1. 引言
近年来,由于科学技术的发展以及基因诊断的进步,人们对高维生物数据有了更深的认识,基因表达谱数据一次性可以获得成千上万个基因片段的表达值,然而很多疾病只与少数几个关键致病基因有关。利用特征选择算法有助于在缺乏先验知识的情况下缩小致病关键基因的候选范围,并深入研究在分子层面上致病机理。目前关于关键特征基因筛选的方法大致可以分为三类:过滤法、缠绕法、混合法 [1] 。过滤法主要是用指标对基因进行排序筛选,方法简单,但忽略了基因间的相互信息,分类准确性较差。缠绕法主要将特征选择与分类器缠绕在一起,使得选择的特征能有较好的分类准确性,然而该方法对于高维数据计算量极大。混合法则是上述两种的结合。基因表达数据的高维性和冗余性使得基于机器学习的混合法有着较好应用。李霞等 [2] 较早地提出了一种基于递归分类树的集成特征选择方法EFST,该方法对不同的分类器都有较好的适应性。李颖新等 [3] 较早的将支持向量机应用到了肿瘤分类特征基因识别中。吕飒丽等 [4] 使用决策森林来进行特征选择,再使用人工神经网络作为分类器,获得了很好的分类效果。张飞等 [5] 在肺鳞状癌细胞发展的特征基因提取中建立了四步筛选方案:相关性筛选、显著性筛选、偏最小二乘算法、基于模式识别分类精度的综合筛选,实证分析显示了多重筛选机制的必要性,构建的分类器对三个集有较好的准确率,重要的是筛选出的特征基因得到了分子生物学层面的解释。银屑病是 [6] [7] 一种常见的慢性复发性炎症性皮肤病,但是银屑病的病因尚未阐明。本文将针对银屑病基因表达谱数据提出一种新的特征选择算法,并构建银屑病基因诊断的分类模型。
2. 模型与算法
2.1. Softmax理论模型
我们将已经有m个标记了的训练样本作为训练集,特征向量x的维度为n + 1,即 ,最终训练集组成的集合为:
,最终训练集组成的集合为: 。(我们对符号的约定如下:特征向量x的维度为n + 1,其中
。(我们对符号的约定如下:特征向量x的维度为n + 1,其中 对应截距项)。
对应截距项)。
在Softmax regression中的假设函数如下:
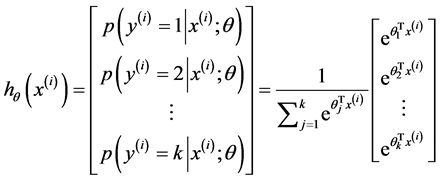
其中θ矩阵可以写成下面的形式:
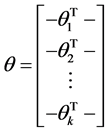
此时,系统损失函数的方程为:
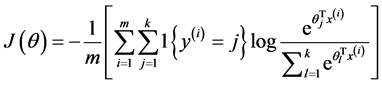
其中的1{.}是一个指示性函数,即当大括号中的值为真时,该函数的结果就为1,否则其结果就为0。
Softmax regression中损失函数的偏导函数如下所示:
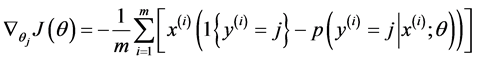
 表示的是损失函数对第j个类别的第l个参数的偏导。
表示的是损失函数对第j个类别的第l个参数的偏导。
Softmax regression中对参数的最优化求解不只一个,每当求得一个优化参数时,如果将这个参数的每一项都减掉同一个数,其得到的损失函数值也是一样的。这说明这个参数不是唯一解,数学公式如下:
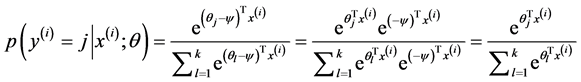
由于在实际的使用过程中一般要加入规则项,加入规则项后的损失函数表达式如下:
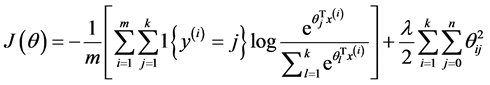
偏导函数表达式如下所示:
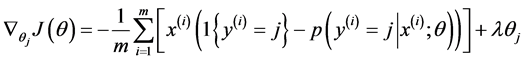
最终通过程序求得的 ,该矩阵大小为
,该矩阵大小为 ,k为分类的类别数,此处k = 2 (针对二分类的问题),对于输入的数据为data (即为输入矩阵),标签labels为
,k为分类的类别数,此处k = 2 (针对二分类的问题),对于输入的数据为data (即为输入矩阵),标签labels为 。
。
2.2. 基于T检验理论模型
T-test检验方法是比较独立样本的一种假设检验方法,此方法的零假设是 是两总体的均值相等,备择假设
是两总体的均值相等,备择假设 是均值不等,通过T检验可以比较两个总体间的均值是否有着显著区别。
是均值不等,通过T检验可以比较两个总体间的均值是否有着显著区别。
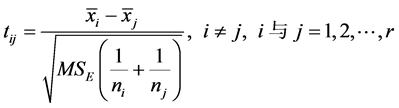
同时有: ,当
,当 或
或 时,可以判断
时,可以判断 与
与 差异显著。T-rank即根据所得到的p-value对基因特征显著程度进行排序的一种算法。
差异显著。T-rank即根据所得到的p-value对基因特征显著程度进行排序的一种算法。
2.3. 融合T-rank的Softmax的特征提取算法
本文提出的融合T-rank和Softmax算法流程图如图1。
3. 实验材料
3.1. 实验数据及预处理
本实验的两个基因表达谱数据集GSE14905 [7] ,GSE13355 [8] [9] 均来自GEO数据库(Gene Expression Omnibus) [10] 。两个数据总共有176个样本,其中91个来自银屑病病例样本,85个来自健康对照组样本。原始.CEL文件分别经过背景校正,log2转换和RMA (Robust Multichip Analysis)算法归一化处理 [11] 。其中归一化算法采用Affymetrix Expression Console TM软件处理(http://www.affymetrix.com/estore/index.jsp)。由于两个数据集来自不同的实验室,我们还利用DWD(Distance Weighted Discrimination) [12] 算法进行了系统偏差的消除。
我们删除了一些总体方差过小判别能力较低的探针集,其中在调用IQR (Inter-Quartile Range)函数时var.cutoff参数设置为0.5,其它参数为默认参数。所有的过滤步骤应用于DWD算法校正之后的数据集,最终有27336个探针集的176个样本被保留进入下一步的分析。
3.2. 特征选择方法
首先我们考虑进行数据的降维,采用Deep learning中的Softmax回归算法,该算法是Logistics回归算法推广,在求解Cost function的时候,能很好的利用L-BFGS求得系统的参数,同时,L-BFGS算法运行速度快。之所以没有直接采用Logistic回归是因为在实际应用中发现如果类别是互斥的,那么多采用Logistics回归,而类别如果是一样的,则多采用Softmax回归算法,本题属于二分类问题,明显类别是不互斥的,综上,我们采用Softmax算法进行特征提取,为了保证算法的可靠性,又融合了T-rank算法。
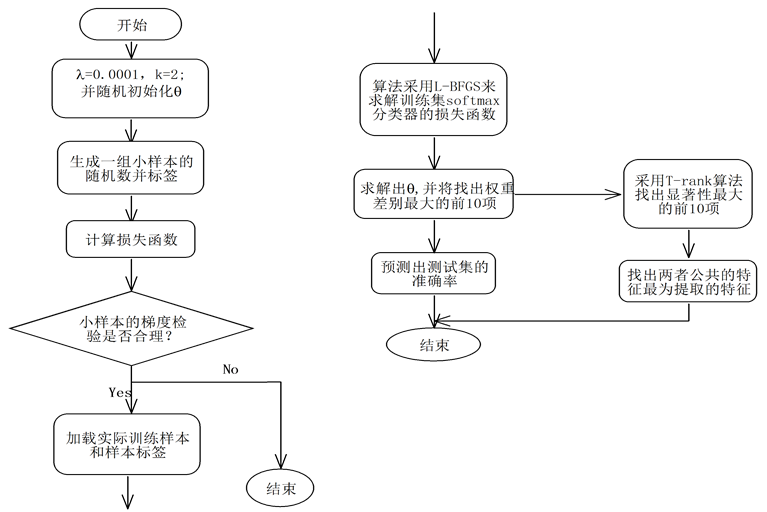
Figure 1. The flow chart by integrating T-rank and Softmax algorithm
图1. 融合T-rank的Softmax算法流程图
3.3. 选用的分类器
为了说明特征提取的效果,我们采用常用的分类算法进行测试,本文以BP神经网络为例,进行特征提取后的分类准确率测试。
3.4. 实验方式及评价指标
在实际中可能会出现样本不平衡的情况,如样本总体为100,其中98个是正常人,而只有2个是病人,如果算法判定所有样本均为正常人,则总的准确率仍可以达到98%,而实际上算法对病人的并不具有很好的分类准确率,为此,我们定义以下分类准确率评价指标:
(1) 样本集总体的分类准确率: 。
。
(2) 样本集中正常人群体的分类准确率: 。
。
(3) 样本集中病人群体的分类准确率: 。
。
4. 实验结果分析
4.1. 特征提取结果
采用Softmax此方法后,就能得到高维特征量的权重(2*27,336维),然后分别对相对应的(正常人和患银屑病的人)权重进行做差取绝对值,然后将权重依次从大到小的排列,运行20次,每次都取权重为前30的特征基因,采用专家打分算法,最终选出前10个特征基因。
将T检验应用于基因表达数据即可检验基因在不同总体样本间表达差异是否显著。通过检验同一基因在正常人与银屑病患者之间的表达是否存在着显著性差异,可以判断该基因是否有可能是银屑病的致病基因之一。在此处,我们可以对每个基因分别进行T检验,取显著性最大,即正常人与银屑病患者表达差异最大的前十个基因作为特征值。将各个基因的T值(显著性)从小到大进行排序,取排名靠前的10个特征,并于Softmax算法得到的10个特征基因取交集,如图2。
从图2也可以发现两种基因特征提取方法提取到的特征存在很大的重合性,从侧面说明了所提取的特征具有较强的稳健性。
4.2. 特征验证与结果分析
我们将数据分成3种不同方式进行训练和测试:
方式一:以GSE14905作为训练集,GSE13355作为测试集;
方式二:以GSE13355作为训练集,GSE14905作为测试集;
方式三:GSE14905和GSE13355中各随机抽取一半作为测试和训练集
采用BP神经网络的算法,对本文提出的融合T-rank的Softmax的特征提取算法得到的8个基因进行分类准确性验证,验证结果如下表1,表2,表3。
从表1中可知,当GSE14905作为训练集,GSE13355作为测试集,其中有22044(41469_at),3280(203691_at),27604(227736_at)这三个基因得到区分银屑病人的准确率为100%。
从表2中可知,当以GSE13355作为训练集,GSE14905作为测试集时,其中依然有27604(227736_at)这个基因得到区分银屑病人的准确率为100%。
从表3中可知,当以GSE14905和GSE13355中各随机抽取一半作为测试和训练集时,其中还有9270(209720_s_at),27604(227736_at),9953(210413_x_at)这三个基因得到区分银屑病人的准确率为100%。

Figure 2. Information genes selected by Softmax algorithm and T-rank
图2. Softmax算法与T-rank法选择出的特征基因

Table 1. The Acc, BAcc1 and BAcc2 of 8 selected genes in case 1
表1. 方式一8个基因编号及其对应的Acc,BAcc1及BAcc2

Table 2. The Acc, BAcc1 and BAcc2 of 8 selected genes in case 2
表2. 方式二8个基因编号及其对应的Acc,BAcc1及BAcc2

Table 3. The Acc, BAcc1 and BAcc2 of 8 selected genes in case 3
表3. 方式三8个基因编号及其对应的Acc,BAcc1及BAcc2

Table 4. The Acc, BAcc of 8 selected genes in comprehensive evaluation
表4. 综合评价所得8个基因的Acc及BAcc
最终我们综合考虑三种检测方式下各个特征基因对应不同群体的分类准确率,对测试的8个特征基因分别求出其在各个检测方式下的准确率的平均值,即
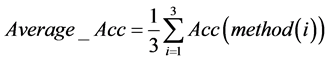
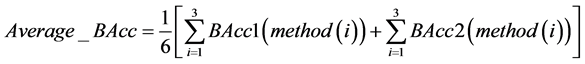
得到下述结果。
通过对表4的观察我们发现27604(227736_at)基因的平均分类准确率达到了100%。考虑到样本个数较少,为了保证模型的稳健性,同时我们也可以看到第9270(209720_s_at),22044(41469_at),9953(210413_x_at),这三个平均准确率次高的基因平均准确率也达到了97%以上,具有很大的参考价值。因此可以取27604(227736_at),9270(209720_s_at),22044(41469_at),9953(210413_x_at)这四个基因作为最终的诊断基因。
为了便于对比,我们首先将GSE14905的合并数据GSE13355采用传统的PCA (Principle Component Analysis)方法进行降维并取前8个主成分(累积贡献率达81.3%)标准化得分来代替原始数据,然后利用LDA (Linear Discriminant Analysis)方法对8个主成分同样在三种情况下进行分类验证,并计算出三种方式下的平均值准确率Average_Acc = 92.37%,Average_Bacc = 92.89%,可以看到本文算法提出的特征准确率明显高于PCA方法,更重要的是,PCA虽然也能够有效的经行降维,但其得到的是所有特征的加权综合,无法判断出究竟是哪个具体基因才是关键诊断基因,这在实际的临床诊断操作上没有本文的方法方便实用。
5. 结论
本文通过融合T-rank的Softmax的特征提取算法,极大程度的利用了Softmax算法和T-rank算法的优点,与传统的PCA+LDA算法相比,有着极大的优势。该算法成功解决了低样本高维数特征提取的难题,而且能成功有效的提取关键特征基因,获得较高准确率疾病诊断模型。
基金项目
本文获教育部人文社科青年基金 (13YJC790105)、湖北工业大学博士科研启动基金(BSQD13050)、湖北工业大学基金项目(2015SW0204)资助。