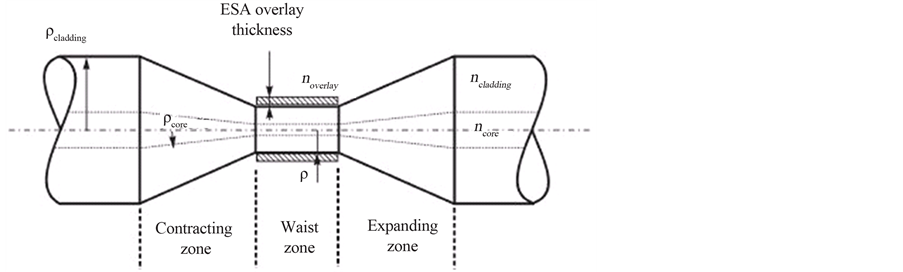
Figure 1. Structure of bridge type tapered fiber
图1. 桥型拉锥光纤结构
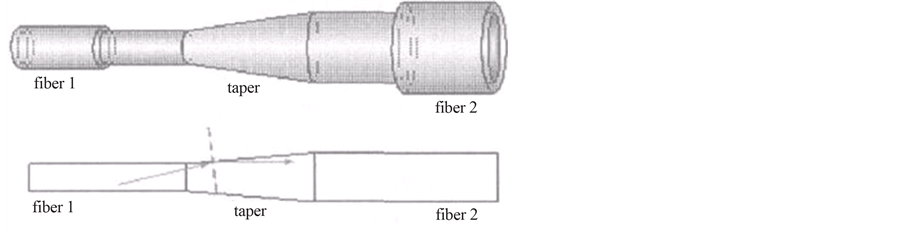
Figure 2. Fused taper between different kinds of fibers
图2. 不同种光纤的熔融拉锥
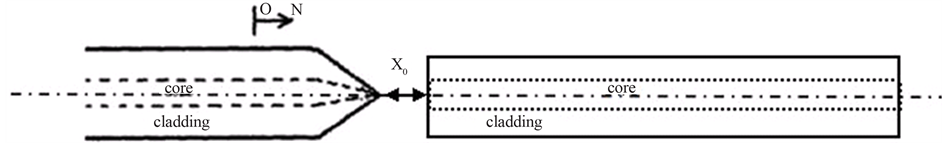
Figure 3. Coupling between tapered fiber and normal fiber
图3. 拉锥光纤与平端面耦合
向尺寸分布,并且在表面张力的作用下,形成具有一定锥体的曲面端面。本文研究了不同放电条件(放电时间和放电强度)下,测量相应光纤端面与平端面光纤耦合时的插入损耗和回波损耗值,并与两平端面光纤耦合时的情况进行了对比分析,得到了插入损耗以及回波损耗与耦合距离的对应规律。
2. 光纤耦合理论
2.1. 回波损耗
回波损耗[16] ,又称为反射损耗,存在于光纤连接器、光纤隔离器等器件中,是电缆链路由于阻抗不匹配所产生的反射,是一对线自身的反射。它是指在光纤连接处,后向反射光(连续不断向输入端传输的散射光)相对输入光的比率的分贝数,回波损耗愈大愈好,以减少反射光对光源和系统的影响。通常要求反射功率尽可能小,这样就有更多的功率传送到负载。典型情况下设计者的目标是至少10 dB的回波损耗。回波损耗RL计算方法为:
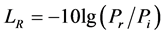
式中Pi是入射到器件上的功率,Pr是被反射的功率。30 dB或40 dB的回波损耗是设计优良的元器件的典型代表值。
2.2. 插入损耗
插入损耗[16] 是指在传输系统的某处由于元件或器件的插入而发生的负载功率的损耗,它表示为该元件或器件插入前负载上所接收到的功率与插入后同一负载上所接收到的功率以分贝为单位的比值,广泛存在于光无源器件中。插入损耗是指发射机与接收机之间,插入电缆或元件产生的信号损耗,通常指衰减。插入损耗以接收信号电平的对应分贝(dB)来表示。
通道的插入损耗是指输出端口的输出光功率与输入端口输入光功率之比,以dB为单位。插入损耗与输入波长有关,也与开关状态有关。定义为:
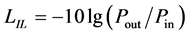
式中Pin表示输入到输入端口的光功率,Pout表示从输出端口接收到的光功率。好的机械开关的插入损耗可以小于1.5 dB;光隔离器典型插入损耗约为1 dB。
2.3. 光纤熔融拉锥
光纤拉锥是一种重要的光纤后处理技术,通过拉锥可以改变光纤的形状、光学性能以及制作各种光纤器件,对拓展光纤的应用具有重要作用。
熔融拉锥技术是指将两根或数根光纤剥去涂覆层,在通光功率监控下用高温烧结拉制成双锥形波导,从而制得全光纤器件的一种技术,因其拉制的光纤大多为双锥形,故又称为FBT(Fused Biconical Taper)技术。其中加热大多用氢气烧,或为获得高温用氢加氧烧,但日本NTT的熔融拉锥机是电加热技术。
生产拉锥机的厂家有很多,国际上著名的公司有美国的E-TEK [17] 和韩国的Korea Electric Terminal Co., Ltd. [18] ,国内有名的公司有上海瞬渺光电技术有限公司[19] 和南京吉隆光纤通信股份有限公司[20] 。拉锥技术最早是人工控制拉锥,后来用电脑控制,自动化程度有所提高,但光纤的剥覆、清洁,均用手工操作。本实验中使用的是南京吉隆光纤通信股份有限公司生产的光纤熔接机。
3. 实验方法
本实验中,着眼于熔融拉锥机的两个放电参数:放电时间和放电强度(偏重)。为缩小实验变量范围,进行了大量预实验,最终确定放电参数范围为0.80 V~1.05 V;放电时间暂定为2850 ms和2950 ms。
3.1. 回波损耗对比
在该过程中,保持拉锥机的放电时间为2850 ms,改变放电强度值(0.8 V,0.85 V,0.9 V,0.95 V,1.05 V),测出各自的回波损耗。为更加直观的看出改善效果,做出各自的折线图,并将五个不同放电强度值的结果展示在一张图中,可以比较不同强度下回波损耗的提高程度。
图4~8为放电强度0.8 V,0.85 V,0.9 V,0.95 V,1.05 V时回损仪测得的拉锥后及平端面回波损耗:
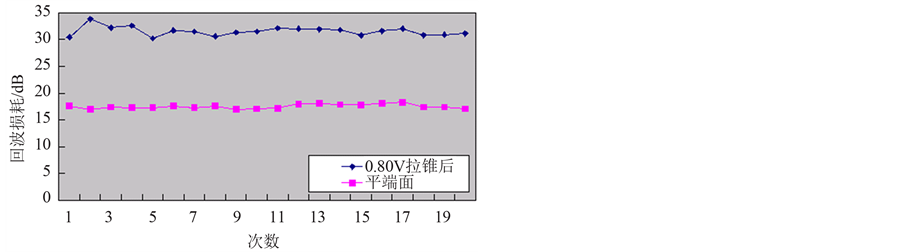
Figure 4. Return loss of flat end and tapered end when discharge intensity is 0.8 V (Table 5)
图4. 平端面与放电强度为0.8 V时拉锥后的回波损耗(表5)
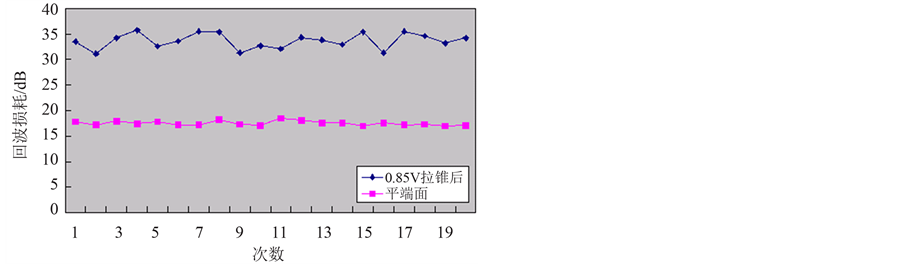
Figure 5. Return loss of flat end and tapered end when discharge intensity is 0.85 V (Table 5)
图5. 平端面与放电强度为0.85V时拉锥后的回波损耗 (表5)
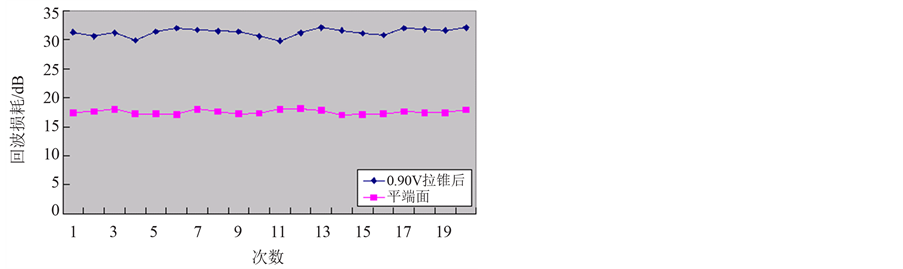
Figure 6. Return loss of flat end and tapered end when discharge intensity is 0.9 V (Table 5)
图6. 平端面与放电强度为0.9 V时拉锥后的回波损耗(表5)
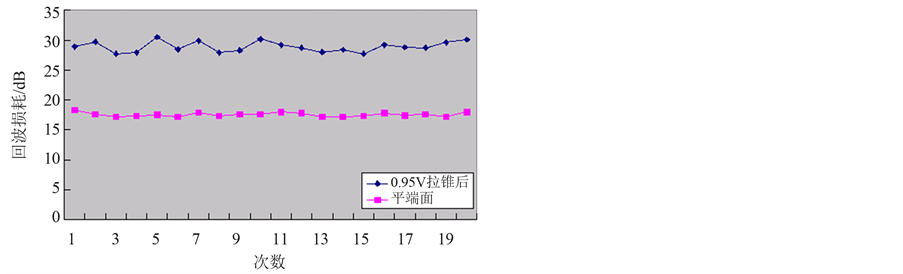
Figure 7. Return loss of flat end and tapered end when discharge indensity is 0.95 V (Table 5)
图7. 平端面与放电强度为0.95 V时拉锥后的回波损耗(表5)
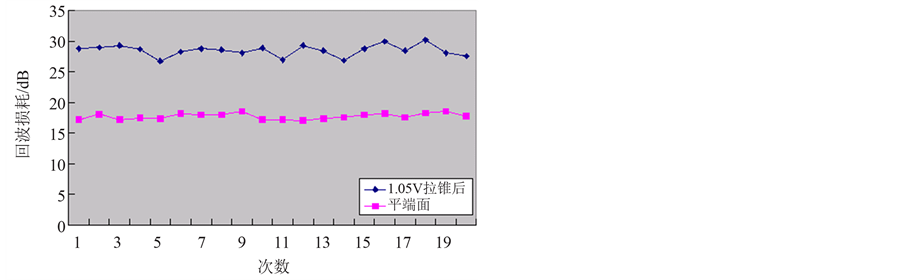
Figure 8. Return loss of flat end and tapered end when discharge indensity is 1.05 V (Table 5)
图8. 平端面与放电强度为1.05 V时拉锥后的回波损耗(表5)
由以上五张图可以看出,拉锥光纤的回波损耗明显大于平端面,即拉锥后回波性能明显改善。
图9反映了不同放电强度下拉锥光纤回波性能:
从图可以直观看出,在0.8 V~1.05 V范围内,放电强度0.85 V时,拉锥光纤的回波损耗大于其他强度。
3.2. 插入损耗对比
研究插入损耗时,熔融拉锥机的放电时间设定为2950 ms,并根据上述回波损耗实验结果将放电强度分别设定为0.8 V、0.9 V,逐渐增大端面间距离(以拉锥机显示屏幕的最小分辨值10 μm为单位),记录下输出端光功率,并根据插入损耗公式IL = −10lg(P0/Pi)将光功率转换为相应的dB值。重复30组实验将测量平均值作为实验结果并与未拉锥(平端面间耦合)时数据进行比较。制成折线图如图10,图11所示:
从折线图看出,经过拉锥,光纤端面的输出功率不再是单调递减,而是先有上升趋势然后逐步下降;且由图直观看出,放电强度为0.8 V时的锥形在端面耦合距离在20~120 μm之间,其输出光功率及插入损耗均明显优于0.9 V放电拉锥和平端面。而0.9 V放电强度拉锥的插入损耗性能与平端面相差不大。
4. 结果分析
4.1. 实验结论
通过回波损耗数据与折线图可以看出,拉锥光纤与平端面耦合后的回波损耗,明显高于未经拉锥情
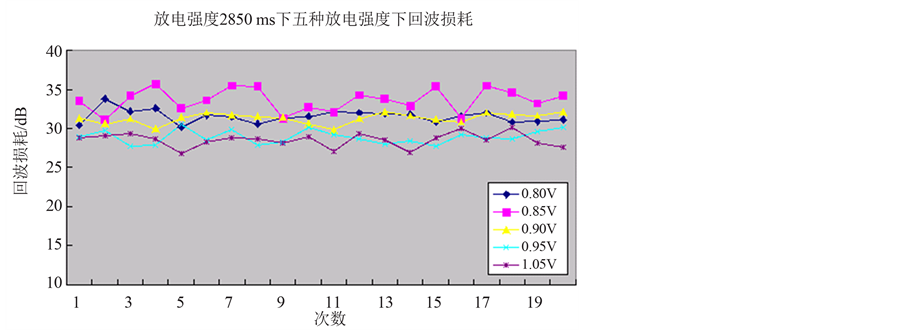
Figure 9. Comparison of return loss between 5 different discharge intensity (Table 5)
图9. 五种拉锥放电强度下回波损耗的比较(表5)
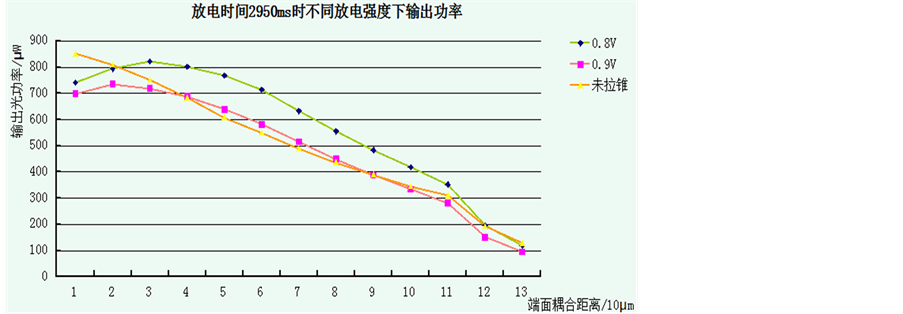
Figure 10. Average output optical powers (μW) (Table 4)
图10. 平均输出光功率(μW) (表4)
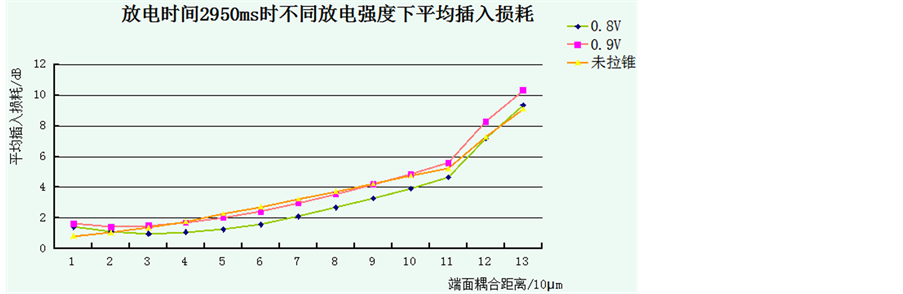
Figure 11. Average insert losses (dB)
图11. 平均插入损耗(dB)
况,即拉锥光纤的回波性能优于未经拉锥光纤,可达到30 dB以上。
分析插入损耗实验数据及折线图,可以发现在满足一定的端面耦合距离条件下,拉锥后光纤的耦合性能优于未经拉锥的平端面光纤,即可利用熔融拉锥提高光纤之间的耦合效率。
本实验采用的是南京吉隆公司生产的熔融拉锥机,并在该机器上完成熔融拉锥、耦合等操作。在实际光纤耦合应用过程中,端面距离在几μm范围内,而该拉锥机的屏幕最小刻度单位为10 μm,精确度不高。而且熔融拉锥过程具有偶然性,可控性不够。端面形状对实验结果有影响,平端面的处理均为手工操作,不能保证端面处理没有瑕疵。由肉眼判断端面距离的移动变化,也会有一定的误差。
本实验着眼于锥形光纤与普通光纤耦合效率的比较。从实验和理论都可以看出锥形光纤的锥角和锥形端面的大小对耦合效率有很大影响。熔融拉锥技术为不同光纤之间的耦合提供了一种简单实用的方式,实现光纤激光器和放大器系统中不同参量光纤的低损耦合,采用光纤拉锥方法来实现光纤连接。
4.2. 结论展望
本实验提出了提高光纤传输系统回波损耗的一种可行方法。随着Gb/s级高速率光纤传输系统、相干检测系统、调频调幅模拟系统的发展,光纤连接器端面引起的反射已成为研究人员日益关注的问题,为这些系统提高高回波损耗势在必行。徐开凯博士等人[21] [22] 实现了一种标准CMOS工艺兼容的硅光源,采用该硅光源可以实现光电子互联和IGBT(绝缘栅双极型晶体管)开关。相对于电互连,光互连的优势很明显:大带宽、低串扰噪声、低驱动电源和系统、长距离互连时有良好的时钟同步性能以及设计简化等。光互连在长距离的通信中已得到了广泛的应用,将光互连应用领域进一步推进到芯片间、乃至芯片上,实现芯片级光互连。
初步推测,本实验高回波损耗成果可以在一定程度上解决该种新型硅光源和光纤之间耦合的高损耗问题,并可以相应设计出具有低插入损耗、高回波损耗的光无源器件,如光纤活动连接器、光纤隔离器、光耦合器及光开关等,真正实现高速低损耗长距离光通信。
基金项目
本研究课题由“南京邮电大学校研究项目(JG00613JX61)”支持。

附录:拉锥光纤插入损耗数据

Table 1. Output power when discharge intensity is 0.8 V
图1. 0.8 V输出功率

Table 2. Output power when discharge intensity is 0.9 V
图2. 0.9 V输出功率

Table 3. Output power without tapering
图3. 平端面输出功率

Table 5. Return losses under five different discharge intensities
图5. 五种放电强度下回波损耗