1. 研究背景
森林火灾已经成为备受关注的环境问题,由于森林火灾不仅会烧死和烧伤树木,也会使得森林面积直接减少,而且会使得森林结构以及环境遭到严重破坏,以至于使得森林的生态系统失去平衡,甚至会造成大量的人畜伤亡。不仅影响森林保护,还会造成巨大经济损失和严重的生态破坏,给人类的生活带来灾难性影响。森林火灾的发生源于多种原因(如人为疏忽和闪电),尽管越来越多的国家斥巨资来控制这场灾难,全世界每年仍有数百万公顷的森林葬身火海。特别是葡萄牙受森林火灾影响严重。从1980到2005,270万公顷的森林面积(相当于阿尔巴尼亚的国土面积)被火灾侵蚀。2003年和2005年火灾季节中受灾面积尤其巨大,相当于领土的4.6%和3.5%,并且有21和18人死亡。森林火灾要发生必须具备三个条件:
可燃物(包括树木等植物)是发生森林火灾的物资基础;森林的可燃物主要包括森林中全部的有机物质,例如:地衣、草类、乔木、枯枝落叶等。
火源是发生森林火灾的主导因素;森林中不同的可燃物的燃点温度也是不相同。一般干枯杂草的燃点为150℃~200℃,木材的燃点为250℃~300℃,那么可以知道森林火灾要发生,就必须需要有外来火源,使得可燃物达到它的可燃点才行。
天气是也发生森林火灾的重要条件;气温,风速,相对湿度以及降水量都会直接影响森林火灾的发生。气温越高,风速越大,相对湿度越低,降水量越小,那么森林火灾发生的可能性也就越大。
快速检测是成功预测火灾的关键要素。由于传统的监视机制费用昂贵且受主观因素的影响大,人们逐渐重视发展自动化的解决方案。这些方案可分为三大类:卫星,红外扫描仪和局部传感器。由于卫星定位的延迟和扫描仪高昂的设备成本和维护成本,这些方案不能用来解决所有的情况。研究表明,天气条件,如气候和相对湿度,是影响火灾发生的关键因素。而自动气象站通常可以提供有效数据,这些数据可以实时采集且成本低廉。
在过去,气象数据已纳入量化指标体系 [1] [2] ,用以预防火灾危险、警告公众和支持消防管理决策。特别是,加拿大森林火险天气指数(FWI)系统 [3] 的设计,在上世纪70年代计算机还十分稀缺的情况下它只需要利用手动收集的四个气象观测读数(气候,相对湿度,风速和降水量)进行简单的计算。目前该指数系统在加拿大和其他一些国家广泛使用。
现今,计算机发展的迅猛,使得对数据的采集越发的实效性和方便。机器学习是信息技术进步的一个体现,使用自动化的数据挖掘工具分析原始数据可以为高层决策者提取有效信息。事实上,机器学习技术已经应用到火灾探测领域 [4] [5] 。国内外,有许多的专家和学者利用不同的统计模型以及机器学习方法来研究森林火灾等级的预测问题。
在国外,在2001年,Han Jiawei采用了多元线性回归模型,决策树,人工神经网络,支持向量机以及随机森林等五种数据挖掘方法来进行森林火灾预测研究 [6] 。其他一些国外学者采用神经网络(NN) [7] 预测人类引起的森林火灾;红外扫描仪和神经网络结合在减少森林火灾误报率方面达到70%的成功率;北美森林大火的卫星图像应用支持向量机 [8] 获得了73%的准确率在森林火灾可能性上;使用卫星和气象数据应用逻辑回归、随机森林和决策树 [9] 来探测斯洛文尼亚森林火灾。
在国内也有不少的学者利用机器学习的方法来研究森林火灾预测。在2007年,黄家荣,刘倩,高光芹等人提出应用人工神经网络的方法来对河南省的森林火灾面积进行预测 [10] 。2009年,杨景标和马晓茜提出利用人工神经网络的多层神经网咯模型来预测广东省的森林火灾成灾面积 [11] 。2012年,许志卿,苏喜友和张颐提出使用气象数据来预测森林火灾的等级并用用支持向量机回归模型来实现森林火灾等级的预测 [12] 。
与这些以前的方法相比,本文提出基于机器学习中支持向量机方法的改进方法-最小二乘支持向量机,由于最小二乘支持向量机对处理样本容量较小的数据具有较高的准确度而且耗时较短。本文选用UCI数据库中的森林火灾数据进行预测处理,选用高斯函数(径向基函数)作为最小二乘支持向量机的核函数,根据一对一的多分类算法设计出最小二乘支持向量机的多分类器,使用粒子群算法选择最优参数。最后与支持向量机、BP神经网络、决策树等方法进行对比。
2. 模型构建
支持向量机(Support Vector Machine)是由Vapnik在20世纪90年代所提出的一种分类算法 [13] 。支持向量机具有非常好的学习性能还有完备的统计学理论基础。支持向量机已经在多个领域具有广泛的应用,例如:模式识别和函数估计 [14] 。支持向量机的一般做法是:将数据映射到高维空间,然后通过构造最优能将这些数据点分开的超平面。本文通过利用Suykens提出的支持向量机的一种改进方法-最小二乘支持向量(Least Squares Support Vector Machine)进行小样本分类研究。最小二乘支持向量可以用来解决分类和函数估计问题。
2.1. 支持向量机(Support Vector Machine)
支持向量机主要是通过构造最优分类超平面来对数据集进行分类的。已知有n个训练样本数据 ,其中
,其中 是第k个输入的数据,
是第k个输入的数据, 是
是 所属的类别。如果要实现最优超平面将所有的训练样本数据正确的分类,那么就必须满足:
所属的类别。如果要实现最优超平面将所有的训练样本数据正确的分类,那么就必须满足:
 (1)
(1)
其中 是非线性函数,b为实常数,我们就可以得到使得
是非线性函数,b为实常数,我们就可以得到使得 最小化的一个超平面,为了使得构造的最优分类超平面能够对那些线性不可分的数据集进行分类,那么就需要在上面(1)式中引入非负的松弛因子
最小化的一个超平面,为了使得构造的最优分类超平面能够对那些线性不可分的数据集进行分类,那么就需要在上面(1)式中引入非负的松弛因子 ,则(1)式可以转化为:
,则(1)式可以转化为:
 (2)
(2)
根据结构风险最小化原则,那么风险的边界可以通过上面(2)式的约束条件下对下式进行最小化:
 (3)
(3)
上面(3)式的解可以通过构造下面的拉格朗日方程求出:
 (4)
(4)
其中, ,
, ,
, 。那么分别对
。那么分别对 以及
以及 求偏微分,并令等于0,可得:
求偏微分,并令等于0,可得:
 (5)
(5)
于是最优问题可以转化到求解下面的二次规划问题:
 (6)
(6)
可以根据Mercer定理 [15] ,得到 。那么(6)式的二次规划问题可以转化为求解下式:
。那么(6)式的二次规划问题可以转化为求解下式:
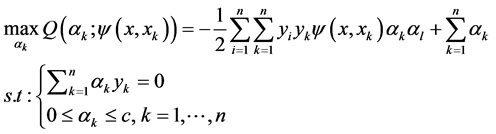
那么就可得到支持向量机的分类决策函数为:
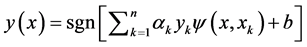
其中, 为实常数,对于多数的样本
为实常数,对于多数的样本 将为零,然而取值
将为零,然而取值 不为零,并且满足(1)式等号成立的样本为支持向量。
不为零,并且满足(1)式等号成立的样本为支持向量。 是核函数。常见的核函数有:线性SVM核函数,径向基SVM核函数,多项式SVM核函数。
是核函数。常见的核函数有:线性SVM核函数,径向基SVM核函数,多项式SVM核函数。
2.2. 最小二乘支持向量机(Least Squares Support Vector Machine)
最小二乘支持向量机将支持向量机中的不等式约束条件变成等式约束条件,并且将误差的平方和损失函数作为训练集的经验损失,这样就把解二次规划问题转化为求解线性方程组问题,这样大大的提高求解问题的速度和收敛的精确度。
已知有n个训练样本数据 ,其中
,其中 是第
是第 个输入的数据,
个输入的数据, 是
是 所属的类别。那么最小二乘支持向量机的优化问题就可以表示为:
所属的类别。那么最小二乘支持向量机的优化问题就可以表示为:
 (7)
(7)
其中, 是允许错分的松弛因子,
是允许错分的松弛因子, 为惩罚因子。可以通过(7)式的对偶形式求出它的最优解,而其对偶形式可以根据目标函数和约束条件来建立拉格朗日函数:
为惩罚因子。可以通过(7)式的对偶形式求出它的最优解,而其对偶形式可以根据目标函数和约束条件来建立拉格朗日函数:
 (8)
(8)
其中, 是拉格朗日乘子。根据KKT条件 [16] 对(8)式进行优化,那么分别对
是拉格朗日乘子。根据KKT条件 [16] 对(8)式进行优化,那么分别对 以及
以及 求偏微分,并令等于0,可得:
求偏微分,并令等于0,可得:
 (9)
(9)
上式(9)可以直接表示成求解如下的线性方程组:
 (10)
(10)
其中 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, 是单位矩阵。
是单位矩阵。 和
和 的值可以从(9)式得出,那么(10)式可以用下面的式子来表示:
的值可以从(9)式得出,那么(10)式可以用下面的式子来表示:
 (11)
(11)
其中 ,可以根据Mercer定理,那么就可以使用核函数
,可以根据Mercer定理,那么就可以使用核函数 ,这样就可以得到:
,这样就可以得到:
 (12)
(12)
常用的核函数有:线性SVM核函数,径向基SVM核函数,多项式SVM核函数。本文建模中所选的核函数为径向基SVM核函数,也就是高斯SVM核函数,其表达式为:
 (13)
(13)
其中 是核宽度参数,利用(11)式和(12)式就可以得到一个分类器,从而避免了支持向量机中比较复杂的二次规划问题。因而只要在给定
是核宽度参数,利用(11)式和(12)式就可以得到一个分类器,从而避免了支持向量机中比较复杂的二次规划问题。因而只要在给定 和
和 的情况下,求出
的情况下,求出 就可以得到训练集的分类决策函数,其表达式为:
就可以得到训练集的分类决策函数,其表达式为:
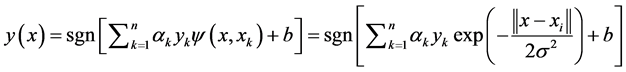
然而,最小二乘支持向量机一般都是基于二分类的,最小二乘支持向量机可以采用多个方法来解决多分类的问题。对于多分类的支持向量机常用的方法有:FLS-SVM训练算法,FLS-SVM多分类算法,一对一的多分类算法以及一对多的多分类算法。一对一的多分类算法虽然计算复杂,但是其精确度较高,而且适合类别较少的情况。本文主要基于一对一的多分类算法的思想,来设计基于最小二乘支持向量机的多分类器。
一对一的多分类算法被Kressel在1999年提出 [17] ,本文在这里所采用的一对一的方法对数据进行多元分类,需要构建 个二分类器,其中
个二分类器,其中 为样本的类别数。那么对于第
为样本的类别数。那么对于第 类和第
类和第 类的样本来说,最优化问题为:
类的样本来说,最优化问题为:
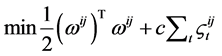
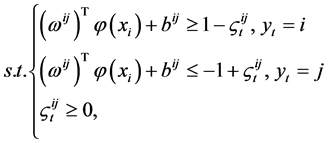
那么对于第 类和第
类和第 类的样本来说,其决策函数为:
类的样本来说,其决策函数为:
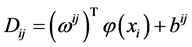
所有的 个二分类器都建立完成后,可以通过不同的方法对测试样本进行分析。然而,较为常用的是采用投票法,也就是说,如果
个二分类器都建立完成后,可以通过不同的方法对测试样本进行分析。然而,较为常用的是采用投票法,也就是说,如果 的输出结果为
的输出结果为 属于第
属于第 类,那么第
类,那么第 类加上一票,否则,第
类加上一票,否则,第 类加上一票。当所有的二分类器都对
类加上一票。当所有的二分类器都对 进行分类了后,得票最多的那个类别就是
进行分类了后,得票最多的那个类别就是 最终的类别。可以用如下的数学表达式来表示:
最终的类别。可以用如下的数学表达式来表示:
如果对第 类和第
类和第 类的决策函数
类的决策函数 的决策值来显示
的决策值来显示 的预测类别,那么第
的预测类别,那么第 类的投票目标函数为:
类的投票目标函数为:
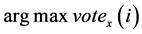
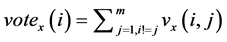
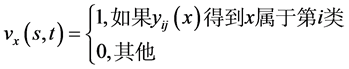
3. 森林火灾数据初步分析
3.1. 数据来源
本文实证分析所选用的森林火灾数据是Montesinho自然公园火灾数据,这个公园里含有很高的植物和动物的多样性。该地区的气候属于地中海气候,年平均气温8至12的范围内. 在实验中使用的数据收集从2000年1月到2003年12月,在本文中主要使用两个数据库。第一个数据库被检查员负责收集Montesinho火灾发生。在日常生活中,每一次森林火灾的发生,都会有几个特征进行注册,如时间,日期,植被的类型,六个组成部分的 FWI 系统和总过火面积。第二数据库由布拉干萨理工学院收集,包含几个气象观测(例如风速),是由一个气象站位于Montesinho公园中心30分钟内记录。两个数据库存储在单个扩展板数,在不同的格式,和大量的手工劳动进行整合成一个单一的数据集共有517个条目。数据来源的网址:http://www.dsi.uminho.pt/˜pcortez/forestfires/。
3.2. 数据变量说明
Month (月份,日期变量):Month表示森林火灾数据被记录时的月份。
FFMC (细小可燃物湿度码):在FWI系统中,FFMC代表了森林 的枯枝落叶和其他的已固化的细小燃料的含水率。细小可燃物大部分由枯枝落叶、地衣、苔藓和其他的小的松散的碎片组成。 细小可燃物的可燃性和易燃性的以通过FFMC这一个相对简单的指标来衡量。FFMC为连续变量。
DMC (粗腐殖质湿度码):DMC主要代表森林腐殖质的地表可燃物的含水率。DMC为连续变量
DC (干旱码):DC是衡量长期干旱对森林可燃物的影响的一个简单指数。干旱码模型跟其他的干旱模型很类似,如KeethByram Drought和 Palmer Drought Index。DC为连续变量。
ISI (初始蔓延指数):ISI可以通过FFMC 和风速计算得到,其代表了森林火灾蔓延的潜在等级。在不同的森林类型中,ISI 是衡量森林火灾蔓延等级的一个很好指标。ISI为连续变量。
Temp (气温):temp是Montesinho国家公园的气象数据。temp越高,森林发生火灾的可能性就越大。temp是连续变量。
Wind (风速):wind是Montesinho国家公园的气象数据。wind越大,森林发生火灾的可能性就越大。wind是连续变量。
RH (相对湿度):RH是Montesinho国家公园的气象数据。RH越大,森林发生火灾的可能性就越小。RH是连续变量。
Rain (降水量):rain是Montesinho国家公园的气象数据。rain越大,森林发生火灾的可能性就越小。rain是连续变量。
Area (森林火灾燃烧的面积):area是Montesinho国家公园森林火灾燃烧的面积。area是分类为变量。本文主要根据国务院一九八八年一月十六日颁发的《森林防火条理》规定,森林火灾分类:(1) 森林火警:受害森林面积不足1公顷或其它林地起火的;(2) 一般森林火灾:受害森林面积在1公顷以上不足100公顷的;(3) 重大森林火灾:受害森林面积在100公顷以上不足1000公顷的;(4) 特大森林火灾:受害森林面积在1000公顷以上的,按照燃烧面积将森林火灾分成4类。
3.3. 数据初步分析
根据月份数据和森林燃烧的次数(频率)建立月份燃烧频率表。其显示结果如图1。
从图1可以看出森林在八月,九月容易发生火灾,而在一月,五月,十一月基本上没发生过火灾,这可能与葡萄牙东北部的Montesinho 国家公园该地区的气象因素有关,可能在该地区的八月,九月气候比较干燥,温度比较高以及风速较大导致这些月份易发生火灾,笔者认为这段时间应该对该地区的气象每天进行观察,使得发生火灾几率大大减少。在一月,五月,十一月基本没有火灾发生。可能在该地区的一月,五月,十一月气候比较潮湿,温度较低导致这些月基本上不会发生火灾。笔者认为对这段时间的气候监测每五天一次,这样可以减少监测成本。
我们选择月份的时间变量,月平均气象条件是相当明显的。接下来是四部分,是由FWI天气条件直
接影响。从气象站数据库,我们选择了四天气属性的FWI 系统。在与时间滞后的FWI 的对比,在这种情况下的值表示的即时记录,由站在火灾检测传感器。火灾面积其为正偏态分布,随着火灾呈现大多数都是小规模。应该指出的是,这种扭曲的特质在其他国家也存在。如前所述,所有条目表示火灾发生但其没有价值意味着一个面积低于100公顷烧毁。为了减少偏度和提高对称性,对数函数 ,这是一种常见的转化趋于改善右偏态分布指标回归的结果,应用于区域属性。最后的变换后的变量将是这项工作的产出目标。
,这是一种常见的转化趋于改善右偏态分布指标回归的结果,应用于区域属性。最后的变换后的变量将是这项工作的产出目标。
为了对数据有进一步的了解,需要知道自变量之间的相关性如何,那么就要对数据进行相关性分析,图2给出了自变量之间相关性的散点图,表1给出了自变量之间的相关性矩阵。
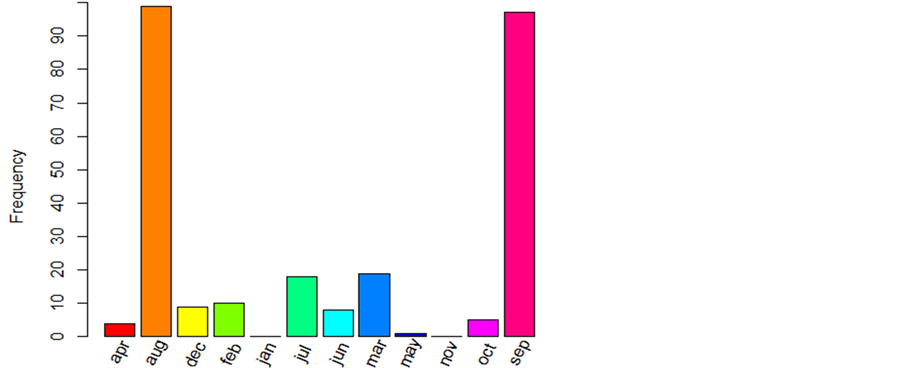
Figure 1. Monthly burning frequency (R)
图1. 月份燃烧频率(R)
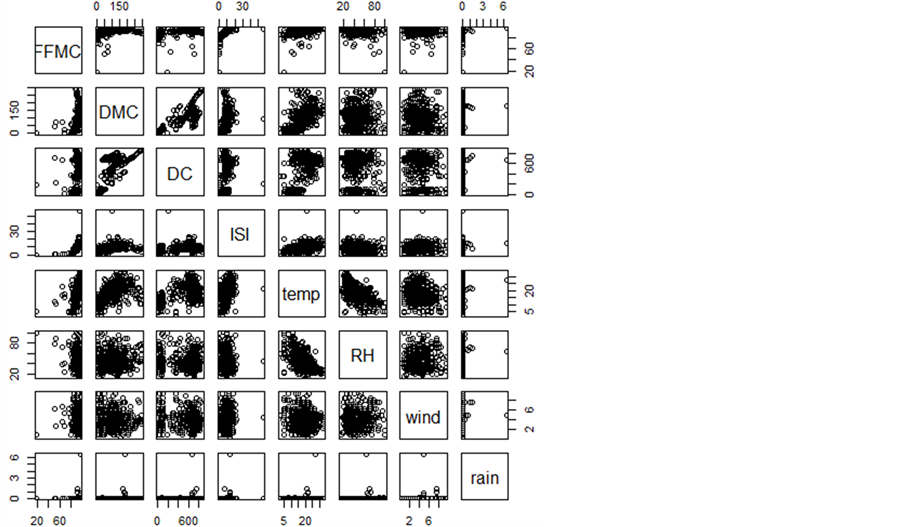
Figure 2. Scatter plot among the forest fire data
图2. 森林火灾数据各个变量之间的散点图
通过各变量之间的散点图我们可以观察到只有粗腐殖质湿度码与干旱码成明显的线性关系而且斜率为正,则说明粗腐殖质湿度码与干旱码成高度的正相关。气温与相对湿度同样成显现的线性关系而且斜率为负值,则说明气温与相对湿度成高度的负相关。我们根据生活常识也知道,气温越高,那么空气的相对湿度就越低。说明森林火灾数据没有没污染,具有高度的可信度。其他变量之间就没有明显的线性关系。透过森林火灾数据就各变量之间的相关性矩阵表,可以观察到只有粗腐殖质湿度码与干旱码的相关系数高达0.68。除了气温与相对湿度的相关系数是−0.53,其他变量之间的相关系数均较小。通过表1和图2,我们可以知道森林火灾数据中的各个变量之间没明显的相关性,大多数变量之间的关系都不是线性关系,因此使用线性回归来拟合森林火灾数据那就不合适了。所以,有许多的学者使用非线性的方法来拟合数据,例如:决策树,神经网络,支持向量机的非线性核函数,因此使用高斯函数作为最小二乘支持向量机的核函数。
对因变量进行分析,本文主要基于我国的国务院一九八八年一月十六日颁发的《森林防火条理》规定,森林火灾分类:(1) 森林火警:受害森林面积不足1公顷或其它林地起火的;(2) 一般森林火灾:受害森林面积在1公顷以上不足100公顷的;(3) 重大森林火灾:受害森林面积在100公顷以上不足1000公顷的;(4) 特大森林火灾:受害森林面积在1000公顷以上的,按照燃烧面积将森林火灾分成4类。那么各类的数目如图3所示。
从图3中可以知道森林火灾等级一般都是森林火警和一般森林火灾,重大森林火灾和特大森林火灾

Table 1. Correlation matrix of forest fire data
表1. 森林火灾数据各个变量之间的相关性矩阵
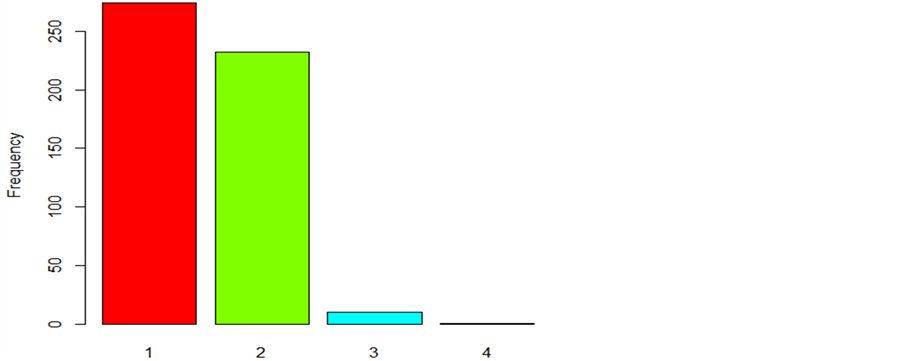
Figure 3. Frequency of different forest fire levels
图3. 森林火灾等级各类别的频数
就非常的少。
4. 森林火灾数据实验结果
本文使用森林火灾数据预测森林火灾的等级,实验数据是来自UCI数据库中的Forest Fires数据。根据一些前人的研究(文献 [6] )的结果,在本文实验中,我们将以上面提到的四个气象特征作为输入变量(自变量)。在数据分析时,我们对数据做了标准化处理,主要是为了消除变量之间的不同变量量纲以及变化幅度所带来的影响。我们也发现数据会出现右偏态现象,我们为了消除这种现象从而提高对称性,我就对y做了对数变换,对数函数 。本文所研究的森林火灾等级有四个级别,而最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)一般都是基于二分类的问题。那么我们需要使用多分类的LS-VM。本文主要是利用一对一的多分类LS-VM方法对森林火灾等级进行分类。在一对一的多分类LS-VM方法中我们需要构建
。本文所研究的森林火灾等级有四个级别,而最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)一般都是基于二分类的问题。那么我们需要使用多分类的LS-VM。本文主要是利用一对一的多分类LS-VM方法对森林火灾等级进行分类。在一对一的多分类LS-VM方法中我们需要构建 个二元分类器,我们所用的多分类LS-VM方法是基于我们上面所设计的那样。为了提高多分类LS-VM方法的分类准确率,我们需要对数据进行归一化进行预处理,一般归一化处理如下:
个二元分类器,我们所用的多分类LS-VM方法是基于我们上面所设计的那样。为了提高多分类LS-VM方法的分类准确率,我们需要对数据进行归一化进行预处理,一般归一化处理如下:
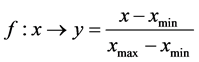
其中, ,
, ,
, ,将数据归一化后,所用数据都被规整到
,将数据归一化后,所用数据都被规整到 范围内,也就是说
范围内,也就是说 。对于最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的核函数选择,我根据数据中各变量之间的相关性,可以知道它们之间的关系是非线性的。因此,我们选择高斯函数(径向基函数)作为最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的核函数。对惩罚因子
。对于最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的核函数选择,我根据数据中各变量之间的相关性,可以知道它们之间的关系是非线性的。因此,我们选择高斯函数(径向基函数)作为最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的核函数。对惩罚因子 和核宽度参数
和核宽度参数 的选择,根据前人的研究 [18] ,我们知道它们的取值在很大程度上决定了最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的性能的优劣。因此,对惩罚因子
的选择,根据前人的研究 [18] ,我们知道它们的取值在很大程度上决定了最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的性能的优劣。因此,对惩罚因子 和核宽度参数
和核宽度参数 的选择就尤其重要了,现在有不少的学者研究了惩罚因子
的选择就尤其重要了,现在有不少的学者研究了惩罚因子 和核宽度参数
和核宽度参数 对核函数为径向基函数(高斯函数)的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)分类效果的影响。根据他们的研究,我们可以知道对核函数为径向基函数(高斯函数)的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的学习能力会随着核宽度参数
对核函数为径向基函数(高斯函数)的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)分类效果的影响。根据他们的研究,我们可以知道对核函数为径向基函数(高斯函数)的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的学习能力会随着核宽度参数 的值从小到大的逐渐地改变,分类效果也将会随之从低到高,再从高到低变化。而惩罚因子
的值从小到大的逐渐地改变,分类效果也将会随之从低到高,再从高到低变化。而惩罚因子 主要是用来控制错分样本的比例以及模型复杂度之间的折中,也就是主要控制数据子空间的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的置信范围以及经验风险的比例,当最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)达到比较好的泛化能力,因而,当数据的子空间不同时,模型最优的惩罚因子 的取值也不同。下面两张图(图4,图5)给出核宽度参数
主要是用来控制错分样本的比例以及模型复杂度之间的折中,也就是主要控制数据子空间的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的置信范围以及经验风险的比例,当最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)达到比较好的泛化能力,因而,当数据的子空间不同时,模型最优的惩罚因子 的取值也不同。下面两张图(图4,图5)给出核宽度参数 和惩罚因子
和惩罚因子 对最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)分类效果的影响。
对最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)分类效果的影响。
本文对最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)的参数选择主要是基于文献 [19] 所提出的粒子群算法。本文通过随机抽样的方法将森林火灾数据随机分成五份(其中有3份样本容量为103,其余的两份样本容量为104),进行五折交叉验证结果如下:
根据上面核宽度参数 和惩罚因子
和惩罚因子 对最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)分类效果的影响曲线图,为了使得参数搜索时间短一些,本文将
对最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)分类效果的影响曲线图,为了使得参数搜索时间短一些,本文将 的搜索范围定为:
的搜索范围定为: ,
, 的搜索范围定为:
的搜索范围定为: ,粒子群算法中的微粒个数设置为10个,迭代次数设置为10次。
,粒子群算法中的微粒个数设置为10个,迭代次数设置为10次。
从表2中我们可知道核宽度参数 最优为0.0001025,惩罚因子
最优为0.0001025,惩罚因子 最优为5.638。通过是粒子群算法的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)参数最优化方法求出最优分类效果,其准确率高达为89.8572%。本文利用决策树,BP神经网络,支持向量机等方法来拟合森林火灾数据,同样使用五折交叉验证的方法来验证
最优为5.638。通过是粒子群算法的最小二乘支持向量机(LS-SVM)参数最优化方法求出最优分类效果,其准确率高达为89.8572%。本文利用决策树,BP神经网络,支持向量机等方法来拟合森林火灾数据,同样使用五折交叉验证的方法来验证
模型的优劣。五折交叉验证方法的结果如表3所示。
从表3,可知其他分类效果的误判率均在20%,而最小二乘支持向量机模型的平均误判率仅为10%左右,这是因为最小二乘支持向量机将支持向量机中解二次规划问题转化成解线性方程组问题,这对于
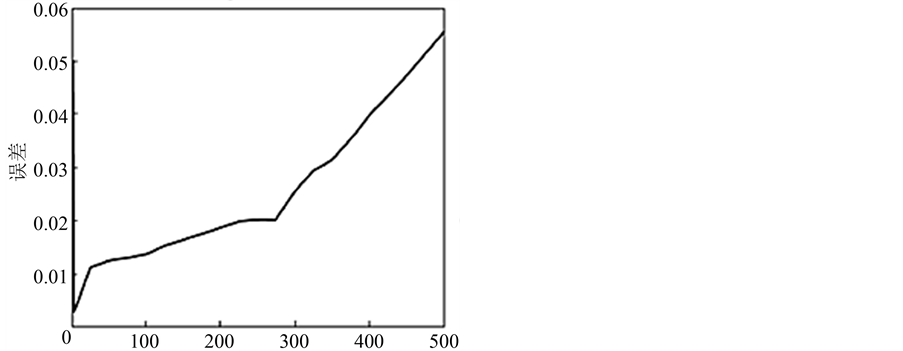
Figure 4. The change of the miscarriage rate of justice with the change of core width parameters
图4. 误判率随核宽度参数变化的曲线
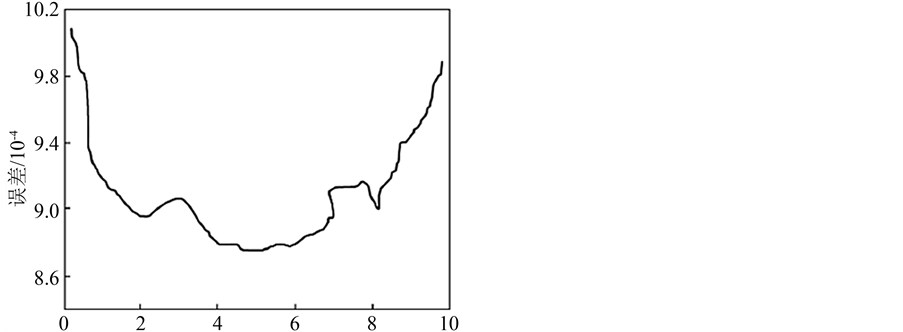
Figure 5. The change of the miscarriage rate of justice with the penalty factor
图5. 误判率随惩罚因子变化的曲线

Table 2. Particle swarm algorithm search parameter results
表2. 粒子群算法搜索参数结果

Table 3. Classification results of various classification methods
表3. 各种分类方法的分类效果
提高求解速度以及收敛精度很重要,并且在计算时所需要的计算资源就要少一些。这也说明了最小二乘支持向量机对于解决那些小样本、非线性等实际问题时具有很强的泛化能力。
5. 结论
本文首先回顾了传统方法对森林火灾等级预测的一些研究,而传统的监视机制费用昂贵且受主观因素的影响大,人们逐渐重视发展自动化的解决方案。这些方案可分为三大类:卫星,红外扫描仪和局部传感器。由于卫星定位的延迟和扫描仪高昂的设备成本和维护成本,这些方案不能用来解决所有的情况。由于计算机的高速发展,数据收集成本较低,出现一些不少学者使用机器学习的方法来预测森林火灾等级预测。然而,预测结果不是很理想。这就需要我们寻找对森林火灾等级预测的精确度更高的方法。因此本文提出基于机器学习中支持向量机方法的改进方法——最小二乘支持向量机,由于最小二乘支持向量机对处理样本容量较小的数据具有较高的准确度而且耗时较短。本文选用UCI数据库中的森林火灾数据进行预测处理,选用高斯函数(径向基函数)作为最小二乘支持向量机的核函数,根据一对一的多分类算法设计出最小二乘支持向量机的多分类器,使用粒子蚁群算法选择最优惩罚系数和核宽度参数。最后与支持向量机、BP神经网络、决策树等方法进行对比。实验结果表明最小二乘支持向量机的方法优于支持向量机、BP神经网络、决策树等方法。最小二乘支持向量机能够很好的解决小样本和非线性等实际问题,最小二乘支持向量机方法在森林火灾等级预测研究中具有很大的应用潜力。
致谢
在本次论文的撰写中,我得到了费宇教授的精心指导,在此,我对费宇教授表示诚挚的感谢以及真心的祝福。并且对国家自然科学基金项目(项目批准号:11561071)和云南省省院省校教育合作咨询共建重点学科——统计学(42111217003)等项目以及给予转载和引用权的资料、图片、文献、研究思想和设想的所有者,表示感谢。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(项目批准号:11561071),项目名称:广义估计方程(GEE)框架下的回归诊断:基于均值和协方差结构同时拟合的研究。云南省省院省校教育合作咨询共建重点学科——统计学(42111217003)。