1. 引言
《保护世界文化和自然遗产公约》里界定的遗址概念为“从历史、审美、人种学或人类学角度看具有突出的普遍价值的人类工程或自然与人联合工程以及考古地址等地方”。它反映了古代人们生产、生活的真实状况,是古代文化文明的见证,是历史遗留的重要精神文化和物质财富,是今人文化认知和文化归属感的溯源。发现和保护遗址,对于继承文明、继往开来具有重要的意义和作用。其中,发现遗址,就涉及到了考古科学。考古科学是信息科学,信息科学的本质精神是信息化、智能化和综合化,这些恰好是计算机技术的特长[1] 。而考古遗址预测模型则是计算机技术在考古科学这一领域的一大应用。考古遗址预测模型是基于对特定区域内已知遗址进行的环境因素分析,如高程、坡度、坡向、水系距离、土地利用类型等,找出遗址分布的统计性规律和特征。然后在这个区域的其他地区用多变量判别函数对遗址存在的可能性进行评价,给出潜在遗址的概率分布[2] 。在国外,遗址预测模型可追溯到20世纪50、60年代的聚落考古研究,其开拓者当属美国考古学家Willey在微鲁河谷所做的区域聚落系统研究[3] 。Michael Märker利用空间数据挖掘技术对伊朗扎格罗斯山脉上的旧石器时代聚落遗址位置进行了预测[4] 。在国内,倪金生[5] 针对山东莒县沭河上游流域的大汶口、龙山和岳石文化时期遗址、彭淑贞[6] 等人针对山东省汶泗流域的大汶口文化时期的遗址、乔文文[7] 等人针对郑洛地区龙山文化遗址进行了预测研究。这些研究大多集中在中原地区及内地的新旧石器时期为主,而其他边疆地区及少数民族地区和其他历史时期的研究非常少[8] 。
拥有“海东盛国”美誉的渤海国,从公元698年至926年间存续了229年之久,其中延边地区是渤海国的腹地,因此,在这里留下了极为丰富的文化遗产。由于现存的渤海国史历史资料比较少,所以渤海国遗址对渤海国史研究显得非常重要[9] 。另外,遗址承载着渤海国故土地区独特的人文历史和文化生态,它对提高该地区文化软实力,具有非常重要的作用。但是目前渤海国遗址发掘的相对少,很多遗址千余年间仍然埋在地下,等待我们去发掘和发现。因此,有必要对其进行预测性研究,也可对预测结果进行检验,验证预测模型的准确性。本文以延边朝鲜族自治州(以下简称延边地区)渤海国时期遗址为研究对象,利用BP神经网络建立预测模型,并生成遗址分布概率图,找出遗址分布的趋势。这种研究在丰富渤海国历史研究的同时,也为解决随着城市化推进,遗址发掘难度加大这一问题提供新的方法和手段,将为发现新的遗址和保护现有的遗址提供科学依据。
2. 研究区概况和数据
2.1. 研究区概况
延边地区位于吉林省东部,地处中、朝、俄三个国交界地,与日本海相望。地理位置为北纬41˚59'47''至44˚30'42'',东经127˚27'43''至131˚18'33''之间,面积约4.27万 km2,2014年末人口约217万。延边地区地貌类型复杂多样,西高东低,包括山地、高原、丘陵、盆地等多种地貌类型。其中山地面积最广,占54.8%,高原面积占6.4%,盆地主要分布在江河湖泊的两岸和山岭之间,面积占25.5%,丘陵面积占13.3%。延边地区平均坡度为7.91˚,总体坡度较缓,但由于多山地丘陵的地貌特征,坡度差异较大。延边地区水资源丰富,河网密集,河系发达,周内主要河流有图们江、牡丹江、绥芬河、第二松花江四大水系8条主要江河和487条大小河流[10] 。
延边地区下辖延吉、图们、珲春、龙井、和龙、敦化6个市和汪清、安图2个县。延边地区历史文化悠久,早在1963年考古学家在安图县明月镇的洞穴内发现距今2.6万年前的“安图人”牙齿化石,同时在和龙、汪清、延吉、珲春等地也发现过旧石器时期的遗址。延边地区较早的居民主要有沃咀和肃慎,今日延边地区基本上是北沃咀的活动范围。历代王朝高句丽、渤海国、辽金等均在延边地区建都或设置行政机构,进行治理。其中渤海国同延边地区的关系非常密切,渤海国仿效唐朝实行5京制,其中西京和东京位于延边地区。因此,到目前为止渤海国遗址数量最多的地区即是延边地区。
2.2. 数据来源
本研究涉及的遗址信息参照了《中国文物地图集—吉林分册》[11] 、《渤海古城址研究》[12] ,以及《吉林省文物志》等系列丛书[13] 。经整理,共得到226处遗址,其分布参照图1。本文用的DEM空间分辨率为30 m,利用该DEM获取高程、坡度、坡向、山脊线、山谷线等地形地貌数据。从矢量化的“延边朝鲜族自治州行政区划图”[14] 中获取研究区的道路图、村屯分布图、水系图等专题图。
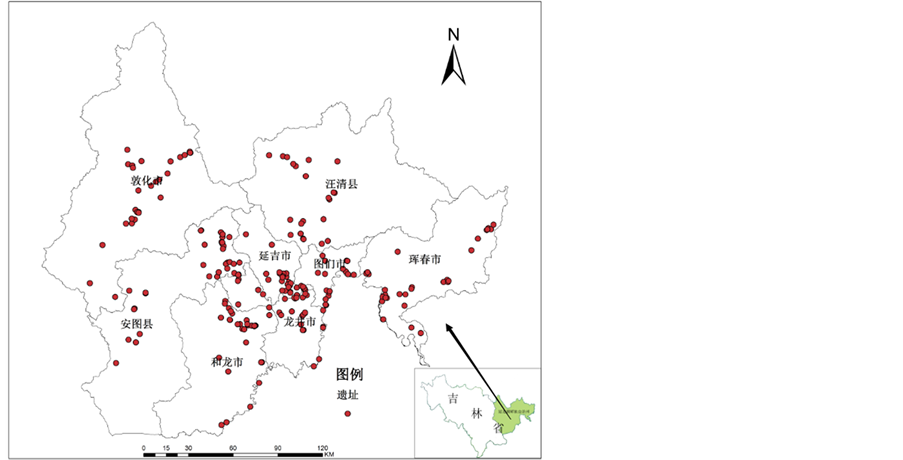
Figure 1. The distribution of Bohai Kingdom sites of Yanbian area
图1. 延边地区渤海国遗址分布图
3. 遗址预测模型建立
3.1. 方法模型
1974年P.werbos提出了有隐含层的学习演算法[15] ,这是已知最早反向传播人工神经网络模式,可惜这一进展在当时未受到重视。1985年,Parker再次提出反向传播网络[16] ,此后,反向传播模型才逐渐广为人知,实现了Minsky [17] 和S.Papert在1969年提出的多层网络设想,正是这一成就促成神经网络研究热潮的兴起。Hecht-Nielesen等人从数学理论上证明了Kolmogorov关于在一个相当宽的范围内,多层反向传播网络能以任意精度逼近定义在紧致子集上的任意非线性连续函数 [18] [19] 。这为反向传播网络的应用提供了理论根据。
BP神经网络即反向传播网络,是最简单的多层神经网络,也是人工神经网络中最具代表性和应用最广泛的一种模型。它是由非线性变换单元组成的前馈型网络,BP神经网络一般是多层的,与之相关的另一个概念是多层感知器(Multi-Layer Perceptron, MLP)。多层感知器除了输入层和输出层以外,还具有若干个隐含层。多层感知器强调神经网络在结构上由多层组成,BP神经网络则强调网络采用误差反向传播的学习算法。大部分情况下多层感知器采用误差反向传播的算法进行权值调整,因此两者一般指的是同一种网络。
从函数拟合的角度看,BP网络具有函数拟合功能。
BP神经网络有以下特点:
1) 网络由多层构成,层与层之间全连接,同一层之间的神经元无连接。多层的网络设计,使BP网络能够从输入中挖掘更多的信息,完成更复杂的任务。
2) BP网络的传递函数必须可微。因此,感知器的传递函数—二值函数在这里没有用武之地。BP网络一般使用Sigmoid函数或线性函数作为传递函数。根据输出值是否包含负值,Sigmoid函数又可分为Log-Sigmoid函数和Tan-Sigmoid函数。一个简单的Log-Sigmoid函数可由下式确定:
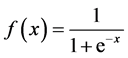
其中x的范围包含整个实数域,函数值在0~1之间,具体应用时可以增加参数,以控制曲线的位置和形状。
3) 采用误差反向传播算法(Back-Propagation Algorithm)进行学习。在BP网络中,数据从输入层经隐含层逐层向后传播,训练网络权值时,则沿着减少误差的方向,从输出层经过中间各层逐层向前修正网络的连接权值。随着学习的不断进行,最终的误差越来越小。
3.2. 样本选取
样本是建立、验证模型时使用的数据,其中要包含遗址和非遗址数据。遗址数据是由文献资料汇总而得,非遗址数据是利用ArcGIS的随机点生成工具,在遗址点以外的区域中生成随机点,假设这些随机点为非遗址点。
研究区域中随机选取的建模样本数量为238个,其中遗址和非遗址数量各119个。遗址中聚落址、山城址、平原城址、墓葬墓群、寺庙址、古建筑址、其他等遗址数量依次为49个、11个、21个、22个、4个、9个、3个,占整个遗址数量的52.7% (见表1)。
验证样本数量为214个,遗址和非遗址数量各107个。遗址中聚落址、山城址、平原城址、墓葬墓群、寺庙址、古建筑址、其他等遗址数量依次为48个、6个、23个、17个、2个、9个、2个,占整个遗址数量的47.3% (见表1)。
3.3. 模型变量选取
BP神经网络模型的因变量只有两个值,即遗址点为1,非遗址点(随机点)为0。自变量是影响遗址分布的自然因素和人文因素,在充分考虑数据的可获取性和模型建立的必要性的基础上,选取海拔高度、坡度、坡向(方位)、距离河流水平距离、地形起伏度、距离山脊线和山谷线的距离等自然因素,还选取了距离道路的距离和距离村屯的距离等人文因素,这些自然和人文因素的数据获取来源如上述“1.2数据来源”中所表示。
3.4. BP神经网络模型的建立
利用SPSS统计分析软件的神经网络模块下的多层感知器来创建模型。功能名称虽然是“多层感知器”,但这仅仅指的是其网络结构为多层,实际上提供的算法为最常见的BP算法,也就是BP神经网络。
用ArcGIS的CreateFisnet工具在研究区域生成均匀分布的采样点(共生成3,009,451个),提取该采样点的变量值。每个点代表120 m × 120 m栅格单元的变量值,理想的情况是栅格单元越小越好。还有需要注意的是BP网络的预测结果都不同,因为网络的初始权值都是随机给定的,所以要进行多次的测试后,选择预测准确率最高的结果,最终选择结果见表2。当通过BP神经网络模型得出的预测值大于0.5时,判定该样本为遗址点,否则为非遗址点。对建模样本119个非遗址中正确预测110个,准确率为84%。对119个遗址中正确预测112个,准确率为94.1%,总准确率为89.1%。对验证样本104个非遗址中正确预测90个,准确率为86.5%;对101个遗址中正确预测91个,准确率为90.1%,总准确率为88.3%。验证样本中的个别样本因缺少自变量值未分类。最后根据采样点的预测值生成遗址分布概率图(图2)。经过计算可知,预测值大于0.5的区域为高概率区,其面积占延边总面积的17.6%;预测值小于0.5的区域为低概率区,其面积为高概率区以外的82.4%。已知的226个遗址在概率图的各概率区分布情况来看,概率0.9~1.0区间的面积占延边地区总面积的7.0%,却存在61.9%的遗址;概率0.8~1.0区间的面积占延边地区总面积的10.9%,却存在76.1%的遗址;概率0.7~1.0区间的面积占延边地区总面积的13.4%,却存在81.4%的遗址;概率0.6~1.0区间的面积占延边地区总面积的15.5%,却存在86.7%的遗址;概率0.5~1.0

Table 1. The total number of modeling samples and validation samples
表1. 建模样本和验证样本数(个)

Table 2. The sites prediction accuracy of modeling samples and validation samples
表2. 建模样本和验证样本遗址预测准确率
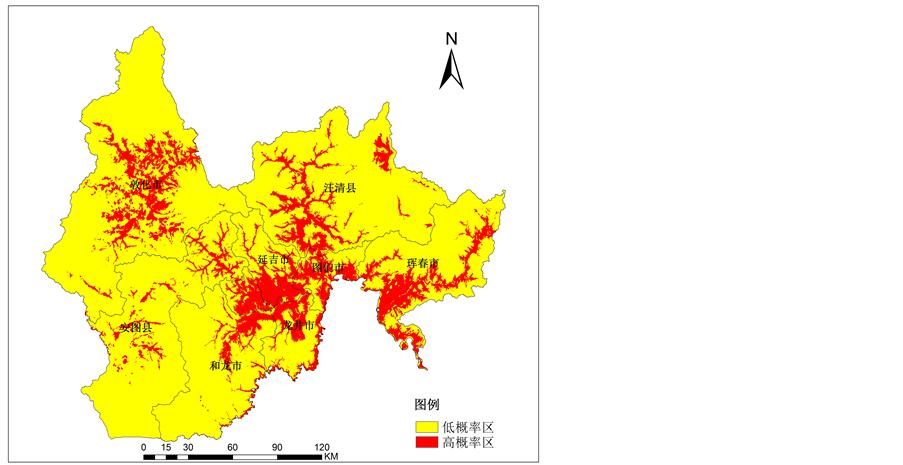
Figure 2. The probability diagram of Bohai Kingdom sites in Yanbian area
图2. 延边地区渤海国遗址分布概率示意图
区间的面积占延边地区总面积的17.6%,却存在88.9%的遗址。这说明本遗址预测模型能够有效地识别出遗址存在的高概率区。
4. 预测结果的分析
下面从高程、坡度、坡向、距离河流的距离、距离道路的距离、距离村屯的距离多种因素,对预测模型的预测结果进行详细分析。
1) 高程(高度)分析
高程是影响人类生活环境的重要因素,为了安全,人类必须居住在一定的海拔高度中。因此它也是地形分析中必不可少的评价因子。本文将研究区域的DEM按60 m的间隔等高程进行分级,将高程分为小于90 m、90~150 m、150~210 m、210~270 m、270~330 m、330~390 m、390~450 m、450~510 m、510~570 m、570 m以上共十个等级,与遗址分布概率图叠置,统计高概率去和低概率去的高程分布比例。研究区域59.81%的面积处于570 m以上,其低概率区占58.85%,高概率区只占0.96%。低概率区高程集中在570 m以上,而高概率区集中在270~330 m、330~390 m、390~450 m、510~570 m等四个高程区间,平均占2%以上,其他高程区间比例小于2%(见表3)。
2) 坡度分析
坡度在很大程度上影响人类的生存和生产活动范围,进而影响遗址的分布,因此,地面坡度大小往往对遗址点的分布有着密切的关系。本文根据研究区的地形特点,采用3度等差分级制图,对研究区坡度划分为0˚~3˚、3˚~6˚、6˚~9˚,9˚~12˚、12˚~15˚、15˚~18˚、18˚~21˚、21˚~24˚、24˚~27˚、大于27˚共10个等级,与遗址的分布概率图叠置,统计高概率区和低概率区的坡度分布情况(见表3)。由表可知,高概率区占研究区域的17.6%,其中坡度0˚~3˚区域占10.1%,超过一半。总体上呈现随坡度的增加所占比例减少的趋势。
3) 坡向分析
在古代,社会生产力水平低,人工取暖条件有限,因此,增加自然热量的坡向是遗址选址的重要因

Table 3. The distribution of height, gradient, slope aspect in the high probability region and low probability region (%)
表3. 高概率区与低概率区的高程、坡度、坡向分布情况(%)
素之一。本文从DEM中提取坡向,并把它分为九类:平地(-1)、北(0˚~22.5˚和337.5˚~360˚)、东北(22.5˚~67.5˚)、为东(67.5˚~112.5˚)、东南(112.5˚~157.5˚)、南(157.5˚~202.5˚)、西南(202.5˚~247.5˚)、西(247.5˚~292.5˚)、西北(292.5˚~337.5˚)。与遗址分布概率图叠置,统计高概率去和低概率去的坡向分布情况(见表3)。由表可知,平地占整个区域的13.1%,其它的坡向分布较均匀。高概率区中所占比例最大的是平地,占5.72%,其次是东北方向,占2.0%。
4) 河流、道路、村屯缓冲区分析
人类生活同水源有着密切的关系,尤其是生产力水平低下的农耕时代,在选择居住地时,水源是重要的考虑因素。交通便捷度也是人类生产生活密切相关,本文在很难获取准确的渤海国时期交通路线信息的状态下,以现代国道作为重要的参照物进行概率分析,这对预测遗址能提供一定的参考价值。另外,为了考察现代聚落同遗址在时空上的连续性,提取了遗址距离现代村屯的距离。本文分别对河流、道路、村屯建立0~500 m、500~1000 m、1000~1500 m、1500~2000 m、大于2000 m的五级缓冲区,分析高概率区和低概率区的河流、道路、村屯缓冲区分布情况。高概率区在河流缓冲区上主要分布在0~500 m、500~1000 m缓冲区内,占研究区域的12.87%和3.39%。高概率区在道路缓冲区上主要分布在0~500 m、500~1000 m、1000~1500 m缓冲区,分别占研究区域的9.76%、5.03%、2.08%。高概率区在村屯缓冲区上主要分布在500~1000 m、1000~1500 m缓冲区,分别占研究区域的6.12%、4.96% (见表4)。这些说明渤海国遗址具有明显的河流、道路、村屯指向性,特别是河流和道路指向性突出。
5) 各县市高概率区分布情况
根据图2中的高概率区和低概率区进行统计分析可知,每个县市中高概率区所占比例由大到小依次为图们市47.9%、龙井市41.3%、延吉市36.5%、珲春市26.2%、敦化市14.9%、汪清县14.6%、和龙市10.7%、安图县8.2%。这说明图们、龙井、延吉、珲春市由于本身所辖面积小,所以高概率区的面积占各市总面积的比重相对高,从而在各自县市内发现遗址的概率也相对高。而整个延边地区来看,高概率区只占整个延边地区总面积的17.6%,其中各县市所占比重依次为敦化市4.1%,珲春市3.1%、汪清县3.0%、龙井市2.1%、延吉市1.4%、安图县1.4%、和龙市1.3%、图们市1.2%。这说明从延边地区来看,所辖面积相对大的敦化市、珲春市、汪清县的遗址分布区占全州总面积的比重相对高。这些地区发现遗址的可能性也相对高。因此,宏观上来看,延边地区发现渤海国遗址概率高的地区为图们市、龙井市、

Table 4. The buffer distribution of the river, the road and the village in the high probability region and low probability region (%)
表4. 高概率区与低概率区的河流、道路、村屯缓冲区分布情况(%)
延吉市、珲春市、敦化市、汪清县等地区。落实到各县市具体乡镇的高概率区集中分布的乡镇有图们市的石岘镇、凉水镇;龙井市的老头沟镇、东盛涌镇、智新镇、德新乡;延吉市的朝阳川镇、依兰镇;珲春市的三家子乡、马川子乡、杨泡乡、哈达门乡、敬信镇;敦化市的官地镇、沙河沿镇、江南镇、贤儒镇、黑石乡;汪清县的百草沟镇、汪清镇、大兴沟、东光镇;和龙市的头道镇、土山镇;安图县的明月镇、石门镇、长兴乡、亮兵镇等。
5. 结论与讨论
本文基于BP神经网络和ArcGIS的叠加分析、缓冲区分析方法,选取研究区域中452个样本的高程、坡度、坡向、道路距离等自然和人文因素,建立预测模型,对预测结果分析得出结果如下:
1) 利用BP神经网络建立的预测模型的预测准确率达到88.7%,并给出了延边地区渤海国遗址概率分布图,进一步揭示了遗址的空间分布规律,为今后渤海国遗址研究提供基础资料。
2) 从预测结果看,每个县市中遗址预测区域所占比重较高的县市为图们市47.9%、龙井市41.3%、延吉市36.5%、珲春市26.2%。遗址预测区域面积占延边地区总面积比重较高的县市为敦化市4.1%,珲春市3.1%、汪清县3.0%。因此,宏观上来说,延边地区发现渤海国遗址概率高的地区为图们、龙井、延吉、珲春、敦化、汪清等地区。
3) 根据影响遗址分布的不同影响因素进行预测分析的结果,遗址预测区域中的高程集中在270~330 m、330~390 m、390~450 m、510~570 m等四个高程区间,遗址预测区域中的坡度集中在0˚~3˚区间,坡向集中在平地和东北方向,遗址预测区域在河流缓冲区上主要分布在0~500 m、500~1000 m缓冲区间,在道路缓冲区上主要分布在0~500 m、500~1000 m、1000~1500 m缓冲区间,在村屯缓冲区上主要分布在500~1000 m、1000~1500 m缓冲区间。
4) 遗址预测结果能够在考古中得到有效利用。考古工作需要大量的财力和物力以及人力。因此,考古工作需要有周密的计划。本研究中的遗址预测模型能够为选定考古范围和制定考古计划提供有效的根据。如我们要想在延边地区进行渤海国遗址考古的话,首先把考古的重点区域选定在概率为0.9~1.0区间的预测率相对高的区域。再结合高程、坡度、坡向、河流缓冲区等因素的分析,进一步得出遗址分布概率高的区域。这将为考古工作带来很多便利。首先,它能够有效地指导考古工作的主动性、可能性、方向性和准确性,从而使得考古工作少走弯路,提高工作效率。其次,可以节省大量的财力、物力、人力和时间。
需要指出,本文中数据样本的栅格数据分辨率(120 m × 120 m)还不够高,如在今后的工作中,进一步提高栅格数据分辨率、采用多种预测模型相互印证、添加更多的环境变量和人文因素的话会提高预测结果的准确性。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41161025)资助。