摘要:
土壤团聚体稳定性是评价土壤质量高低的重要指标,开展团聚体稳定性定量评估对于土壤质量评价具有重要意义。国内外对于土壤团聚体稳定性的定量研究很少,当前尚无成熟的团聚体稳定性量化理论与技术。鉴于此,该文提出了一种评估土壤团聚体稳定性的搅拌破碎能量法。通过实时监测土水溶液搅拌过程中的搅拌机电功率和溶液温度,由能量转化守恒定律计算出土壤搅拌破碎能量,从而确定土壤团聚体的稳定性。通过纯水和完全破碎土样与团聚土样的对比试验,验证了方法的可行性,即同等试验条件下,系统损耗相同,而且团聚土样和完全破碎土样或者纯水的搅拌功率差为搅拌破碎功率。在此基础上通过红壤、黑土和塿土3种对照土样的测试,并与Yoder湿筛法作对比,验证方法的实用性。测量结果表明,红壤稳定性最好,其搅拌破碎能量最大,为48.59 J/g-1,而塿土和黑土则分别为28.67和25.59 J/g-1,表现出相近的弱稳定性。Yoder湿筛法测定的平均质量直径分别为红壤0.69 mm,塿土0.35 mm,黑土0.41 mm,其稳定性评估结果与搅拌破碎能量法一致,证明了方法的实用性。
Abstract:
It is of great importance to quantify the stability of soil aggregate, as an important indicator for soil quality assessment. However, there were no standard theories and techniques to quantify the index. Here a mechanic stirring method to quantify the stability energy of soil aggregate is introduced, where a stirred-dispersive energy was recorded from the real-time change of the motor power and temperature of soil water system. Additionally, companied pure-water test, as well as dispersed and undispersed soil were conducted, and validated the innovating method. Moreover, various types of soils from different Chinese provinces were collected, that is Red earths from Jiangxi Province, Black soils from Jilin Province, and Lou soil from Yangling, Shaanxi Province, for the test of aggregate stability with Yoder wet-sieving method. The stirred dispersive energies of Red earths, Black soils, and Lou soil were 48.59, 25.59, and 28.67 J/g-1, indicating a highest stability of Red earths, followed by Black soils and Lou soil (similar). An evident-validating was found using wet sieving, with a corresponding Mean Weight Diameters (MWD) of 0.69, 0.41, and 0.35 mm, respectively. To sum up, our results showed the accuracy and practicability of the stirred dispersive energy method.
1. 引言
土壤团聚体是土壤结构的基本单元 [1] ,其稳定性是决定和影响土壤抗侵蚀性最重要的物理性质,也是评价土壤质量高低的重要指标 [2] 。关于土壤团聚体稳定性的评估方法很多,例如湿筛法、水滴法或人工模拟降雨法等 [3] ,但均存在一定局限性 [4] 。应用最多的为Yoder湿筛法 [3] ,利用团聚体分析仪的套筛上下振荡分离土壤,但其未进行分散能量的测定。绝大多数研究中分散团聚体的机械能是定性的 [5] ,其定量研究很少。近来有学者提出应用超声仪器分散土壤,通过分析土水悬液中超声能量变化特点,估算出用于分散土壤团聚体的能量 [5] [6] [7] [8] ,以此定量评价土壤团聚体稳定性。但所依赖的超声能量法影响参数较多,并且商用超声仪器功率太大 [9] ,不适用于弱稳定性土壤,因而大大限制了其应用领域。搅拌方式因其简单方便且无需添加分散剂的方式受到广大土壤学家的支持,并被广泛应用于土样的分散进而进行土壤理化性质的测定 [10] 。在搅拌过程中,如果能计算出搅拌破碎土壤的能量的大小,就可以有效定量评估土壤团聚体的稳定性,然而未见相关文献报导测定该能量。
针对上述现状,本文拟通过实时监测土水溶液搅拌过程中的搅拌机电功率和溶液温度的变化,由能量转化守恒定律计算出土壤搅拌破碎能量,从而确定土壤团聚体的稳定性。本文采用稳定介质(纯水和完全破碎土样)和团聚土样的功率特性对比检验测量方法的可行性,并对3种不同质地土样进行土壤搅拌破碎能量测定,通过对比Yoder湿筛法测定结果,进一步检验破碎能量法的实用性。
2. 材料和方法
2.1. 搅拌破碎能量测量原理
搅拌机正常工作时,在电能驱动下电动机通过转轴输出转动机械能,控制分散叶片旋转搅拌土水溶液,搅拌过程中,机械能又转化为分散土壤团聚体的破碎能量、土水溶液热能、土水溶液热损耗等。根据能量转化守恒定律,搅拌机输入的搅拌功率P可以表示为
(1)
式中
为土壤破碎功率,
为土水溶液热功率,
为系统损耗功率,主要包括电机损耗功率和土水溶液中由于热传导等方式的损耗功率。
土水溶液热功率PH与溶液温度变化率成正比,表现为
(2)
式中cw、cs表示纯水和土壤的比热容,mw、ms表示纯水和土壤的质量,ΔT/Δt表示搅拌时间内温度的变化。
对于纯水或完全破碎土样等稳定介质,由于没有破碎能量,搅拌机输入功率只是用于搅拌溶液增加系统热能和系统损耗功率,表现为
(3)
在同等试验条件(即搅拌机转速、试验环境、溶液起始温度等)下,可以认为系统损耗功率PS相同。试验过程中发现,相同搅拌时间内,土水溶液和完全破碎土样的温度变化基本相同,原因在于所用搅拌机采用串激整流子电动机,通过电子恒转矩调速,在低速时力矩恒定,从而搅拌溶液所产生的热能基本一致,即PH相同。
由(1)和(3)可以差分得到土壤搅拌破碎功率为
(4)
对PL在搅拌时间内积分可得到土壤搅拌破碎能量L,即
(5)
土壤团聚体稳定性的强弱可以通过计算得到的L值的大小判断,稳定性不同的土样得到的破碎能量L大小也不同。L的值越大,土样的稳定性越强。反之,L的值越小,则稳定性越弱。
2.2. 试验系统
试验系统如图1所示。主要包括串激整流子电动机(U450/80-220)、分散叶片(不锈钢材料,直径为50 cm)、料筒(容积为1.2 L)、温度探头(直径为2.2 mm,长度为8 mm,德国贺利氏公司,精密度为0.002℃)、变频器、数据采集器和计算机等。电动机固定在支架上,通过转轴连接分散叶片,主要为料筒中溶液提供搅拌破碎能量;电动机高度可手动调节,可以确保每次搅拌试验分散叶片位于同一深度;分散叶片与转轴采用可分离结构,便于更换;分散叶片的搅拌速度,即电动机转速,由变频器控制,采用恒转矩调速模式,转速可实时显示。搅拌功率由数据采集器通过实时监测变频器输入功率的变化来实现。数据采集器同时通过温度探头实时监测料筒内溶液温度,采样频率为1 HZ,采样结果由串口上传给计算机,实现数据显示、存储、运算等功能。
2.3. 试验设计
测试土样分别取自于江西赣州、吉林长春和陕西杨凌,土样基本信息见表1。采集表层原状土(0~20 cm),其机械组成及其主要胶结物质如表2所示,其中土壤类型按国际制土壤质地分级标准划分,主要胶结物质则参照文献资料 [11] [12] [13] 。
 1.电动机 2.分散叶片 3.料筒 4.温度传感器探头 5.变频器 6.数据采集器 7.计算机
1.电动机 2.分散叶片 3.料筒 4.温度传感器探头 5.变频器 6.数据采集器 7.计算机
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of system
图1. 系统结构框图
表1. 土样基本信息

Table 2. Mechanical composition and cement of soil aggregates
表2. 土样机械组成及团聚体主要胶结物质
首先对试验方法进行了验证:采用两种稳定介质(600 mL纯水和60 g过2 mm筛的风干土样与600 mL纯水充分搅拌后的完全破碎土样悬浮液)对测量方法的前提假设进行验证,并将塿土完全破碎状态的功率特性与团聚状态进行对比,确定破碎功率。然后对红壤、黑土和塿土3种土样进行搅拌破碎能量测试,测量结果与Yoder湿筛法进行对比。
搅拌破碎土壤试验操作如下:将过2 mm筛的60 g风干土样加600 mL纯水配制成土水溶液;用搅拌机对该土水溶液进行低速(3000 r/m)搅拌破碎,分别搅拌60,180,300,420,900,1800 s。搅拌破碎过程中采集搅拌机的电功率;将搅拌破碎完成的土水溶液进行筛分、烘干、称重,并对比土壤机械组成确定破碎过程为土壤完全破碎过程;然后,采用600 mL纯水或完全破碎土样溶液在同等试验条件下进行相同时间的搅拌试验,并测出相应的电功率。采用Yoder湿筛法 [10] 进行对照,即称取测试土样50 g进行30 min预湿润;然后将土样倒入套筛(孔径分别为5,2,1,0.5和0.25 mm);打开振筛机(FT-3型电动固粒分析仪–南京土壤仪器厂),振幅为3.2 cm,振速30次/min;振荡1 min后用水冲洗各层套筛团聚体至烧杯中,静置30 min,倒掉上清液,沙浴烘干称重。
2.4. 搅拌破碎能量计算过程
考虑到溶液内部温差问题及搅拌机搅拌作用,将数据采集器所测输入功率采用连续10个数据的滑动平均,作为搅拌功率。根据土水溶液的搅拌功率P和纯水或完全破碎土样溶液的搅拌功率P',由公式(4)计算出土壤破碎功率PL,进而根据公式(5)计算出搅拌时间内的土壤搅拌破碎能量L。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 搅拌破碎能量测量方法验证
图2给出纯水和塿土完全破碎和团聚两种不同状态在搅拌破碎过程中搅拌机输入的搅拌功率的变化。由图2(a)知,完全破碎塿土的搅拌功率随搅拌时间变化与纯水的基本一致,符合零分散能量介质的共同特征。将完全破碎塿土和纯水的搅拌功率作进一步对比,可以发现数据点都在平分线附近,均为40 ± 1 W,如图2(b)所示。不同的零分散能量介质在搅拌破碎过程中搅拌功率基本相同,因此,对比公式(3)知,同等试验条件下系统损耗相等的假设可以成立。对比图2(a)中塿土团聚状态和完全破碎状态的搅拌功率知,两者逐步靠近,符合团聚土样逐步分散的物理过程,其差值即为土壤破碎功率。由此可知,通过监测团聚和完全破碎土样或纯水的搅拌功率,便可获得土壤搅拌破碎功率PL,进而推导得出分散土壤团聚体的破碎能量L。
3.2. 搅拌破碎能量测量结果
图3给出红壤、塿土和黑土3种土样搅拌破碎能量L的变化情况。L越大,则表明分散土壤所需的能量越大,因而表现为较强的稳定性。
在土壤搅拌破碎过程中,3种土样都首先经历了一个快速破碎过程,即土壤经过水的充分浸润后,大团聚体因稳定性差在搅拌机搅拌作用下快速破碎,迅速释放出小的团聚体,其破碎能量表现为L的快速增长,整个过程约为300 s。这时红壤的L最大,其大团聚体明显表现出较强的稳定性,而塿土和黑土的L则相近,稳定性相近。
由于小团聚体和微团聚体之间的粘结相对紧密,因而L在搅拌时间300 s后增长缓慢,其中黑土的L于900 s后趋于平缓,而红壤则于1200 s后趋于平缓,土样逐步达到完全破碎状态。对于塿土,L则于搅拌时间700~1100 s表现出二次快速增长过程,这可能与塿土中钙离子与有机阴离子和粘粒的胶结作用 [13] [14] [15]
 (a)
(a) 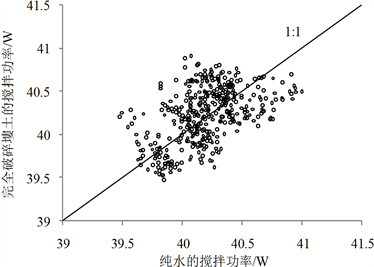 (b)
(b)
Figure 2. The input stirring power for aggregate soil, pure water and dispersed soil
图2. 搅拌过程中纯水和塿土的搅拌功率的变化
以及二次复钙过程 [15] (即二次团聚过程)有关。
在搅拌时间1800 s,3种土样的搅拌破碎能量L分别为红壤48.59 J/g-1,塿土28.67 J/g-1,黑土25.59 J/g-1,表现出稳定性为红壤最稳定。这是因为红壤的主要胶结物质为氧化铁等无机氧化物,而氧化铁可强烈吸附在粘粒表面形成氧化物胶膜,使土粒结合紧密,形成稳定的团聚体 [11] 。塿土和黑土粘粒含量基本相同(表1),搅拌破碎能量L也相近,其稳定性基本一致。
总体而言,土壤搅拌破碎能量L与搅拌时间呈非线性关系,且基本上均是先快速后缓慢,最后恒定的过程,呈现出土壤团聚体从初始团聚状态到完全分散状态的逐渐分散的物理过程,与Zhu et al. (2009) [6] 应用超声能量法所测结果一致。
3.3. 与Yoder湿筛法的对比验证
平均质量直径(MWD)是反映土壤团聚体大小分布的常用指标,MWD值越大,表明土壤团聚体的团聚程度越高,稳定性越好 [1] 。表3给出了Yoder湿筛法测定的土壤团聚体粒径组成和平均质量直径。
由MWD的值可以看出3种土样分别为红壤0.69 mm,黑土0.41 mm,塿土0.35 mm,表现出稳定性为红壤最好。观察大团聚体(2~1 mm)组成可知,红壤最多。大团聚体含量多,土壤不易被分散,稳定性好,进一步表明红壤最稳定。
表4给出了搅拌机搅拌1 800 s后的土壤团聚体粒径组成和平均质量直径。与Yoder湿筛法测量结果
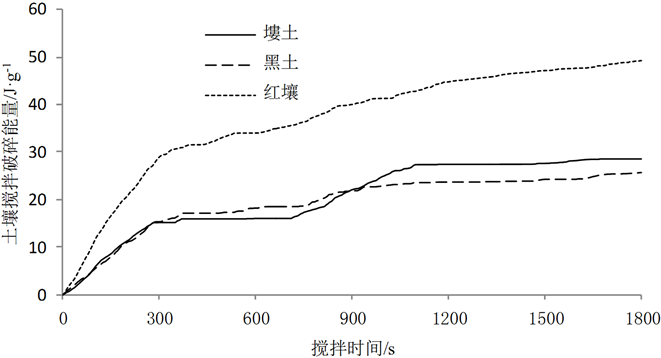
Figure 3. Soil stirred dispersive energy as a function of stirring time
图3. 土壤搅拌破碎能量与搅拌时间关系曲线

Table 3. The composition and stability of soil aggregates determined by the wet-sieving method
表3. Yoder湿筛法测定的土壤团聚体粒径组成和平均质量直径

Table 4. The composition and stability of soil aggregates determined by the wet-sieving method after stirring 1800 s
表4. 搅拌1800 s后的土壤团聚体粒径组成和平均质量直径
对比可以发现,在一定的搅拌破碎能量作用下,各粒级团聚体含量(2~1 mm, 1~0.5 mm, 0.5~0.25 mm)明显减少,并导致土壤颗粒(<0.25 mm)含量增大。此外,红壤的MWD (0.14 mm)和搅拌破碎能量(48.59 J/g-1)均为最大,稳定性最好,而黑土和红壤则表现出相近的弱稳定性。
综上分析,搅拌破碎能量法与Yoder湿筛法评估稳定性方面得到的结果一致,均为红壤最稳定,而黑土和塿土则相近,稳定性较差。研究结果证明了搅拌破碎能量法的准确性与实用性。
4. 结论
本文提出了一种评估土壤团聚体稳定性的搅拌破碎能量法。纯水和完全破碎土样这两种稳定介质的搅拌破碎试验结果表明:同等试验条件下,系统损耗相同;团聚土样和完全破碎土样或者纯水的功率差为破碎功率。土壤分散过程中,其搅拌破碎能量与搅拌时间呈先速增后减缓到平稳的非线性关系,且搅拌破碎能量越大,土壤越稳定。红壤搅拌破碎能量最大,因而最稳定,黑土和塿土的搅拌破碎能量均小,表现出相近的弱稳定性,这与Yoder湿筛法评估稳定性结果一致。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目(41101201);西北农林科技大学基本业务费专项(2452015092);十二五国家科技支撑计划(2015BAC01B01);黄土高原土壤侵蚀与旱地农业国家重点实验室专项经费。