1. 引言
复杂网络借助于图论和统计物理的一些方法,可以用来捕捉并描述系统的演化机制、演化规律(结构)和整体行为,成为了学术界研究的一个热点,许多现实世界中的网络都具有小世界效应例如电力网络、交通网络、生物网络、社会关系网络。一个网络具有小世界效应是指该网络具有较小的平均路径长度和较大的聚类系数这两个主要的属性,这里较小的平均路径长度是指网络的平均路径长度按照网络的阶的对数形式增长。
网络中生成树数目的计算作为网络的另外一个重要的结构性质在数学、物理和其他学科里,是一个基本的问题。生成树与网络的诸多方面有着紧密的联系 [1] ,包括可靠性 [2] 、最优同步 [3] 、运输 [4] 、随机游走 [5] 等。例如:一个网络的生成树数目与网络中两个节点之间的有效电阻密切相关 [6] ,并且还可以反过来决定两节点之间的平均首达时间;作为随机游走的一个基本量,生成树数目在不同理论和应用领域都有广泛的应用。另一方面,对于一个连通网络,在保持节点数不变的情况下,其生成树数目最大的结构网络具有最好的同步能力。网络中的生成树一直是许多研究关注的焦点。在许多文章中已经研究了特定网络中生成树数目,例如,方形格 [7] ,希尔宾斯基网络 [8] ,伪分形无标度网络 [9] 。赵海兴等人计算出了文献 [10] [11] [12] 中的模型的生成树数目,作为所提出计算生成树数目的新方法。这些研究说明了不同网络结构中的生成树有不同的影响。
本文提出了一类具有小世界现象的五正则网络并且得到了其相应的拓扑特性,例如直径、聚类系数。结果表明我们的模型具有离散指数度分布、高聚类系数、较小的直径,满足小世界网络的主要特性;给出了此类五正则网络的生成树数目的计算方法并得到了相应的公式,根据生成树数目确定了生成树的熵。
2. 网络生成的迭代算法
正则图是每个顶点的度相同的图 [13] 。若每个顶点的度均为
,称为
-正则图。本文通过迭代的方法构造了一类五正则图。为了正确计算
如图2所示的生成树数目,首先构建一个新模型
如图1所示,用
来表示经过
步后的网络,网络
的生成算法如下:当
时的初始网络
是一个五个节点连接四条边的四叉树,当
时网络
是由两个四叉树粘贴而成,使得最底层的每个叶子节点的度为5,对于
,
通过如下的方式得到:对
中在
步生成的四叉树的每个叶子节点再生出四个叶子节点,然后复制这个四叉树,粘贴这两个四叉树的最底层叶子节点并使得它们的度为5 (如图1)。计算得到

Figure 1. Construction of
, showing the first three steps of the iterative process
图1.
的前三步迭代构造
了网络
的总点数
和总边数
。
本文所研究的五正则网络模型
是由两条边连接两个
构成的(如图2)。并计算得到了
的总点数
和总边数
。
3. 拓扑特性
3.1. 直径(Diameter)
直径指网络中所有节点对之间最小距离的最大值,它反映网络最大传递延迟的属性。小的直径与小世界网络的概念是一致的,这里用直径代替平均路径长度来说明网络的小世界特性。用
表示本网络模型的时间步
时的直径。由图2知,
,
,在接下来的每一迭代步
中,直径随着新点的增加而增加。网络的直径满足公式:
.
用归纳法可证明公式成立。并且
.
因此直径随着节点数的增加呈对数形式增长,因为平均路径长度小于直径
,并且平均路径长度比直径增加的更缓慢,所以该五正则网络满足小世界网络特性。
3.2. 聚类系数(Clustering Coefficient)
聚类系数是用来衡量一个复杂网络的集团化程度,它是网络的另一个重要特征参数。节点
的聚集系数
描述的是网络中与该节点直接相连的节点之间的连接关系,即与该节点直接相邻的节点间实际存
在的边数目占最大可能存在的边数的比例,
的表达式为
,式中
表示节点
的度,
表
示节点
的邻接节点之间实际存在的边数。网络的聚集系数
为所有节点聚集系数的算术平均值,即
,其中
为网络的阶。计算的详细过程如下:

Figure 2. Construction of
, showing the first three steps of the iterative process
图2.
的前三步迭代构造
在
步,
。在接下来的每一步
,都有
.
显然,当
时,
,具有较高的聚类系数,满足小世界特性。
4. 生成树数目(Spanning Trees)
生成树
是一个连通图
的一个极小连通子图,包含
的所有
个顶点,有
条边的连通图。若
为森林,则称它为
的一个生成森林。我们找出了
和
的关系(如图3)。假设
表示在
中第
步时的生成树数目,
表示在
中第
步时具有两个分支的生成森林数目,那么通过计算
的生成树数目来求得原模型
的生成树数目,他们的关系如公式(1):
(1)
由图3和图4容易看出
在第
步时的生成树数目是通过迭代的方法由
步得到的,并且
步的生成树是由
步生成树和生成森林共同构成的,
有以下几种情形:
由图5可以看出
的包含两个分支的生成森林有以下几种情形:
(2)
其中:
令
因此可得
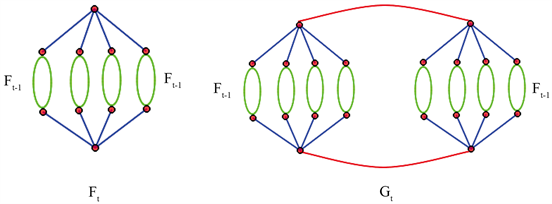
Figure 3. The network model
and
at step
图3.
步时的网络
和
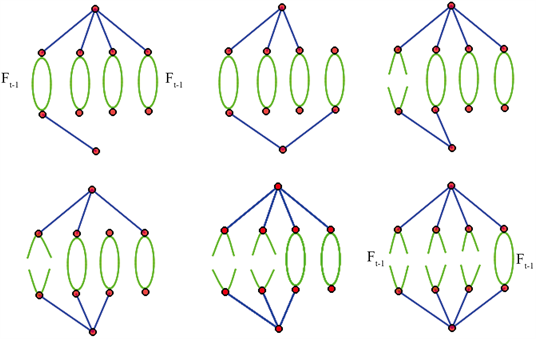
Figure 4. The number of span ning trees of
图4.
的生成树数目
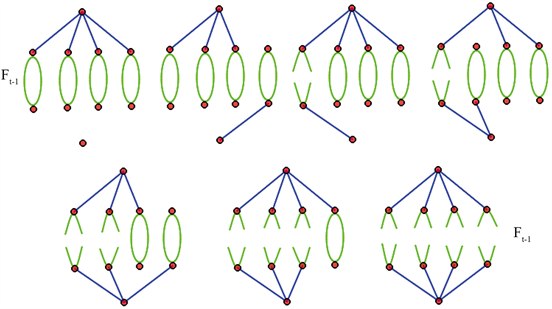
Figure 5. The number of span ning forests with two components of
图5.
中具有两个分支的生成森林数目
注意到
,代入(2)式得:
(3)
同理
,可得:
(4)
根据(3),(4)式可推出公式(1)得到
的生成树数目:
则通过生成树数目计算出了
的生成树的熵:
.
的生成树数目的熵与其他的网络进行比较。文献 [1] 中分形无标度网络的生成树的熵为1.0397,文献 [9] 中伪分形无标度网络的生成树的熵为0.8959,文献 [12] 中四正则网络的生成树的熵为1.099,对于方形格 [7] 和二维希尔宾斯基网络 [8] ,它们的生成树的熵分别是1.1662和1.0486,上面提出的网络都有是具有相同平均度4。文献 [10] 中平均度为5的网络的生成树的熵为1.2109,文献 [14] 中平均度为6的阿波罗网络的生成树的熵为1.354,它们都于小于1.386。因此,该小世界正则网络上的生成树数目比其他具有相同平均度网络的生成树的数目较大。这说明了两个网路生成树存在差别的主要原因在于它们的结构差异。
5. 总结
本文用迭代的方法构造了一类具有小世界效应的五正则网络模型,分析并得到了网络包括直径和聚类系数的主要拓扑特性。生成树作为网络结构性质的一个重要物理量,我们给出了此类五正则网络的生成树数目计算方法,得出生成树数目公式及熵。研究发现,所研究网络的生成树的熵与具有相同平均度的其他网络形成了鲜明的对比,这一五正则小世界网络上的生成树数目比其他具有自相似结构网络生成树的数目要多,也说明了不同网络之间的结构差异,我们给出的生成树数目的计算方法也可以应用到其他自相似网络上。
基金项目
国家自然基金项目(No. 11561056)、青海省自然科学基金项目(No.2016-ZJ-947Q)。