1. 引言
提高并网风电场运行的稳定性与经济性,对于电力系统安全可靠经济运行有着重要意义 [1] [2] 。我国风电场并网技术要求明确规定,风电场的无功电源包括风电机组及风电场无功补偿装置 [3] ;文献 [4] 指出双馈风电机组(Doubly-Fed Induction Generator, DFIG)是重要的无功源,可利用DFIG进行就近无功补偿;文献 [5] 提出静止无功补偿装置(Static Var Compensator, SVC)能够迅速准确地平抑双馈风电场并网点电压的波动,具有快速灵活的无功功率调节能力。基于此,诸多文献从不同角度讨论了风电场双馈风电机组与SVC间的协调控制。文献 [6] [7] 在稳态运行时优先调整DFIG机组无功出力,无功缺额则由SVC补偿,有效利用了风电机组的无功调节能力;在此基础上,文献 [8] 考虑了故障情况下风电场的控制运行,提出在电网故障时应首先充分发挥SVC的调节能力;文献 [9] 优先安排SVC进行无功调节,剩余无功分配在各DFIG之间进行,保证了各机组均留有一定的无功裕度;文献 [10] [11] 建立了综合考虑风电场并网点(point of common coupling, PCC)的电压偏移量和无功源无功裕度的目标函数,通过协调DFIG和SVC的无功出力,使得风电场PCC电压满足要求,同时提高了无功源无功裕度。
上述无功电压协调控制策略,均从稳定性角度讨论双馈风电机组与SVC的无功电压协调控制问题,所建模型仅考虑了风电场电压偏差以及无功源的无功裕度。然而随着风电场规模的逐步扩大,其功率传输量逐渐增加,从而导致风电场有功损耗的增加,并引发电压波动。因此,优化无功调节设备的无功出力,降低风电场有功损耗,对于电网的安全稳定及经济运行具有重要意义。
本文针对当前风电场运行模式难以有效兼顾稳定性与经济性的问题,提出了风电场运行经济性和稳定性目标。以SVC与双馈风电机组的无功功率为控制对象,建立了风电场无功电压多目标优化控制模型。运用模糊多目标决策方法将风电场无功电压优化转换为一个多目标、多约束的非线性规划问题,并采用粒子群算法进行求解。最后,以实际算例仿真验证了本文提出的多目标优化方法的有效性。
2. 模糊多目标决策方法
多目标决策问题大多具有以下特点 [12] :(1) 无最优解,只有满意解;(2) 目标往往相互联系又相互矛盾;(3) 决策与决策者对决策客体的认知有着直接的联系。并网风电场无功电压优化控制问题本质上是一个多目标多约束决策问题,因此风电场无功电压优化可采用模糊的、多层次的、多目标的决策方法进行求解。
2.1. 目标函数
一般的,多目标优化问题(multi-objective optimization problem, MOP)可描述为以下形式
 (1)
(1)
式中: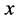 为决策变量;
为决策变量; 为目标函数;
为目标函数; 为决策向量的取值空间;
为决策向量的取值空间; 为等式或不等式约束条件函数。
为等式或不等式约束条件函数。
2.2. 期望值、最大容差及隶属度函数
由各目标单独求解单目标优化问题,可得各目标的期望值:
 (2)
(2)
各目标可以接受的最劣值可以由决策者给出,设为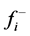 ,则第
,则第 个目标的最大容差为
个目标的最大容差为
 (3)
(3)
对于模糊最小化目标,各目标值的隶属函数应为
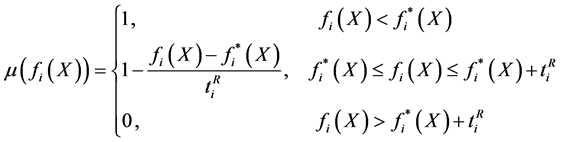 (4)
(4)
2.3. 加权的最小隶属度偏差模型
根据模糊判决原则,式(1)可以转化为如下单目标非线性规划模型:
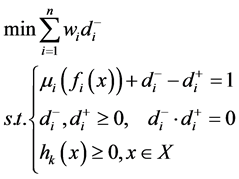 (5)
(5)
其中,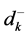 、
、 分别表示各目标隶属函数的正、负偏差变量;
分别表示各目标隶属函数的正、负偏差变量; 表示目标权重。只要最小化负偏差,就可以使得模糊目标接近期望值。
表示目标权重。只要最小化负偏差,就可以使得模糊目标接近期望值。
3. 风电场无功电压多目标优化模型
3.1. 风电场典型结构
风电场主要结构有放射式、单边环式、双边环式、复合环式等 [13] 。由于放射式接线方式具有接线简单,运行方便、经济等优点,目前我国风电场接线方式多选择该种接线形式,如图1所示。
图1中,稳态运行时,双馈风电机组会发出无功功率,对PCC进行无功补偿,既充分发挥了双馈风

Figure 1. Structure of radial wind farm
图1. 放射式风电场结构图
电机组的无功调节能力,也减小了风电场运行对SVC的容量要求;但另一方面,输电线路上无功功率的流动会引起有功损耗,过大的有功损耗会对风电场运行的经济性带来影响。因此,为尽可能提高风电场运行的稳定性和经济性,需要对优化目标作进一步分析。
3.2. 优化控制目标
1) 经济性目标
本文中,风电场运行的经济性目标主要考虑风电场内输电线路的有功损耗。为降低风电场有功损耗,提高风电场运行的经济性,引入风电场有功损耗指标如式(6)所示。
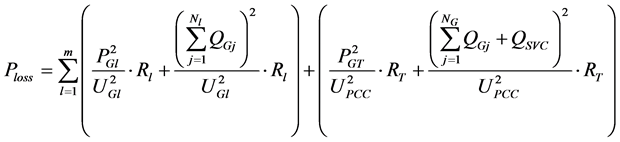 (6)
(6)
式中: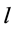 为风电场内输电线路编号,
为风电场内输电线路编号, ;
; 和
和 分别为线路
分别为线路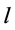 上和全风电场中参与无功电压控制的DFIG机组数;
上和全风电场中参与无功电压控制的DFIG机组数;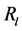 和
和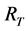 分别为线路
分别为线路 和变压器T支路的电阻;
和变压器T支路的电阻; 和
和 分别为线路
分别为线路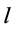 和变压器T上流过的有功功率;
和变压器T上流过的有功功率; 和
和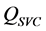 分别为参与无功调节的各台风电机组和SVC的实际无功输出;
分别为参与无功调节的各台风电机组和SVC的实际无功输出;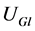 为线路
为线路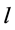 上最靠近PCC的风电机组所接变压器高压侧电压;
上最靠近PCC的风电机组所接变压器高压侧电压; 为PCC实际电压。
为PCC实际电压。
本文在风电场内风电机组发出有功功率一定,即 和
和 一定的基础上,优化风电机组和SVC的无功出力,使风电场有功损耗最小。当风电场电压水平接近额定值,即
一定的基础上,优化风电机组和SVC的无功出力,使风电场有功损耗最小。当风电场电压水平接近额定值,即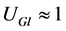 ,且
,且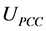 达到上级调度下达的电压控制指令时,由式(6)可知,风电机组和SVC发出无功越少,即
达到上级调度下达的电压控制指令时,由式(6)可知,风电机组和SVC发出无功越少,即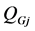 和
和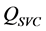 越小,风电场有功损耗越小。
越小,风电场有功损耗越小。
2) 稳定性目标
为更好地对风电场运行稳定性目标进行优化,本文从以下两个指标进行分析:
一是无功源无功裕度指标。为充分发挥DFIG的无功潜力,同时也为提高SVC的无功储备,引入无功源无功裕度指标 [14] ,如式(7)所示。
 (7)
(7)
式中: 为参与无功调节的各台风电机组的无功最大输出极限;
为参与无功调节的各台风电机组的无功最大输出极限;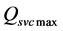 为SVC可调无功功率上限。
为SVC可调无功功率上限。
二是风电场电压偏差指标 [15] 。为降低风电场内各台机组机端电压偏差,提高风电场PCC电压稳定性,引入风电场电压偏差指标,如式(8)所示。
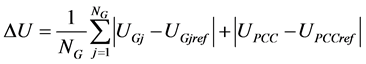 (8)
(8)
式中: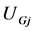 和
和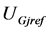 分别为可控DFIG机组
分别为可控DFIG机组 的实际电压和参考电压,本文取
的实际电压和参考电压,本文取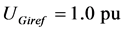 ;
; 为上级调度下达的PCC电压控制指令。为避免对风电场进行频繁控制,当PCC电压在控制偏差允许范围内对风电场进行优化,即满足
为上级调度下达的PCC电压控制指令。为避免对风电场进行频繁控制,当PCC电压在控制偏差允许范围内对风电场进行优化,即满足
 (9)
(9)
式中 为PCC允许的控制误差,本文取
为PCC允许的控制误差,本文取 。
。
4. 基于模糊多目标决策的风电场无功电压多目标优化模型
4.1. 优化控制模型
本文从兼顾风电场稳定性和经济性的角度出发,以每台风力发电机组和SVC的无功输出为控制变量,建立了风电场无功电压多目标优化控制模型,优化风电场内各无功调节设备的无功输出。优化控制模型如式(10)和式(11)所示, 、
、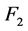 分别代表风电场运行的稳定性和经济性优劣,
分别代表风电场运行的稳定性和经济性优劣,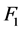 、
、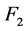 值越小,风电场稳定性和经济性越好。
值越小,风电场稳定性和经济性越好。
 (10)
(10)
 (11)
(11)
式中: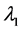 、
、 分别为无功源无功裕度指标和风电场电压偏差指标在目标函数
分别为无功源无功裕度指标和风电场电压偏差指标在目标函数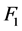 中的权重系数;
中的权重系数; 为风电场中参与无功电压控制的DFIG机组集合。
为风电场中参与无功电压控制的DFIG机组集合。
由于目标函数 、
、 无法同时达到最小值,模型难以求解,因此本文基于上述提出的风电场无功电压多目标优化控制模型,采用模糊多目标决策方法对其进行模型转换,建立了加权的最小隶属度偏差模型,将各目标无量纲化,使各目标的隶属函数值尽可能地接近于1 [16] 。因此,风电场无功电压模糊决策模型可以写成如下的形式:
无法同时达到最小值,模型难以求解,因此本文基于上述提出的风电场无功电压多目标优化控制模型,采用模糊多目标决策方法对其进行模型转换,建立了加权的最小隶属度偏差模型,将各目标无量纲化,使各目标的隶属函数值尽可能地接近于1 [16] 。因此,风电场无功电压模糊决策模型可以写成如下的形式:
 (12)
(12)
式中: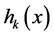 为式(14)和式(15)表示的优化控制约束条件,
为式(14)和式(15)表示的优化控制约束条件,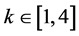 ;对于无功源无功裕度指标,取可接受最劣值
;对于无功源无功裕度指标,取可接受最劣值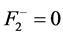 ;对于风电场有功损耗指标,定义可接受最劣值
;对于风电场有功损耗指标,定义可接受最劣值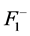 为
为
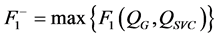 (13)
(13)
4.2. 优化控制约束
1) 潮流方程约束 [17]
 (14)
(14)
式中: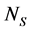 为风电场内总节点数,
为风电场内总节点数, ;
; 、
、 分别为风电场内各节点注入的有功和无功;
分别为风电场内各节点注入的有功和无功;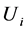 、
、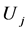 为各节点的电压幅值;
为各节点的电压幅值;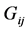 、
、 分别为节点
分别为节点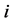 、
、 之间的电导和电纳;
之间的电导和电纳; 为节点
为节点 、
、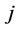 的电压相角差。
的电压相角差。
2) 控制变量约束
 (15)
(15)
式中: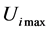 、
、 分别表示风电场内节点
分别表示风电场内节点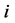 电压运行允许上、下限;
电压运行允许上、下限;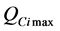 、
、 分别为各风电机组和SVC的无功出力上下限。
分别为各风电机组和SVC的无功出力上下限。
4.3. 模型求解
本文采用粒子群优化算法(particle swarm optimization algorithm, PSO)对式(12)进一步求解 [18] 。PSO算法搜索具有速度快、效率高,求解连续变量的优化问题效果较好,且易收敛于最优解的优点 [19] 。风电场中 台双馈风电机组和
台双馈风电机组和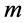 台SVC可以视为PSO算法中粒子的(
台SVC可以视为PSO算法中粒子的(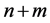 )个变量,风电机组和SVC的无功输出值可视为粒子中变量的值,目标函数值视为PSO算法的适应度。
)个变量,风电机组和SVC的无功输出值可视为粒子中变量的值,目标函数值视为PSO算法的适应度。
风电场无功电压优化控制模型的求解步骤如下:
1) 输入风电场无功电压运行数据、风电场模型和相关参数。
2) 通过对当前DFIG机组和SVC的无功出力进行分析,决策者设定风电场稳定性目标和经济性目标的期望值,进而求出最大容差。
3) 求取各目标值的隶属度函数值,并建立加权的最小隶属度偏差模型。采用PSO算法求解,得出最优方案。PSO算法具体步骤如下:
① 设定粒子群算法的相关参数,如粒子群规模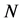 、最大迭代次数
、最大迭代次数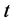 、惯性权重系数
、惯性权重系数 、加速系数
、加速系数 、
、 ,粒子速度最大值
,粒子速度最大值 、最小值
、最小值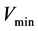 等参数。
等参数。
② 对双馈风电机组和SVC进行编号,通过随机初始化粒子群,得到 种可行解。将初始粒子值代入潮流计算,求得每个粒子适应度值
种可行解。将初始粒子值代入潮流计算,求得每个粒子适应度值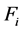 。
。
③ 计算每个粒子的历史最优解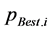 以及全局粒子历史最优解
以及全局粒子历史最优解 ,其中,
,其中, ,
, ,
,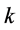 为迭代次数。
为迭代次数。
④ 对每个粒子进行速度和位置更新。每次更新后,检查速度是否超过速度最大值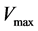 或最小值
或最小值 ,如果超出该范围,将速度限制为该极值。同时,检查每个粒子的位置是否超过了约束条件,如果超过该范围,将位置限制为该极值。
,如果超出该范围,将速度限制为该极值。同时,检查每个粒子的位置是否超过了约束条件,如果超过该范围,将位置限制为该极值。
⑤ 将更新后的粒子位置代入潮流计算,计算粒子更新后的适应值。如果粒子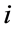 的适应值
的适应值 优于此前的个体极值
优于此前的个体极值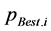 ,则令
,则令 。令
。令 ,如果
,如果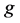 优于此前的全局历史最优值
优于此前的全局历史最优值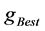 ,则令
,则令 。
。
⑥ 若迭代次数 ,则停止计算,输出与全局历史最优值
,则停止计算,输出与全局历史最优值 相对应的双馈风电机组和SVC无功出力解;否则返回步骤③。
相对应的双馈风电机组和SVC无功出力解;否则返回步骤③。
4)结束计算,输出风电场无功电压控制最优方案。
5. 算例分析
5.1. 算例概述
本文仿真算例采用某实际风电场,如图2所示,以某并网型双馈风电场模型为例。该风电场总装机
容量为60 MW,共有40台1.5 MW的风电机组,每台DFIG经690 V/35 kV变压器接入35 kV馈线系统,40台风机分为3组(一、二组各13台,三组14台)各条输电线路长度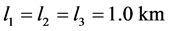 ,每组各风机间距500 m,在并网点低压侧母线上装有一台10 Mvar的SVC。优化前,双馈风电机组和SVC均运行在恒电压控制模式。
,每组各风机间距500 m,在并网点低压侧母线上装有一台10 Mvar的SVC。优化前,双馈风电机组和SVC均运行在恒电压控制模式。
在Matlab/Simulink搭建上述算例系统,优化算法中粒子群规模为 ,终止迭代次数为
,终止迭代次数为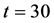 ,惯性权重
,惯性权重 ,
, ,完成一次优化运算约耗时15 s,考虑信号传输等其他因素,本文无功电压优化控制周期取1min。
,完成一次优化运算约耗时15 s,考虑信号传输等其他因素,本文无功电压优化控制周期取1min。
根据算例中风电场运行情况和无功调节设备信息,将该风电场稳定性目标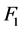 和经济性目标
和经济性目标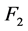 的期望值及可接受最劣值分别设为
的期望值及可接受最劣值分别设为 ,
,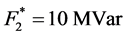 ,
, ,
, 。
。
下面采用模糊多目标决策方法对风电场运行经济性和稳定性进行优化。
5.2. 风电场运行经济性仿真对比
图3为PCC电压标幺值为0.99时,优化前后风电场、双馈风电机组和SVC的无功输出曲线。由图3

Figure 2. Structure of simulation system
图2. 仿真系统结构图
 实线——优化前;虚线——优化后
实线——优化前;虚线——优化后
Figure 3. Curve: Reactive power output of wind farm, DFIG, and SVC before and after optimization
图3. 优化前后风电场、双馈风电机组和SVC无功输出曲线
可见,本文优化模型合理降低了双馈风电机组的无功出力,同时适当增加了SVC的无功出力。表1为在两种典型运行工况下,即风电机组出力分别为额定出力的40%和80%时,风电场运行的经济性优化结果对比。
由表1可以看出,优化后,风电场的有功损耗减小。这是由于优化前双馈风电机组无功出力较多,线路上的无功功率流动带来了较多的有功功率损耗。而本文所提优化决策方法提高了PCC电压,同时合理限制了双馈风电机组的无功出力,使线路上流动的无功功率减小,因此风电场内的有功损耗有一定程度的降低,兼顾了风电场运行的经济性优化要求。
5.3. 风电场运行稳定性仿真对比
图4为额定出力的40%和80%时,风电场内40台DFIG优化后的机端电压曲线,此处假设所有双馈

Table 1. Economy optimization results of wind farm under different operating conditions
表1. 不同运行工况下风电场运行经济性优化结果对比

Table 2. Stability optimization results of wind farm under different operating conditions
表2. 不同运行工况下风电场运行稳定性优化结果对比

Figure 4. Curve: Voltage of DFIG under different operating conditions after optimization
图4. 不同运行工况下DFIG机端电压优化结果
风电机组均参与无功电压优化。由于优化前双馈风电机组运行在恒电压控制模式,因此各台机组机端电压基本一致,维持在额定值,即 。从图4可以看出,优化后各台风电机组机端电压偏差均在±2%允许范围内。表2给出了两种典型运行工况下风电场运行稳定性优化结果对比。可以看出,本文所提模型优化协调DFIG和SVC的无功出力,风电机组的无功输出减少,减小了无功传输过程中线路上的电压降落,从而提高了PCC电压水平,减小了PCC电压偏差。此外,优化决策方法还提高了无功源的无功裕度,提高了风电场运行的稳定性。
。从图4可以看出,优化后各台风电机组机端电压偏差均在±2%允许范围内。表2给出了两种典型运行工况下风电场运行稳定性优化结果对比。可以看出,本文所提模型优化协调DFIG和SVC的无功出力,风电机组的无功输出减少,减小了无功传输过程中线路上的电压降落,从而提高了PCC电压水平,减小了PCC电压偏差。此外,优化决策方法还提高了无功源的无功裕度,提高了风电场运行的稳定性。
6. 结论
本文基于风电场运行经济性和稳定性目标,建立了风电场无功电压模糊多目标优化模型,并采用粒子群算法进行求解,可解决风电场并网运行无法有效兼顾稳定性与经济性的问题。
1) 采用本文所提优化方法,提高了风电场PCC电压水平,并合理限制了双馈风电机组的无功出力,降低了风电场内有功损耗,兼顾了风电场运行的经济性优化要求。
2) 本文所提优化决策方法从无功源无功裕度和电压偏差两个角度提高了风电场运行的稳定性。一方面,减小了PCC电压偏差,同时控制DFIG极端电压偏差在±2%允许范围内;另一方面,通过合理利用双馈风电机组的无功调节能力,有效地提高了风电场的无功源无功裕度,为系统储备了更多的无功容量。
基金项目
基金项目国家科技支撑计划(2015BAA01B04)和国家电网公司重大项目(52272214002C)。