摘要:
本文利用最新的IPCC第五次评估报告AR5发布的BCC-CSM1.1数据与SDSM统计降尺度方法耦合驱动新安江水文模型,对气候变化情景下赣江流域未来洪水的变化趋势进行分析和探讨。结果表明,RCP2.6、RCP4.5和RCP8.5情景下洪水量级相对于基准期分别减小15%、9%和11%左右。三种情景下,未来不同时期的洪水均值、最大值和最小值的洪水重现期在基准期下均有不同程度的减小,其中最大值洪水减小幅度最大,1000年一遇洪水仅相当于基准期100年一遇,150年一遇洪水仅相当于基准期15年一遇。
The Xinanjiang hydrological model was driven by the SDSM statistical downscaled BCC-CSM1.1 outputs, which were released in the latest IPCC fifth assessment report AR5 to explore flood fre-quency changes of the Ganjiang basin under future climate change scenarios. The results indicate that the averages of flood magnitude with different return periods under the RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios are reduced by 15%, 9% and 15% relative to the baseline period, respectively. The return periods of average, maximum and minimum floods of future different periods reduce in some extents. The annual maximum flood reduces remarkably; a design flood of 1000-year (or 150-year) return period under future scenario is equal to that of 100-year (or 15-year) under the baseline period.
1. 引言
近年来,洪涝灾害等极端事件在全球范围频繁发生,且频率、强度等都存在上升趋势。降水径流关系的变异对气候变化十分敏感,尤其在社会经济迅速发展的高度城市化地区,未来降水变异性的增加可能使洪水风险加大[1] 。赣江是鄱阳湖水系中的最大河流,长江第七大支流,纵贯江西省南部和中部,赣江径流是鄱阳湖进入长江的主要径流之一。研究赣江流域的洪水响应特征,对于了解未来气候变化情景下赣江流域甚至鄱阳湖流域的洪水风险率变化趋势具有十分重要的意义[2] 。
目前,主要通过水文模型与大尺度气候模式的耦合方式,评价未来气候变化情景下的洪水频率变化情势,进而分析整个水文循环系统对气候变化的脆弱性。刘浏等[3] 应用陆面水文模型VIC与区域气候模式PRECIS耦合,探讨了西苕溪流域未来洪水对气候变化的响应。郭生练[4] 以月平均流量和月最大洪峰流量的相关关系为基础,建立了洪水频率评价模型,并用非参数方法估计各级流量的条件概率。利用月水量平衡模型求得未来不同气候变化情况下的月均流量过程,并探讨气候变化对洪峰流量及洪水频率的影响。肖恒等[5] 筛选出五个相对独立的CMIP5模式与VIC模型珠江流域的21个主要干支流控制站日流量过程。以洪峰流量和洪水总量为指标,评估了IPCC RCP4.5情景下未来30年洪水对气候变化的响应。
本文利用最新的IPCC 第五次评估报告AR5发布的GCM数据与统计降尺度方法耦合驱动水文模型,对气候变化情景下赣江流域未来洪水的变化趋势进行分析和探讨。
2. 研究区域和数据
赣江为江西鄱阳湖流域五河(赣、抚、信、饶、修)之首,发源于江西、福建两省交界处武夷山的黄竹岭,自南向北流经赣州、万安、樟树等20多个县市至南昌市注入鄱阳湖,由南至北纵贯江西全境。干流长766 km,外洲水文站以上集水域面积80,948 km2 [6] ,占鄱阳湖流域面积的51.5%。赣江流域地处南岭以北,长江以南,地势由南向北逐渐降低。赣州以上为上游,以贡水为主,自河源至赣州市全长255 km。赣州至新干县为中游,河长303 km;新干县以下为下游区,自新干县至吴城干流长208 km。流域属亚热带湿润季风区,气候温和,雨量丰沛。年平均降水量1542.6 mm,降水主要集中在4~6月,约占全年降水量的46.8%。多年实测入湖径流量638亿m3,超过鄱阳湖流域总入湖水量42%,平均径流系数为0.514 [7] 。径流主要由降水形成,年径流的地区分布及年际、年内变化与降水量变化趋势相似,有明显的季节性和地区性,同时在地区、时程分配上又极不均匀。
本文选用IPCC第五次评估报告发布中的BCC-CSM1.1气候模式。获取了该模式历史时期(1961-2005年)以及在IPCC三种代表性浓度路径RCP2.6、RCP4.5和RCP8.5情景下未来气候时期(2010~2099)的模拟大尺度气候因子数据。应用SDSM统计降尺度技术将GCM输出的大尺度气候因子降解到流域水文模型尺度,作为流域水文模型的输入。本文选取了赣江流域内6个国家气象站点(宜春、吉安、遂川、赣州、南昌、樟树),这些站点分布比较均匀,基本上能代表该区域的气候特征。建立水文模型的数据包括三类:6个气象站点1961~2010年实测资料逐日降雨、逐日气温数据、以及赣江流域附近南昌、铜鼓和梅港蒸发站实测逐日蒸发数据以及赣江流域出口控制站外洲站的1961~2010年的逐日流量数据。
3. 新安江模型适用性检验
本文在统计降尺度得到的预报结果的基础上,利用新安江水文模型,分析未来气候变化情景下赣江径流极值事件的变化情况。尽管获取了历史时期的蒸发资料,为了获得未来时期的蒸发数据驱动水文模型。因此将赣江流域多年平均日蒸发观测值E与多年平均日气温T建立关系,如图1所示,回归分析表明E与T之间满足指数关系,相关系数达到0.9459,最终以此关系将日气温转换为日蒸发代入模型。
建立新安江模型所需要的资料为逐日降水、蒸发和流量数据。采用泰森多边形法对多个站点的降水和蒸发数据进行空间插值得到赣江流域的面降水量和面蒸发量。本文以1961~1970年赣江流域平均日降水、蒸发资料及赣江下游控制站外洲日径流资料作为输入,对新安江模型的适用性进行检验。将1961~1967年作为率定期,1968~1970年作为检验期。通过罗森布瑞克法(Rosenbrock)优选模型参数,率定期和检验期的效率系数分别为85.64%和88.79%,水量平衡系数分别为0.9799和0.9825。图2展示了检验期和率定期的赣江径流实际值与模拟值对比情况,结果表明,所建立的新安江模型对于赣江流域径流有很好的模拟效果,基本满足实际应用。
4. 赣江未来洪水极值事件变化趋势分析
首先分别将RCP2.6、RCP4.5、RCP8.5情景下,SDSM模型降尺度BCC-CSM1.1得到的基准时期(1961~2005)和未来时期(2010~2099)赣江流域的逐日气温通过前述回归关系转化成逐日蒸发。然后,将SDSM模型降尺度得到的三种情景下得到的赣江流域逐日降水,以及逐日蒸发数据输入经过验证后的赣
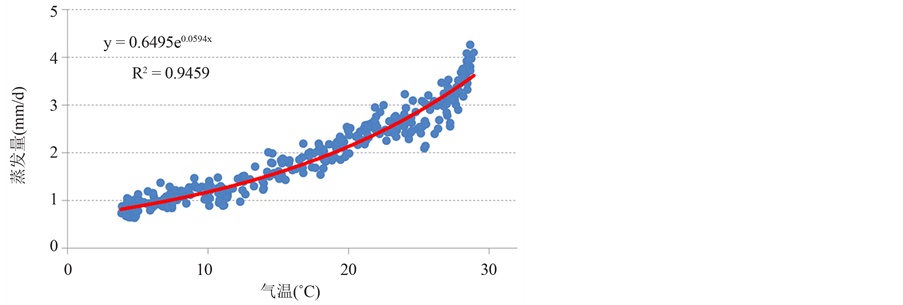
Figure 1. Relationship between mean annual daily evaporation and air temperature
图1. 多年平均逐日蒸发与气温回归关系
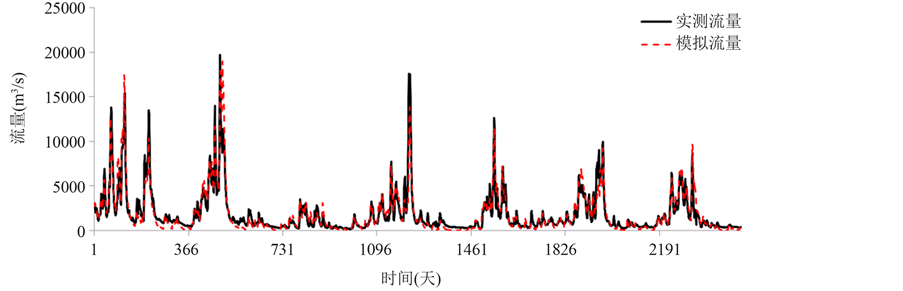 (a)
(a)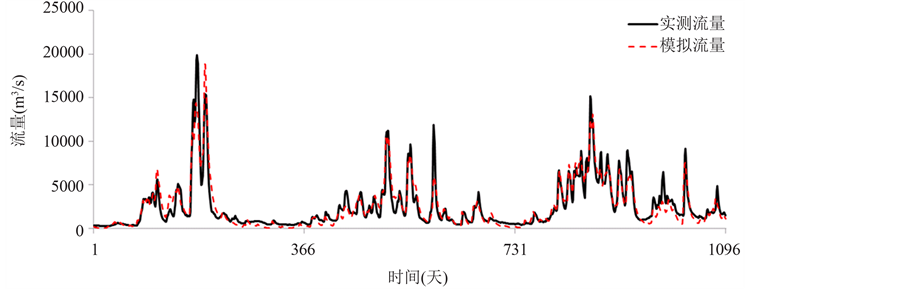 (b)
(b)
Figure 2. The calibration and verification results of Xinanjiang model in the Ganjiang basin
图2. 赣江流域新安江模型率定期和检验期模拟效果
江流域新安江模型,得到基准时期以及各对应情景下未来赣江日径流过程。采用年最大法获取洪水序列,采用P-III型曲线,通过适线法得到各时期的洪水频率曲线。分别得到基准期以及三种气候情景下的洪水频率曲线,如图3所示。其中基准期洪水频率曲线采用1961~2005年的新安江模型模拟洪水序列拟合,RCP2.6、RCP4.5以及RCP8.5情景下的洪水频率曲线分别采用各自情景下2010~2099年共90年的模拟洪水序列拟合。
表1给出了三种情景下的不同重现期洪水的频率相对于基准期的变化,可以看出各情景下洪水量级相对于基准期均减少,RCP2.6情景下,2~1000年重现期的洪水减小幅度在−16.7%~−11.1%之间,RCP4.5情景下,减小幅度在−8.1%~−10.2%之间,而RCP8.5情景下,减小幅度在−11.4%~−10.5%之间;RCP2.6和RCP8.5情景下,减小的幅度随洪水重现期的减小而减小,RCP4.5情景下却是相反,减小的幅度随洪水重现期的减小而增加。
为了便于统计,将未来气候情景分为3个时期:2020s(2010~2039年),2050s(2040~2069年),2080s (2070~2099年)。表2计算给出了未来不同时期的最大洪水、最小洪水以及洪水均值,同时分别给出了对应各自情景下洪水频率曲线和基准期洪水频率曲线的洪水重现期。从表中可以看出未来不同时期的洪水均值、最大值和最小值的洪水重现期在基准期下均有不同程度的减小。未来情景下重现期为2~2.5年的洪水均值在基准期下约为1.5年。各时期最小值洪水的重现期在在基准期下无明显变化。但是各时期最大值洪水在基准期下洪水重现期变化较大,如RCP8.5情景下2020s时期出现的1000年一遇重现期洪水仅相当于基准期100年一遇;RCP2.6情景下2020s时期的150年一遇洪水仅相当于基准期15年一遇。对比不同时期,三种情景下2050s时期的洪水量级相对于2020s时期和2080s时期较小。
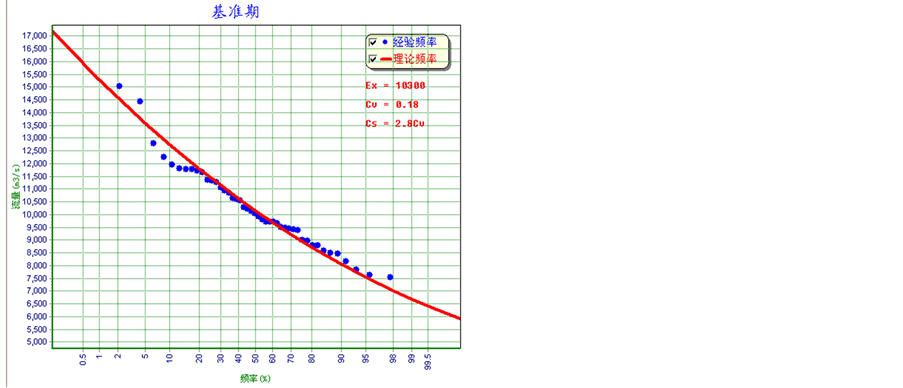
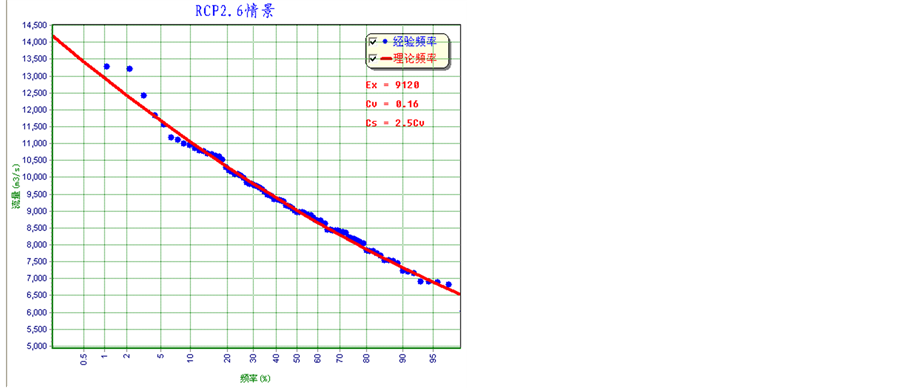
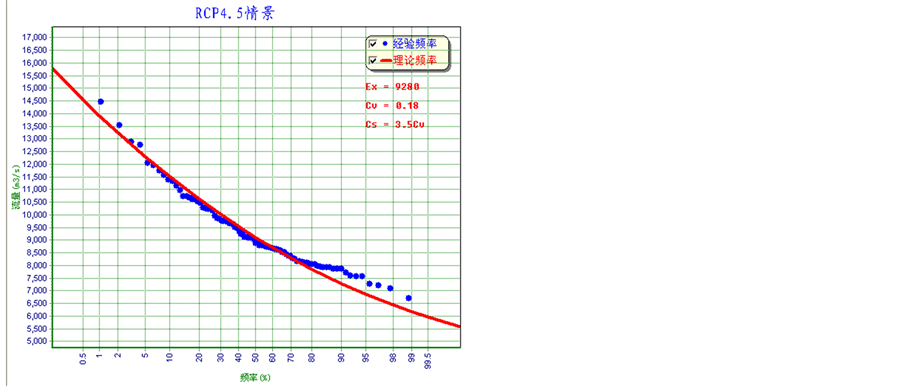
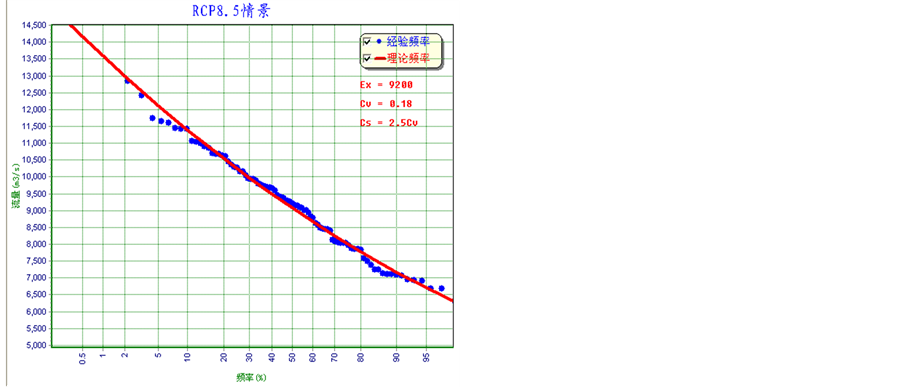
Figure 3. Fitted annual maximum flood frequency curves for baseline period and three future scenarios in the Gangjiang basin
图3. 三种未来情景下及基准期赣江流域年最大洪水序列拟合频率曲线

Table 1. Comparison of design flood changes between future scenarios and baseline period
表1. 未来情景与基准期设计洪水变化的比较

Table 2. Return periods changes for different periods under three scenarios
表2. 三种情景下未来不同时期洪水重现期的变化
5. 结论与展望
利用全球气候模式BCC-CSM1.1经统计降尺度后的结果驱动新安江模型,得到未来气候变化情景下赣江径流系列。通过对年最大日径流序列进行频率分析,分析未来气候变化情景下赣江洪水极值事件变化趋势。结果表明:三种情景下洪水量级相对于基准期均减少,RCP2.6情景下减小15%左右,RCP4.5情景下减小9%左右,RCP8.5减小11%左右。未来不同时期的洪水均值、最大值和最小值的重现期与基准期相比均有不同程度的减小,其中洪水最大值减小幅度最大,1000年一遇洪水仅相当于基准期100年一遇,150年一遇洪水仅相当于基准期15年一遇。

NOTES
作者简介:郭家力(1984-),男,湖北孝感人,讲师,博士,主要从事水文学及水资源开发利用方面的研究。