1. 引言
As对植物是具有毒害作用的,当植物体内聚集过量的As时会抑制植物体内对水分和营养的吸收,破坏叶绿素。受到轻度As污染,植物表现为植株矮小,叶片失绿;中度As污染植物表现为扭曲生长;重度As污染,植物表现为地上部分发黄,根部出现黑褐色直至死亡 [1] 。As对植物的危害最终会通过食物链进入到人体内,危害人类的健康,有关As污染对人类健康的危害报道时有发生 [2] [3] [4] [5] 。传统检测水稻农田中重金属的含量都是野外采集样本拿到实验室内进行化学分析,精度高但是费时费力,具有局限性,随着高光谱遥感的发展,快速的检测水稻农田污染情况已经实现。
近年来人工智能应用的领域越来越广泛,已有很多的学者将人工智能神经网络应用在农田环境污染的检测上,最常用的神经网络为BP神经网络 [6] [7] [8] ,但BP算法的速度慢,容易陷入局部极小点。动态模糊神经网络是集神经网络和模糊系统功能于一体,解决了模糊神经网络在参数确定上的不确定性同时还能够实时的解决非线性问题与单纯的神经网络形成鲜明的对比,提供在线的学习方法以及学习的快速性,它的网络结构不用预先设定好,而是在不断的学习过程中动态的逐渐的形成模糊规则,与常规的模糊神经网络方法相比较而言削弱了计算速度慢,陷入局部极小点的弊端 [9] - [17] 。在国内外,在重金属污染胁迫下,水稻受重金属污染的程度与叶片中叶绿素的含量的相关性均有大量的报道,如Broge等人研究表明,在400 nm~700 nm特定的波段范围内,叶绿素含量与植被光谱反射率有明显的相关关系,能很好的反应植被受重金属胁迫的程度 [18] ;陈思宁等人通过研究发现,反射率的蓝移程度和叶绿素的含量存在较强的相关性 [19] ;任红艳等人表明通过水稻的光谱特征,可以找到对水稻重金属胁迫更为敏感的光谱指数 [20] ;Reza Amiri et al.通过叶绿素的含量和植被指数的相关性来进行分析 [21] 。本文以水稻农田为研究对象,尝试利用动态模糊神经网络模型来预测叶绿素含量来判断水稻污染情况,从而为实时、大面积的有效监测农田受As污染提供依据,动态模糊神经网络模型应用的处理流程见图1所示。
2. 数据的采集
2.1. 研究区概况
研究区选取了吉林省吉林市三块污染程度不同的水稻种植区域分别为:A号采样区吉林省农科院试验田(126˚28'2.8E,43˚57'1.8N)、B号采样区吉林公路旁水稻(126˚24'14.6E,43˚59'14.9N)、C号采样区吉林化工厂附近的农田(126˚37'35.5E,43˚55'10.5N)。水稻品种为吉梗105,该土壤种植区域以黑壤为主,属于中温带大陆性季风气候,年平均气温3℃~5℃,年平均降水量650~750 mm。三块样地的气候、降水、光照、土质以及排水等条件基本一致。以采样区土壤环境背景值作为衡量的标准 [22] 。根据单因子指数评价法计算结果,A号采样区为无污染,B号采样区、C号采样区污染等级依次为1级污染和2级污染,且2级污染大于1级污染,结合三块采样地分别对应实际测得的成熟期水稻叶绿素含量见表1所示。

Table 1. The division of pollution grade corresponds to the chlorophyll range
表1. 污染等级的划分对应的叶绿素值域
2.2. ASD光谱数据的采集
使用美国ASD公司生产的FieldSpec Pro3型光谱仪采集水稻光谱反射率,测定前用圆形标准白板进行校正,视场角为10˚,探头放在水稻的顶部并垂直向下约1 m的位置,在2009年8~9月进行光谱数据采集,选择在晴朗无风的天气,光谱采集的时间为10:00~14:00,波长范围为3500~2500 nm,其中在350~1000 nm波长范围内的光谱分辨率为1.4 nm,在1000~2500 nm的光谱分辨率为2 nm。每个样本点分别采集10条光谱数据,对10条光谱数据取其平均值作为该样本点的光谱数据,这样得到了A、B、C三个采样区的光谱数据。
2.3. 地面采样点叶绿素含量的测量
水稻叶片中叶绿素含量的测量使用Konica Minolta公司生产的SPAD-502叶绿素计进行测量,与冠层光谱测量同步进行。但SPAD-502叶绿素计的读数并不是植物叶片中叶绿素含量的真实值,而是与植物叶片中叶绿素含量有高度的相关性,所以被广泛的用来检测植物的叶绿素含量。在测量叶绿素含量时,每个采样点的水稻植株都选择上、中、下三个垂直的不同叶片,每个叶片测量6次,最终取其平均值作为该水稻采样点的SPAD值(SPAD-502叶绿素计的读数)。SPAD值与叶绿素含量实际值的转换公式 [23] 如下所示
式中:X为SPAD-502叶绿素计的读数;Y为实际叶片中叶绿素的含量,单位为μg∙cm−2。
2.4. 研究区土壤及叶片中重金属砷含量的测定
在野外采集完研究区样本点的光谱数据和叶绿素值之后,以每个采样点为中心,采集每个采样点0~10 cm深度的表层土,将采样土收集到干净的保鲜袋中,并排除保鲜袋中的空气,带回实验室,在实验室中经过自然的风干,剔掉碎石子及杂草等处理 [24] 以备后续的使用,土壤及叶片中重金属As的含量由中国农业科学院和东北师范大学测试中心平行完成。
3. 动态模糊神经网络模型
3.1. 动态模糊神经网络
本文所用的动态模糊神经网络中的动态指的是网络结构不是预先设定的,而是动态变化的,在开始学习之前,没有一条模糊规则,模糊规则是在不断的学习过程中,不断有输入参数加入到这个模型中逐渐增长而形成的,无需领域的专家知识就可以对系统自动建模,形成模糊规则,并且动态模糊神经网络还有简单有效的学习算法、学习速度快、实时建模的特点,该方法能够实时的处理非线性关系 [25] 。
动态模糊神经网络的结构包括5层:第一层为输入层,每一个节点表示一个输入变量;第二层为隶属函数层,每一个节点表示一个隶属函数,第三层可以理解为模糊规则数层,有多少个节点就有多少个模糊规则;第四层为归一化层;第五层为输出层,动态模糊神经网络的结构见图2所示。该隶属函数用高斯函数表示为:
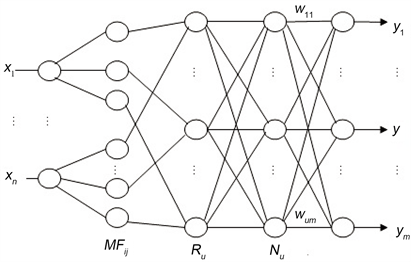
Figure 2. The structure of dynamic fuzzy neural network
图2. 动态模糊神经网络结构图
式中:
是
的第j个隶属函数;cij是xi的第j个高斯函数的中心;
是xi的第j个隶属函数的宽度;r是输入变量的个数;u是规则数。
3.2. 动态模糊神经网络的输入参数
本文根据前人的研究,筛选出对叶绿素敏感的15个植被指数,分别为归一化植被指数NDVI、优化的比值植被指数MSR、比值植被指数RVI、红边位置指数REP、叶绿素吸收反射率指数CARI、优化的叶绿素吸收率指数MCARI、绿色归一化植被指数GNDVI、改进的归一化植被指数MNDVI、RDVI、优化的土壤调整植被指数OSAVI、MSAVI、冠层结构无关色素指数SIPI、SRA、三角植被指数TVI、MERIS地球叶绿素指数MTCI共计15个植被指数,分别与实测的叶绿素含量建立相关关系,可知决定系数大于0.5的有8个植被指数,再在matlab里建立多元逐步回归模型,筛选出更为敏感的植被指数。剩下的更为敏感的植被指数见图3所示,在图3中绿色代表C号采样区的采样点,蓝色代表B号采样区的采样点,黄色代表A号采样区的采样点,从图3也能看出,土壤中重金属的含量和水稻叶片中叶绿素的含量有明显的相关性。公式见表2所示,得到的多元回归模型为:
式中:X1为NDVI值;X2为MNDVI值;X3为MTCI值;X4为GNDVI值;X5为MSR值;Y为叶绿素含量值(μg∙cm−2);R2为决定系数。
3.3. 动态模糊神经网络模型的输出参数
由前人的研究已经知道,当植被受到重金属污染胁迫时,叶绿素的含量会发生明显的变化,所以用叶绿素的含量可以间接的反应土壤中重金属的含量,即知道了叶绿素的含量可大致估计出土壤污染的等级,结合实验区三块采样地实测的叶绿素含量,将叶绿素含量作为动态模糊神经网络的输出参数。
4. 动态模糊神经网络模型精度的检验
将2009年8~9月份吉林省吉林市A、B、C号三块采样区分别实际测得的ASD数据所构建的NDVI,MNDVI,MTCI,MSR,GNDVI五个植被指数作为动态迷糊神经网络模型的输入参数,实测的叶绿素含

Table 2. Calculation formula of five vegetation indices
表2. 筛选出来的5个植被指数的计算公式
量作为输出参数,在MATLAB软件中进行模型的训练,用来建立重金属污染胁迫下叶绿素含量的反演模型,A号采样区、B号采样区、C号采样区采集的样本点的个数分别均为11个样本点,则动态模糊神经网络模型反演的叶绿素结果见图4所示。
将2009年8~9月份吉林省长春市长春西新东(D号采样区)实测的ASD数据构建的5个相同的植被指数作为模型的输入参数,实测的叶绿素含量作为输入参数带入已经训练好的动态模糊神经网络模型中进行模型的检验,在MATLAB中得到见图5所示的结果,可以看出由动态模糊神经网络预测的叶绿素含量值和实测的叶绿素含量值基本吻合,将相同的输入参数带入到检验区中,检验区为吉林省长春市的一块水稻农田(D号采样区)得到多元逐步回归方程:
式中:X1为NDVI值;X2为MNDVI值;X3为MTCI值;X4为GNDVI值;X5为MSR值;Y为叶绿素含量值(μg∙cm−2)。由多元逐步回归反演得到的叶绿素的结果与实测值发生了1/16的偏差,可以看出,用动态模糊神经网络模型反演叶绿素的含量来预测土壤中重金属污染等级效果要比多元逐步回归模型要好,且由动态模糊神经网络预测的污染等级和实际土壤污染等级一致。
5. 结论
1) 动态模糊神经网络模型预测叶绿素的精度比多元逐步回归模型预测叶绿素的精度要高,对土壤中重金属污染等级的评价达到100%,说明动态模糊神经网络模型能更好的分析非线性的问题。
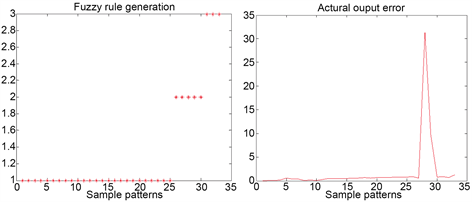
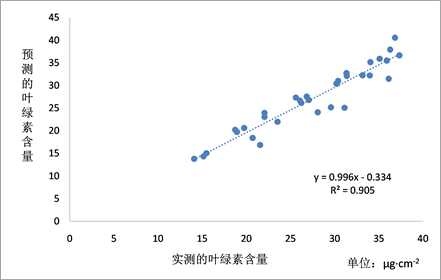
Figure 4. Prediction results of dynamic fuzzy neural network
图4. 动态模糊神经网络的预测结果

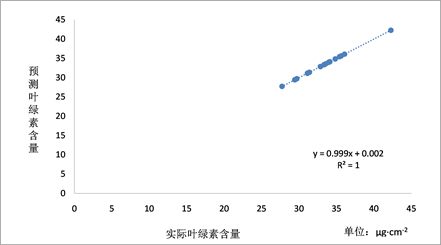
Figure 5. Test results of dynamic fuzzy neural network
图5. 动态模糊神经网络的检验结果
2) 研究农田土壤中重金属污染等级的问题可以间接的通过反演水稻叶片中叶绿素含量来进行估计,土壤中重金属含量越高水稻叶片中叶绿素含量就越低。
3) 本文由于受到采样点的影响,采样点位置较接近,且数量少的局限性,虽然用动态模糊神经网络模型反演出的叶绿素含量值与实测值拟合度高,但是用多元逐步回归模型预测出的叶绿素含量值也与实测值比较接近,所以没能明显的体现出动态模糊神经网络模型在研究非线性问题上的优势,在以后的研究中会打破局限性体现动态模糊神经网络的优越性能。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金项目41571405和40771155。